Research on Seepage Barriers of Massive and Superimposed Thick Oil Layers in the Low Oil Formation of No. 9 Block in Tahe Oilfield
-
摘要:
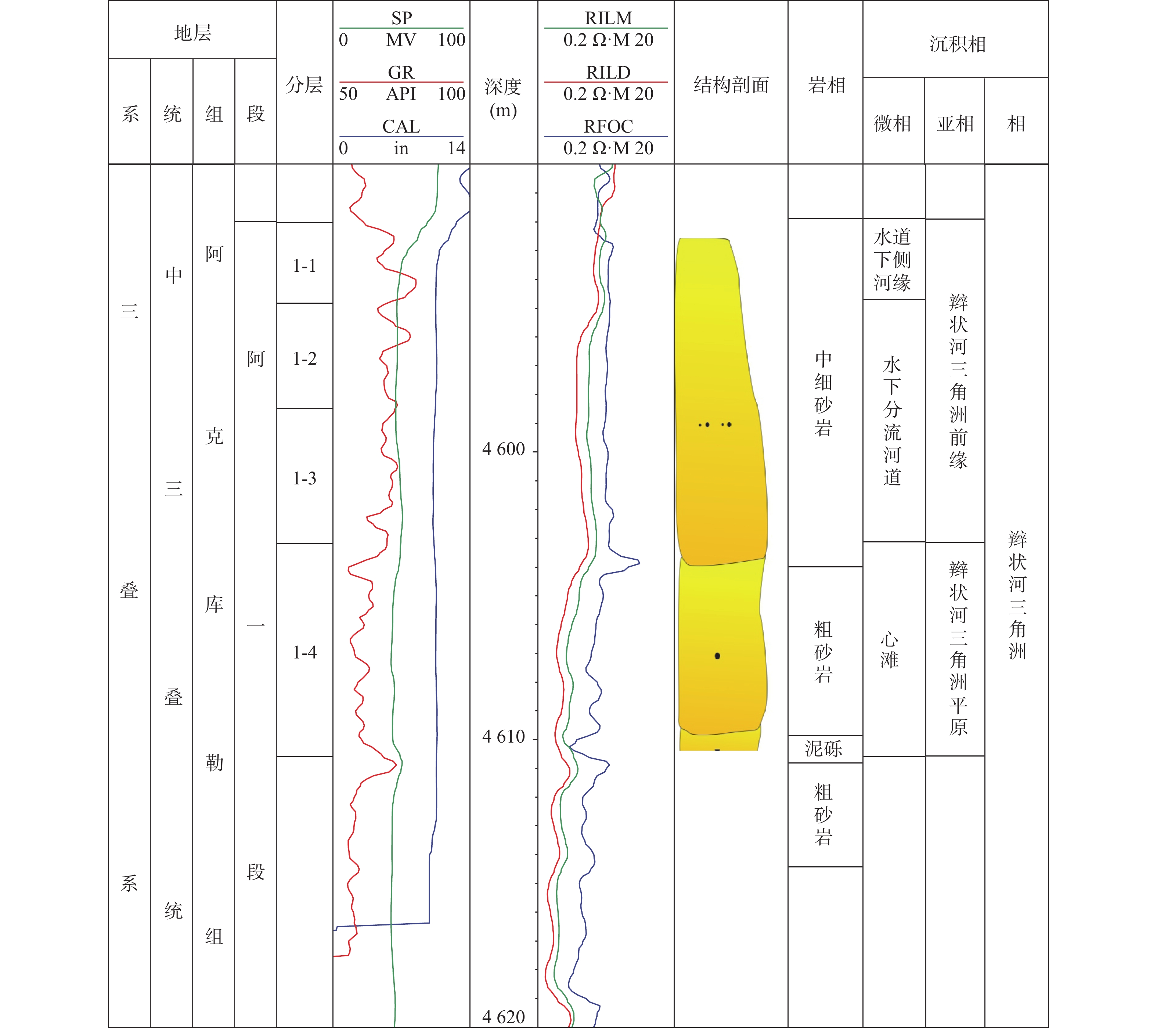
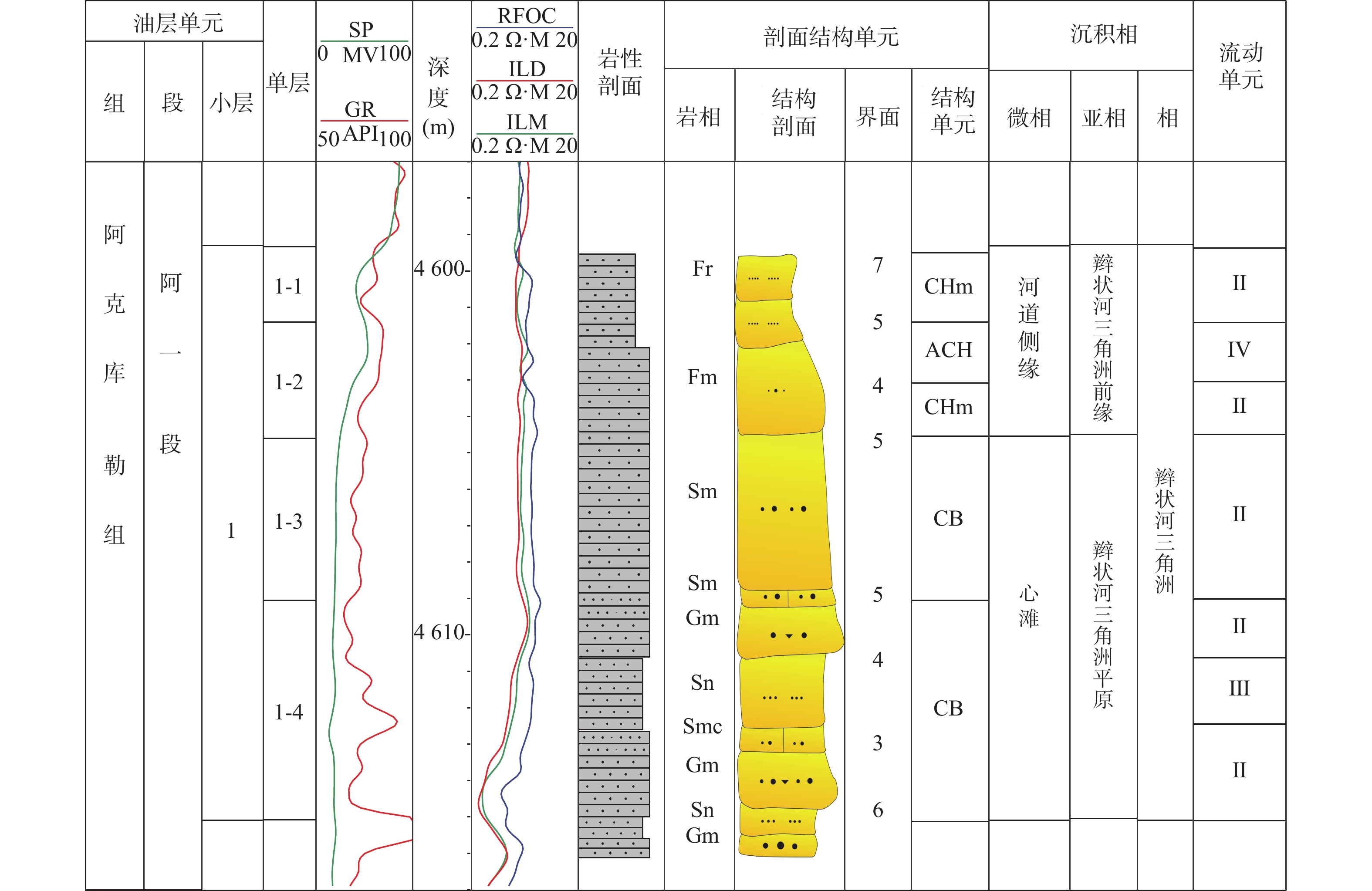
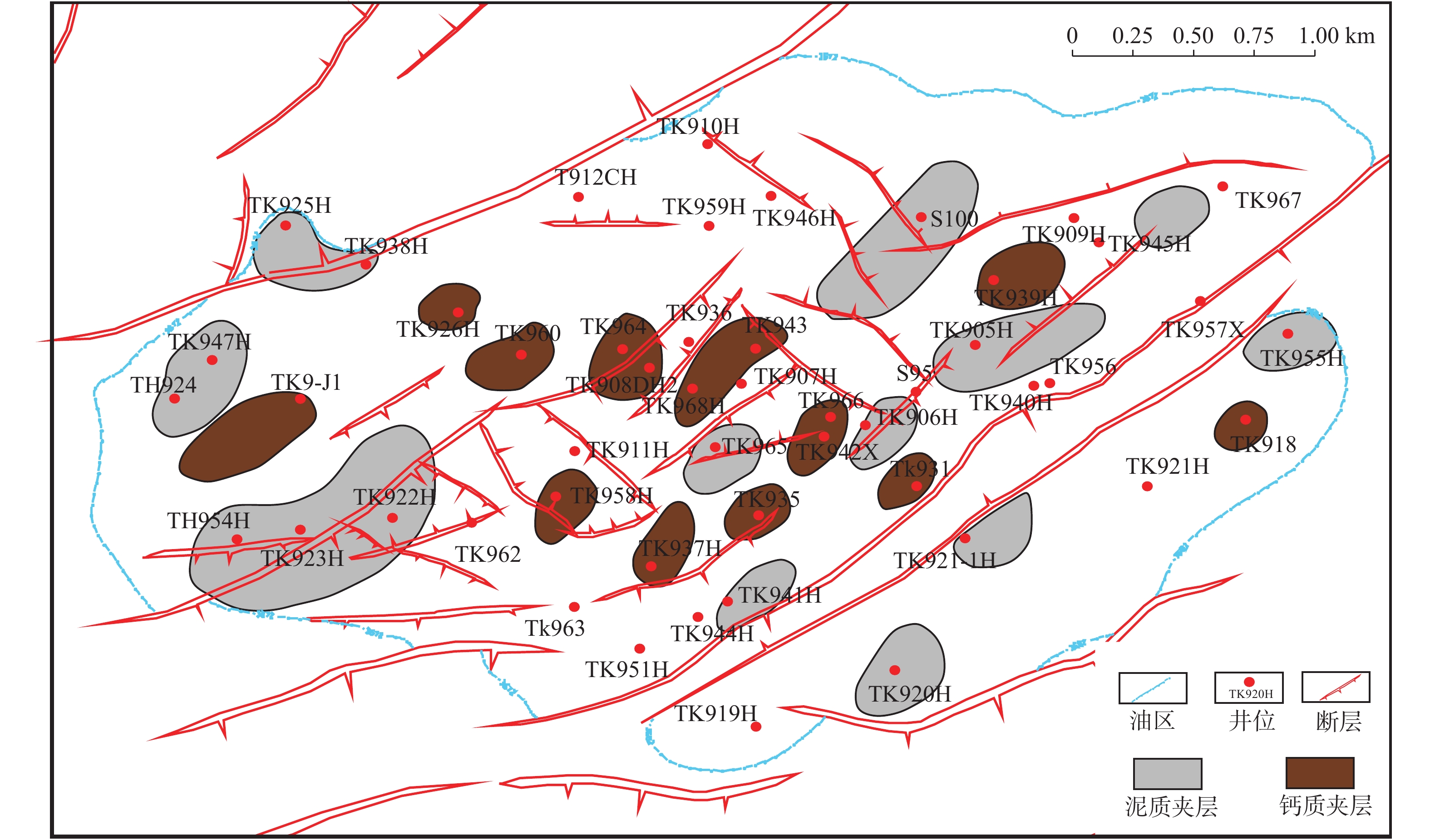
塔河油田9区三叠系阿克库勒组下油组储层为典型的块状叠置辫状河三角洲储层,夹层分布及连通性极其复杂,封闭断层和泥质屏障、钙质胶结帯等不同级次渗流屏障控制着油藏内部油水运动。为深化储层空间非均质表征,在储层构型分析基础上,笔者采用层次分析方法,动静态相结合,对渗流屏障类型及其级次进行划分,分析泥质屏障、钙质胶结帯形成机理及其受控因素,建立块状厚油层渗流屏障分布地质模型。研究表明:塔河油田9区下油组主要渗流屏障为封闭断层屏障和层间、层内发育的泥质及钙质隔夹层;依据渗流阻挡作用分为4个级次,东北向封闭性断层及复合河道顶部6级界面是1级渗流屏障,3~5级构型界面控制了2~4级泥质、钙质渗流屏障的发育,建立完全不遮挡型、部分遮挡型及完全遮挡型等3种渗流屏障模式。通过分级次定量表征渗流屏障的空间分布,深化储层空间非均质性研究,为基于流动单元的精细地质建模奠定基础。
Abstract:The low oil formation reservoir of No. 9 block in the Tahe Oilfield is a superimposedmassive braided river delta reservoir, moreover, distribution and connectivity of the interlayers as well as complexity produced the sealing faults, argillaceous barriers, calcareous cemented zones and other different–level seepage barriers to control the movement of oil and water within the reservoir is to deepen the heterogeneity of the reservoir space; and the analytic hierarchy process is adopted based on the analysis of the reservoir configuration, and combined with dynamic and static, to clarify the seepage barrier types and levels;the formation mechanism of calcareous cement zone and its controlling factors is analyzed by researcher, so that establishes a geological model for the distribution of seepage barriers in massive thick oil layers; Researches show that the main seepage barriers of the low oil formation in No. 9 Block of Tahe Oilfield are sealing faults barriers, mud barriers, and calcium cemented zones, what is more, it can be divided into four levels according to the seepage blocking effect, and northeast sealing faults and the 6–level interface at the top of the composite channel are the first–level seepage barrier, the 3~5 level configuration interface controls the 2~4 level mud and calcareous seepage barriers; to establish three types of seepage barrier modes composed by completely uncover, partial cover, and completely cover. The spatial distribution of seepage barriers is characterized by hierarchical and sub–quantitative methods, which deepening the study of reservoir spatial heterogeneity, and laying the foundation for fine geological modeling based on flow units.
-

-
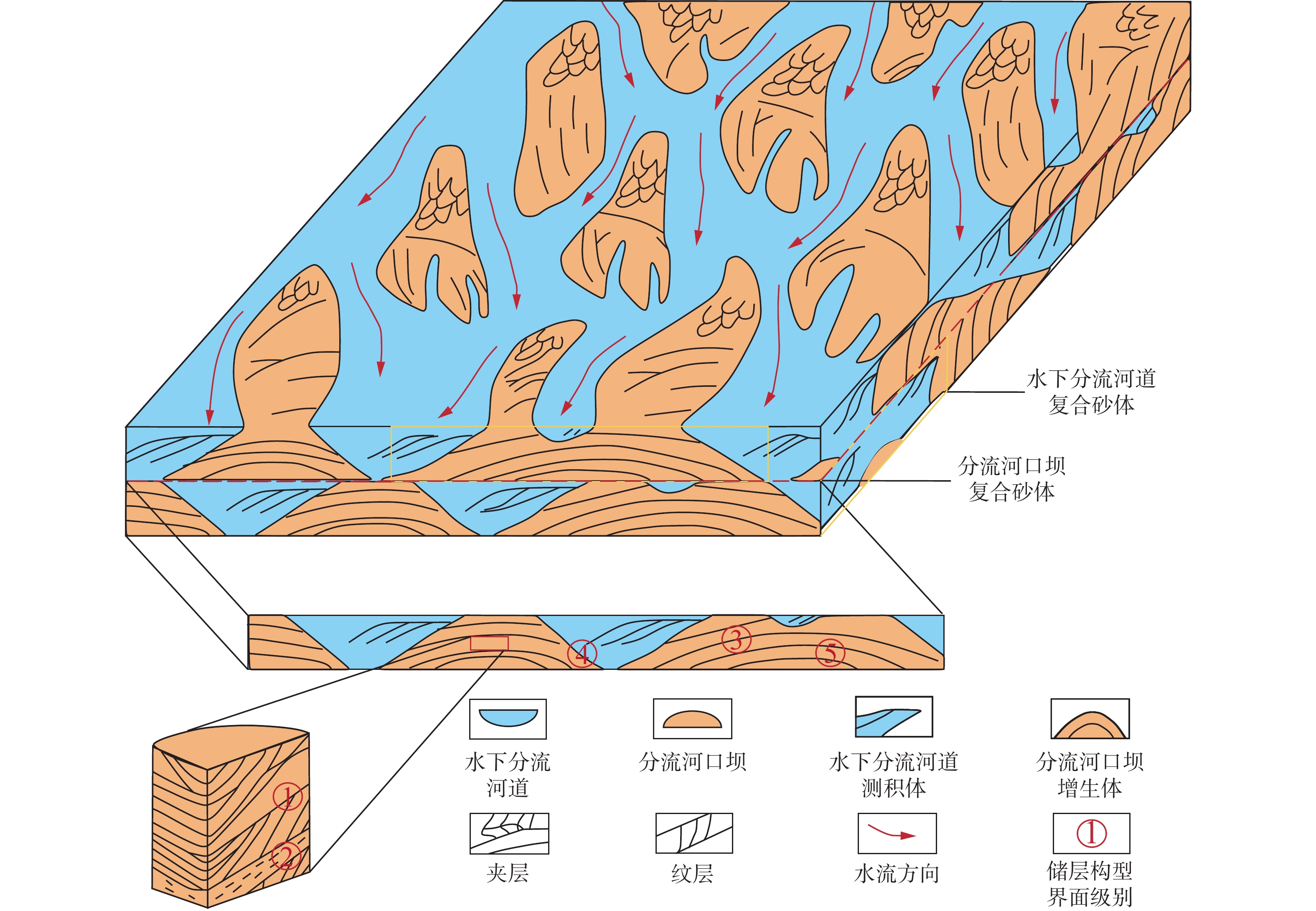
图 4 塔河油田9区三叠系下油组三角洲前缘储层构型模式图(据徐丽强等,2016修改)
Figure 4.
表 1 渗流屏障级次及特征
Table 1. Seepage barrier grades and characteristics
渗流屏障
级别定义 对应构型界面级别 通体级别 一级 封闭性断层及垂向不同期次沉积体系间的非渗透性边界 6级(区域稳定沉积的泥岩隔层、不整合) 连通体 二级 同期水道与心滩坝沉积组合之间
非渗透性边界5级(沉积体系组合之间的泥岩或者泛滥平原沉积) 连通单元 三级 同期水道与心滩项之间的界面 4级(泥质河道、泥质半充填河道和洪水
漫流细粒沉积)连通单元 四级 心滩坝内部的非渗透性沉积 3级(心滩坝内部落淤层,坝上沟道 渗流单元 表 2 不同构型单元非均质性参数统计表
Table 2. Statistical table of heterogeneity parameters of different configuration units
层号 辫状河道 心滩 水下/水上分流河道 水下/水上河道侧缘 平均值 变异
系数突进
系数级差 平均值 变异
系数突进
系数级差 平均值 变异
系数突进
系数级差 平均值 变异
系数突进
系数级差 T2a1-1 — — — — — — — — 103 0.6 4 49.3 93.7 0.7 6.7 563.5 T2a1-2 68.3 0.42 1.7 3.6 — — — — 120.3 0.52 4 69.4 140.9 0.62 3 14.9 T2a1-3 221.9 0.55 2.5 11.5 136.1 0.4 1.9 7.4 150.6 0.5 3 34.3 106.5 0.52 2.9 10.7 T2a1-4 207.6 0.58 3.6 32 160.4 0.56 3.5 51.3 — — — — — — — — 平均 165.9 0.52 2.6 15.7 148.3 0.48 2.7 29.3 125.4 0.54 3.7 51 113.7 0.61 4.2 196.4 -
陈欢庆, 赵应成, 舒治睿, 等. 储层构型研究进展[J]. 特种油气藏, 2013, 20(5): 7-12 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2013.05.002
CHEN Huanqing, ZHAO Yingcheng, SHU Zhirui, et al. Advances in reservoir architecture research[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2013, 20(5): 7-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2013.05.002
段冬平, 侯加根, 郭素华, 等. 塔河油田九区三叠系油气藏隔夹层识别及其展布研究[J]. 科技导报, 2010, 28(19): 21-25
DUAN Dongping, HOU Jiagen, GUO Suhua, et al. Identification and distribution of interlayer in Triassic reservoir in block 9 of Tahe Oilfield [J]. Science and Technology Guide, 2010, 28 (19): 21-25.
付国民, 赵俊欣, 杨磊, 等. 塔河油田9区三叠系中上统高分辨率层序地层及沉积演化[J]. 兰州大学学报: 自然科学版, 2007, 43(3): 13-17.
FU Guomin, ZHAO Junxin, YANG Lei, et al. High resolution sequence ofstratigraphy and sedimentary evolution of middle-upper Triassic in the9th area, Tahe oil field[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University ( NaturalSciences) , 2009, 43( 3) : 13 - 17.
付国民, 周丽梅, 刘蕊, 等. 塔河三叠系下油组河流相储层夹层成因类型及其分布规律[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2009, 31(3): 260-264 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2009.03.006
FU Guomin, ZHOU Limei, LIU Rui, et al. Fluvial Facies Reservoir Interbed Genesis Category and Distribution Characteristic in Low Oil Group Triassic Tahe Oilfield[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2009, 31(3): 260-264. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2009.03.006
郭建华, 刘辰生, 朱锐. 阿克库勒地区三叠系层序地层学及储集砂体成因类型[J]. 沉积学报, 2007, 25( 2) : 169 - 177. .
GUO Jianhua, LIU Chensheng, ZHU Rui. Sequence stratigraphy and sandbody genetic types of Triassic system in Akekule area[J]. Acta Sedmentologica Sinica, 2007, 25( 2) : 169 - 177.
何拓平, 李元昊, 陈朝兵, 等. 深水重力流储层宏观非均质性控制因素-以华庆地区长63为例[J]. 西北地质, 2020, 53(1): 177-188
HE Tuoping, LI Yuanhao, CHEN Zhaobin, et al. Macroscopic Heterogeneity Controlling Factors of Deepwater Gravity Flow Reservoirs[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2020, 53(1): 177-188.
贺婷婷, 段太忠, 赵磊, 等. 塔里木盆地塔河油田T区三叠纪沉积模式[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(4): 822-833
HE Tingting, DAUN Taizhong, ZHAO Lei, et al. Triassic sedimentary model in Block T of Tahe oilfield, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(4): 822-833.
贺婷婷, 段太忠, 赵磊, 等. 塔河油田九区三叠纪下油组夹层识别及分布规律[J]. 东北石油大学学报, 2017, 41(6): 26-35 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4107.2017.06.004
HE Tingting, DUAN Taizhong, ZHAO Lei, et al. Identification and distribution of interlayer in Lower Triassic oil formation in block 9 of Tahe Oilfield [J]. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 2017, 41 (6): 26-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4107.2017.06.004
李顺明, 宋新民, 蒋有伟, 等. 高尚堡油田砂质辫状河储集层构型与剩余油分布[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2011, 38(4): 474-482
LI Shunming, SONG Xinmin, JIANG Youwei, et al. Architecture and remaining oil distribution of the sandy braided river reservoir in the Gaoshangpu Oilfield[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2011, 38(4): 474-482.
孙天建, 穆龙新, 吴向红, 等. 砂质辫状河储层构型表征方法——以苏丹穆格莱特盆地 Hegli 油田为例[J]. 石油学报, 2014a, 35(4): 715–734 doi: 10.7623/syxb201404012
SUN Tianjian, MU Longxin, WU Xianghong, et al. A quantitative method for architectural characterization of sandy braided- river reservoirs: taking Hegli oilfield of Muglad Basin in Sudan as an example[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2014a, 35(4): 715–734. doi: 10.7623/syxb201404012
孙天建, 穆龙新, 赵国良. 砂质辫状河储集层隔夹层类型及其表征方法—以苏丹穆格莱特盆地Hegli油田为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(1): 112–120
SUN Tianjian, MU Longxin, ZHAO Guoliang. Classification and characterization of barrier-intercalation in sandy braided river reservoirs: Taking Hegli Oilfield of Muglad Basin in Sudan as an example[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2014, 41(1): 112–120.
万琼华, 罗伟, 梁杰, 等. 基于储层构型的流动单元渗流屏障级次研究[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 41(1): 77-84
WAN Qionghua, LUO Wei, LIANG Jie, et al. Reservoir Architecture-based Classification of Seepafe Barriers of Flow Unit[J]Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition), 2019, 41(1): 77-84.
王珂, 戴俊生, 贾开富, 等. 塔河油田1区三叠系储层流动单元研究[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2014, 26(3): 120-130 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2014.03.020
WANG Ke, DAI Junsheng, JIA Kaifu, et al. Research on reservoir flow units of Triassic in block-1, Tahe Oilfield[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2014, 26(3): 120-130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2014.03.020
王石, 万琼华, 陈玉琨, 等. 基于辫状河储层构型的流动单元划分及其分布规律[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2015, 22(5): 47-51, 68 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2015.05.008
WANG Shi, WAN Qionghua, CHEN Yukun, et al. Flow units division and their distribution law based on braided river reservoir architecture[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2015, 22(5): 47-51, 68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2015.05.008
吴胜和 , 岳大力 , 刘建民 , 等. 地下古河道储层构型的层次建模研究[J]. 中国科学: D 辑: 地球科学, 2008, 38(增刊Ⅰ): 111-121.
WU Shenghe, YUE Dali, LIU Jianmin, et al. Hierarchy modeling of subsurface palaeochannel eservoir architecture[J]. Science in China: Series D: Earth Sciences, 2008, 51(Supp. Ⅱ): 126-137.
吴胜和. 储层表征与建模[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2010: 136–174
WU Shenghe. Reservoir characterization and modeling[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2010: 136-174.
徐丽强, 李胜利, 于兴河, 等. 辫状河三角洲前缘储层构型分析——以彩南油田彩9井区三工河组为例[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2016, 23(5): 50-57, 82 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2016.05.008
XU Liqiang, LI Shengli, YU Xinghe, et al. Analysis of reservoir architecture in the braided river delta front: A case study of the Sangonghe Formation in Block Cai9 of Cainan oilfield[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2016, 23(5): 50-57, 82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2016.05.008
Kelly S. Scaling and hierarchy in braided rivers and their deposits: C[M]//Sambrook Smith G H, Best J L, Bristow C S, et al. Braided rivers: Process, deposits, ecology and management. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing, 2006: 75–106.
Leeder M R. Fluviatile fining upwards cycles and the magnitude of paleochann[J]. Geological Magazine, 1973, 110(3): 265-276. doi: 10.1017/S0016756800036098
Miall A D. Architectural elements analysis: A new method of facies analysis applied to fluvial deposits[J]. Earth Science Review, 1985, 22(4): 261-308. doi: 10.1016/0012-8252(85)90001-7
Miall A D. Architectural elements and bounding surfaces in fluvial deposits: anatomy of the Kayenta formation (lower jurassic), Southwest Colorado[J]. Elsevier, 1988, 55(3–4).
-




 下载:
下载: