Geological Conditions and Favorable Area Prediction of Shale Gas in Wufeng Formation–Longmaxi Formation of Kuankuo–Fuyan Area, Northern Guizhou
-
摘要:
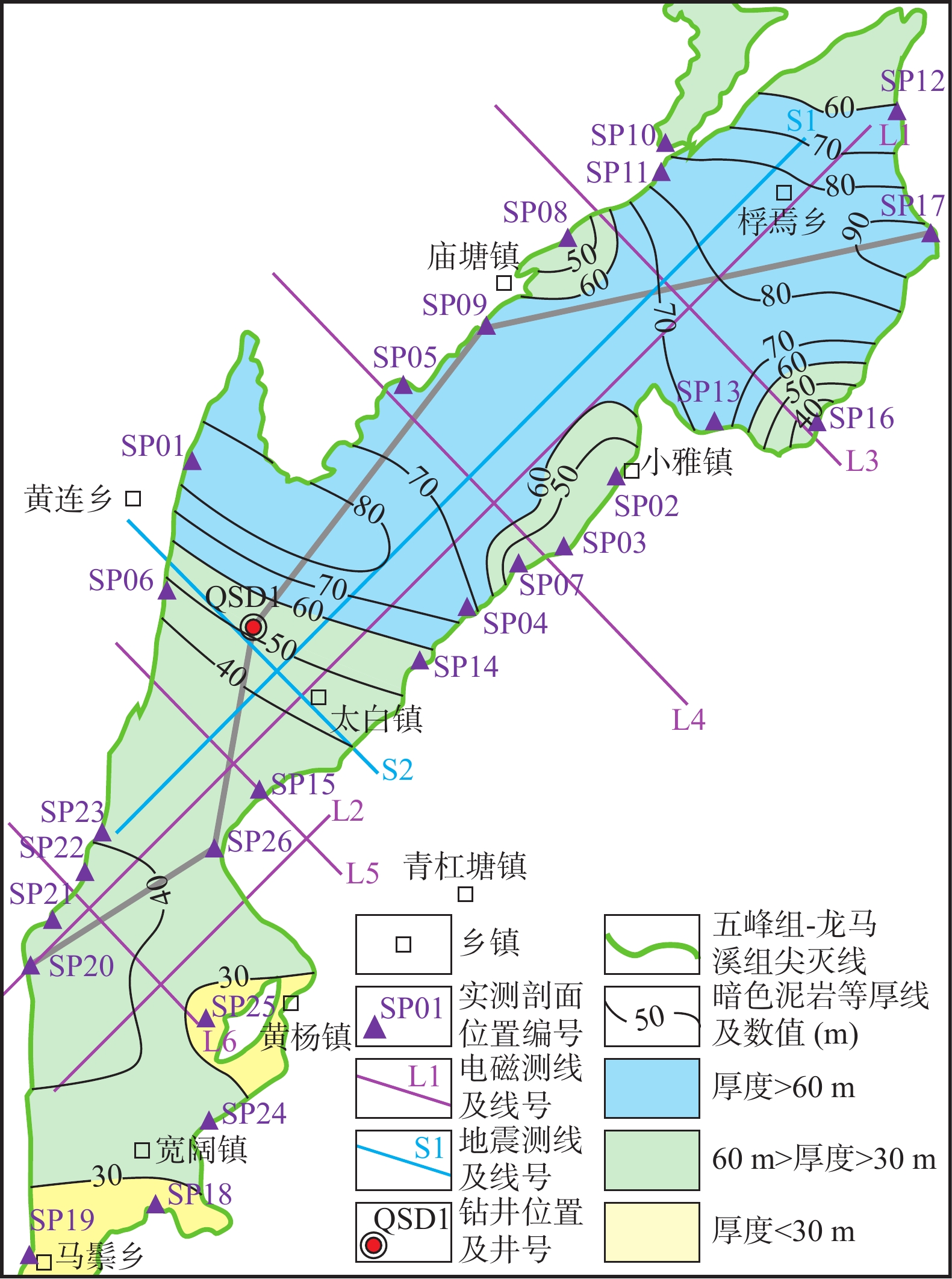
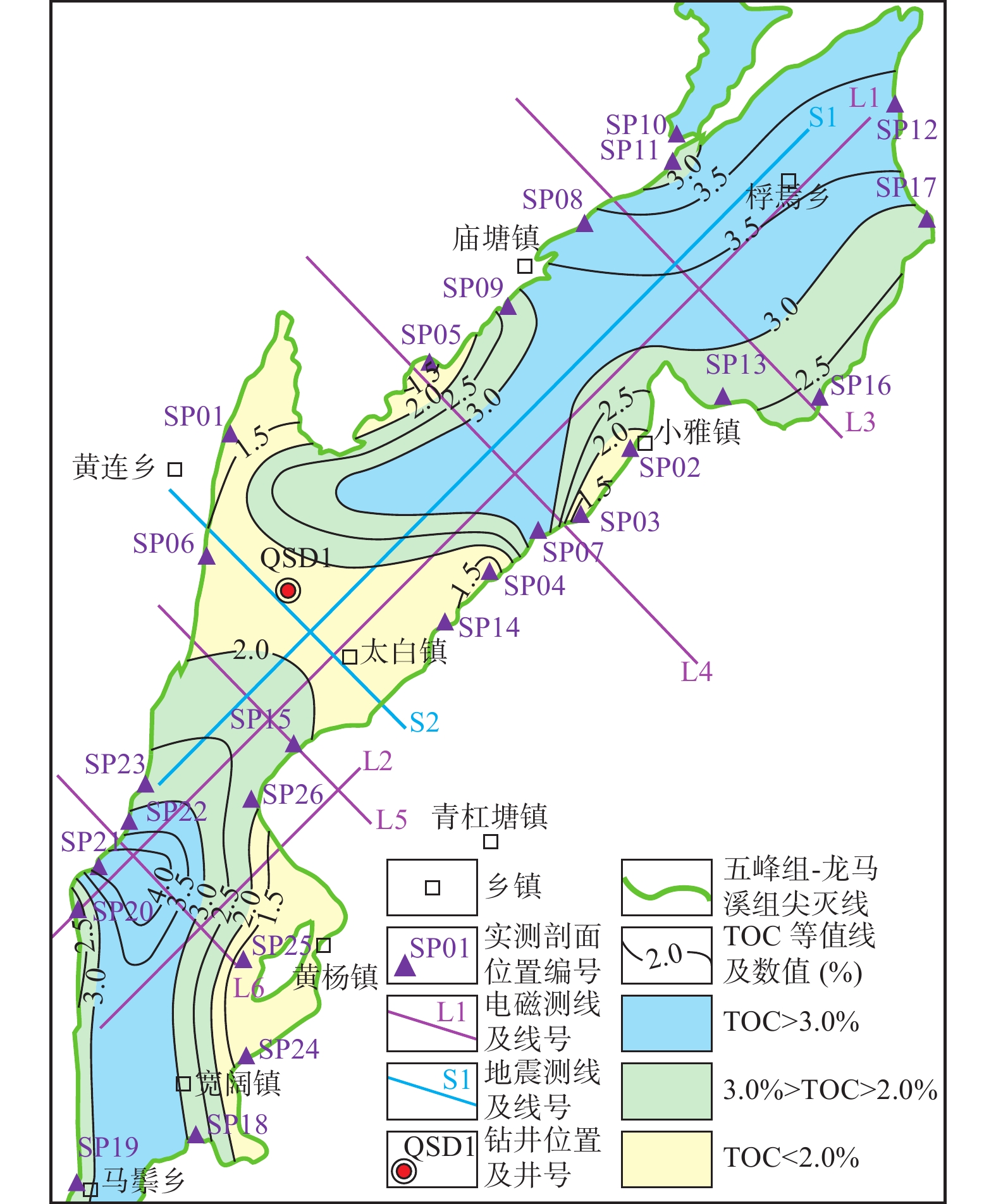
为对黔北宽阔–浮焉地区五峰组–龙马溪组页岩气有利区进行预测,在前人研究成果调研基础上,利用26条露头剖面资料、QSD1钻井资料、样品分析测试资料,结合地震、电磁资料,对研究区五峰组–龙马溪组底面埋深、页岩的岩类学特征及沉积相、分布、总有机碳含量(TOC)、有机质成熟度(Ro)、脆性矿物含量的变化进行了分析并预测了页岩气有利区。研究区五峰组–龙马溪组底面埋深多为0~1 500 m,最大埋藏深度为1 926 m;主要由泥岩、粉砂质泥岩组成,夹薄层泥质粉砂岩、偶见泥灰岩,为泥质深水陆棚微相沉积;地层厚度普遍超过30 m,东北部地层厚度大,最大厚度超过90 m,西南部地层厚度小,最大厚度不足50 m;TOC分布具有中部低(<2.0%)、东北部和西南部高(>3.5%)的特征;Ro为1.20%~3.17%、平均值多大于2.50 %,主要为过成熟烃源岩;脆性矿物含量多在50%以上,具有中部低(<60%)、东北部和西南部高(>70%)的特征。综合上述页岩气有利区预测指标,分3类预测了有利区的分布,浮焉–小雅向斜中部Ⅰ类有利区是下步页岩气勘探的首选靶区。
Abstract:In order to predict the favorable shale gas area of Wufeng Formation – Longmaxi Formation in Kuankuo – Fuyan area, Northern Guizhou Province, on the basis of previous research results, based on data of 26 outcrop profiles and well QSD1, sample analysis and testing, combined with seismic and electromagnetic data, the buried depth of the bottom of Wufeng Formation – Longmaxi Formation, the petrological characteristics and sedimentary facies types of shale, the changes of total organic carbon (TOC), organic matter maturity (Ro) and brittle mineral content are analyzed, and the favorable areas for shale gas are predicted. The buried depth of the bottom of Wufeng Formation – Longmaxi Formation in the study area is mostly 0~1 500 m, and the maximum buried depth is 1 926 m; It is mainly composed of mudstone and silty mudstone, intercalated with thin argillaceous siltstone and occasional marlstone, which is argillaceous deep–water shelf sediments; The thickness of the strata is generally more than 30m, in the northeast is large, and the maximum thickness is more than 90 m, in the southwest is small, and the maximum thickness is less than 50 m; The distribution of TOC is low (<2.0%) in the middle and high (>3.5%) in the northeast and southwest; Ro is between 1.20% and 3.17%, and the average value is more than 2.50%, which is mainly over mature source rock; The content of brittle minerals is more than 50%, which is low (<60%) in the middle and high (>70%) in the northeast and southwest. Based on the above prediction indexes of shale gas favorable areas, the distribution of favorable areas is predicted in three categories. The type I favorable area in the middle of Fuyan Xiaoya syncline is the preferred target area for shale gas exploration in the next step.
-

-
图 2 贵州省宽阔–浮焉地区地质简图(贵州省地质调查院,2010)及资料分布示意图
Figure 2.
图 5 五峰组—龙马溪组地层对比及沉积相分析剖面图(露头及钻井位置见图4)
Figure 5.
表 1 五峰组—龙马溪组页岩气地质条件基础数据表
Table 1. Basic data of shale gas geological conditions of Wufeng Fm.–Longmaxi Fm.
剖面名称 五峰组厚度 (m) 龙马溪组厚度(m) 脆性矿物含量(%) Ro(%) TOC(%) 顶部层位 SP01 4.33 76 60.8(50~73)/5 3.04(2.85~3.20)/7 1.18(0.47~3.31)/23 S1x SP02 10.8 30.5 70.0(63~78)/3 2.99(2.56~3.57)/7 1.89(0.28~6.3)/21 S1x SP03 4.1 38 62.3(49~78)/4 2.66(2.24~3.08)/4 1.29(0.44~4.63)/16 S1x SP04 6.99 66.59 50.3(46~58)/3 2.79(2.54~3.18)/6 1.17(0.26~5.03)/23 S1x SP05 6.3 58.25 37.0/1 2.76(2.07~3.17)/3 1.38(0.22~4.90)/13 S1x SP06 4.8 35.4 44.8(20~59)/4 2.88(2.75~3.04)/4 1.88(0.20~6.48)/16 S1x SP07 7.56 38.11 50.5(50~51)/2 2.84(2.58~3.04)/5 3.20(0.72~6.72)/12 S1x SP08 6.52 34.36 73.0/1 2.83/1 3.81(2.76~4.53)/7 S1x SP09 4.9 61.1 / / / S1x SP10 11.7 56.4 65.8(53~74)/4 3.05(2.93~3.20)/3 3.19(0.43~5.49)/7 S1x SP11 13.3 70.4 60.0/1 2.80/1 2.99(2.34~3.89)/4 S1x SP12 5.7 55.6 54.5(53~56)/2 2.86(2.50~3.17)/3 3.71(0.81~5.81)/9 S1x SP13 4.5 69.8 71.3(57~86)/3 2.85(2.70~3.01)/5 2.62(0.32~4.93)/18 S1x SP14 6.67 50.7 48.0/1 3.07(2.96~3.17)/2 1.57(0.24~5..21)/6 S1x SP15 9.1 25.7 74.0/1 1.68(1.20~2.52)/3 2.20(0.50~3.70)/6 S1x SP16 10.71 20.55 81.0/1 2.30(1.9~2.68)/2 2.40(0.62~4.31)/7 S1x SP17 11.25 80.05 71.5(63~80)/2 2.66(2.46~2.85)/2 2.91(0.51~3.82)/8 S1x SP18 7.12 18.36 74.0/1 2.44(2.23~2.65)/2 2.92(0.70~5.22)/11 S1x SP19 8.27 >10.63 67.5(66~69)/2 2.75(2.45~3.04)/2 2.85(1.62~4.31)/8 S1l SP20 9.62 36.42 71.0/1 2.58(2.29~2.75)/3 2.49(0.66~4.91)/13 S1x SP21 19.68 23.37 68.0/1 2.64(2.36~2.93)/4 4.03(0.99~6.01)/14 S1x SP22 19.44 >28.87 68.0(64~72)/2 2.80(2.30~3.08)/4 3.16(0.86~6.43)/16 S1l SP23 6.75 28.01 69.0/1 2.51(2.08~2.85)/5 2.75(0.88~4.85)/9 S1x SP24 5.89 30.04 69.0/1 2.84(2.77~2.94)/3 1.01(0.41~2.53)/5 S1x SP25 4.72 23.74 62.0/1 2.88(2.75~3.01)/2 1.08(0.61~1.90)/3 S1x SP26 7.27 28.03 / / / S1x QSD1 5.5 49.5 56(41~80)/27 / 1.84(0.10~3.17)/11 S1x 注:脆性矿物含量、Ro、TOC数据:平均值(最小值~最大值)/样品数;S1x.新滩组,S1l.龙马溪组。 表 2 宽阔–浮焉地区五峰组—龙马溪组露头样品有机质碳同位素数据表
Table 2. Carbon isotope data of the Wufeng Fm.–Longmaxi Fm. in the Kuankuo–Fuyan area
样品编号 13 CPDB/‰ 有机质类型 样品编号 13 CPDB/‰ 有机质类型 样品编号 13 CPDB/‰ 有机质类型 sp17-7-s −30.6 Ⅰ型 sp02-6a −29.7 Ⅱ1型 sp04-12a −28.6 Ⅱ1型 sp21-18H −30.6 sp04-6-1a −29.7 sp01-25-s11a −28.5 sp13-9-sa −30.5 sp07-11 −29.7 sp02-14a −28.5 sp16-17-s −30.5 sp01-12-s6a −29.6 sp06-13 −28.4 sp19-11H −30.5 sp02-9a −29.6 sp07-21a −28.3 sp19-13H −30.5 sp08-5-sa −29.6 sp10-22-sa −28.3 sp19-7H −30.5 sp01-15-s7a −29.5 sp12-17a-sa −28.3 sp21-7H −30.5 sp01-7-s1a −29.5 sp01-30-s16a −28.2 sp13-5-sa −30.4 sp11-6-sa −29.5 sp02-18a −28.2 sp18-8H −30.4 sp22-13H −29.5 sp03-11a −28.2 sp21-3H −30.4 sp23-10H −29.5 sp03-12 −28.2 sp16-19-s −30.3 sp03-6 −29.3 sp01-33-s20a −28.1 sp20-7H −30.3 sp17-13-s −29.3 sp05-11a −28.1 sp15-5-s −30.2 sp22-30H −29.3 sp05-14a −28.1 sp13-3-sa −30.1 sp02-4 −29.2 sp04-30 −28 sp14-17-s −30 sp12-4-sa −29.2 sp02-24a −27.9 sp21-12H −30 sp22-17H −29.2 sp04-22a −27.8 sp22-23H −30 sp06-7 −29.1 sp04-18a −27.7 sp10-10-s −29.9 Ⅱ1型 sp07-5 −29.1 sp06-21 −27.3 Ⅱ2型 sp24-2H −29.9 sp20-15H −29.1 sp06-4a −27.3 sp03-4a −29.8 sp23-18H −29 sp04-23a −27 sp10-12-s −29.8 sp25-19H −29 sp03-19a −26.9 sp10-6-sa −29.8 sp24-9H −28.8 注:δ13C (‰)值≤−30‰为I 型,−30‰~−27.5‰为II1 型,−27.5‰~−25‰为II2 型,>−25‰为III 型(黄籍中,1988)。 表 3 宽阔–浮焉地区五峰组—龙马溪组露头样品有机质显微组分数据表
Table 3. Organic macerals data of the Wufeng Fm.–Longmaxi Fm. in the Kuankuo–Fuyan area
样品编号 腐泥组(%) 腐殖组(%) 类型指数 干酪根类型 样品编号 腐泥组(%) 腐殖组(%) 类型指数 干酪根类型 sp01-12-s6a 78 22 82.8 Ⅰ sp10-22-sa 80 20 87.5 Ⅰ sp01-15-s7a 78 22 81.5 Ⅰ sp10-6-sa 98 2 96.5 Ⅰ sp01-25-s11a 81 19 85.5 Ⅰ sp11-6-sa 81 19 83 Ⅰ sp01-33-s20a 77 23 86 Ⅰ sp12-17a-sa 71 29 83 Ⅰ sp01-7-s1a 86 14 90.5 Ⅰ sp12-4-sa 83 17 82.8 Ⅰ sp02-14a 81 19 85.5 Ⅰ sp13-3-sa 86 14 89.3 Ⅰ sp02-4 87 13 89.8 Ⅰ sp13-5-sa 93 7 94 Ⅰ sp02-6a 93 7 94 Ⅰ sp13-9-sa 98 2 96.5 Ⅰ sp03-11a 73 27 84 Ⅰ sp14-17-sa 46 54 57.3 Ⅱ1 sp03-19a 81 19 86.8 Ⅰ sp15-5-s 86 14 85.5 Ⅰ sp03-4a 94 6 89.5 Ⅰ sp16-17-s 34 66 47.3 Ⅱ1 sp03-6 85 15 88.8 Ⅰ sp17-13-s 97 3 94.8 Ⅰ sp04-12a 72 28 83.5 Ⅰ sp17-7-s 84 16 89.5 Ⅰ sp04-22a 70 30 81.3 Ⅰ sp18-8H 92 8 86 Ⅰ sp04-23a 68 32 80.3 Ⅰ sp19-11H 97 3 94.8 Ⅰ sp05-11a 77 23 82.3 Ⅰ sp19-13H 98 2 96.5 Ⅰ sp06-4a 82 18 87.3 Ⅰ sp20-7H 95 5 91.3 Ⅰ sp06-7 85 15 90 Ⅰ sp21-12H 96 4 93 Ⅰ sp07-21a 93 7 92.8 Ⅰ sp22-17H 94 6 89.5 Ⅰ sp07-5 87 13 86 Ⅰ sp22-23H 98 2 96.5 Ⅰ sp08-5-sa 98 2 96.5 Ⅰ sp23-10H 95 5 91.3 Ⅰ sp10-10-sa 98 2 96.5 Ⅰ sp24-2H 94 6 89.5 Ⅰ sp10-12-sa 94 6 93.3 Ⅰ sp25-19H 95 5 91.3 Ⅰ 表 4 宽阔–浮焉地区五峰组—龙马溪组露头样品暗色泥质岩矿物组成统计表
Table 4. Mineral composition statistics of outcrop samples from Wufeng Fm.– Longmaxi Fm. in Kuankuo–Fuyan area
矿物成分 石英 钾长石 斜长石 方解石 白云石 菱铁矿 黄铁矿 硬石膏 黏土矿物 最大值(%) 80 5 15 29 5 2 11 15 80 最小值(%) 10 2 3 1 2 2 1 2 14 平均值(%) 48.5 3.1 6.5 8.8 3.5 2 2.8 5.4 37.9 样品数 48 32 40 23 6 4 12 5 48 -
陈竹新, 贾东, 魏国齐, 等. 龙门山北段冲断前锋构造带特征[J]. 石油学报, 2008,29(5): 657-668.
CHEN Zhuxin, JIA Dong, WEI Guoqi, et al. Characteristics of thrust structures in the northern Longmenshan front belt [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2008, 29(5): 657-668.
丁道桂, 潘文蕾, 彭金宁, 等. 扬子板块中、古生代盆地的改造变形[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2008,29(5): 597-606
DING Daogui, PAN Wenlei, Peng Jinning, et al. Transformation and deformation of the Meso-Paleozoic basins in the Yangtze Plate [J]. Oil & Gas Geology,2008, 29(5): 597-606.
樊薛沛, 李金龙, 张玉萍, 等. 长岭断陷烃源岩有机质类型判断[J]. 天然气技术与经济, 2018, 12(3): 14-18.
FAN Xuepei, LI Jinlong, ZHANG Yuping, et al. Organic-matter Types of Source Rocks, Changling Fault Depression[J]. Natural Gas Technology and Economy, 2018,12(3): 14-18.
贵州省地质调查院. 贵州省1∶250 000建造构造图[R].贵州:贵州省地质调查院, 2010.
郭彤楼, 张汉荣. 2014. 四川盆地焦石坝页岩气田形成与富集高产模式[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 41(1): 28-36
GUO Tonglou, ZHANG Hanrong. 2014. Formation and enrichment mode of Jiaoshiba shale gas field, Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 41(1): 28-36.
郭旭升, 胡东风, 文治东, 等. 2014. 四川盆地及周缘下古生界海相页岩气富集高产主控因素: 以焦石坝地区五峰组—龙马溪组为例[J]. 中国地质, 41(3): 893-901
GUO Xusheng, HU Dongfeng, WEN Zhidong, et al. 2014. Major factors controlling the accumulation and high productivity in marine shale gas in Lower Paleozoic of Sichuan Basin and its periphery: a case study of Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation in Jiaoshiba area [J]. Geology in China, 41(3): 893-901.
郭旭升. 南方海相页岩气"二元富集"规律: 四川盆地及周缘龙马溪组页岩气勘探实践认识[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(7): 1209-1218
GUO Xusheng. Rules of two-factor enrichiment for marine shale gas in southern China—Understanding from the Longmaxi Formation shale gas in Sichuan basin and its surrounding area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(7): 1209-1218.
郭旭升. 四川盆地涪陵平桥页岩气田五峰组—龙马溪组页岩气富集主控因素[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2019, 30(1): 1-10 doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2018.12.007
GUO Xusheng. Controlling factors on shale gas accumulations of Wufeng-Longmaxi Formations in Pingqiao shale gas field in Fuling area, Sichuan Basi[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2019, 30(1): 1-10. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2018.12.007
贺永忠, 向坤鹏, 安亚运, 等. 黔北正安地区五峰组—龙马溪组页岩气地质特征及有利区预测[J]. 中国地质调查, 2020, 7( 3) : 21 - 29.
HE Yongzhong, XIANG Kunpeng, AN Yayun, et al. Geological characteristics and favorable areas prediction of shale gas in Wufeng - Longmaxi Formation in Zheng'an area of Northern Guizhou[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2020, 7( 3) : 21 - 29.
黄籍中. 用稳定碳同位素δ13C值识别干酪根类型的尝试[J]. 石油实验地质, 1980, (02): 49-54.
HUANG Jizhong. An attempt to identify kerogen types using stable carbon isotope δ13C value[J]. Petroleum Experimental Geology, 1980, (02): 49-54.
黄籍中.干酪根的稳定碳同位素分类依据[J]. 地质地球化学, 1988, (03):66-68.
HUANG Jizhong. Classification basis of stable carbon isotope of kerogen [J]. Geology & Geochemistry, 1988, (03):66-68.
姜振学, 宋岩, 唐相路, 等. 中国南方海相页岩气差异富集的控制因素[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(3): 1-12 doi: 10.11698/PED.2020.03.18
JIANG Zhenxue, SONG Yan, TANG Xianglu, et al. Controlling factors of marine shale gas differential enrichment in southern China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(3): 1-12. doi: 10.11698/PED.2020.03.18
姜振学, 唐相路, 李卓, 等. 川东南地区龙马溪组页岩孔隙结构全孔径表征及其对含气性的控制[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23(2): 126-134 doi: 10.13745/j.esf.2016.02.013
JIANG Zhenxue, TANG Xianglu, LI Zhuo, et al. The whole-aperture pore structure characteristics and its effect on gas content of the Longmaxi Formation shale in the southeastern Sichuan basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2016, 23(2): 126-134. doi: 10.13745/j.esf.2016.02.013
蒋恕, 唐相路, Steve O, 等. 页岩油气富集的主控因素及误辩: 以美国、阿根廷和中国典型页岩为例[J]. 地球科学, 2017, 42(7): 1083-1091
JIANG Shu, TANG Xianglu, Steve O, et al. Enrichment factors and current misunderstanding of shale oil and gas: case study of shales in U. S. , Argentina and China[J]. Earth Science, 2017, 42(7): 1083-1091.
李皎, 何登发, 梅庆华. 四川盆地及邻区奥陶纪构造—沉积环境与原型盆地演化[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(4): 427-445 doi: 10.7623/syxb201504004
LI Jiao, HE Dengfa, MEI Qinghua. Tectonic-depositional environment and proto-type basins evolution of the Ordovician in Sichuan Basin and adjacent areas[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(4): 427-445. doi: 10.7623/syxb201504004
刘树根, 罗志立, 戴苏兰, 等. 龙门山冲断带的隆升和川西前陆盆地的沉降[J]. 地质学报, 1995, 69(3): 205-214
LIU Shugen, LUO Zhili, DAI Sulan, et al. The uplift of the Longmenshan thrust belt and subsidence of the western Sichuan foreland basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1995, 69(3): 205-214.
邱振, 邹才能, 王红岩, 等. 中国南方五峰组—龙马溪组页岩气差异富集特征与控制因素[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(2): 163-175
QIU Zhen, ZOU Caineng, WANG Hongyan, et al. Discussion on characteristics and controlling factors of differential enrichment of Wufeng-Longmaxi formations shale gas in South China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2020, 31(2): 163-175.
尚玥, 赵涵, 王强, 等. 黔北务川—正安—道真地区上奥陶统五峰组—下志留统龙马溪组沉积相分析[J]. 矿物岩石, 2020, 40(4): 86-96
SHANG Yue, ZHAO Han, WANG Qiang, et al. Analysis of Sedimentary Facies of the Upper Ordovician Wufeng Formation-Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation in the Wuchuan-Zheng'an-Daozhen Area, Northern Guizhou Province[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2020, 40(4): 86-96.
孙莎莎, 芮昀, 董大忠, 等. 中、上扬子地区晚奥陶世—早志留世古地理演化及页岩沉积模式[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(6): 1087-1106 doi: 10.11743/ogg20180601
SUN Shasha, RUI Yun, DONG Dazhong, et al. Paleogeographic evolution of the Late Ordovician-Early Silurian in Upper and Middle Yangtze regions and depositional model of shale[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(6): 1087-1106. doi: 10.11743/ogg20180601
四川油气区石油地质志编写组. 四川油气区 中国石油地质志 卷十[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1989, 1-79.
王茜, 黄永建, 张治锋, 等. 上扬子地区新地1 井五峰组—龙马溪组下段高分辨化学层序地层学分析[J]. 中国地质,2020. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20201222.1046.002.html.
WANG Qian, HUANG Yongjian, ZHANG Zhifeng, et al. High resolution chemical sequence stratigraphy analysis of Wufeng Formation and lower Longmaxi Formation in the well Xindi 1, upper Yangtze Region[J]. Geology in China, 2020.https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20201222.1046.002.html.
吴纪修, 王志刚, 辛云路, 等. 南方地区页岩气基础地质调查黔绥地1井钻井工艺及完井地质[J]. 探矿工程(岩土钻掘工程), 2018, 45(2): 12-17
WU Jixiu, WANG Zhigang, XIN Yyunlu, et al. Drilling Technology of Qiansuidi Well-1 for Basic Geological Survey of Shale Gas in the Southern Area of Guizhou Province and Completion Geologic[J]. Exploration Engineering (Rock & Soil Drilling and Tunneling), 2018, 45(2): 12-17.
伍坤宇, 张廷山, 杨洋, 等. 昭通示范区黄金坝气田五峰—龙马溪组页岩气储层地质特征[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(1): 275-287 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2016.01.020
WU Kunyu, ZHANG Tingshan, YANG Yang, et al. Geological characteristics of Wufeng − Longmaxi shale − gas reservoir in the Huangjinba gas field, Zhaotong National Shale Gas Demonstration Area[J]. Geology in China, 2016, 43(1): 275-287. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2016.01.020
解习农, 郝芳, 陆永潮, 等. 南方复杂地区页岩气差异富集机理及其关键技术[J]. 地球科学, 2017, 42(7): 1045-1056
XIE Xinong, HAO Fang, LU Yongchao, et al. Differential enrichment mechanism and key technology of shale gas in complex areas of south China[J]. Earth Science, 2017, 42(7): 1045-1056.
徐政语, 蒋恕, 熊绍云, 等. 扬子陆块下古生界页岩发育特征与沉积模式[J]. 沉积学报, 2015, 33(1): 21-35 doi: 10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.2015.01.003
XU Zhengyu, JIANG Shu, XIONG Shaoyun, et al. Characteristics and depositional model of the Lower Paleozoic organic rich shale in the Yangtze continental block [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2015, 33(1): 21-35. doi: 10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.2015.01.003
徐政语, 梁兴, 王维旭, 等. 上扬子区页岩气甜点分布控制因素探讨—— 以上奥陶统五峰组—下志留统龙马溪组为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2016, 39(9): 35-43 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2016.09.004
XU Zhengyu, LIANG Xing, WANG Weixu, et al. Controlling factors for shale gas sweet spots distribution in the Upper Yangtze region: A case study of the Upper Ordovician Wufeng Formation–Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2016, 39(9): 35-43. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2016.09.004
杨平, 汪正江, 余谦, 等. 四川盆地西南缘五峰—龙马溪组页岩气资源潜力分析[J]. 中国地质, 2019, 46(3): 601-614.
YANG Ping, WANG Zhengjiang, YU Qian, et al. An resources potential analysis of Wufeng- Longmaxi Formation shale gas in the southwestern margin of Sichuan Basin[J]. Geology in China, 2019, 46(3): 601- 614.
翟刚毅, 王玉芳, 包书景, 等. 我国南方海相页岩气富集高产主控因素及前景预测[J]. 地球科学, 2017, 42(7): 1057-1068
ZHAI Gangyi, WANG Yufang, BAO Shujing, et al. Major factors controlling the accumulation and high productivity of marine shale gas and prospect forecast in southern China[J]. Earth Scienc, 2017, 42(7): 1057-1068.
张国伟, 郭安林, 王岳军, 等. 中国华南大陆构造与问题[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2013, 43(10): 1553-1582.
ZHANG Guowei, GUO Anlin, WANG Yuejun, et al. Continental tectonics and problems in South China [J]. Chinese Sciences: Geosciences, 2013, 43(10): 1553-15827.
张金川, 金之钧, 袁明生. 页岩气成藏机理和分布[J]. 天然气工业, 2004, 24(7): 15-18 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2004.07.005
ZHANG Jinchuan, JIN Zhijun, YUAN Mingsheng. Reservoiring mechanism of shale gas and its distribution[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2004, 24(7): 15-18. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2004.07.005
张金川, 聂海宽, 徐波, 等. 四川盆地页岩气成藏地质条件[J]. 天然气工业, 2008, 28(2): 151-156 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2008.02.045
ZHANG Jinchuan, NIE Haikuan, XU Bo, et al. Geological condition of shale gas accumulation in Sichuan basin [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2008, 28(2): 151-156. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2008.02.045
张金川, 薛会, 张德明, 等. 页岩气及其成藏机理[J]. 现代地质, 2003, 17(4): 466 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2003.04.019
ZHANG Jinchuan, XUE Hui, ZHANG Deming, et al. Shale gas and its reservoir forming mechanism [J]. Geoscience, 2003, 17(4): 466. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2003.04.019
张岳桥, 董树文, 李建华, 等. 中生代多向挤压构造作用与四川盆地的形成和改造[J]. 中国地质, 2011, 38(2): 233-250 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2011.02.001
ZHANG Yueqiao, DONG Shuwen, LI Jianhua, et al. Mesozoic multi-directional compressional tectonics and formation-reformation of Sichuan basin [J]. Geology in China, 2011, 38(2): 233-250. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2011.02.001
赵文智, 李建忠, 杨涛, 等. 中国南方海相页岩气成藏差异性比较与意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2016, 43(4): 499-510 doi: 10.11698/PED.2016.04.01
ZHAO Wenzhi, LI Jianzhong, YANG Tao, et al. Geological difference and its significance of marine shale gases in South China [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2016, 43(4): 499-510. doi: 10.11698/PED.2016.04.01
中国地质调查局油气资源调查中心. 贵州遵义安页1井页岩气、油气调查获重大突破[J]. 中国地质调查, 2016, 3(4): 76-77 doi: 10.19388/j.zgdzdc.2016.04.012
Oil & Gas Survey Center of China Geological Survey. Major breakthrough in shale gas and oil and gas survey of Anye 1 well in Zunyi, Guizhou [J]. Geological Survey of China, 2016, 3 (4): 76-77. doi: 10.19388/j.zgdzdc.2016.04.012
邹才能, 杜金虎, 徐春春, 等. 四川盆地震旦系—寒武系特大型气田形成分布、资源潜力及勘探发现[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(3): 278-293 doi: 10.11698/PED.2014.03.03
ZOU Caineng, DU Jinhu, XU Chunchun, et al. Formation, distribution, resource potential and discovery of the Sinian−Cambrian giant gas field, Sichuan Basin, SW China [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(3): 278-293. doi: 10.11698/PED.2014.03.03
邹才能, 赵群, 丛连铸, 等. 中国页岩气开发进展、潜力及前景[J]. 天然气工业, 2021, 41(1): 1-14
ZOU Caineng, ZHAO Qun, CONG Lianzhu, et al. Development progress, potential and prospect of shale gas in China [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(1): 1-14.
邹才能, 赵群, 张国生, 等. 能源革命: 从化石能源到新能源J]. 天然气工业, 2016, 36(1): 1 − 10.
ZOU Caineng, ZHAO Qun, ZHANG Guosheng, et al. Energy revolution: From a fossil energy era to a new energy era[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2016, 36(1): 1 − 10.
Curtis J B. Fractured shale-gas systems[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2002, 86 (11) : 1921-1938.
Ross D J, Bustin R M. The importance of shale composition and pore structure upon gas storage potential of shale gas reservoirs[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2009, 26(6): 916-927. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2008.06.004
-




 下载:
下载: