Sandbox Physical Simulation Experiment of Extensional Structure under Different Stretching Modes and Speeds
-
摘要:
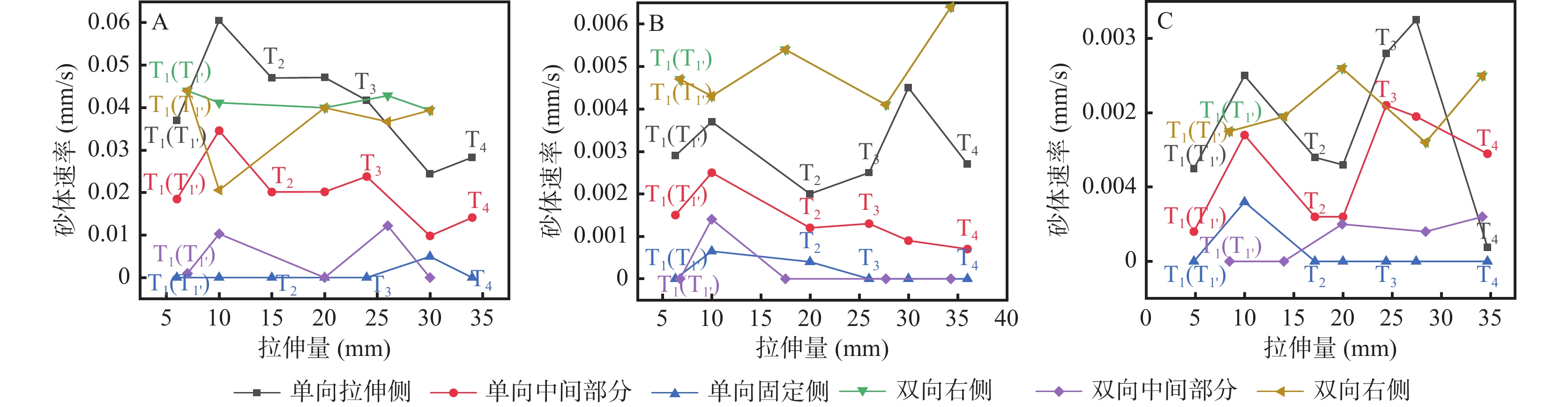
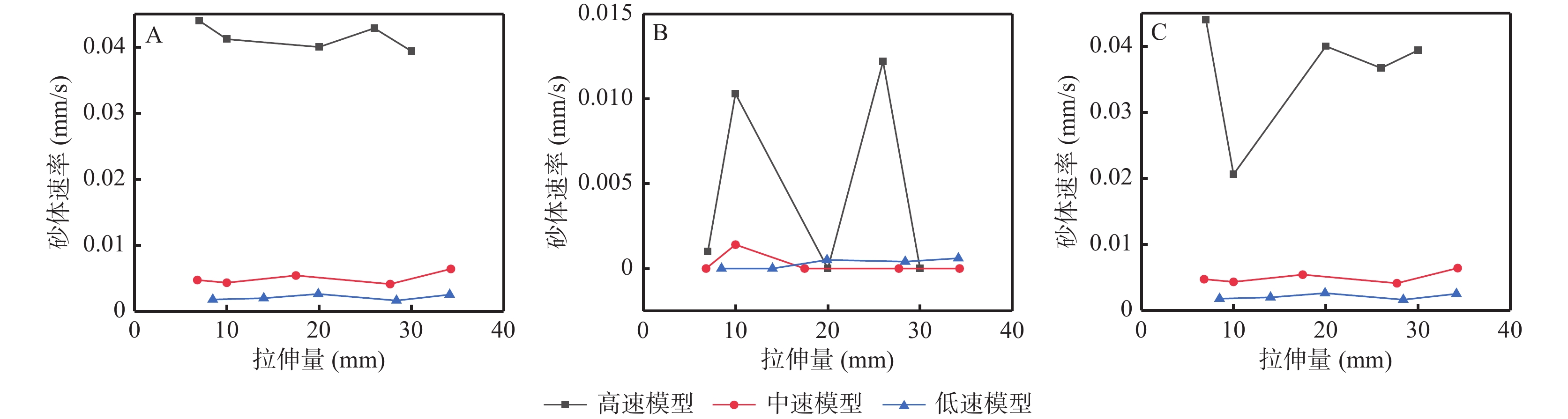
砂箱构造物理模拟实验是室内模拟自然界地质构造变形过程、成因机制以及动力学过程的一种高效方法。影响岩石变形的速度和力的作用方式等是影响伸展构造物理模拟实验的结果和构造形态的主要因素。基于此,为探究砂箱物理模拟实验中拉伸速度和拉伸方式(力的作用方式)对伸展构造变形特征的影响,笔者在已有研究基础上,将高(0.01 mm/s)、中(0.001 mm/s)、低(0.000 5 mm/s)3种不同拉伸速度与单向拉伸、双向拉伸2种不同拉伸方式相结合,设计6组实验进行对比研究。结果表明:①拉伸速度对砂体的最终形态无显著影响,但对断层的发育过程有一定的影响,而拉伸方式对断层的发育过程和最终形态的影响均较为显著,且断层形成前砂体速度会增大到一定高值,并于断层形成后快速减小。②单向拉伸模型砂体最终均形成一个不对称的地堑,双向拉伸模型砂体最终均形成一个典型的地堑。③不对称地堑通常形成于相对拉伸或差异拉伸的环境中,相对拉伸侧发育形成一系列阶梯状正断层,而相对固定侧发育一条断距较大的正断层,且先存构造的位置往往决定了后期构造发育的初始位置。这一认识为伸展构造砂箱物理模拟实验中的模型设置和参数选取奠定了基础。
Abstract:Sandbox structural physics simulation experiment is an efficient method to simulate the deformation process, genesis mechanism and dynamic process of natural structural deformation in laboratory. Factors affecting the rate of rock deformation and the mode of action of forces are the main factors affecting the results of physical simulation experiments of extensional tectonics and tectonic morphology. Based on this, in order to investigate the effects of tensile speed and tensile mode (mode of the stress action) on extensional structural deformation characteristics in sandbox physical simulation experiment. This article is based on existing research, three different stretching speeds of high (0.01 mm/s), medium (0.001 mm/s) and low (0.000 5 mm/s) are combined with two different stretching methods of unidirectional and bidirectional stretching, and six sets of experiments are designed for comparative study. The results show that: ① Tensile velocity has no significant effect on the final morphology of the sand body, but has a certain influence on the development process of the fault, while the influence of the tensile mode on both the development process and the final morphology of the fault is more significant, and the velocity of the sand body increases to a certain high value before the formation of the fault and decreases rapidly after the formation of the fault. ② The sand body of the unidirectional stretching model eventually forms an asymmetric graben tectonic feature. The sand bodies of the two–way stretching model eventually form a typical graben tectonic feature. ③ Asymmetric graben structures are usually formed in a relatively stretched or differentially stretched environment, with a series of stepwise positive faults on the relatively stretched side and a large positive fault on the relatively fixed side, and the location of the pre–existing structure often determines the initial location of the later structure development. This understanding lays the foundation for the model setting and parameter selection in sandbox analogue modeling of the extensional structure.
-
Key words:
- structural physical simulation /
- extensional structure /
- PIV /
- geometrical morphology /
- stress–strain
-

-
表 1 各组模型断层形成时刻
Table 1. The fault formation time of each models
断层 单向高速拉伸 单向中速拉伸 单向低速拉伸 双向高速拉伸 双向中速拉伸 双向低速拉伸 拉伸量(mm) 时间(s) 拉伸量(mm) 时间(s) 拉伸量(mm) 时间(s) 拉伸量(mm) 时间(s) 拉伸量(mm) 时间(s) 拉伸量(mm) 时间(s) T1 6 600 6.32 6320 4.85 9700 7 350 6.8 3400 8.48 8480 T1' 6 600 6.32 6320 4.85 9700 7 350 6.8 3400 8.48 8480 T2 15 1500 20 20000 17.15 34300 T3 24 2400 26 26000 24.4 48800 T4 34 3400 36 36000 34.7 69400 -
白鸾羲. 鄂尔多斯周缘上更新统角度不整合面的时代厘定及其构造意义[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所, 2021
BAI Luanxi. Timing of angular unconformities in Upper Pleistocene around the Ordos Block and its tectonic significance: case studies in the Hetao Basin and Shanxi Graben system[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geophysics, China Seismological Bureau, 2021.
陈兴鹏. 伸展、走滑应力叠加、配比条件下构造变形特征的物理模拟实验研究[D]. 东营: 中国石油大学(华东), 2017
CHEN Xingpeng. Structural Deformation Characteristic Analysis with Superposition and Ratios of Extensional and Strike-Slip Stress: Insights from Physical Analog Experiments[D]. Dongying: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2017.
陈竹新, 雷永良, 贾东, 等. 构造变形物理模拟与构造建模技术及应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019
CHEN Zhuxin, LEI Yongliang, JIA Dong, et al. Physical Analog and Structural Modeling Techniques and Applications [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2019.
邓宾, 赵高平, 万元博, 等. 褶皱冲断带构造砂箱物理模型研究进展[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2016, 40(03): 446-464 doi: 10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2016.03.004
DENG Bin, ZHAO Gaoping, WAN Yuanbo, et al. A Review of Tectonic Sandbox Modeling of Fold-and-thrust Belt [J]. Geotectonicaet Metallogenia, 2016, 40(03): 446-464. doi: 10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2016.03.004
胡林, 李才, 金秋月, 等. 伸展背景下塑性地层对断裂发育特征影响的实验分析[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(05): 1749-1757
HU Lin, LI Cai, JIN Qiuyue, et al. Experimental Analysis on Influence of Plastic Formation on Characteristics of Fault Development under Extensional Stress [J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(05): 1749-1757.
赖冬. 莺歌海盆地底辟构造特征及其油气意义[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2019
LAI Dong. Geometry and kinematics of diapir and its implication in the Yinggehai Basin: insights from analogue experiments [D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2019.
罗强, 何宇, 黄家强, 等. 川西北前陆扩展砂箱物理模拟及其深层晚期扩展变形特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(06): 1031-1040
LUO Qiang, HE Yu, HUANG Jiaqiang, et al. Analogue experiments on the piggyback propagation in northwestern Sichuan and latest propagation in its deeps [J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(06): 1031-1040.
孟元库, 汪新文, 李波, 等. 华北克拉通中部沁水盆地热演化史与山西高原中新生代岩石圈构造演化[J]. 西北地质, 2015, 48(02): 159-168 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2015.02.016
MENG Yuanku, WANG Xinwen, LI Bo, et al. Thermal evolution history of Qinshui basin in the central north China Craton and Mesozoic-cenozoic lithospheric tectonic evolution of Shanxi plateau [J]. Northwestern Geology, 2015, 48(02): 159-168. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2015.02.016
潘文华. 双滑脱层褶皱-冲断带变形场演化规律的物理模拟研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2020
PAN Wenhua. Study on the evolution law of deformation field of fold-thrust belt with double detachments: Insight from analogue modelling[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2020.
漆家福, 吴景富, 马兵山, 等. 南海北部珠江口盆地中段伸展构造模型及其动力学[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(02): 203-221 doi: 10.13745/j.esf.sf.2019.1.16
QI Jiafu, WU Jingfu, MA Binshan, et al. The structural model and dynamics concerning middle section, Pearl River Mouth Bsin in north margin of South China Sea [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(02): 203-221. doi: 10.13745/j.esf.sf.2019.1.16
瞿伟, 王运生, 徐超, 等. 渭河盆地构造应力场有限元数值模拟[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2017, 42(12): 1749-1755
QU Wei, WANG Yunsheng, XU Chao, et al. Tectonic Stress Field of the Weihe Basin Using the Finite Element Method [J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2017, 42(12): 1749-1755.
谢玉洪. 浅表走滑构造系统砂箱物理模拟研究进展[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2021, 45(06): 1127-1145 doi: 10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2021.02.015
XIE Yuhong. A Review on Analogue Modelling of Strike-slip Tectonics [J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2021, 45(06): 1127-1145. doi: 10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2021.02.015
赵仕俊, 赵锡奎, 杨少春. 地质构造物理模拟实验模型的相似分析[J]. 西北地质, 2005(04): 14-18 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2005.04.003
ZHAO Shijun, ZHAO Xikui, YANG Shaochun. Similar analysis of geological structure physical model [J]. Northwestern Geology, 2005(04): 14-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2005.04.003
Ahmad M I, Dubey A K, Toscani G, et al. Kinematic evolution of thrusts wedge and erratic line length balancing: insights from deformed sandbox models [J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2014, 103(1): 329-347. doi: 10.1007/s00531-013-0947-8
Asensio E, Khazaradze G, Echeverria A, et al. GPS studies of active deformation in the Pyrenees [J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2012, 190(2): 913-921. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2012.05525.x
Deng Bin, Jiang Lei, Zhao Gaoping, et al. Insights into the velocity-dependent geometry and internal strain in accretionary wedges from analogue models [J]. Geological Magazine, 2018, 155(5): 1089-1104. doi: 10.1017/S0016756816001266
Deng Bin, Koyi H, Fan Caiwei, et al. Modelling asymmetric deformation along a curved strike-slip basement-fault system[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2021, 110(1): 165-182. doi: 10.1007/s00531-020-01943-4
Erdős Z, Huismans R S, van der Beek P, et al. Extensional inheritance and surface processes as controlling factors of mountain belt structure[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2014, 119(12): 9042-9061. doi: 10.1002/2014JB011408
Fan Xiaogen, Jia Dong, Yin Hongwei, et al. Analogue modeling of the northern Longmen Shan thrust belt (eastern margin of the Xizang plateau) and strain analysis based on Particle Image Velocimetry[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2020, 198: 13.
Hagke C V, Reber J, Philippon M. Cutting-Edge Analogue Modeling Techniques Applied to Study Earth Systems[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2019, 7: 265. doi: 10.3389/feart.2019.00265
Hatzfeld D, Molnar P. Comparisons of the kinematics and deep structures of the Zagros and Himalaya and of the Iranian and Xizang plateaus and geodynamic implications [J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2010, 48, RG2005.
Lohrmann J, Kukowski N, Adam J, et al. The impact of analogue material properties on the geometry, kinematics, and dynamics of convergent sand wedges [J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2003, 25(10): 1691-1711. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8141(03)00005-1
Reber J E, Cooke M L, Dooley T P. What model material to use? A Review on rock analogs for structural geology and tectonics[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020, 202: 103-107.
Toscani G, Bonini L, Ahmad M I, et al. Opposite verging chains sharing the same foreland: Kinematics and interactions through analogue models (Central Po Plain, Italy)[J]. Tectonophysics, 2014, 633: 268-282. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2014.07.019
Yan D P, Xu Y B, Dong Z B, et al. Fault-related fold styles and progressions in fold-thrust belts: Insights from sandbox modeling[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research-Solid Earth, 2016, 121(3): 2087-2111. doi: 10.1002/2015JB012397
Yan J, Hu J, Gong W, et al. Late Cenozoic magnetostratigraphy of the Yuncheng Basin, central North China Craton and its tectonic implications[J]. Geological Journal, 2020, 55(11): 7415-7428. doi: 10.1002/gj.3744
Yu S B, Chen H Y, Kuo L C. Velocity field of GPS stations in the Taiwan area [J]. Tectonophysics, 1997, 274(1-3): 41-59. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(96)00297-1
-




 下载:
下载: