Geochronology, Geochemistry and Their Geological Significances of Spodumene Pegmatite Veins in the Dahongliutandong Deposit, Western Kunlun, China
-
摘要:
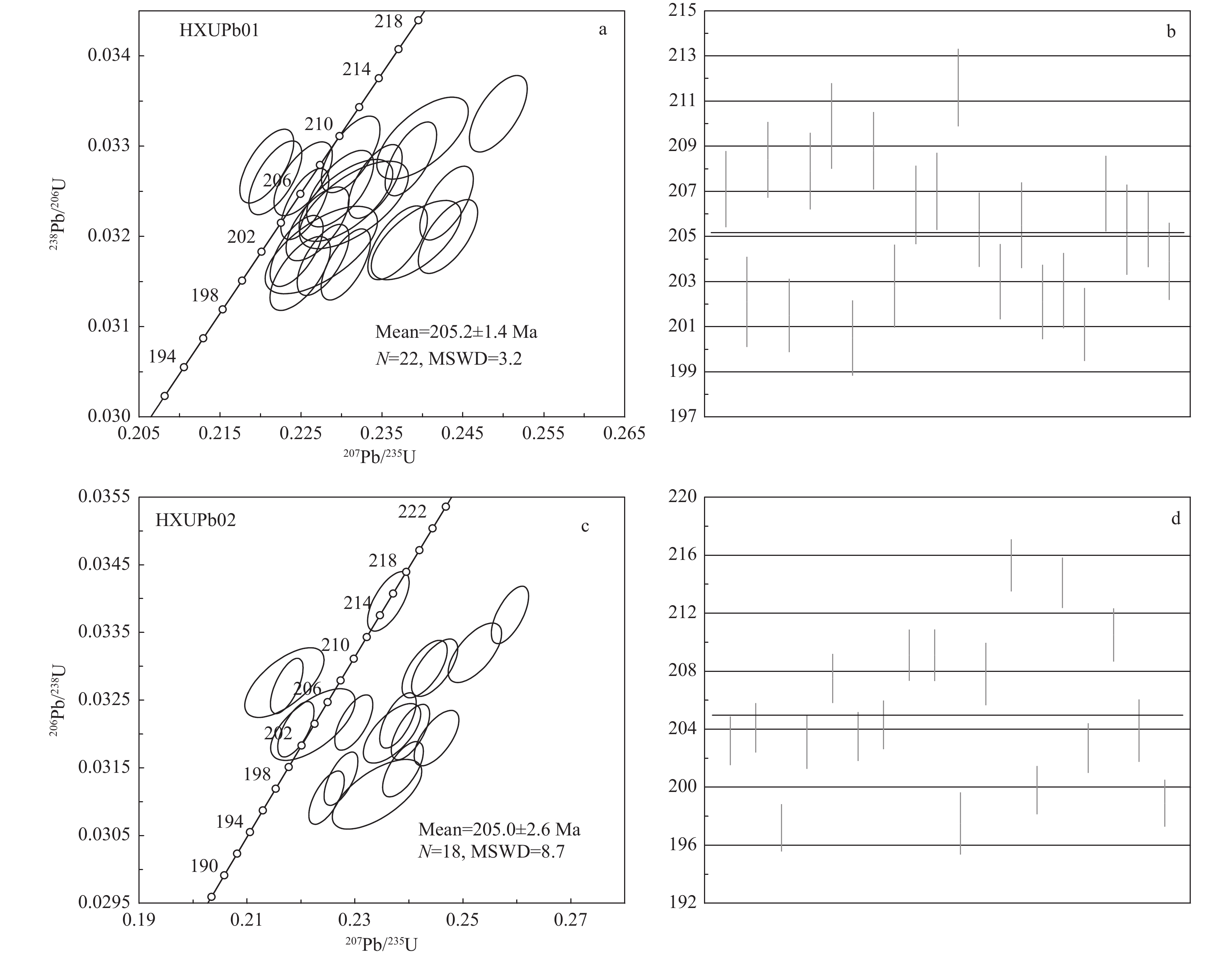
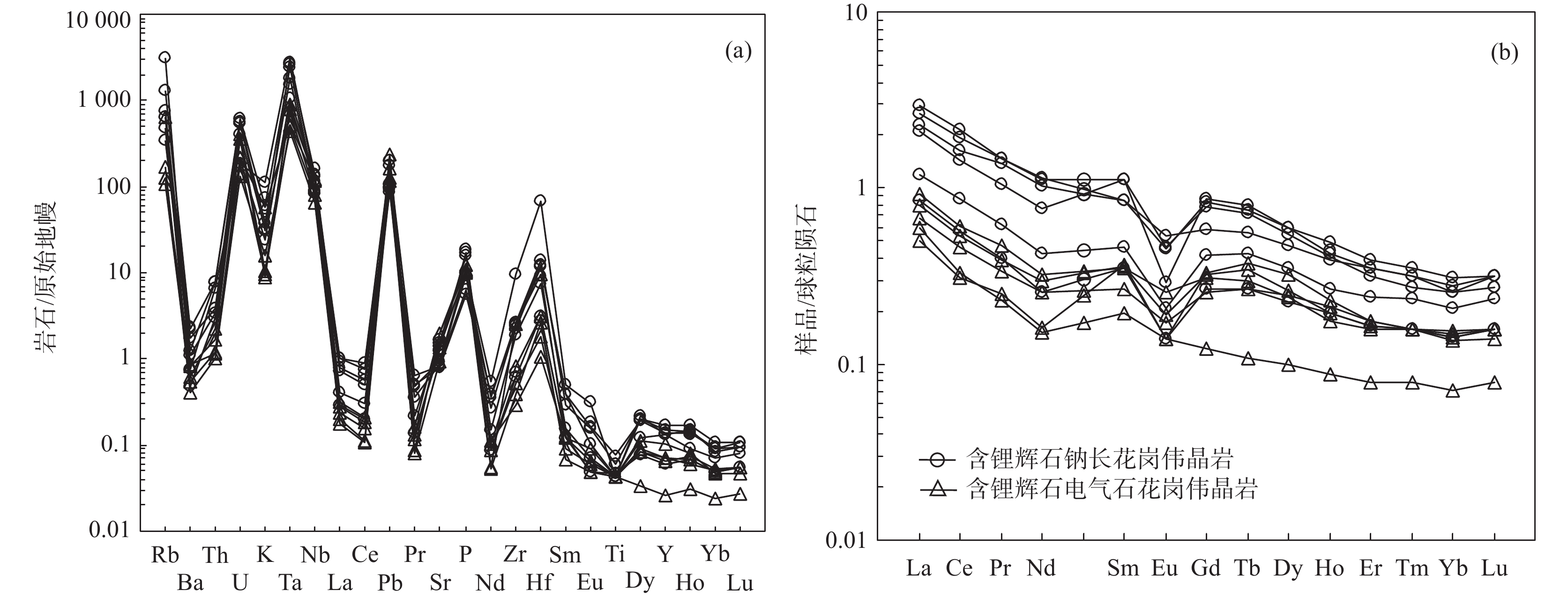
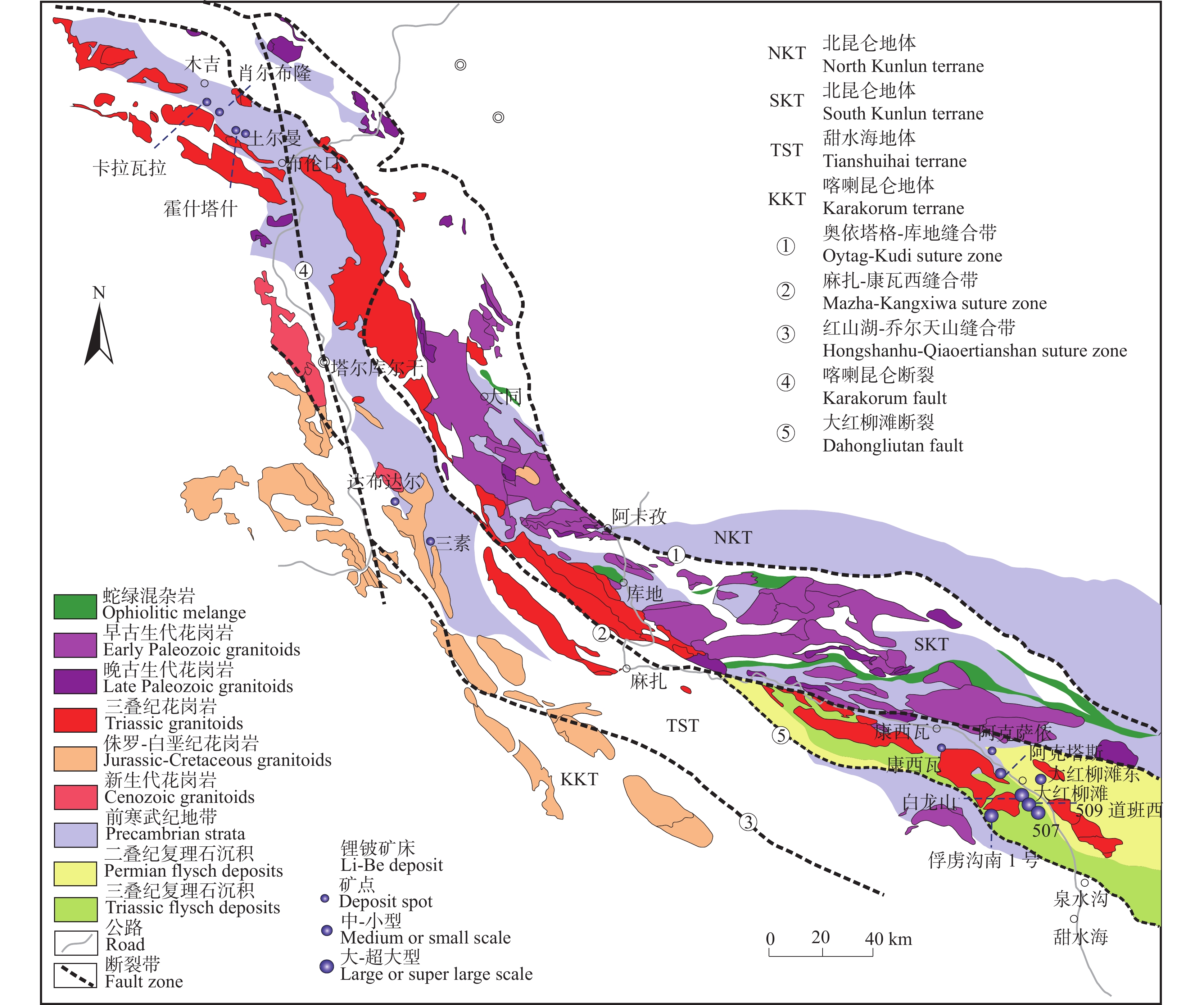
西昆仑地区是中国重要的伟晶岩型锂铍成矿带,近年来在大红柳滩一带取得重大找矿突破,已形成大型矿产资源基地。笔者对西昆仑大红柳滩东锂辉石花岗伟晶岩进行了详细的岩相学、年代学和地球化学研究,能够为本区伟晶岩型锂矿成矿作用研究提供新的依据。利用LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Pb定年,获得大红柳滩东含锂辉石钠长花岗伟晶岩及含锂辉石电气石花岗伟晶岩年龄分别为(205.2±1.4)Ma和(205.0±2.6)Ma,形成时代为晚三叠世。岩石地球化学研究表明,大红柳滩东含锂辉石花岗伟晶岩以高Si、富Al、富Na、钙碱质,高分异,低K、Fe、Mg、Ca和Ti为特征,属强过铝质花岗伟晶岩。岩石明显富集Rb、U、Nb、Ta、Pb、P、Hf等元素,亏损Ba、Th、La、Ce、Pr、Sr、Nd、Sm、Ti等元素;稀土总量较低,∑REE值为0.56×10−6~3.34×10−6,具有弱−中等的负铕异常,δEu值为0.30~0.89。大红柳滩东伟晶岩均具有低且负的εHf(t)值(–4.6~0)和古老的二阶段Hf模式年龄TDM2(1497~1208 Ma),反映其源岩为古老地壳物质的部分熔融。结合西昆仑地区已有年代学资料和区域地质构造演化特征,认为大红柳滩一带伟晶岩矿床形成于南昆仑地体与甜水海地体后碰撞背景下。
-
关键词:
- 地球化学 /
- 花岗伟晶岩 /
- LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Pb定年 /
- 大红柳滩东 /
- 西昆仑
Abstract:West Kunlun is an important pegmatite−type Li−Be metallogenic belt in China. In recent years, a great breakthrough in prospecting has been made in Dahongliutan area, and a large mineral resource base has been formed. In this paper, detailed researches on petrography, geochronology and geochemistry of the spodumene granite pegmatites in Dahongliutandong, West Kunlun, can provide a new basis for the study of pegmatite−type lithium mineralization in this area. By using LA−ICP−MS zircon U−Pb dating, the ages of spodumene−bearing albite pegmatite and spodumene−bearing tourmaline granite pegmatite in the Dahongliutandong are 205.2±1.4Ma and 205.0±2.6Ma, respectively, in the Late Triassic. Geochemical study shows that spodumene−bearing granite pegmatites in the Dahongliutandong is characterized by high Si, rich Al, Na, calc−alkali, high differentiation and low K, Fe, Mg, Ca and Ti, and belongs to strongly peraluminous granite pegmatite. The pegmatites are obviously rich in elements such as Rb, U, Nb, Ta, Pb, P, Hf, but depleting in elements such as Ba, Th, La, Ce, Pr, Sr, Nd, Sm and Ti. The total amount of rare earth is low, with ∑REE of 0.56×10−6~3.34×10−6, weak−medium negative Eu anomaly and δEu of 0.30~0.89. The pegmatites in the Dahongliutandong have low and negative εHf(t) values (–4.6~0) and the old two−stage Hf model age TDM2 (1497~1208 Ma), which indicates that their source rocks are from partial melting of ancient crustal materials. Based on the chronological data and the evolution characteristics of regional geological structure in West Kunlun, it is considered that pegmatite deposits in Dahongliutan area were formed in the background of post-collision between South Kunlun terrane and Tianshuihai terrane.
-
Key words:
- geochemistry /
- granite pegmatites /
- zircon LA−ICP−MS U−Pb dating /
- Dahongliutandong /
- West Kunlun
-

-
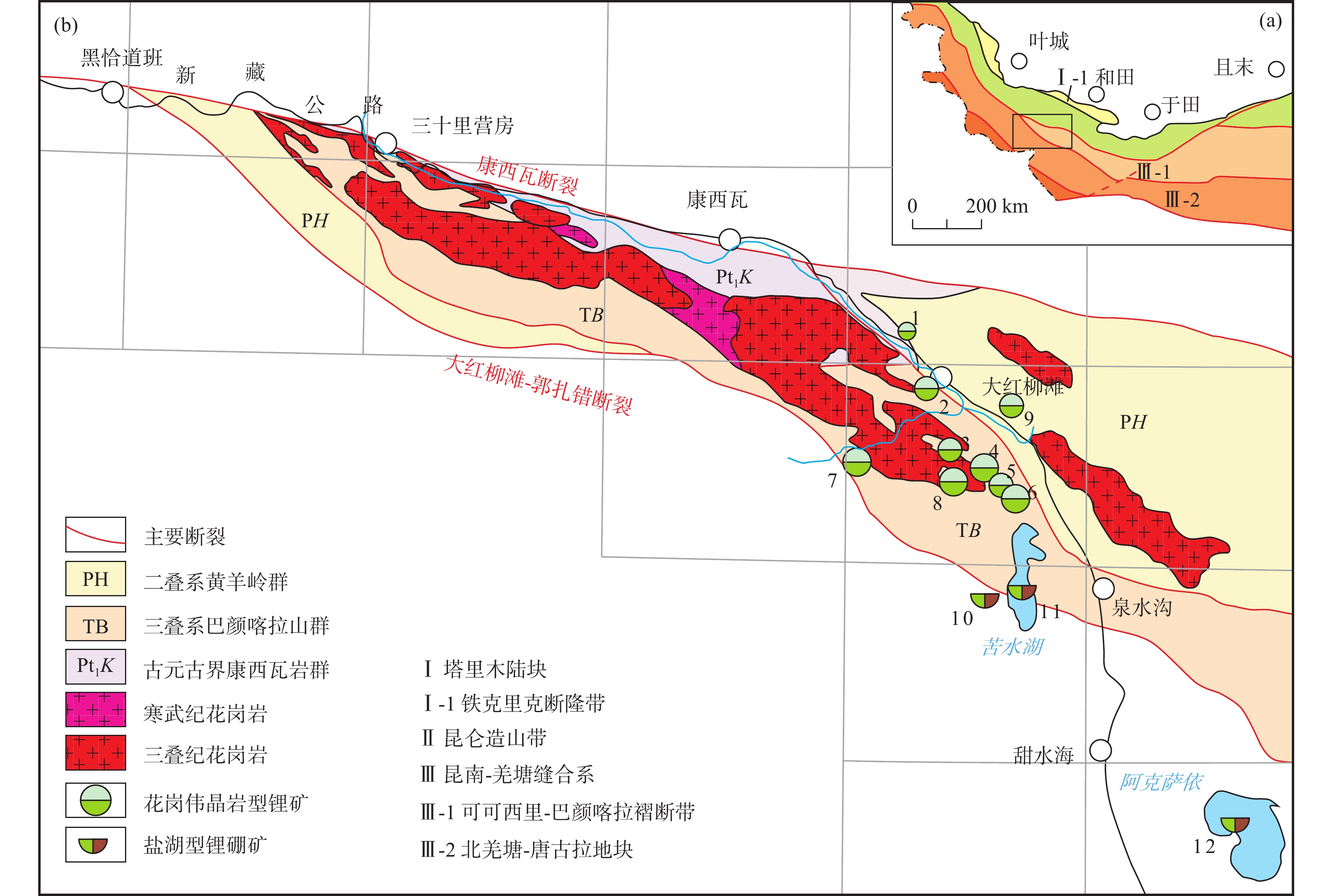
图 1 西昆仑造山带地质简图及锂铍矿床分布图(据王核等,2021;Yan et al.,2022)
Figure 1.
图 2 大红柳滩一带锂矿床分布图(据李侃等,2019修改)
Figure 2.
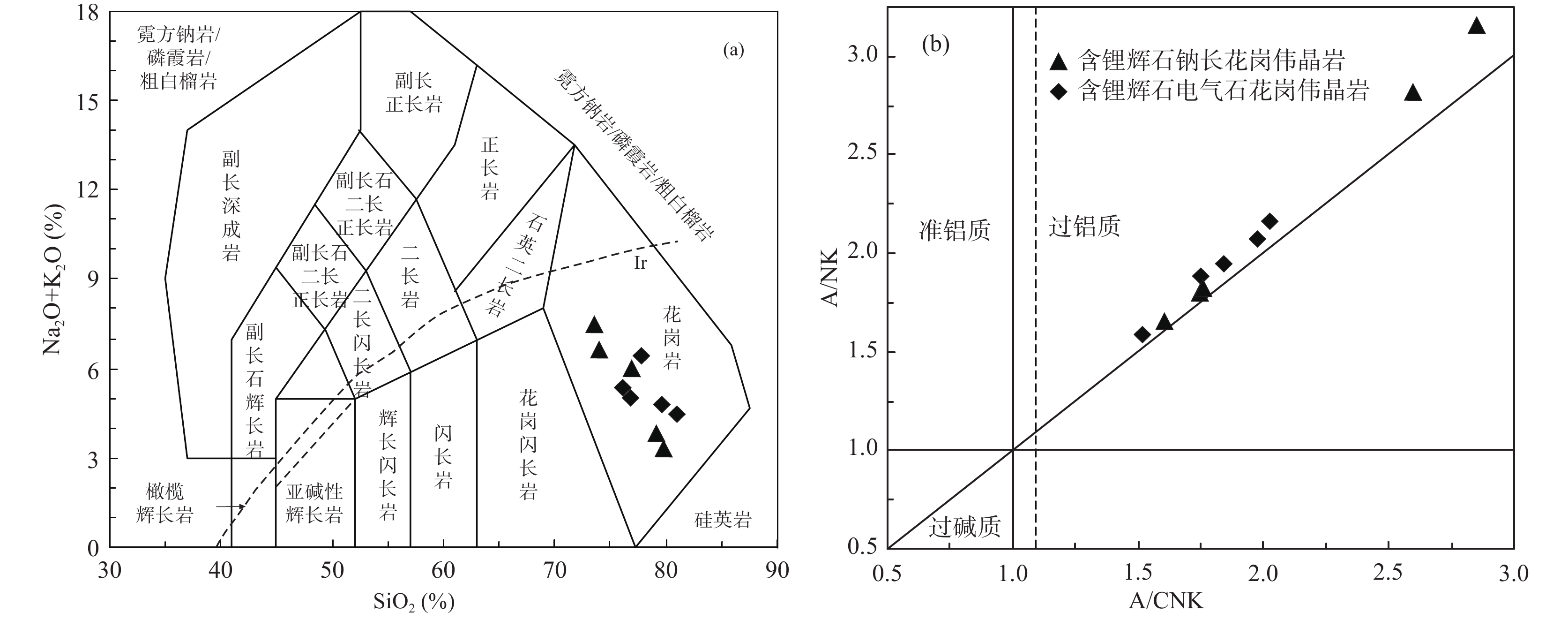
图 7 大红柳滩东锂辉石花岗伟晶岩的(K2O+Na2O)−SiO2(a)(据Middlemost,1994)及A/CNK−A/NK图解(b)(Mania et al.,1989)
Figure 7.
图 8 大红柳滩东锂辉石花岗伟晶岩的微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(a)及稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分曲线图(b)(标准化数值据Sun et al.,1989)
Figure 8.
表 1 大红柳滩东锂辉石花岗伟晶岩LA−ICP−MS锆石U−Pb测年结果
Table 1. LA−ICP−MS zircon U−Pb data for Dahongliutandong spodumene pegmatites
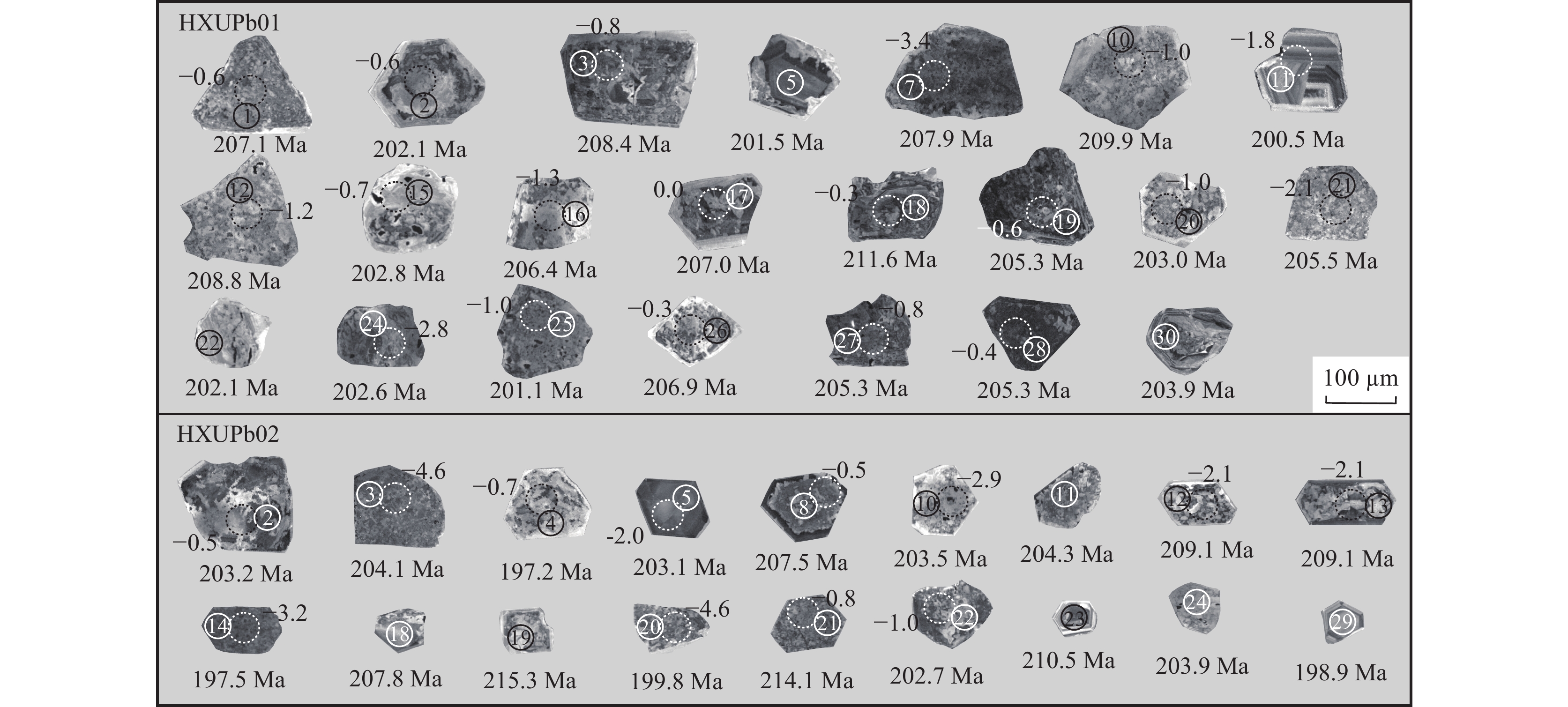
样品编号 含量(10−6) Th/U 207Pb/206Pb 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 207Pb/206Pb 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U Pb* Th U 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 年龄(Ma) 1σ 年龄(Ma) 1σ 年龄(Ma) 1σ HXUPb01(含锂辉石钠长花岗伟晶岩) 1 2390.9 2755.9 68709.3 0.040 0.0493 0.0006 0.2218 0.0022 0.0327 0.0003 164.2 26.8 203.4 1.8 207.1 1.7 2 98.9 126.8 2900.4 0.044 0.0519 0.0011 0.2275 0.0046 0.0319 0.0003 279.9 48.9 208.1 3.8 202.1 2.0 3 586.1 51.0 16707.8 0.003 0.0527 0.0006 0.2386 0.0021 0.0329 0.0003 317.0 24.2 217.2 1.7 208.4 1.7 5 192.2 6.2 5682.3 0.001 0.0521 0.0006 0.2277 0.0021 0.0317 0.0003 289.9 25.2 208.3 1.7 201.5 1.6 7 2655.5 192.5 76296.6 0.003 0.0489 0.0006 0.2208 0.0022 0.0328 0.0003 144.0 27.4 202.5 1.8 207.9 1.7 10 70.7 166.5 1983.7 0.084 0.0527 0.0009 0.2400 0.0037 0.0331 0.0003 314.8 38.4 218.4 3.1 209.9 1.9 11 57.3 4.2 1705.4 0.002 0.0517 0.0007 0.2249 0.0025 0.0316 0.0003 272.5 28.8 206.0 2.0 200.5 1.7 12 77.1 7.9 2201.7 0.004 0.0510 0.0006 0.2311 0.0024 0.0329 0.0003 240.9 27.7 211.1 2.0 208.8 1.7 15 103.5 7.4 2998.2 0.002 0.0544 0.0009 0.2392 0.0037 0.0320 0.0003 386.2 37.4 217.8 3.0 202.8 1.8 16 45.8 13.4 1318.2 0.010 0.0513 0.0007 0.2298 0.0027 0.0325 0.0003 254.6 30.9 210.1 2.3 206.4 1.7 17 629.6 60.6 18112.3 0.003 0.0501 0.0006 0.2253 0.0024 0.0326 0.0003 200.9 28.3 206.3 2.0 207.0 1.7 18 263.3 26.9 7326.3 0.004 0.0543 0.0006 0.2494 0.0024 0.0334 0.0003 382.8 25.3 226.1 1.9 211.6 1.7 19 4399.2 1254.7 127321.8 0.010 0.0506 0.0005 0.2255 0.0020 0.0324 0.0003 223.0 24.3 206.5 1.6 205.3 1.7 20 115.3 21.7 3340.8 0.006 0.0552 0.0007 0.2432 0.0024 0.0320 0.0003 419.7 25.9 221.0 2.0 203.0 1.7 21 120.0 55.9 3460.9 0.016 0.0517 0.0009 0.2305 0.0038 0.0324 0.0003 271.0 41.1 210.6 3.2 205.5 1.9 22 464.4 91.6 13671.9 0.007 0.0512 0.0006 0.2245 0.0022 0.0318 0.0003 249.6 26.1 205.6 1.8 202.1 1.7 24 128.0 8.0 3732.4 0.002 0.0539 0.0007 0.2369 0.0024 0.0319 0.0003 365.9 27.0 215.9 2.0 202.6 1.7 25 1440.0 291.9 42465.6 0.007 0.0528 0.0006 0.2305 0.0020 0.0317 0.0003 321.3 23.9 210.6 1.7 201.1 1.6 26 168.2 16.6 4838.9 0.003 0.0522 0.0006 0.2342 0.0022 0.0326 0.0003 291.8 25.4 213.6 1.8 206.9 1.7 27 164.4 18.7 4741.4 0.004 0.0520 0.0011 0.2315 0.0044 0.0324 0.0003 283.9 46.7 211.5 3.7 205.3 2.0 28 272.2 16.5 7818.8 0.002 0.0545 0.0006 0.2430 0.0022 0.0324 0.0003 392.4 24.1 220.9 1.8 205.3 1.7 30 71.9 11.6 2101.6 0.005 0.0513 0.0007 0.2270 0.0026 0.0321 0.0003 254.2 29.7 207.8 2.1 203.9 1.7 HXUPb02(含锂辉石电气石花岗伟晶岩) 2 180.0 27.3 5228.3 0.005 0.0544 0.0006 0.2403 0.0024 0.0320 0.0003 387.5 25.5 218.6 1.9 203.2 1.7 3 244.6 3.2 7122.3 0.000 0.0518 0.0006 0.2298 0.0023 0.0322 0.0003 276.2 26.8 210.0 1.9 204.1 1.7 4 103.9 3.2 3129.5 0.001 0.0525 0.0006 0.2247 0.0022 0.0311 0.0003 305.7 25.6 205.8 1.8 197.2 1.6 5 358.7 52.7 10329.3 0.005 0.0537 0.0009 0.2369 0.0035 0.0320 0.0003 356.2 36.6 215.8 2.9 203.1 1.8 8 1544.6 125.6 44470.6 0.003 0.0482 0.0005 0.2174 0.0020 0.0327 0.0003 108.4 25.6 199.7 1.7 207.5 1.7 10 130.1 32.6 3805.5 0.009 0.0495 0.0006 0.2190 0.0022 0.0321 0.0003 173.3 27.3 201.1 1.9 203.5 1.7 11 367.4 57.6 10581.2 0.005 0.0536 0.0006 0.2380 0.0022 0.0322 0.0003 353.7 24.9 216.7 1.8 204.3 1.7 12 74.9 3.5 2115.0 0.002 0.0534 0.0007 0.2429 0.0028 0.0330 0.0003 347.1 29.1 220.8 2.3 209.1 1.8 13 83.1 4.4 2339.3 0.002 0.0538 0.0007 0.2448 0.0028 0.0330 0.0003 363.5 29.5 222.3 2.3 209.1 1.8 14 126.0 1191.0 3668.3 0.325 0.0546 0.0014 0.2341 0.0055 0.0311 0.0003 394.1 54.8 213.6 4.5 197.5 2.1 18 138.2 295.6 3892.2 0.076 0.0480 0.0012 0.2169 0.0049 0.0328 0.0003 98.6 56.7 199.3 4.1 207.8 2.2 19 61.5 5.2 1697.1 0.003 0.0504 0.0006 0.2362 0.0026 0.0340 0.0003 214.7 28.6 215.3 2.1 215.3 1.8 20 199.3 26.0 5839.1 0.004 0.0550 0.0007 0.2389 0.0025 0.0315 0.0003 413.3 26.7 217.5 2.1 199.8 1.7 21 1250.6 128.4 34010.7 0.004 0.0556 0.0006 0.2587 0.0023 0.0338 0.0003 434.8 23.4 233.6 1.8 214.1 1.7 22 173.6 14.5 5015.0 0.003 0.0556 0.0007 0.2451 0.0027 0.0319 0.0003 437.9 27.9 222.6 2.2 202.7 1.7 23 222.8 8.9 6163.0 0.001 0.0551 0.0008 0.2522 0.0033 0.0332 0.0003 416.1 32.0 228.4 2.7 210.5 1.8 24 176.3 22.9 5071.3 0.005 0.0501 0.0013 0.2222 0.0052 0.0321 0.0004 201.3 56.7 203.7 4.3 203.9 2.2 29 221.1 13.2 6537.8 0.002 0.0526 0.0006 0.2274 0.0021 0.0313 0.0003 312.1 24.6 208.0 1.7 198.9 1.6 表 2 大红柳滩东锂辉石花岗伟晶岩主量元素(%)、稀土和微量元素(10–6)分析结果
Table 2. Results of major elements (%), REE and trace elements (10–6) of Dahongliutandong spodumene pegmatites
样品号 HX-H3 HX-H4 HX-H5 HX-H8 HX-H10 HX-H13 HX-H14 HX-H15 HX-H16 HX-H17 岩性 含锂辉石钠长花岗伟晶岩 含锂辉石电气石花岗伟晶岩 SiO2 72.60 72.32 76.00 77.58 77.29 75.25 78.26 76.97 79.68 74.75 TiO2 0.01 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 Al2O3 18.24 18.10 16.26 15.21 15.45 17.04 14.64 15.01 13.34 17.33 Fe2O3 0.05 0.10 0.07 0.24 0.29 0.07 0.01 0.01 0.10 0.01 FeO 0.15 0.12 0.10 0.15 0.10 0.10 0.20 0.10 0.10 0.20 MnO 0.05 0.06 0.05 0.12 0.12 0.07 0.07 0.05 0.10 0.06 MgO 0.06 0.07 0.05 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.02 0.02 0.04 0.02 CaO 0.15 0.16 0.14 0.28 0.26 0.28 0.25 0.23 0.30 0.22 Na2O 5.51 5.46 4.76 2.45 2.70 4.62 4.37 4.60 4.10 4.78 K2O 0.94 1.83 1.13 0.73 0.96 0.27 0.29 1.75 0.32 0.47 P2O5 0.20 0.12 0.14 0.35 0.37 0.23 0.22 0.24 0.27 0.23 LOI 0.77 1.16 0.73 0.68 0.76 0.39 0.31 0.47 0.44 0.20 Total 98.74 99.52 99.42 97.82 98.34 98.35 98.64 99.45 98.78 98.27 A/CNK 1.76 1.61 1.75 2.85 2.60 2.03 1.84 1.52 1.75 1.98 Sc 4.92 4.15 3.14 2.56 2.14 4.37 3.69 2.48 3.12 4.40 Ga 28.20 30.70 26.00 23.60 25.10 22.00 18.70 16.80 17.60 20.70 W 0.58 0.50 0.44 0.64 0.67 0.51 0.39 0.58 0.38 0.51 Bi 0.40 0.36 0.30 0.56 1.62 0.12 0.32 0.55 0.15 0.15 V 2.04 2.35 1.31 0.69 0.34 0.45 0.23 0.13 0.28 0.75 Li 6520.00 3280.00 4780.00 10700.00 9600.00 9650.00 7500.00 4570.00 6420.00 9080.00 Be 126.00 40.10 34.60 136.00 126.00 234.00 225.00 238.00 265.00 24.00 B 11.30 14.40 12.20 12.00 12.00 7.72 7.42 11.10 8.33 9.19 Rb 403.00 843.00 476.00 216.00 305.00 80.30 68.50 399.00 81.10 107.00 Cs 31.90 32.70 22.40 13.30 13.30 10.20 10.50 18.30 18.60 4.10 Ba 12.40 15.90 8.78 7.58 3.29 5.72 3.81 5.92 4.33 2.82 Th 0.32 0.65 0.67 0.29 0.25 0.14 0.10 0.10 0.19 0.09 U 11.40 12.90 11.80 4.32 8.56 7.62 3.90 4.55 8.42 2.74 Ta 113.00 97.70 74.70 43.00 29.70 37.20 20.60 21.00 32.00 18.20 Nb 99.20 64.70 58.40 93.20 59.90 82.20 56.80 85.00 85.80 46.60 Pb 7.08 7.56 6.21 6.97 6.67 9.01 9.06 16.90 11.40 8.42 Sr 19.30 16.70 18.00 31.80 26.80 29.00 32.00 42.30 41.10 19.40 Zr 29.70 25.20 28.20 21.20 6.97 9.36 5.86 3.22 28.90 4.33 Hf 4.28 3.59 3.83 2.33 0.96 0.95 0.55 0.32 3.01 0.80 Cu 10.70 12.40 8.06 1.59 1.37 1.77 1.52 1.42 1.25 1.85 Zn 23.40 25.80 27.80 74.10 69.90 25.30 40.20 80.20 72.00 87.10 Sn >200 >200 108.00 193.00 160.00 178.00 34.50 38.50 >200 41.00 Y 0.76 0.62 0.69 0.60 0.27 0.32 0.30 0.32 0.46 0.12 续表2 样品号 HX-H3 HX-H4 HX-H5 HX-H8 HX-H10 HX-H13 HX-H14 HX-H15 HX-H16 HX-H17 岩性 含锂辉石钠长花岗伟晶岩 含锂辉石电气石花岗伟晶岩 La 0.54 0.70 0.50 0.28 0.20 0.19 0.16 0.22 0.12 0.14 Ce 0.99 1.32 0.89 0.53 0.35 0.33 0.28 0.37 0.19 0.20 Pr 0.13 0.14 0.10 0.06 0.04 0.04 0.03 0.05 0.02 0.02 Nd 0.48 0.52 0.36 0.20 0.12 0.14 0.12 0.15 0.08 0.07 Sm 0.13 0.17 0.17 0.07 0.05 0.06 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.03 Eu 0.03 0.03 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.01 0.01 Gd 0.17 0.16 0.18 0.09 0.06 0.07 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.03 Tb 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.00 Dy 0.15 0.14 0.15 0.09 0.06 0.07 0.06 0.06 0.08 0.03 Ho 0.03 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 Er 0.07 0.05 0.06 0.04 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.01 Tm 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 Yb 0.05 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.02 0.02 0.03 0.03 0.02 0.01 Lu 0.008 0.007 0.008 0.006 0.004 0.004 0.004 0.004 0.004 0.002 ΣREE 2.81 3.34 2.54 1.45 0.96 0.98 0.84 1.06 0.71 0.56 LREE/HREE 4.49 6.25 4.06 3.91 4.01 3.53 3.22 4.17 2.00 5.35 LaN/YbN 7.31 11.41 8.15 5.74 5.98 5.68 4.41 6.31 3.74 8.37 δEu 0.53 0.50 0.30 0.47 0.45 0.56 0.66 0.78 0.40 0.89 δCe 0.92 1.03 0.98 1.01 0.98 0.96 0.96 0.91 0.87 0.88 LaN/SmN 2.68 2.66 1.90 2.58 2.39 2.23 2.52 2.63 1.38 3.01 GdN/YbN 2.65 3.01 3.38 2.03 1.90 2.27 1.69 2.12 2.45 1.72 表 3 大红柳滩东锂辉石花岗伟晶岩锆石Lu−Hf同位素组成
Table 3. Zircon Lu−Hf isotopic compositions of Dahongliutandong spodumene pegmatites
测点号 t(Ma) 176Yb/177Hf 176Lu/177Hf 176Hf/177Hf 2σ (176Hf/177Hf)i εHf(t) 2σ TDM1(Ma) TDM2(Ma) fLu/Hf HXUPb01(含锂辉石钠长花岗伟晶岩) 1 207.1 0.001632 0.000032 0.282626 0.000010 0.282626 −0.6 0.4 820 1247 −1.00 2 202.1 0.004044 0.000080 0.282629 0.000012 0.282629 −0.6 0.4 816 1243 −1.00 3 208.4 0.001964 0.000039 0.282620 0.000010 0.282620 −0.8 0.3 828 1260 −1.00 7 207.9 0.003916 0.000064 0.282548 0.000012 0.282548 −3.4 0.4 924 1422 −1.00 10 209.9 0.002892 0.000060 0.282613 0.000008 0.282613 −1.0 0.3 838 1275 −1.00 11 200.5 0.000092 0.000003 0.282598 0.000006 0.282598 −1.8 0.2 856 1314 −1.00 12 208.8 0.003062 0.000061 0.282609 0.000010 0.282609 −1.2 0.3 843 1284 −1.00 15 202.8 0.001188 0.000025 0.282626 0.000009 0.282626 −0.7 0.3 820 1250 −1.00 16 206.4 0.002045 0.000043 0.282607 0.000010 0.282607 −1.3 0.4 845 1290 −1.00 17 207.0 0.000484 0.000010 0.282643 0.000013 0.282643 0.0 0.5 796 1208 −1.00 18 211.6 0.002014 0.000040 0.282632 0.000013 0.282632 −0.3 0.4 812 1230 −1.00 19 205.3 0.001206 0.000021 0.282627 0.000012 0.282627 −0.6 0.4 819 1247 −1.00 20 203.0 0.008771 0.000185 0.282620 0.000014 0.282619 −1.0 0.5 831 1266 −0.99 21 205.5 0.006352 0.000124 0.282586 0.000014 0.282586 −2.1 0.5 875 1339 −1.00 24 202.6 0.000481 0.000009 0.282567 0.000010 0.282567 −2.8 0.3 897 1382 −1.00 25 201.1 0.012967 0.000237 0.282618 0.000018 0.282618 −1.0 0.6 834 1270 −0.99 26 206.9 0.001770 0.000034 0.282634 0.000010 0.282634 −0.3 0.4 809 1229 −1.00 27 205.3 0.001362 0.000024 0.282622 0.000009 0.282622 −0.8 0.3 824 1256 −1.00 28 205.3 0.000782 0.000013 0.282632 0.000012 0.282632 −0.4 0.4 811 1235 −1.00 HXUPb02(含锂辉石电气石花岗伟晶岩) 2 203.2 0.000954 0.000022 0.282631 0.000010 0.282631 −0.5 0.4 812 1237 −1.00 3 204.1 0.001893 0.000019 0.282516 0.000013 0.282516 −4.6 0.5 966 1496 −1.00 4 197.2 0.024472 0.000819 0.282632 0.000013 0.282629 −0.7 0.5 828 1247 −0.98 5 203.1 0.004587 0.000089 0.282589 0.000011 0.282589 −2.0 0.4 870 1333 −1.00 8 207.5 0.000570 0.000025 0.282629 0.000017 0.282629 −0.5 0.6 815 1239 −1.00 10 203.5 0.004761 0.000138 0.282563 0.000012 0.282563 −2.9 0.4 905 1391 −1.00 12 209.1 0.003349 0.000096 0.282584 0.000014 0.282584 −2.1 0.5 877 1340 −1.00 13 209.1 0.007375 0.000195 0.282584 0.000014 0.282584 −2.1 0.5 879 1340 −0.99 14 197.5 0.036880 0.000802 0.282562 0.000019 0.282559 −3.2 0.7 922 1403 −0.98 20 199.8 0.005263 0.000061 0.282517 0.000015 0.282517 −4.6 0.5 965 1497 −1.00 21 214.1 0.009715 0.000244 0.282617 0.000021 0.282616 −0.8 0.7 836 1265 −0.99 22 202.7 0.009710 0.000293 0.282619 0.000014 0.282618 −1.0 0.5 834 1268 −0.99 注:1. εHf(t) = 10000 × {[(176Hf/177Hf)S – (176Lu/177Hf)S × (eλt – 1)] / [(176Hf/177Hf)CHUR,0– (176Lu/177Hf) CHUR × (eλt – 1)] – 1};
2. TDM1 = 1/λ × ln{1 + [(176Hf/177Hf)S – (176Hf/177Hf) DM]/ [(176Lu/177Hf)S – (176Lu/177Hf)DM]};
3. TDM2 = TDM – (TDM – t) × [(fcc – fs)/(fcc – fDM)]. fLu/Hf = (176Lu/177Hf)S /(176Lu/177Hf) CHUR – 1;
4. λ = 1.867 × 10−11/a;(176Lu/177Hf)S 和(176Hf/177Hf)S 为样品测量值;(176Lu/177Hf) CHUR = 0.0332; (176Hf/177Hf)CHUR,0 = 0.282772; (176Lu/177Hf)DM = 0.0384;(176Hf/177Hf) DM = 0.28325;(176Lu/177Hf)平均地壳 = 0.015; fcc = [(176Lu/177Hf)平均地壳/(176Lu/177Hf) CHUR] – 1; fs = fLu/Hf; fDM = [(176Lu/177Hf)DM /(176Lu/177Hf) CHUR] – 1; t 为锆石结晶年龄。
-
白洪阳, 王核, 闫庆贺, 等. 新疆西昆仑雪凤岭锂矿床铌钽铁矿、锡石年龄及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2022, 38(7): 2139-2152 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2022.07.19
BAI Hongyang, WANG He, YAN Qinghe, et al. Columbite-tantalite and cassiterite ages of Xuefengling lithium deposit in West Kunlun, Xinjiang and their geological significance[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2022, 38(7): 2139-2152. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2022.07.19
陈海云, 孙妍, 包平, 等. 西昆仑上其木干岩体岩石成因及地质意义——地球化学及U-Pb年代学证据[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2014, 33(4): 657-670 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2014.04.005
CHEN Haiyun, SUN Yan, BAO Ping, et al. Petrogenesis and geological significance of Shangqimugan plutons in Western Kunlun: Evidence from geochemistry and U-Pb chronology[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2014, 33(4): 657-670. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2014.04.005
陈衍景, 薛莅治, 王孝磊, 等. 世界伟晶岩型锂矿床地质研究进展[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(10): 2971-2995 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.10.004
CHEN Yanjing, XUE Lizhi, WANG Xiaolei, et al. Progress in geological study of pegmatite-type lithium deposits in the world[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(10): 2971-2995. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.10.004
丁坤, 梁婷, 周义, 等. 西昆仑大红柳滩黑云母二长花岗岩岩石成因: 来自锆石U-Pb年龄及Li-Hf同位素的证据[J]. 西北地质, 2020, 53(1): 24-34
DING Kun, LIANG Ting, ZHOU Yi, et al. Petrogenesis of the Dahongliutan biotite monzogranite in western Kunlun orogen: Evidence from zircon U-Pb age and Li-Hf isotope[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2020, 53(1): 24-34.
蒋少涌, 王春龙, 张璐, 等. 伟晶岩型锂矿中矿物原位微区元素和同位素示踪与定年研究进展[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(10): 3017-3038 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.10.006
JIANG Shaoyong, WANG Chunlong, ZHANG Lu, et al. In situ trace element tracing and isotopic dating of pegmatite type lithium deposits: an overview[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(10): 3017-3038. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.10.006
康磊, 校培喜, 高晓峰, 等. 西昆仑慕士塔格岩体的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年: 对古特提斯碰撞时限的制约[J]. 地质论评, 2012, 58(4): 763-774 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0371-5736.2012.04.017
KANG Lei, XIAO Peixi, GAO Xiaofeng, et al. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating of the zircon from Muztagata pluton in Western Kunlun Orogenic Belt: Constraints on the time of Paleotethys’ collision[J]. Geological Review, 2012, 58(4): 763-774. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0371-5736.2012.04.017
李杭, 洪涛, 杨智全, 等. 稀有金属花岗伟晶岩锆石、锡石与铌钽铁矿U-Pb和白云母40Ar/39Ar测年对比研究—以阿尔金中段吐格曼北锂铍矿床为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(9): 2869-2892 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.09.16
LI Hang, HONG Tao, YANG Zhiquan, et al. Comparative studying on zircon, cassiterite and coltan U-Pb dating and 40Ar/39Ar dating of muscovite rare-metal granitic pegmatites: A case study of the northern Tugeman lithium-beryllium deposit in the middle of Altyn Tagh[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2020, 36(9): 2869-2892. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.09.16
李建康, 李鹏, 严清高, 等. 中国花岗伟晶岩的研究历程及发展态势[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(10): 2996-3016 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.10.005
LI Jiankang, LI Peng, YAN Qinggao, et al. History of granitic pegmatite research in China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(10): 2996-3016. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.10.005
李建康, 王登红, 张德会, 等. 川西典型伟晶岩型矿床的形成机制及大陆动力学背景[M]. 北京: 原子能出版社, 2007, 72 – 122
LI Jiankang, WANG Denghong, ZHANG Dehui, et al. Mineralization Mechanism and Continental Geodynamic of Pegmatite Type Deposits in Western Sichuan, China[M]. Beijing: Atomic Energy Press, 2007, 72 – 122.
李侃, 高永宝, 滕家欣, 等. 新疆和田县大红柳滩一带花岗伟晶岩型稀有金属矿成矿地质特征、成矿时代及找矿方向[J]. 西北地质, 2019, 52(4): 206-221 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2019.04.016
LI Kan, GAO Yongbao, TENG Jiaxin, et al. Metallogenic geological characteristics, mineralization age and resource potential of the granite-pegmatite-type rare metal deposits in Dahongliutan area, Hetian County, Xinjiang[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2019, 52(4): 206-221. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2019.04.016
李善平, 潘彤, 王秉璋, 等. 柴达木盆地北缘锲墨格山含绿柱石花岗伟晶岩特征及构造意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2021, 45(3): 608-619 doi: 10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2021.03.009
LI Shanping, PAN Tong, WANG Bingzhang, et al. Characteristics and tectonic significance of beryl-bearing pegmatites in Qiemoge Mountain, northern margin of Qaidam Basin[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2021, 45(3): 608-619. doi: 10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2021.03.009
李文渊, 张照伟, 高永宝, 等. 昆仑古特提斯构造转换与镍钴锰锂关键矿产成矿作用研究[J]. 中国地质, 2022, 49(5): 1385-1407 doi: 10.12029/gc20220503
LI Wenyuan, ZHANG Zhaowei, GAO Yongbao, et al. Tectonic transformation of the Kunlun Paleo-Tethyan orogenic belt and related mineralization of critical mineral resources of nickel, cobalt, manganese and lithium[J]. Geology in China, 2022, 49(5): 1385-1407. doi: 10.12029/gc20220503
李永, 王威, 杜晓飞, 等. 西昆仑509道班西锂铍稀有金属矿白云母40Ar/39Ar定年及对区域成矿的限定[J]. 中国地质, 2022, 49(6): 2031-2033
LI Yong, WANG Wei, DU Xiaofei, et al. 40Ar/39Ar dating of muscovite of the west 509 Daoban Li-Be rare metal deposit in the West Kunlun orogenic belt and its limitation to regional mineralization[J]. Geology in China, 2022, 49(6): 2031-2033.
梁婷, 滕家欣, 王登红, 等. 新疆大红柳滩锂铍稀有金属矿床[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2021, 1 – 262
LIANG Ting, TENG Jiaxin, WANG Denghong, et al. Li-Be Rare Metal Deposit in Dahongliutan, Xinjiang[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2021, 1 – 262.
鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 等. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录: 来自新疆温泉-胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J/OL]. 现代地质. https://doi.org/10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2022. 022
LU Hao, LIU Huan, HU Feng, et al. Records of Mesozoic collision orogenic events on the eastern part of the West Kunlun Orogenic Belt: Evidence from the chronology and geochemistry of Triassic intrusive rocks in Wenquan-Shenglidaban area, Xinjiang [J/OL]. Geoscience. https://doi.org/10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2022. 022
乔耿彪, 张汉德, 伍跃中, 等. 西昆仑大红柳滩岩体地质和地球化学特征及对岩石成因的制约[J]. 地质学报, 2015, 89(7): 1180-1194 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2015.07.003
QIAO Gengbiao, ZHANG Hande, WU Yuezhong, et al. Petrogenesis of the Dahongliutan monzogranite in Western Kunlun: constraints from SHRIMP zircon U-Pb geochronology and geochemical characteristics[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2015, 89(7): 1180-1194. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2015.07.003
秦克章, 赵俊兴, 何畅通, 等. 喜马拉雅琼嘉岗超大型伟晶岩型锂矿的发现及意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2021, 37(11): 3277-3286 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2021.11.02
QIN Kezhang, ZHAO Junxing, HE Changtong, et al. Discovery of the Qiongjiagang giant lithium pegmatite deposit in Himalaya, Xizang, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2021, 37(11): 3277-3286. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2021.11.02
唐俊林, 柯强, 徐兴旺, 等. 西昆仑大红柳滩地区龙门山锂铍伟晶岩区岩浆演化与成矿作用[J]. 岩石学报, 2022, 38(3): 655-675 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2022.03.05
TANG Junlin, KE Qiang, XU Xingwang, et al. Magma evolution and mineralization of Longmenshan lithium-beryllium pegmatite in Dahongliutan area, West Kunlun[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2022, 38(3): 655-675. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2022.03.05
滕家欣, 高永宝, 贺永康, 等. 西昆仑锰锂铅锌铁区域成矿规律与资源潜力[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2021, 1 – 420
TENG Jiaxin, GAO Yongbao, HE Yongkang, et al. Metallogenic Regularity and Resource Potential of Manganese, Lithium, Lead, Zinc and Iron in West Kunlun[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2021, 1 – 420.
涂其军, 韩琼, 李平, 等. 西昆仑大红柳滩一带锂辉石矿基本特征和勘查新进展[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(11): 2862-2873 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.11.011
TU Qijun, HAN Qiong, LI Ping, et al. Basic characteristics and exploitation progress of the spodumene ore deposit in the Dahongliutan area, West Kunlun[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(11): 2862-2873. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.11.011
王秉璋, 韩杰, 谢祥镭, 等. 青藏高原东北缘茶卡北山印支期(含绿柱石)锂辉石伟晶岩脉群的发现及Li-Be成矿意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2020, 44(1): 69-79 doi: 10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2019.02.016
WANG Bingzhang, HAN Jie, XIE Xianglei, et al. Discovery of the indosinian (Beryl-bearing) spodumene pegmatitic dike swarm in the Chakabeishan area in the northeastern margin of the Xizang plateau: implications for Li-Be mineralization[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2020, 44(1): 69-79. doi: 10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2019.02.016
王核, 李沛, 马华东, 等. 新疆和田县白龙山超大型伟晶岩型锂铷多金属矿床的发现及其意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2017, 41(6): 1053-1062 doi: 10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2017.06.005
WANG He, LI Pei, MA Huadong, et al. Discovery of the Bailongshan superlarge lithium-rubidium deposit in Karakorum, Hetian, Xinjiang, and its prospecting implication[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2017, 41(6): 1053-1062. doi: 10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2017.06.005
王核, 徐义刚, 闫庆贺, 等. 新疆白龙山伟晶岩型锂矿床研究进展[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(10): 3085-3098 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.10.010
WANG He, XU Yigang, YAN Qinghe, et al. Research progress on Bailongshan pegmatite type lithium deposit, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(10): 3085-3098. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.10.010
王威, 杜晓飞, 刘伟, 等. 西昆仑509道班西锂铍稀有金属矿地质特征与成矿时代探讨[J]. 岩石学报, 2022, 38(7): 1967-1980 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2022.07.10
WANG Wei, DU Xiaofei, LIU Wei, et al. Geological characteristic and discussion on metallogenic age of the West 509-Daoban Li-Be rare metal deposit in the West Kunlun Orogenic Belt[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2022, 38(7): 1967-1980. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2022.07.10
魏小鹏, 王核, 胡军, 等. 西昆仑大红柳滩二云母花岗岩地球化学和地质年代学研究及其地质意义[J]. 地球化学, 2017, 46(1): 66-80 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2017.01.006
WEI Xiaopeng, WANG He, HU Jun, et al. Geochemistry and geochronology of the Dahongliutan two-mica granite pluton in western Kunlun orogen: Geotectonic implications[J]. Geochimica, 2017, 46(1): 66-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2017.01.006
吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 等. Lu−Hf 同位素体系及其岩石学应用[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(2): 185-220 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.02.001
WU Fuyuan, LI Xianhua, ZHENG Yongfei, et al. Lu−Hf isotopic systematics and their applications in petrology[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007, 23(2): 185-220. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.02.001
吴福元, 王汝成, 刘小驰, 等. 喜马拉雅稀有金属成矿作用研究的新突破[J]. 岩石学报, 2021, 37(11): 3261-3276 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2021.11.01
WU Fuyuan, WANG Rucheng, LIU Xiaochi, et al. New breakthroughs in the studies of Himalayan rare-metal mineralization[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2021, 37(11): 3261-3276. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2021.11.01
徐兴旺, 李杭, 石福品, 等. 阿尔金中段吐格曼地区花岗伟晶岩型稀有金属成矿特征与找矿预测[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(11): 3303-3316 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.11.03
XU Xingwang, LI Hang, SHI Fupin, et al. Metallogenic characteristics and prospecting of granitic pegmatite-type rare metal deposits in the Tugeman area, middle part of Altyn Tagh[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2019, 35(11): 3303-3316. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.11.03
许志琴, 王汝成, 赵中宝, 等. 试论中国大陆“硬岩型”大型锂矿带的构造背景[J]. 地质学报, 2018, 92(6): 1091-1106 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2018.06.001
XU Zhiqin, WANG Rucheng, ZHAO Zhongbao, et al. On the Structural Backgrounds of the Large-scale "Hard-rock Type" Lithium Ore Belts in China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2018, 92(6): 1091-1106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2018.06.001
许志琴, 朱文斌, 郑碧海, 等. 新能源锂矿战略与大陆动力学研究——纪念南京大学地球科学与工程学院100周年华诞[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(10): 2937-2954 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.10.002
XU Zhiqin, ZHU Wenbin, ZHENG Bihai, et al. New energy strategy for lithium resource and the continental dynamics research—celebrating the centenary of the School of Earth Sciences and Engineering, Nanjing University[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(10): 2937-2954. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.10.002
张辉, 吕正航, 唐勇. LCT型伟晶岩及其锂矿床成因概述[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(10): 2955-2970 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.10.003
ZHANG Hui, LV Zhenghang, TANG Yong. A review of LCT pegmatite and its lithium ore genesis[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(10): 2955-2970. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.10.003
张宇, 唐名鹰, 何玉良, 等. 新疆西昆仑独尖山地区二云母二长花岗岩岩石地球化学、锆石U-Pb年龄与Hf同位素特征[J/OL]. 中国地质. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20201019.1317.002.html
ZHANG Yu, TANG Mingying, HE Yuliang, et al. Geochemistry, zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotopic characteristics of two-mica monzonites in Dujianshan area of Western Kunlun, Xinjiang[J/OL]. Geology in China. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20201019.1317.002.html
赵俊兴, 何畅通, 秦克章, 等. 喜马拉雅琼嘉岗超大型伟晶岩锂矿的形成时代、源区特征及分异特征[J]. 岩石学报, 2021, 37(11): 3325-3347 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2021.11.06
ZHAO Junxing, HE Changtong, QIN Kezhang, et al. Geochronology, source features and the characteristics of the fractional crystallization in pegmatite at the Qiongjiagang giant pegmatite-type lithium deposit, Himalaya, Xizang[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2021, 37(11): 3325-3347. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2021.11.06
赵振华. 微量元素地球化学原理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1997, 113 – 138
ZHAO Zhenhua. Principle of Trace Element Geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1997, 113 – 138.
邹天人, 李庆昌. 中国新疆稀有及稀土金属矿床[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2006, 1 – 284
ZOU Tianren, LI Qingchang. Rare and Rare Earth Metallic Deposits in Xinjiang, China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2006, 1 – 284.
Blichert-Toft J, Albarède F. The Lu-Hf isotope geochemistry of chondrites and the evolution of the mantle-crust system[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1997, 148(1−2): 243 – 258.
Černý P, Ercit T S. The classification of granitic pegmatites revisited[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 2005, 43: 2005-2026. doi: 10.2113/gscanmin.43.6.2005
Černý P, London D, Novak M. Granitic pegmatites as reflections of their sources[J]. Elements, 2012, 8: 257-261. doi: 10.2113/gselements.8.4.257
Černý P. Geochemical and petrogenetic features of mineralization in rare-element granitic pegmatites in the light of current research[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 1992, 7: 393-416. doi: 10.1016/0883-2927(92)90002-K
Chu N C, Taylor R N, Chavagnac V. Hf isotope ratio analysis using multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: An evaluation of isobaric interference corrections[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2002, 17, 1567-1574. doi: 10.1039/b206707b
DeBievre P, Taylor P D P. Table of the isotopic compositions of the elements[J]. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry Ion Processes, 1993, 123, 149-166. doi: 10.1016/0168-1176(93)87009-H
Ding K, Liang T, Yang X Q, et al. Geochronology, petrogenesis and tectonic significance of Dahongliutan pluton in Western Kunlun orogenic belt, NW China[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26: 3420-3435. doi: 10.1007/s11771-019-4264-7
Dittrich T, Seifert T, Schulz B, et al. Archean Rare-Metal Pegmatites in Zimbabwe and Western Australia: Geology and Metallogeny of Pollucite Mineralisations[M]. Switzerland: Springer, 2019, 1-125.
Fei G C, Menuge J F, Chen C S, et al. Evolution of pegmatite ore-forming fluid: The Lijiagou spodumene pegmatites in the Songpan-Garze Fold Belt, southwestern Sichuan province, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2021, 139: 104441. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.104441
Fei G C, Menuge J F, Li Y Q, et al. Petrogenesis of the Lijiagou spodumene pegmatites in Songpan-Garze Fold Belt, West Sichuan, China: Evidence from geochemistry, zircon, cassiterite and coltan U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopic compositions[J]. Lithos, 2020, 364-365: 105555. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2020.105555
Gao Y B, Bagas L, Li K, et al. Newly discovered Triassic lithium deposits in the Dahongliutan area, Northwest China: A case study for the detection of lithium-bearing pegmatite deposits in rugged terrains using remote-sensing data and images[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2020, 8: 591966. doi: 10.3389/feart.2020.591966
Gao Y B, Zhao X M, Bagas L, et al. Newly discovered Ordovician Li-Be deposits at Tugeman in the Altyn-Tagh Orogen, NW China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2021, 139: 104515. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.104515
Griffin W L, Pearson N J, Belousova E, et al. The Hf isotope composition of cratonic mantle: LAM-MC-ICPMS analysis of zircon megacrysts in kimberlites[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000, 64: 133-147. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00343-9
Griffin W L, Wang X, Jackson S E, et al. Zircon chemistry and magma mixing, SE China: In-situ analysis of Hf isotopes, Tonglu and Pingtan igneous complexes[J]. Lithos, 2002, 61(3-4): 237-269. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(02)00082-8
Jiang Y H, Jia R Y, Liu Z, et al. Origin of Middle Triassic high-K calc-alkaline granitoids and their potassic microgranular enclaves from the western Kunlun orogen, northwest China: A record of the closure of Paleo-Tethys[J]. Lithos, 2013, 156-159: 13-30. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.10.004
Kesler S E, Gruber P W, Medina P A, et al. Global lithium resources: Relative importance of pegmatite, brine and other deposits[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2012, 48: 55-69. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2012.05.006
Linnen R L, Lichtervelde M V, Cerny P. Granitic pegmatites as sources of strategic metals[J]. Elements, 2012, 8(4): 275-280. doi: 10.2113/gselements.8.4.275
London D, Evensen J M. Beryllium in silicic magmas and the origin of beryl-bearing pegmatites[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2002, 50(1): 445-486. doi: 10.2138/rmg.2002.50.11
London D. Granitic pegmatites: an assessment of current concepts and directions for the future[J]. Lithos, 2005, 80: 281-303. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2004.02.009
London D. Ore-forming processes within granitic pegmatites[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2018, 101: 349-383. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.04.020
London D. The magmatic-hydrothermal transition in the Tanco rare-element pegmatite: evidence from fluid inclusions and phase equilibrium experiments[J]. American Mineralogist, 1986, 71: 376-395.
Ludwig K R. Users Manual for Isoplot 3.00: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication, 2003, 25-32.
Maniar P D, Piccoli P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101: 635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
Middlemost E A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994, 37(3/4): 215-224.
Pan T, Ding Q F, Zhou X, et al. Columbite-tantalite group mineral U-Pb geochronology of Chaqiabeishan Li-rich granitic pegmatites in the Quanji Massif, NW China: Implications for the genesis and emplacement ages of pegmatites[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2021, 8: 606951. doi: 10.3389/feart.2020.606951
Simmons W B, Webber K L. Pegmatite genesis: State of the art[J]. European Journal of Mineralogy, 2008, 20(4): 421-438. doi: 10.1127/0935-1221/2008/0020-1833
Soderlund U, Patchett P J, Vervoort J D, et al. The 176Lu decay constant determined by Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotope systematics of Precambrian mafic intrusions[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 219: 311-324. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(04)00012-3
Sun S S and McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalt: Implications for mantle composition and process[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J(eds. ). Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 1989, 42: 313-345.
Wang H, Gao H, Zhang X Y, et al. Geology and geochronology of the super-large Bailongshan Li–Rb–(Be) rare-metal pegmatite deposit, West Kunlun orogenic belt, NW China[J]. Lithos, 2020, 360-361: 105449. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2020.105449
Xu Z Q, Fu X F, Wang R C, et al. Generation of lithium-bearing pegmatite deposits within the Songpan-Ganze orogenic belt, East Xizang[J]. Lithos, 2020, 354-355: 105281. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2019.105281
Yan Q G, Li J K, Li X J, et al. Source of the Zhawulong granitic pegmatite-type lithium deposit in the Songpan-Ganzê orogenic belt, Western Sichuan, China: Constrants from Sr-Nd-Hf isotopes and petrochemistry[J]. Lithos, 2020, 378-379: 105828. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2020.105828
Yan Q H, Qiu Z W, Wang H, et al. Age of the Dahongliutan rare metal pegmatite deposit, West Kunlun, Xinjiang (NW China): constraints from LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating of columbite-(Fe) and cassiterite[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2018, 100: 561-573. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.11.010
Yan Q H, Wang H, Chi G X, et al. Recognition of a 600-km-long Late Triassic rare-metal (Li–Rb–Be–Nb–Ta) pegmatite belt in the Western Kunlun orogenic belt[J]. Economic Geology, 2022, 117(1): 213-236. doi: 10.5382/econgeo.4858
Yuan H L, Gao S, Dai M N, et al. Simultaneous determinations of U-Pb age, Hf isotopes and trace element compositions of zircon by excimer laser-ablation quadrupole and multiple-collector ICP-MS[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 247, 100-118. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.10.003
Zhang Q C, Liu Y, Wu Z H, et al. Late Triassic granites from the northwestern margin of the Xizang Plateau, the Dahongliutan example: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications for the evolution of the Kangxiwa Palaeo-Tethys[J]. International Geology Review, 2019, 61(2): 175-194. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2017.1419444
Zhou J S, Wang Q, Xu Y G, et al. Geochronology, petrology, and lithium isotope geochemistry of the Bailongshan granite-pegmatite system, northern Xizang: Implications for the ore-forming potential of pegmatites[J]. Chemical Geology, 2021, 584: 120484. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2021.120484
-



 下载:
下载: