Hydrochemical and Isotopic Characteristics and Water Assessment Analysis of Surface Water and Groundwater Near Bolokenu–Aqikekuduke Fault in Xinjiang
-
摘要:
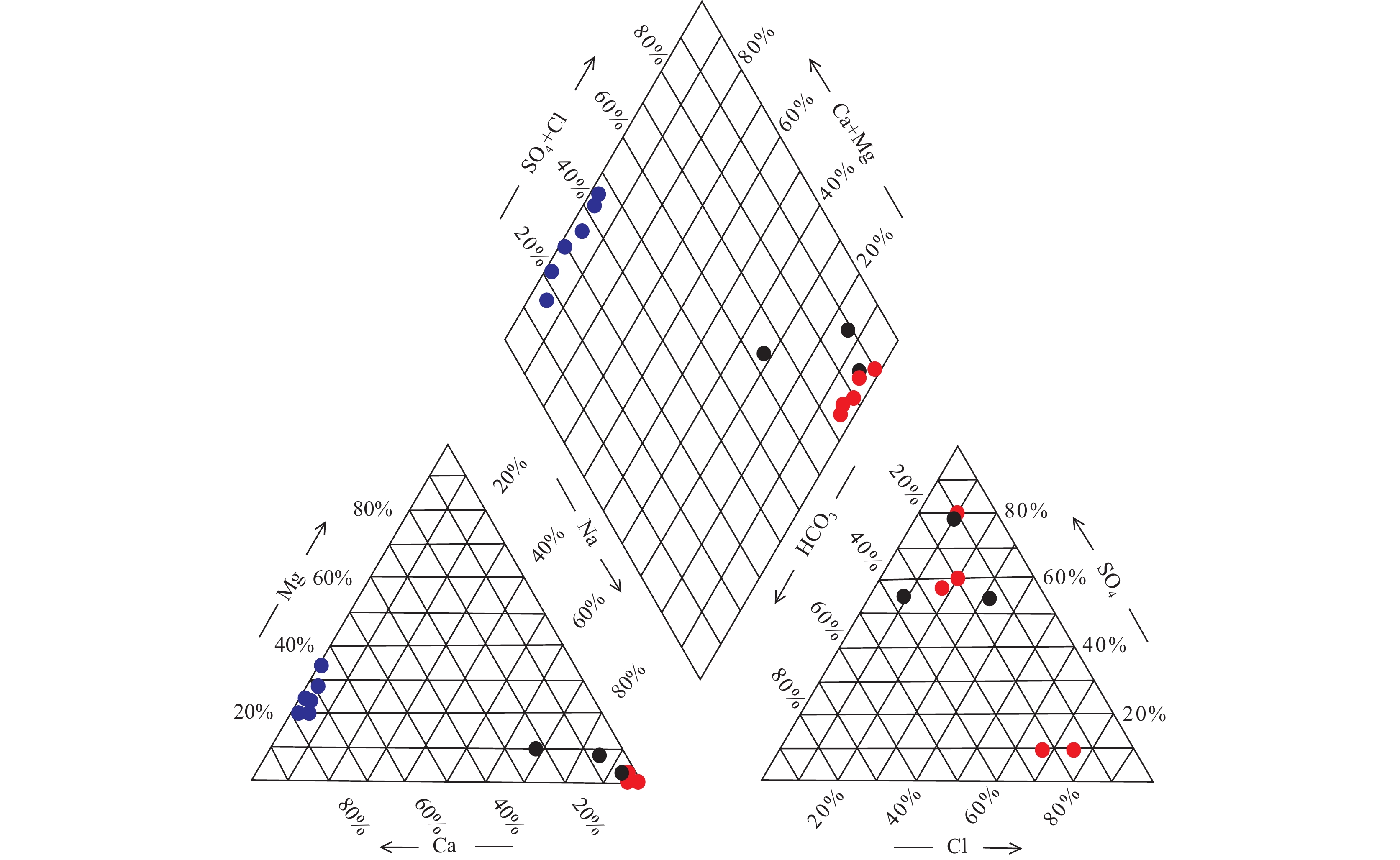
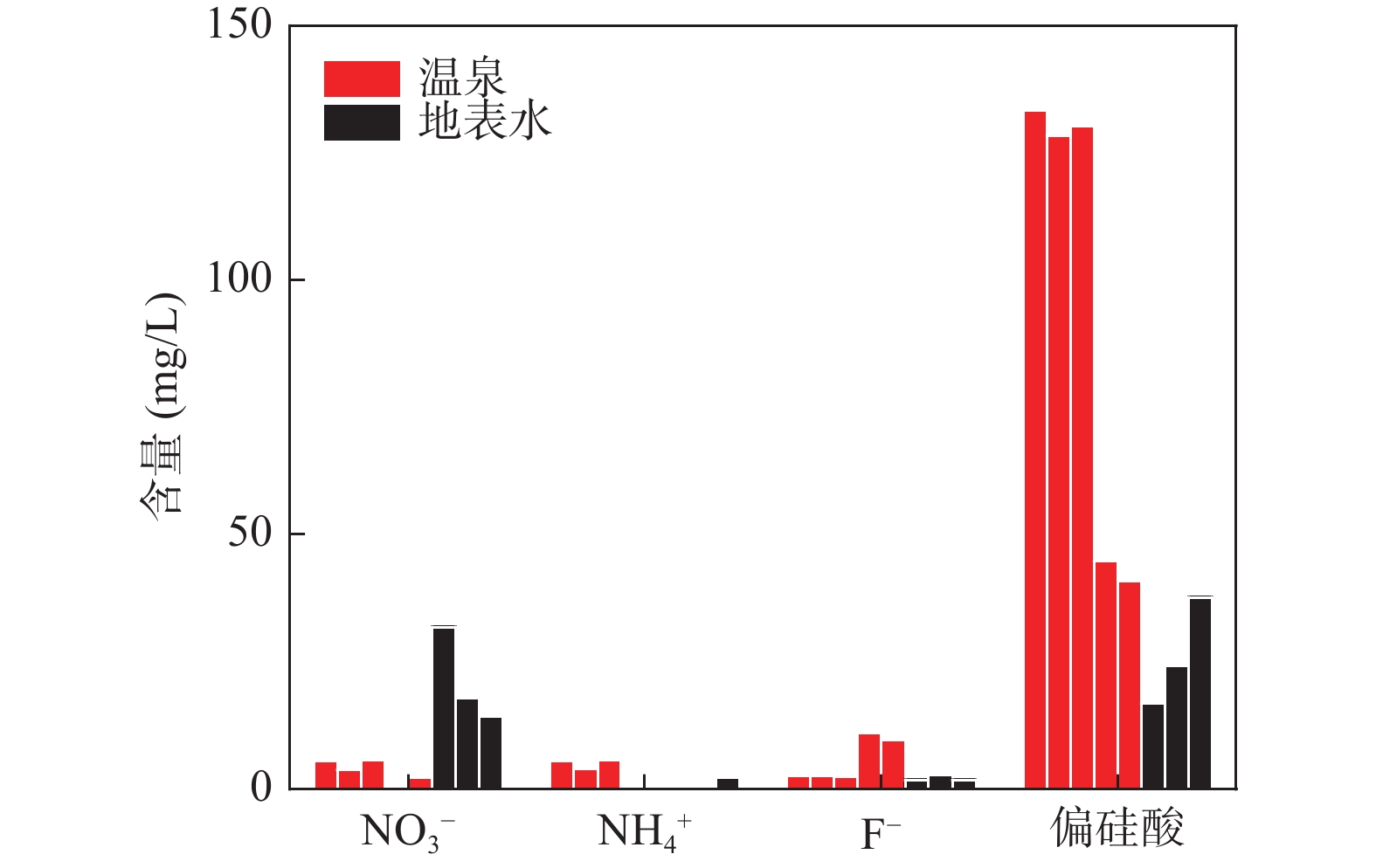
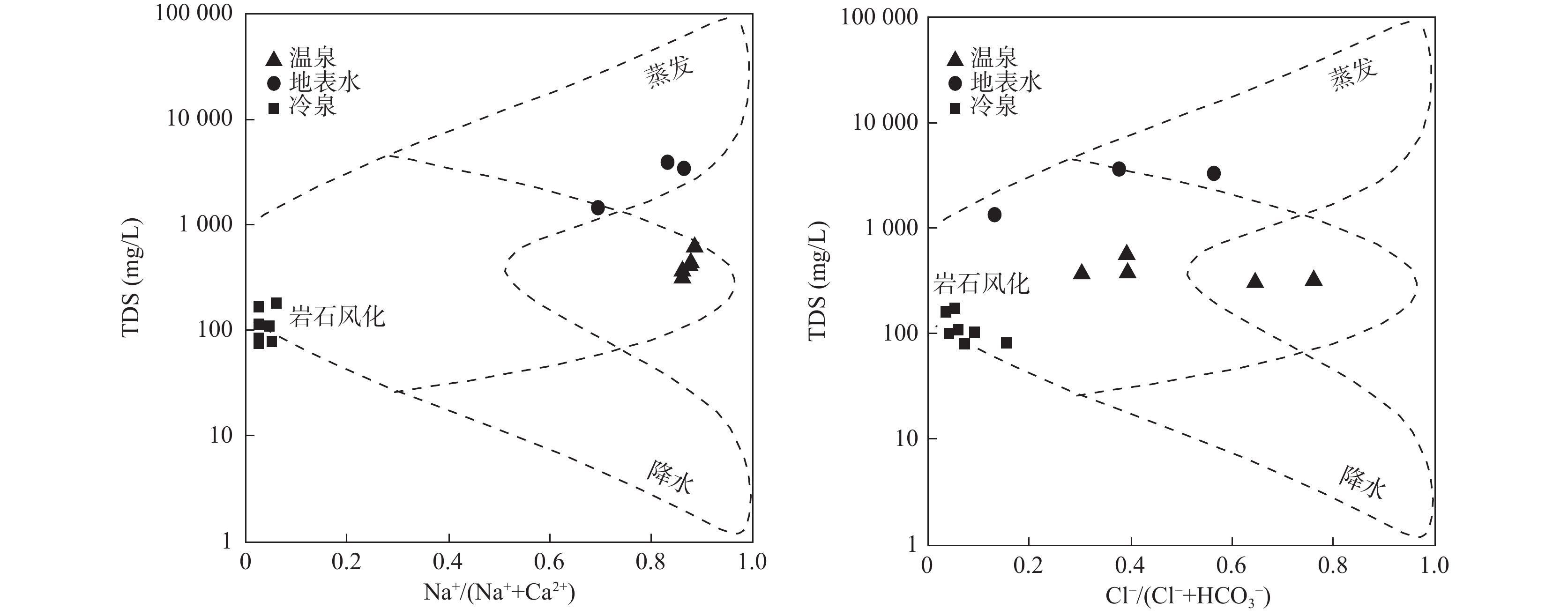
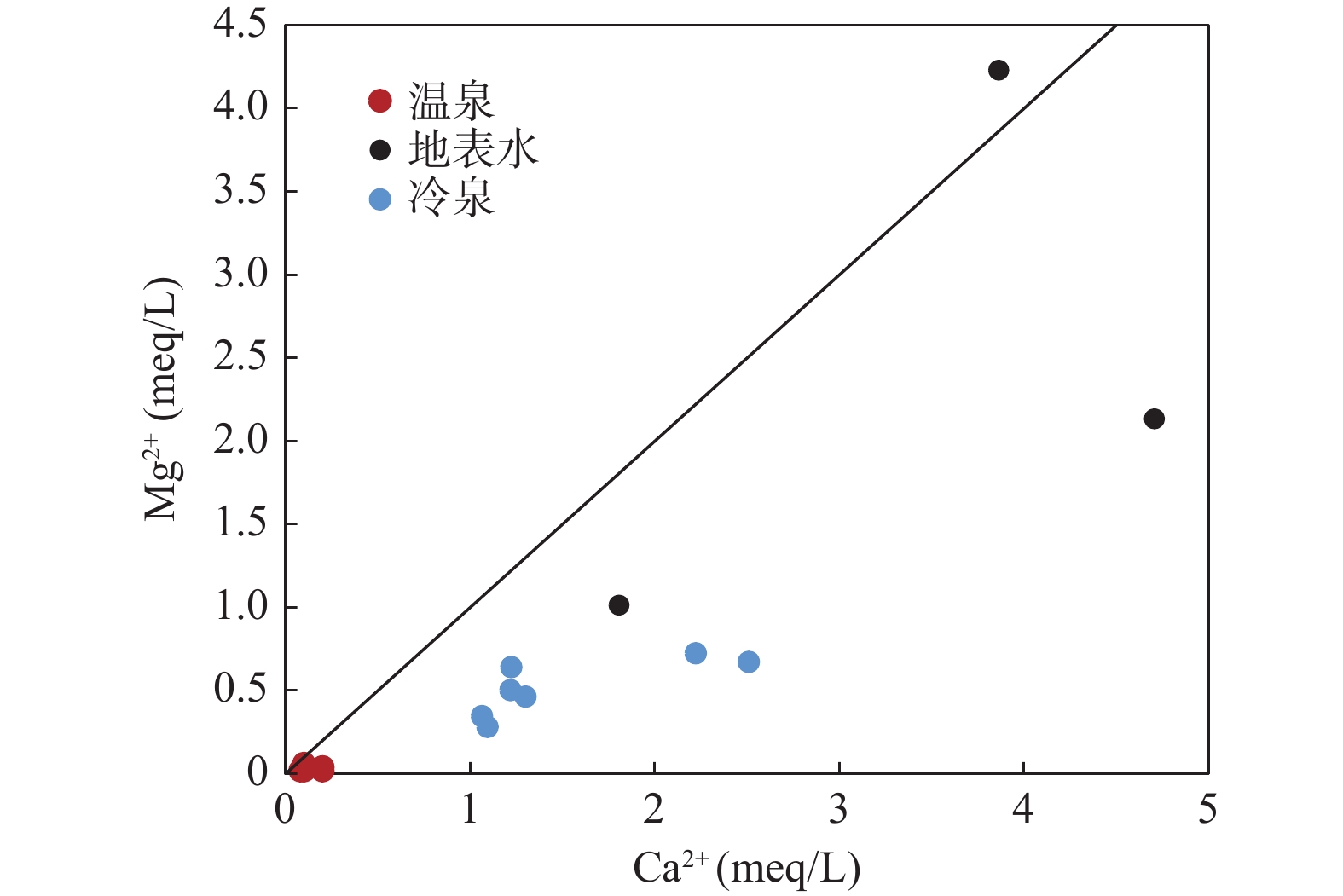
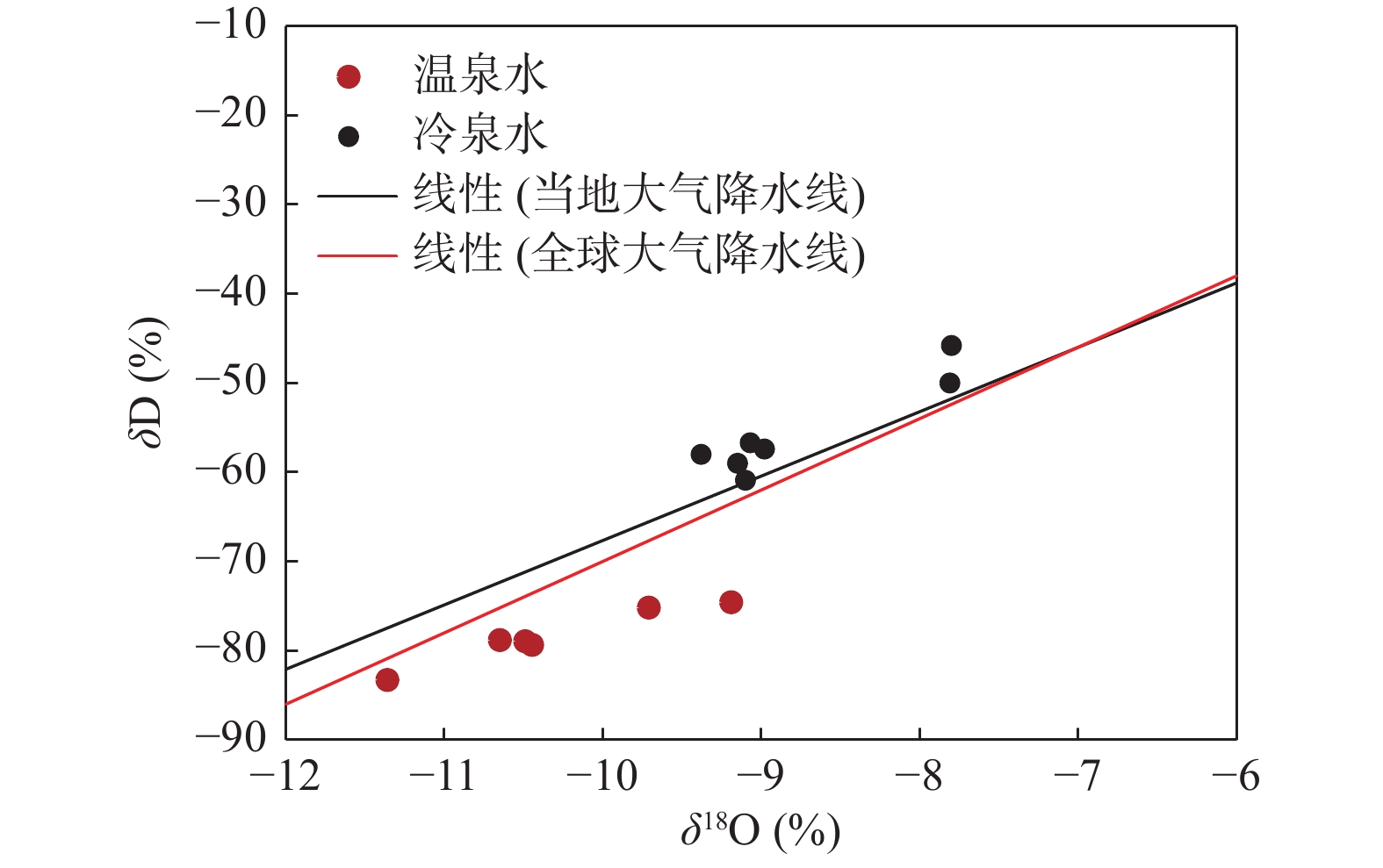
新疆地区属于西北干旱地区,水资源紧缺,为了研究其地下水的水文地球化学特征及水质情况,在博阿断裂附近采集与收集温泉水、地表水和冷泉水共15个样品,进行了水化学和氢氧同位素特征分析,并进行了水质评价。结果表明,研究区地表水的水化学类型主要为SO4−Na、Cl·SO4−Na和HCO3·SO4−Ca·Na型。温泉水的水化学类型为SO4·HCO3−Na/HCO3·SO4−Na和HCO3·Cl−Na型。冷泉水的水化学类型为SO4·HCO3−Mg·Ca、HCO3−Ca、HCO3−Mg·Ca和SO4·HCO3−Ca型。研究区冷泉水中Mg2+、Ca2+、HCO3−的主要来源是白云石、方解石和石膏溶解。温泉水中的Na+、K+、HCO3−和Ca2+主要来自于长石类矿物的溶解。地表水中的主要离子来源则比较复杂,并且其含量受到了蒸发作用的强烈影响,而且地表水处于氧化环境。温泉水和冷泉水主要补给来源为大气降水,补给高程为2874~4161 m。温泉水和地表水的水质极差,不适合饮用。通过研究博阿断裂附近地表水和地下水的水化学和同位素特征,可为当地水资源的合理开发利用与管理提供理论支撑。
Abstract:Xinjiang is an arid area in Northwest China, which is short of water resources. In order to study the hydrogeochemical characteristics and water quality of its groundwater, 15 samples including hot spring water, surface water and cold spring water were collected near the Boa fault. The hydrochemistry and hydrogen and oxygen isotope characteristics were analyzed, and the water quality was evaluated. The results show that the hydrochemical types of surface water in the study area are mainly SO4−Na, Cl·SO4−Na and HCO3·SO4−Ca·Na type. The hydrochemical types of hot spring water are SO4·HCO3−Na/HCO3·SO4−Na and HCO3·Cl−Na type. The hydrochemical types of cold spring water are SO4·HCO3−Mg·Ca, HCO3−Ca, HCO3−Mg·Ca and SO4·HCO3−Ca type. The main sources of Mg2+, Ca2+, HCO3− in the cold spring water in the study area are dolomite, calcite and gypsum dissolution. Na+, K+, HCO3− and Ca2+ in hot spring water mainly come from the dissolution of feldspar minerals. The main ion sources in surface water are complex, and their contents are strongly affected by evaporation, and the surface water is in an oxidizing environment. The main supply source of hot spring water and cold spring water is atmospheric precipitation, and the supply elevation varies from 2874.5 m to 4287 m. The water quality of hot spring water and surface water is very poor, which is not suitable for drinking. The study of hydrochemical and isotopic characteristics of surface water and groundwater near Boa fault can provide theoretical support for the rational development, utilization and management of local water resources.
-

-
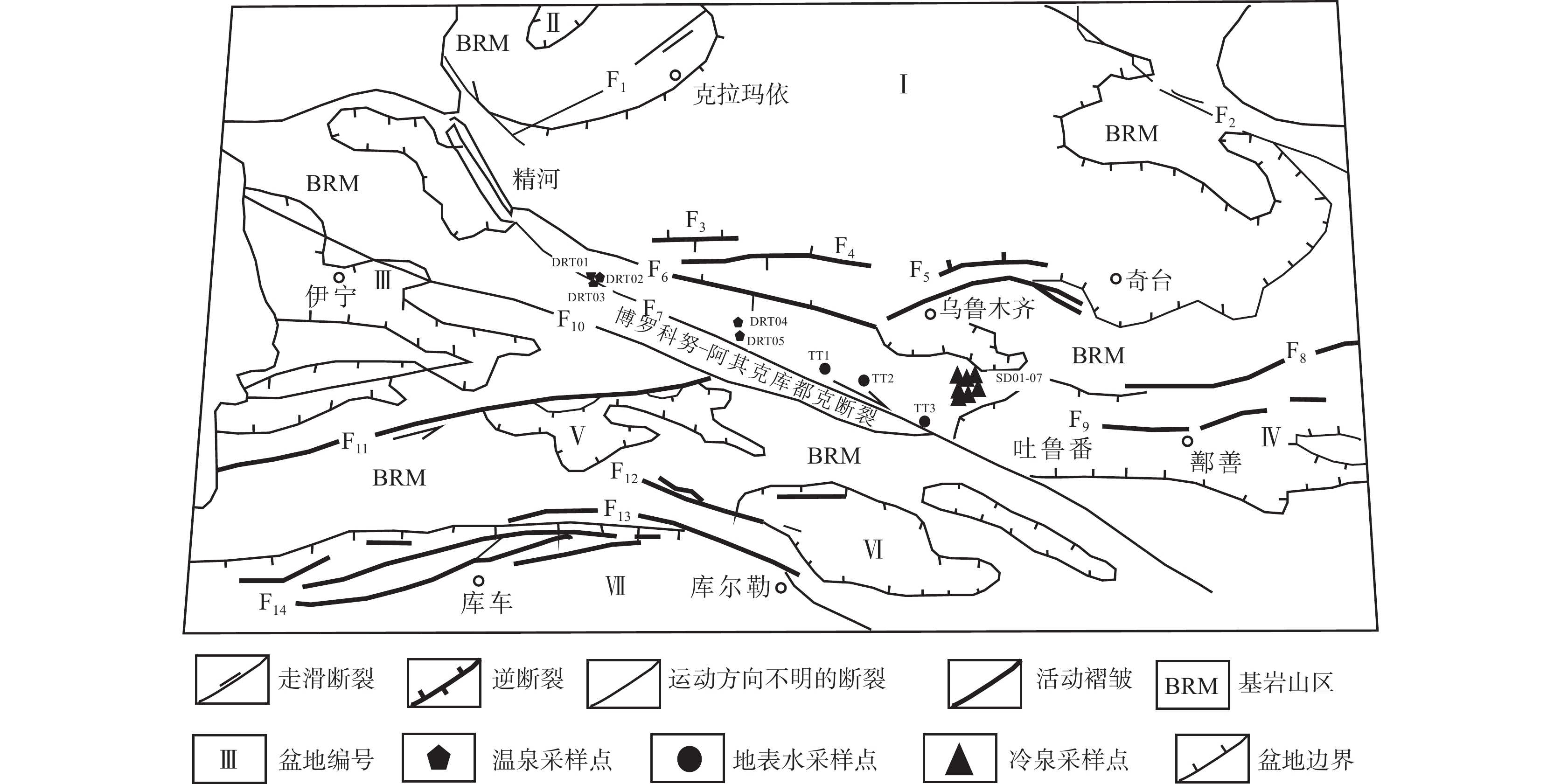
图 1 天山地区主要活动断裂及采样点位置(杨晓平等,2000)
Figure 1.
表 1 水化学同位素测试分析结果表
Table 1. Analysis results of water chemistry and isotope test
编号 水温
(℃)pH TDS
(mg/L)Na+
(mg/L)Ca2+
(mg/L)Mg2+
(mg/L)Cl−
(mg/L)SO42−
(mg/L)HCO3−
(mg/L)NO3−
(mg/L)NH4+
(mg/L)δD δ18O DRT1 49 9.95 387.74 103.26 2.00 0.24 14.32 54.73 23.19 5.54 5.51 −78.94 −10.49 DRT2 38.7 9.84 378.83 100.89 2.00 0.73 14.32 61.45 34.18 3.81 3.95 −83.28 −11.36 DRT3 50 9.92 553.73 163.12 1.60 0.24 15.75 158.44 25.63 5.74 5.70 −78.81 −10.65 DRT4 37.4 9.29 328.84 111.07 4.01 0.24 96.63 16.32 34.18 0.14 0.52 −74.57 −9.19 DRT5 29.5 8.82 304.75 109.08 4.01 0.49 82.32 15.36 48.83 2.26 0.39 −75.17 −9.71 TT1 22 8.24 3633.91 1081.49 77.25 50.76 207.74 1982.86 363.82 31.84 <0.04 −− −− TT2 25 8.58 3145.98 1072.95 36.12 12.17 518.99 1239.95 423.65 17.92 0.16 −− −− TT3 23 8.01 1338.64 332.22 94.11 25.61 67.36 537.86 451.73 14.29 2.20 −− −− SD01 −− 7.87 97.00 1.40 24.36 6.04 5.98 28.79 61.36 −− −− −60.9 −9.1 SD02 −− 7.84 79.00 1.24 21.27 4.17 4.27 19.13 57.27 −− −− −59 −9.15 SD03 −− 7.70 170.00 3.68 50.18 8.08 9.40 13.78 169.47 −− −− −50 −7.81 SD04 −− 7.60 95.00 0.87 25.99 5.57 4.78 18.51 77.72 −− −− −56.7 −9.07 SD05 −− 7.62 98.00 0.55 24.45 7.70 3.42 21.18 81.81 −− −− −57.4 −8.98 SD06 −− 7.70 77.00 0.78 21.87 3.39 8.20 19.54 46.75 −− −− −58 −9.38 SD07 −− 7.97 155.00 1.31 44.43 8.70 6.49 23.03 142.00 −− −− −45.8 −7.8 表 2 研究区补给高程表
Table 2. Recharge elevation in the study area
编号 δDV-SMOW(‰) δ18OV-SMOW(‰) 补给高程(m) DRT1 −78.94 −10.49 4066.30 DRT2 −83.28 −11.36 4160.65 DRT3 −78.81 −10.65 4063.48 DRT4 −74.57 −9.19 3971.30 DRT5 −75.17 −9.71 3064.35 DRT6 −79.35 −10.45 3155.19 SD01 −60.9 −9.1 3109 SD02 −59 −9.15 3662.5 SD03 −50 −7.81 2874.5 SD04 −56.7 −9.07 3667.5 SD05 −57.4 −8.98 3570 SD06 −58 −9.38 3943 SD07 −45.8 −7.8 3579 表 3 地下水质量评分表
Table 3. Groundwater quality scoring table
类别 I II III IV V Fi 0 1 3 6 10 表 4 地下水质量分级表
Table 4. Groundwater quality classification table
级别 优秀 良好 较好 较差 极差 F 0.8 0.8~2.5 2.5~4.25 4.25~7.2 >7.2 表 5 研究区水质F分值法评价结果表
Table 5. Evaluation results of F-score method for water quality in the study area
DRT1 DRT2 DRT3 DRT4 DRT5 TT1 TT2 TT3 F值 7.72 7.65 7.87 7.62 7.41 8.11 8.43 8.03 -
[1] 陈锋, 刘涛, 顾新鲁, 等. 新疆地热水分布与地质构造的关系[J]. 西部探矿工程, 2016, 2: 144-148
CHEN Feng, LIU Tao, GU Xinlu, et al. Relationship between geothermal water distribution and geological structure in Xinjiang[J]. West-china Exploration Engineering, 2016, 2: 144-148.
[2] 陈礼明. 福建地热水氢氧环境同位素特征浅析[J]. 福建地质, 2019, 1: 61~68
CHEN Liming. Isotopic Characteristic Analysis of Hydrogen—oxygen Environment in Geothermal Wate in Fujian Province[J]. Geology of Fujian, 2019, 1: 61~68.
[3] 陈首. 新疆沙湾县南山温泉地热资源地质特征[J]. 四川地质学报, 2017, 37(1): 91-95
CHEN Shou. Geological Features of Geothermal Resources in the Nanshan Hot Spring in Shawan, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 2017, 37(1): 91-95.
[4] 陈哲夫, 成守德, 梁云海, 等. 新疆开合构造与成矿[M]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆科技卫生出版社, 1997.
CHEN Zhefu, CHENG Shoude, LIANG Yunhai, et al. Opening-closing tectonics and mineralization in Xinjiang[M]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Science and Health Press, 1997.
[5] 冯先岳. 新疆古地震[M]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆科技卫生出版社, 1997.
FENG Xianyue. Paleoearthquake in Xinjiang[M]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Science and Health Press, 1997.
[6] 高朋, 施成鹏, 范明东. 基于地下水化学特征对博阿断裂带导水性的探讨[J]. 甘肃水利水电技术, 2021, 57(2): 53-55
GAO Peng, SHI Chengpeng, FAN mingDong. Discussion on the hydraulic conductivity of Bolokenu-Aqikekuduke fault zone based on the chemical characteristics of groundwater[J]. Gansu Water Resources and Hydropower Technology, 2021, 57(2): 53-55.
[7] 顾新鲁, 刘涛, 陈锋, 等. 新疆地热资源成因类型及控热模式分析[J]. 新疆地质, 2015, 33(2): 275-278 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2015.02.024
GU Xinlu, LIU Tao, CHEN Feng, et al. Analysis on Genetic Type and Heat Controlling Pattern of Xinjiang Geothermal Resources[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2015, 33(2): 275-278. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2015.02.024
[8] 韩朝辉, 王郅睿, 田辉, 等. 汉中盆地地下水水化学特征及其成因研究[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(4): 263−273.
HAN Chaohui, WANG Zhirui, TIAN Hui, et al. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Genesis of Groundwater in the Hanzhong Basin[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(4): 263−273.
[9] 蒋万军, 赵丹, 王广才, 等. 新疆吐-哈盆地地下水水文地球化学特征及形成作用[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(4): 825-833
JIANG Wandan, ZHAO Dan, WANG Guangcai, et al. Hydro-geochemical Characteristics and Formation of Groundwater in Tu-Ha Basin, Xinjiang[J]. Geoscience, 2016, 30(4): 825-833.
[10] 雷米, 周金龙, 吴彬, 等. 新疆昌吉州东部平原区地下水水文地球化学演化分析[J]. 干旱区研究, 2020, 37(1): 105-115
LEI Mi, ZHOU Jinlong, WU Bin, et al. Hydrogeochemical Evolution Process of Groundwater in the Eastern Plains in Changji Hui Autonomous Prefecture, Xinjiang[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2020, 37(1): 105-115.
[11] 李晖, 蒋忠诚, 王月, 等. 新疆地区大气降水中稳定同位素的变化特征[J]. 水土保持研究, 2009, 5: 157-161
LI Hui, JIANG Zhongcheng, WANG Yue, et al. Variation Characteristics of Stable Isotopes in the Precipitation of Xinjiang[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2009, 5: 157-161.
[12] 李学礼, 刘金辉, 史维浚, 等. 新疆准噶尔盆地北部天然水的同位素研究及其应用[J]. 地球学报, 2000, 21(4): 401-406.
LI Xueli, LIU Jinhui, SHI Weijun, et al. The Isotopic Study and Application of Natural Water in Northern Junggar Basin,Xinjian[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 2000, 21(4): 401-406.
[13] 刘瑞平, 徐友宁, 亢文婷. 基于phreeqci和netpath联合反演水文地球化学过程——以小秦岭太峪水库为例[J]. 西北地质, 2019, 52(1): 239-243
LIU Ruiping, XU Youning, KANG Wening, et al. Based on Phreeqci and Netpath Joint Inversion Hydrology Geochemistry Process: Example from the Xiaoqinling Tianyu Reservoir[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2019, 52(1): 239-243.
[14] 马致远, 党书生, 翟美静, 等. 蓝田汤峪地区地热流体同位素水文地球化学特征及其指示意义[J]. 西北地质, 2017, 50(2): 214-223
MA Zhiyuan, DANG Shusheng, ZHAI Meijing, et al. The Characteristics of Isotopes and Hydrogeochemistry for Geothermal Water in the Tangyu Town in Lantian County[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2017, 50(2): 214-223.
[15] 孟春芳, 孙珂. F分值法评价新乡市地下水质量[J]. 地下水, 2015, 37(2): 37-38
MENG Chunfang, SUN Ke. Evaluation of groundwater quality in Xinxiang City by F-score method[J]. Groundwater, 2015, 37(2): 37-38.
[16] 倪高倩, 张恒, 韦玉婷, 等. 四川地热流体水文地球化学及同位素特征简析. 新能源进展, 2016, 4(3): 184~194
NI Gaoqian, ZHANG Heng, WEI Yuting, et al. Hydrogeochemical and isotope characteristics of geothermal fluid in Sichuan[J]. Advances in New and Renewable Energy, 2016, 4(3): 184~194
[17] 任福弘, 沈照理. 水文地球化学. 中国大百科全书———地质学[M]. 北京: 中国大百科全书出版社, 1993: 507−508.
REN Fuhong, SHEN Zhaoli. Hydro-geochemistry, China Encyclopedia: Geology [M], Beijing: China Encyclopedia Press, 1993, 507−508.
[18] 沈照理. 水文地质学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1985.
SHEN Zhaoli. Hydrogeology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1985.
[19] 孙占学, 李学礼, 史维竣. 江西中低温地热水的同位素水文地球化学. 华东地质学院学报, 1992, 15(3): 243~248
SUN Zhanxue, LI Xueli, SHI Weijun. Isotopic hydrogeochemistry of mid-low temperature geothermal water in Jiangxi province[J]. Journal of East China Geological Institute, 1992, 15(3): 243~248
[20] 王书峰. 乌鲁木齐河流域水文地球化学特征的初步研究[J]. 新疆环境保护, 1985, 1: 17-23
WANG Shufeng. Preliminary study on hydrogeochemical characteristics of Urumqi River Basin[J]. Environmental Protection of Xinjiang, 1985, 1: 17-23.
[21] 王新娟, 许苗娟, 韩旭, 等. 基于同位素和水化学的北京平谷盆地地下水循环研究[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(5): 127−139.
WANG Xinjuan, XU Miaojuan, HAN Xu, et al. Study on Groundwater Cycle in Beijing Pinggu Basin Based on Isotopes and Hydrochemistry[J]. Northwestern Geology,2023,56(5): 127−139.
[22] 王一凡, 张永祥, 王昊, 等. 地下水质量综合评价方法的对比分析及应用[J]. 河北工业科技, 2014, 31(6): 457-462
WANG Yifan, ZHANG Yongxiang, WANG Hao, et al. Comparative analysis and application of groundwater quality comprehensive evaluation methods[J]. Hebei Journal of Industrial Science & Technology, 2014, 31(6): 457-462.
[23] 杨晓平, 沈军. 天山内部博罗可努断裂精河—阿拉山口段晚更新世以来的活动特征[J]. 地震地质, 2000, 22(3): 305-315
YANG Xiaoping, SHEN Jun. Late quaternary activity of Jinghe--Alashankou section of the Boluokenu fault, interior Tianshan[J]. Seismology and Egology, 2000, 22(3): 305-315.
[24] 叶思源, 孙继朝, 姜春永. 水文地球化学研究现状与进展[J]. 地球学报, 2002, 23(5): 477-482
YE Siyuan, SUN Jichao, JIANG Chunyong. Current Situation and Advances in Hydrogeochemical Researches[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2002, 23(5): 477-482.
[25] 殷秀兰, 凤蔚, 王瑞久, 等. 新疆乌鲁木齐河流域北部平原区水文地球化学[J]. 地球学报, 2015, 36(1): 77-84 doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2015.01.09
YIN Xiulan, FENG Wei, WANG Ruijiu, et al. Research on Hydrogeochemistry in Northern Plain of the Urumqi River Basin, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2015, 36(1): 77-84. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2015.01.09
[26] 张保健. 鲁西北地区地下热水的水文地球化学特征及形成条件研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2011.
ZHANG Baojian. Hydrogeochemicial characteristics and formation conditions of the geothermal water in Northwestern Shandong province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2011.
[27] 张帆, 王广才, 张茂省, 等. 产出水识别及受污染地下水水化学和氢氧稳定同位素特征[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(3): 98−108.
ZHANG Fan, WANG Guangcai, ZHANG Maosheng, et al. Identification of Produced Water and Characteristics of Hydrochemistry and Stable Hydrogen−Oxygen Isotopes of Contaminated Groundwater[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(3): 98−108.
[28] 张锡根. 同位素地球化学在地热勘探中的应用[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 1988, 1: 28~31.
ZHANG Xigen. Application of isotopic geochemistry in geothermal exploration[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 1988, 1: 28-31.
[29] 张未.吉林省长岭县浅层地下水水文地球化学演化规律分析[J].水资源与水工程学报, 2016,27(5): 59-63.
ZHANG Wei. Analysis of evolution law of hydrology and geochemistry of shallow groundwater in Changling county of Jilin Province[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 2016, 27(5): 59-63.
[30] 赵江涛, 周金龙, 梁川, 等. 新疆焉耆盆地平原区地下水演化的主要水文地球化学过程分析[J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(6): 1397-1406 doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.06.2016091807
ZHAO Jiangtao, ZHOU Jinlong, LIANG Chuan, et al. Hydrogeochemical process of evolution of groundwater in plain area of Yanqi, Xinjiang[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(6): 1397-1406. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017.06.2016091807
[31] 中国各省地热资源全解析[J]. 地热能, 2020, 5: 30−36
Analysis of geothermal resources in every province of China[J]. Geothermal Energy, 2020, 5: 30-36.
[32] 周金龙. 新疆地下水研究[M]. 郑州: 黄河水利出版社, 2010.
ZHOU Jinlong. Study on groundwater in Xinjiang[M]. Zhengzhou: The Yellow River Water Conservancy Press. 2010.
[33] Craig H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters[J]. Science, 1961, 133 (3465), 1702-1703. doi: 10.1126/science.133.3465.1702
[34] YanYan GAO, Jie CHEN, Hui QIAN, et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and processes of groundwater in an over 2260 year irrigation district: A comparison between irrigated and nonirrigated areas[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2022, 606: 127437. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.127437
[35] YanYan GAO, Hui QIAN, Wenhao REN, et al. Hydrogeochemical characterization and quality assessment of groundwater based on integrated-weight water quality index in a concentrated urban area[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 260: 121006. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121006
[36] Gibbs R J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry[J]. Science, 1970, 170(3962): 1088-1090. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1088
[37] Lasaga, A. C. , Soler, J. M. , Burch, T. E. , Nagy, K. L. Chemical weathering rate laws and global geochemistry cycles[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 1994, 58 (10): 23610-2386.
[38] SONG Chao, Han Guilin, WANG Pan, et al. Hydrochemical and isotope characteristics of spring water discharging from Qiushe Loess Section in Lingtai, northwestern China and their implication to groundwater recharge[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 2017, 5(4): 364-373.
[39] WANG Hua, MAO Xumei, WANG Tao, et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of hot springs exposed from fault zones in western Guangdong and their 14C age correction[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 2019, 7(1): 1-14.
[40] Wang Mengmeng, Zhouxun, Liu Yu, et al. Major, trace and rare earth elements geochemistry of geothermal waters from the Rehai high-temperature geothermal field in Tengchong of China[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2020, 119(2).
[41] Xing L. N. , Guo H. M. , Zhang Y. H. Groundwater hydrochemical characteristics and processes along flow paths in the North China Plain[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 70-71: 250-264. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.03.017
-



 下载:
下载: