Geochemical Characteristics and Geological Significance of Granites in Eastern Songliao Basin
-
摘要:
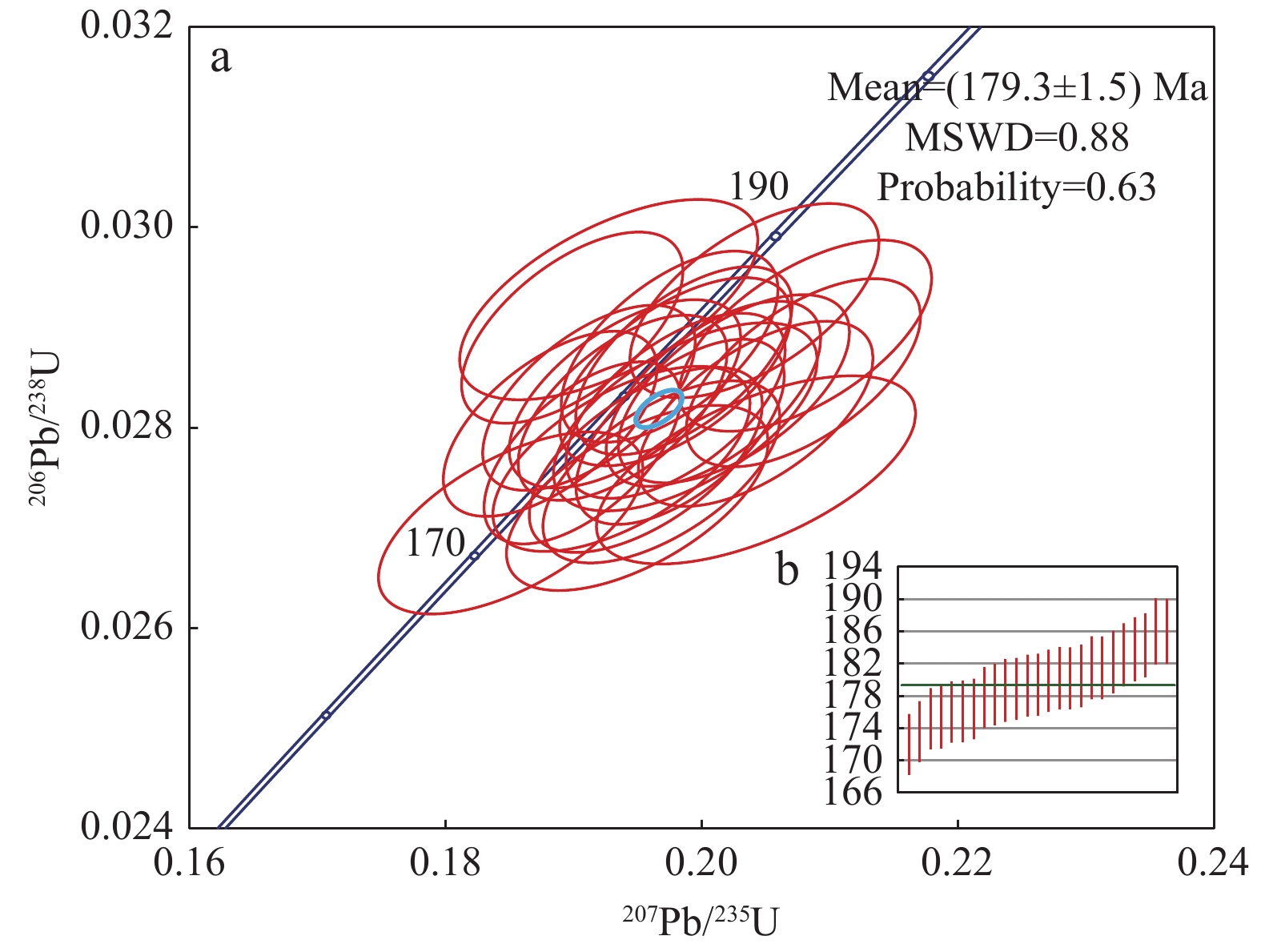
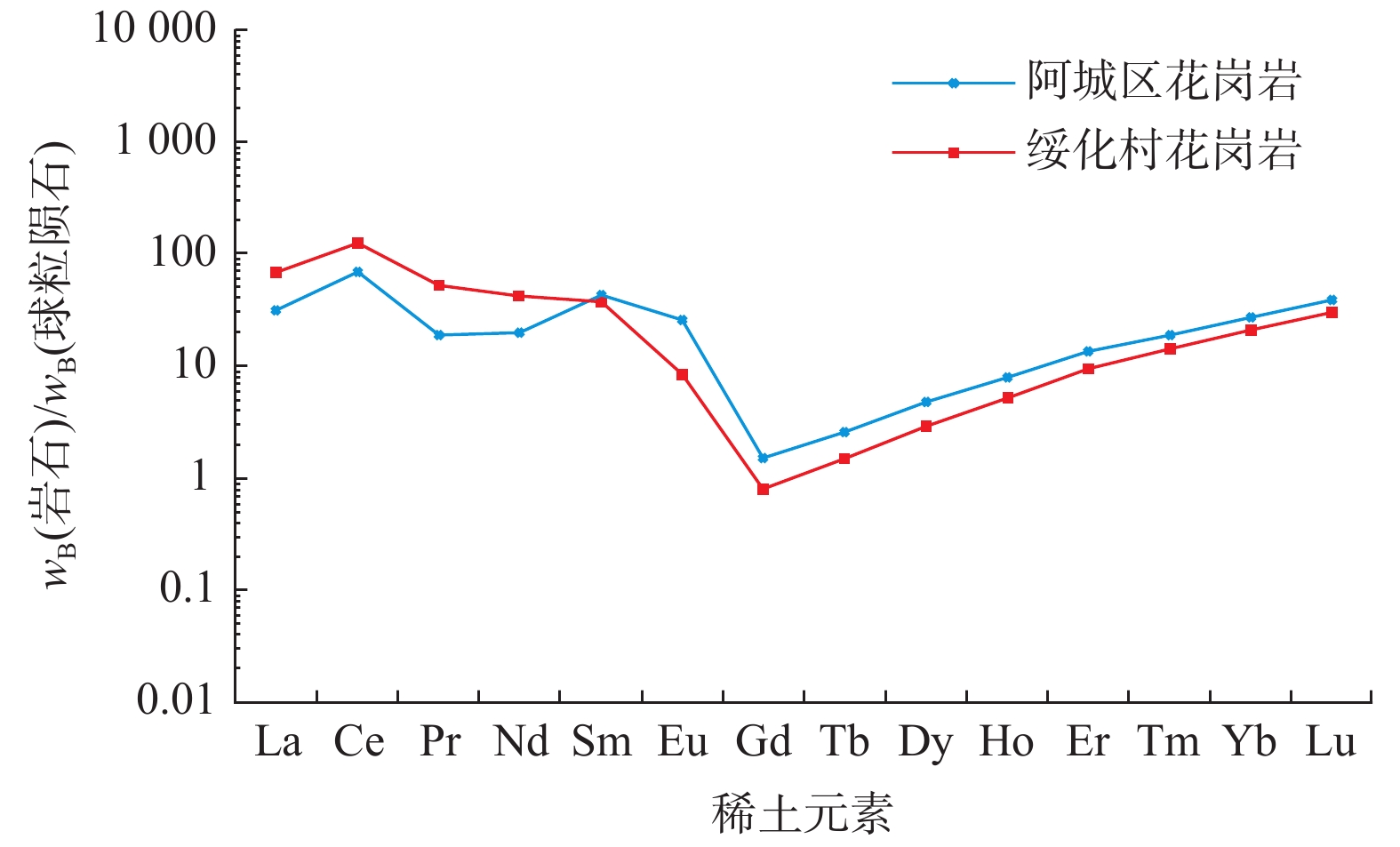
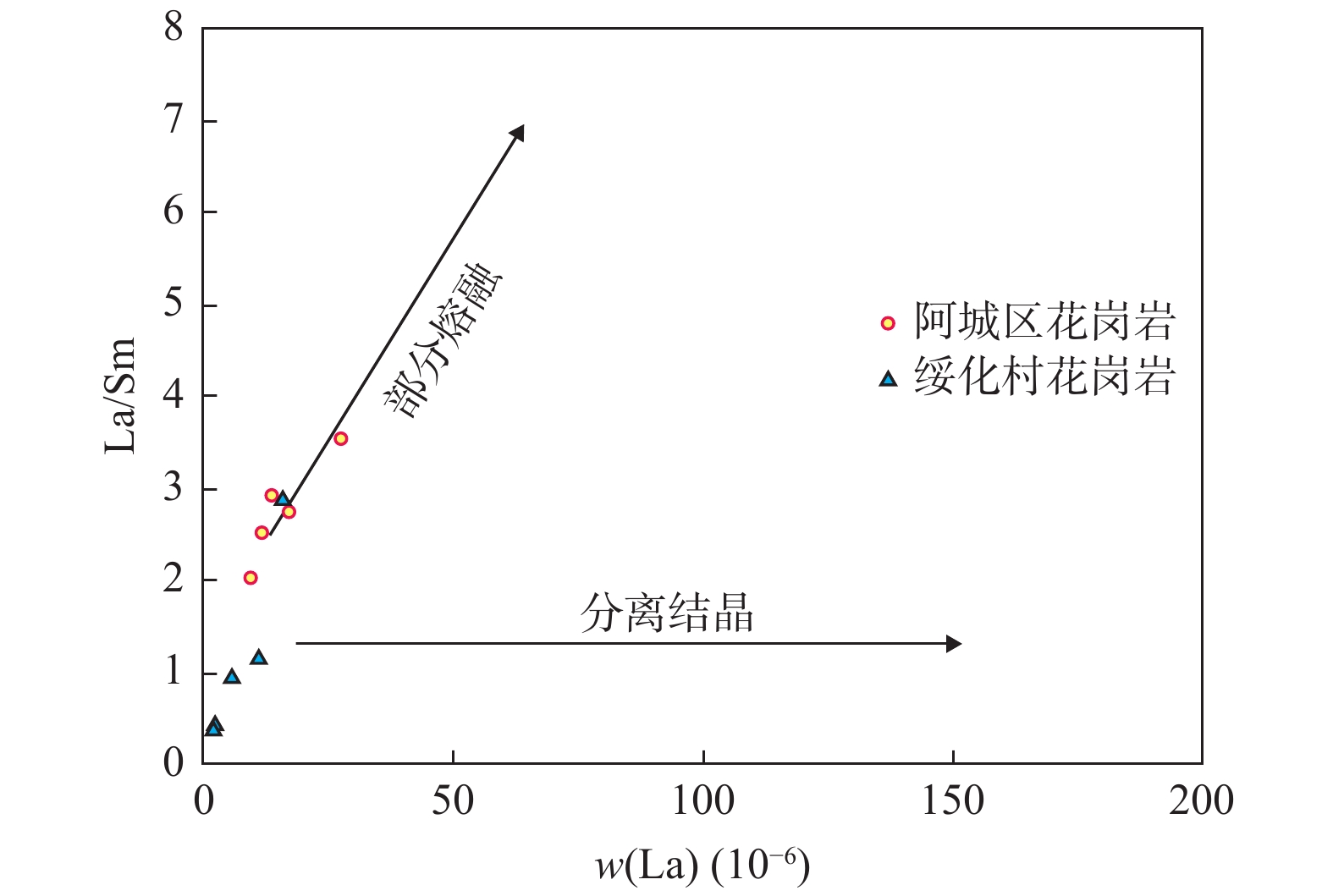
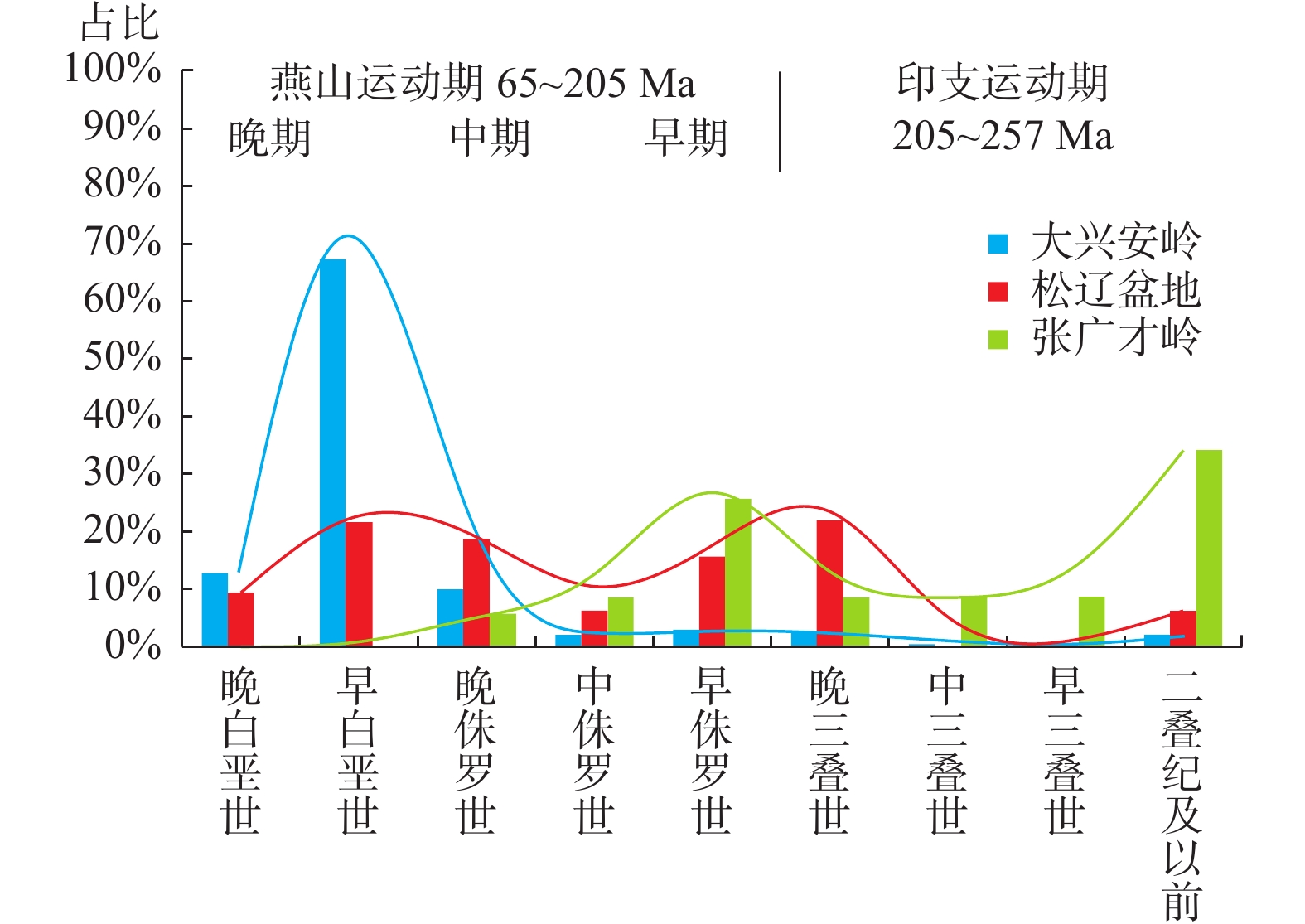
笔者对松辽盆地东部与张广才岭西部含黑云母花岗岩进行LA–ICP–MS 测年和微量稀土元素地球化学分析,探究其成岩时代与成岩环境。样品锆石振荡生长环带明显,Th/U值较大,揭示其属于岩浆成因。锆石U–Pb测年测得年龄分别为(179.3±1.5) Ma和(177.5±1.4) Ma,属于早侏罗世末期。轻稀土元素分馏明显,重稀土元素无明显分馏,Eu、Ce元素具有正异常。样品形成于板块俯冲聚敛环境。该地区花岗岩在形成过程中主要受控于部分熔融作用,岩脉有地壳和地幔双重性,可能有地幔混染现象。通过统计大兴安岭、松辽盆地与张广才岭花岗岩年龄,发现张广才岭处花岗岩形成时期早于松辽盆地花岗岩形成时期,进一步验证前人推测古太平洋板块和蒙古–鄂霍茨克洋板块发生双俯冲+拆沉作用。
Abstract:LA–ICP–MS dating and trace REE geochemical analysis of biotite–bearing granites in the eastern part of Songliao basin and the western part of Zhangguangcai range are carried out to explore their diagenetic age and environment in this paper . The sample zircon oscillatory growth zone is obvious, and the Th/U ratio is big, indicating that it belongs to magmatic origin. The ages of zircon U–Pb dating are (179.3±1.5)Ma; (177.5±1.4)Ma, belonging to the end of Early Jurassic. Light rare earth elements have obvious fractionation, heavy rare earth elements have no obvious fractionation, and Eu and Ce elements have positive anomalies. The sample was formed in the subduction and accumulation environment of the plate. The formation of granites in the two regions is mainly controlled by partial melting. The two dikes have the duality of crust and mantle, may have mantle contamination. Based on the statistics of the ages of the granites in the Greater Khingan Mountains, Songliao basin and Zhangguangcai range, it is found that the granites in Zhangguangcai range were formed earlier than those in Songliao basin. Validate the previous speculation that the ancient Pacific plate and the Mongolia–Okhotsk ocean plate have double subduction and delamination.
-
Key words:
- geochemistry /
- granite /
- U–Pb chronology /
- tectonic setting /
- Songliao basin
-

-
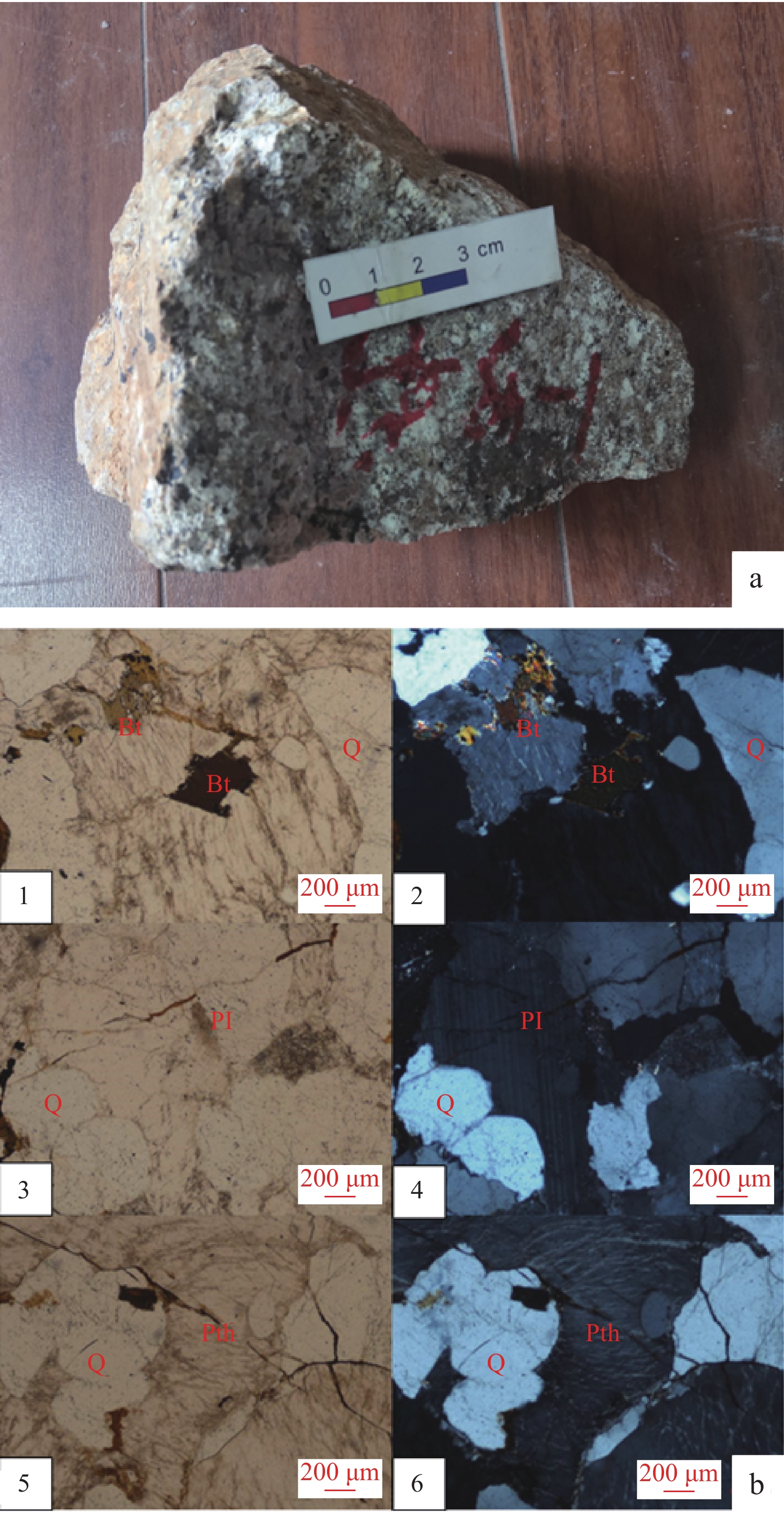
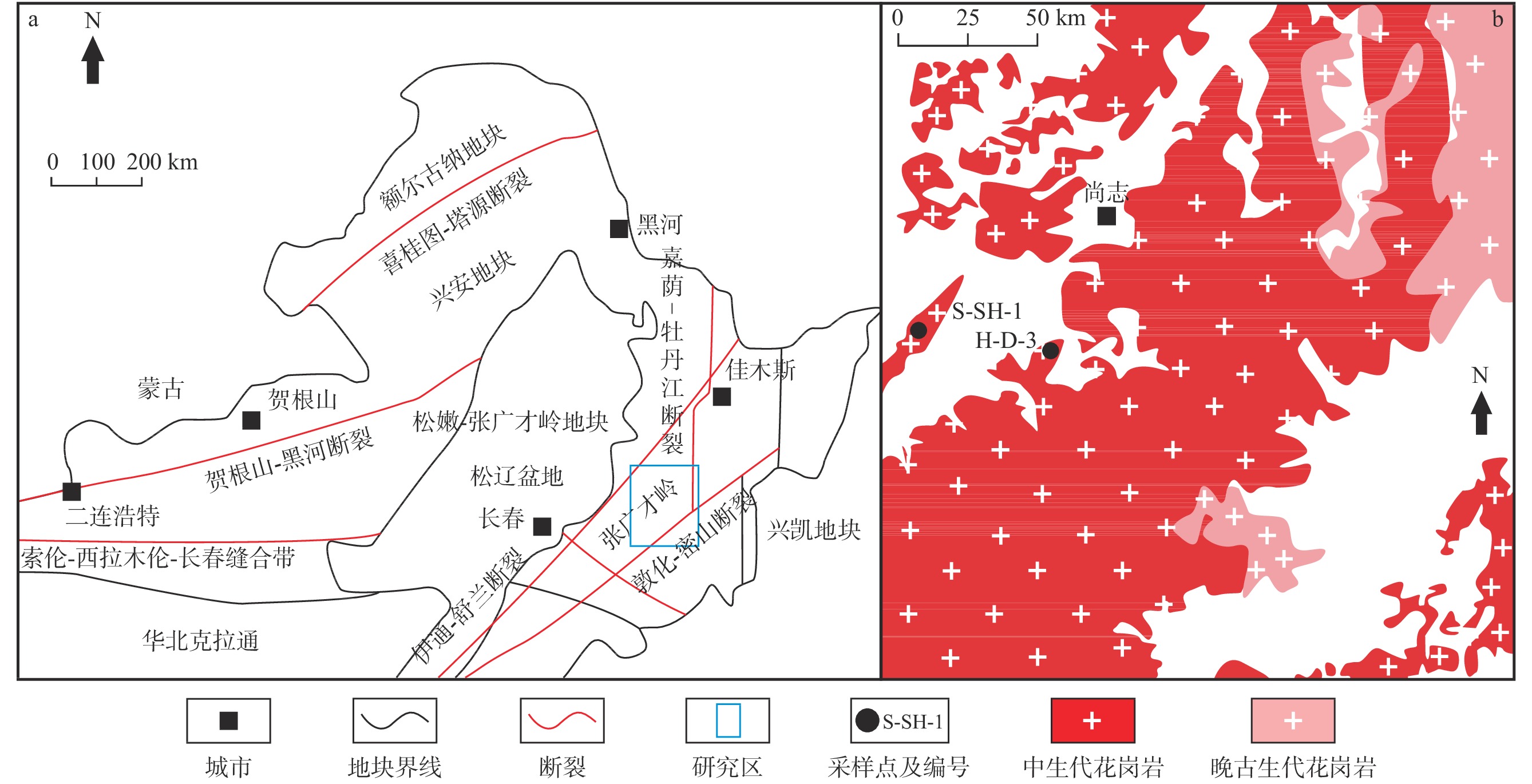
图 1 中国东北部构造简图(a)、松辽盆地东部–张广才岭中生代岩浆岩分布图(b)(据任永健,2019修)
Figure 1.
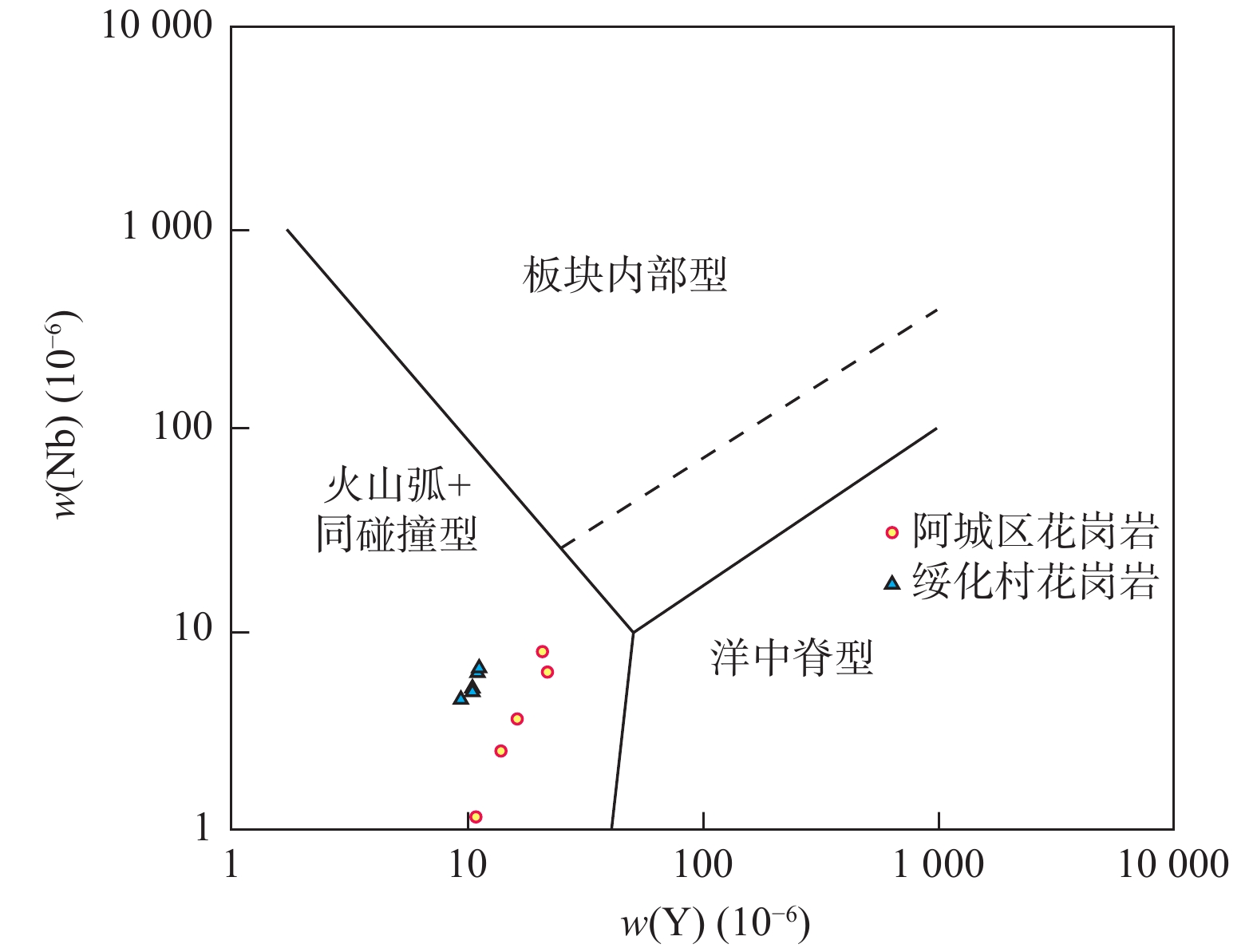
图 9 Nb–Y构造环境判别图(据Pearce et al.,1984)
Figure 9.
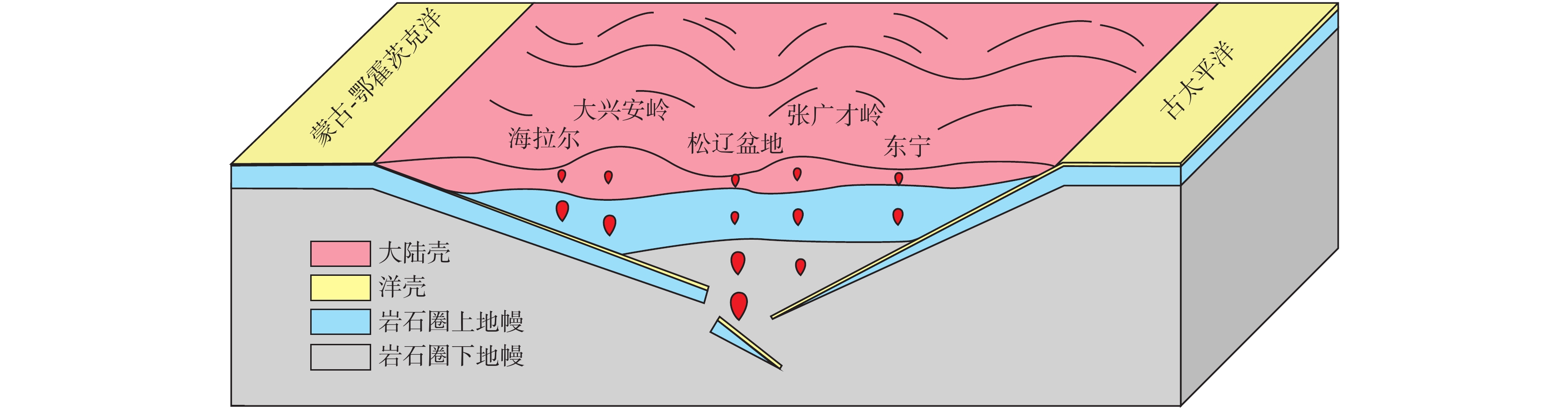
图 12 古太平洋板块俯冲和蒙古-鄂霍茨克洋版块俯冲、拆沉作用模式图(据杨雅军等,2022修)
Figure 12.
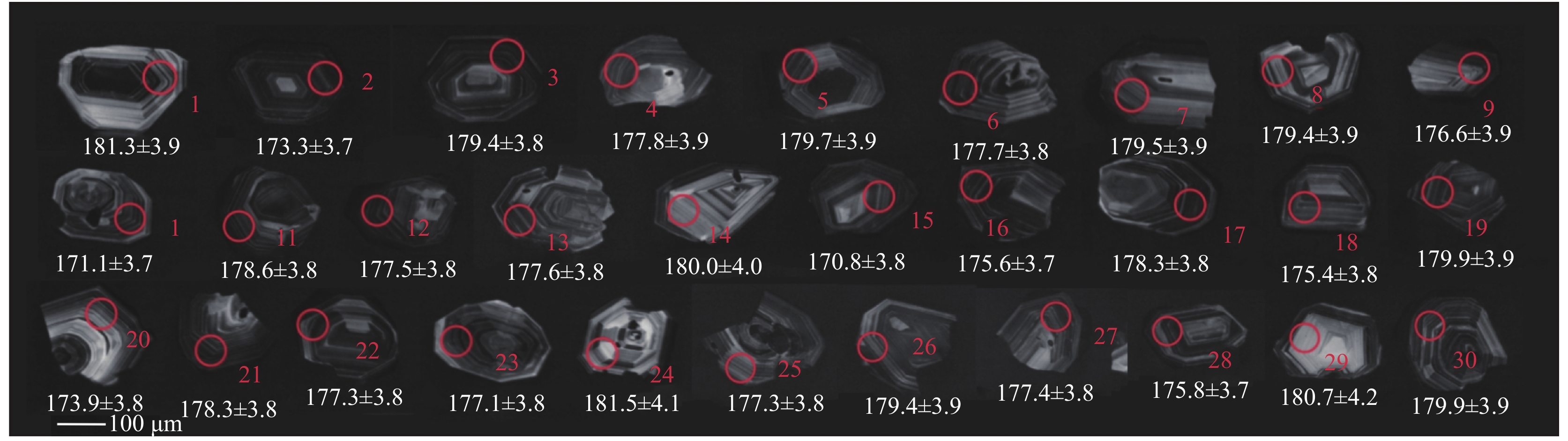
表 1 绥化村花岗岩(S-SH-1)样品锆石测年结果表
Table 1. Zircon dating results of Suihuacun granite (S-SH-1) sample
点号 U Th Pb Th/U 同位素比值 年龄(Ma) 谐和度 (10–6) 207Pb/206Pb ± 1σ 207Pb/235U ± 1σ 206Pb/238U ± 1σ 207Pb/206Pb ± 1σ 207Pb/235U ± 1σ 206Pb/238U ± 1σ S-SH-1-001 787.25 424.80 26.99 0.54 0.0507 0.0017 0.1937 0.0066 0.0277 0.0006 229.0 76.4 179.8 5.6 176.1 3.9 98% S-SH-1-002 610.16 332.24 21.39 0.54 0.0496 0.0015 0.1940 0.0060 0.0283 0.0006 178.3 69.0 180.0 5.1 180.2 3.9 100% S-SH-1-003 580.54 263.11 20.33 0.45 0.0475 0.0014 0.1899 0.0057 0.0290 0.0006 73.2 69.3 176.5 4.9 184.3 4.0 96% S-SH-1-004 693.84 366.37 24.10 0.53 0.0509 0.0014 0.1980 0.0057 0.0282 0.0006 235.1 63.0 183.4 4.8 179.4 3.9 98% S-SH-1-006 565.66 289.23 19.66 0.51 0.0526 0.0015 0.2042 0.0061 0.0281 0.0006 312.7 64.6 188.7 5.1 178.9 3.9 95% S-SH-1-007 773.82 869.86 30.92 1.12 0.0499 0.0014 0.1938 0.0054 0.0282 0.0006 188.0 61.8 179.9 4.6 179.3 3.8 100% S-SH-1-008 622.87 324.97 21.32 0.52 0.0513 0.0016 0.1956 0.0060 0.0277 0.0006 252.5 67.9 181.4 5.1 176.0 3.8 97% S-SH-1-009 774.11 380.43 27.58 0.49 0.0477 0.0019 0.1928 0.0077 0.0293 0.0007 85.6 92.8 179.0 6.6 186.0 4.1 96% S-SH-1-010 853.63 384.03 28.68 0.45 0.0498 0.0013 0.1907 0.0051 0.0278 0.0006 187.2 58.7 177.2 4.3 176.4 3.8 100% S-SH-1-012 696.59 405.52 24.14 0.58 0.0518 0.0016 0.1969 0.0061 0.0276 0.0006 277.0 68.4 182.5 5.2 175.2 3.8 96% S-SH-1-013 778.72 385.45 27.03 0.49 0.0514 0.0014 0.2009 0.0055 0.0283 0.0006 259.1 60.3 185.9 4.7 180.2 3.9 97% S-SH-1-014 573.68 313.01 19.27 0.55 0.0496 0.0018 0.1851 0.0068 0.0271 0.0006 177.6 83.3 172.4 5.9 172.0 3.8 100% S-SH-1-015 689.19 347.64 23.77 0.50 0.0487 0.0014 0.1882 0.0055 0.0280 0.0006 132.3 65.9 175.1 4.7 178.2 3.8 98% S-SH-1-016 739.51 448.71 26.93 0.61 0.0497 0.0014 0.1975 0.0056 0.0288 0.0006 182.0 63.1 183.0 4.7 183.1 3.9 100% S-SH-1-017 755.55 375.12 25.37 0.50 0.0518 0.0018 0.1950 0.0068 0.0273 0.0006 276.4 76.7 180.9 5.7 173.6 3.8 96% S-SH-1-018 647.84 378.09 23.37 0.58 0.0503 0.0015 0.1979 0.0060 0.0286 0.0006 207.1 67.1 183.4 5.1 181.5 3.9 99% S-SH-1-021 358.56 151.36 12.04 0.42 0.0537 0.0022 0.2043 0.0082 0.0276 0.0006 358.8 88.3 188.7 6.9 175.4 3.9 93% S-SH-1-022 420.38 229.11 14.75 0.55 0.0513 0.0017 0.1987 0.0068 0.0281 0.0006 253.2 76.1 184.1 5.8 178.7 3.9 97% S-SH-1-023 665.75 352.93 23.82 0.53 0.0528 0.0015 0.2080 0.0060 0.0286 0.0006 321.1 63.2 191.8 5.1 181.5 3.9 94% S-SH-1-024 504.33 254.67 18.24 0.50 0.0506 0.0016 0.2041 0.0064 0.0293 0.0006 221.4 70.2 188.6 5.4 186.0 4.0 99% S-SH-1-026 760.81 399.46 26.73 0.53 0.0490 0.0014 0.1912 0.0055 0.0283 0.0006 148.1 64.3 177.7 4.7 179.9 3.9 99% S-SH-1-027 961.29 525.01 33.85 0.55 0.0514 0.0014 0.1983 0.0054 0.0280 0.0006 260.5 59.4 183.7 4.6 177.8 3.8 97% S-SH-1-028 821.54 599.28 30.68 0.73 0.0503 0.0014 0.1986 0.0056 0.0287 0.0006 206.5 62.3 184.0 4.7 182.2 3.9 99% S-SH-1-029 657.00 262.17 22.56 0.40 0.0517 0.0015 0.2025 0.0060 0.0284 0.0006 273.5 64.7 187.3 5.0 180.5 3.9 96% S-SH-1-030 675.37 361.07 24.49 0.53 0.0522 0.0016 0.2081 0.0065 0.0289 0.0006 293.8 68.7 192.0 5.5 183.8 4.0 96% 表 2 阿城区花岗岩(H-D-3)样品锆石测年结果表
Table 2. Zircon dating results of Acheng granite (H-D-3) samples
点号 U Th Pb Th/U 同位素比值 年龄(Ma) 谐和度 (10–6) 207Pb/206Pb ± 1σ 207Pb/235U ± 1σ 206Pb/238U ± 1σ 207Pb/206Pb ± 1σ 207Pb/235U ± 1σ 206Pb/238U ± 1σ H-D-3-001 646.04 389.25 23.40 0.60 0.0494 0.0014 0.1943 0.0058 0.0285 0.0006 166.4 66.9 180.3 4.9 181.3 3.9 99% H-D-3-002 1111.21 1061.47 42.11 0.96 0.0496 0.0012 0.1863 0.0048 0.0273 0.0006 175.3 57.4 173.5 4.1 173.3 3.7 100% H-D-3-003 928.60 557.41 33.19 0.60 0.0488 0.0013 0.1899 0.0051 0.0282 0.0006 139.0 59.9 176.6 4.3 179.4 3.8 98% H-D-3-004 362.17 310.08 13.71 0.86 0.0513 0.0017 0.1977 0.0067 0.0280 0.0006 253.3 75.5 183.2 5.7 177.8 3.9 97% H-D-3-005 550.99 343.51 19.96 0.62 0.0492 0.0015 0.1916 0.0060 0.0283 0.0006 156.1 70.0 178.0 5.1 179.7 3.9 99% H-D-3-006 1028.47 1121.34 41.04 1.09 0.0497 0.0013 0.1915 0.0050 0.0280 0.0006 180.1 57.8 177.9 4.3 177.7 3.8 100% H-D-3-007 356.46 203.77 12.61 0.57 0.0496 0.0017 0.1930 0.0067 0.0282 0.0006 174.6 78.8 179.2 5.7 179.5 3.9 100% H-D-3-008 274.01 207.36 10.25 0.76 0.0551 0.0020 0.2143 0.0080 0.0282 0.0006 415.1 80.2 197.1 6.7 179.4 3.9 91% H-D-3-009 239.30 232.46 9.27 0.97 0.0557 0.0021 0.2132 0.0082 0.0278 0.0006 439.1 83.6 196.3 6.9 176.6 3.9 89% H-D-3-010 891.02 865.63 33.06 0.97 0.0495 0.0013 0.1834 0.0050 0.0269 0.0006 169.2 60.5 171.0 4.3 171.1 3.7 100% H-D-3-011 1172.31 603.72 40.81 0.51 0.0497 0.0013 0.1924 0.0051 0.0281 0.0006 179.3 59.0 178.7 4.4 178.6 3.8 100% H-D-3-012 843.67 543.12 30.29 0.64 0.0490 0.0013 0.1887 0.0052 0.0279 0.0006 148.6 61.7 175.5 4.4 177.5 3.8 99% H-D-3-013 557.34 511.28 21.26 0.92 0.0486 0.0015 0.1872 0.0058 0.0279 0.0006 128.1 69.9 174.2 4.9 177.6 3.8 98% H-D-3-014 239.55 206.64 9.19 0.86 0.0494 0.0020 0.1928 0.0078 0.0283 0.0006 165.8 91.6 179.0 6.6 180.0 4.0 99% H-D-3-015 282.14 220.97 10.09 0.78 0.0506 0.0020 0.1874 0.0073 0.0269 0.0006 223.8 87.0 174.4 6.2 170.8 3.8 98% H-D-3-016 907.67 725.05 33.38 0.80 0.0493 0.0013 0.1876 0.0050 0.0276 0.0006 161.6 59.9 174.6 4.3 175.6 3.7 99% H-D-3-017 1217.89 1012.25 45.95 0.83 0.0494 0.0012 0.1911 0.0050 0.0280 0.0006 168.0 57.8 177.6 4.2 178.3 3.8 100% H-D-3-018 397.75 307.89 14.57 0.77 0.0498 0.0017 0.1893 0.0064 0.0276 0.0006 184.0 76.2 176.0 5.5 175.4 3.8 100% H-D-3-019 544.42 578.29 21.87 1.06 0.0488 0.0015 0.1903 0.0058 0.0283 0.0006 136.3 69.0 176.9 5.0 179.9 3.9 98% H-D-3-020 469.44 305.12 16.52 0.65 0.0505 0.0016 0.1904 0.0061 0.0273 0.0006 218.0 71.1 176.9 5.2 173.9 3.8 98% H-D-3-021 1057.08 420.85 35.81 0.40 0.0496 0.0013 0.1917 0.0051 0.0280 0.0006 175.2 59.7 178.0 4.4 178.3 3.8 100% H-D-3-022 1015.52 724.53 37.34 0.71 0.0483 0.0013 0.1858 0.0049 0.0279 0.0006 115.1 59.7 173.1 4.2 177.3 3.8 98% H-D-3-023 586.65 407.74 21.28 0.70 0.0488 0.0014 0.1876 0.0056 0.0279 0.0006 139.6 67.6 174.5 4.8 177.1 3.8 99% H-D-3-024 249.08 206.93 9.64 0.83 0.0472 0.0021 0.1858 0.0082 0.0286 0.0007 57.9 102.5 173.0 7.0 181.5 4.1 95% H-D-3-025 542.70 423.44 20.14 0.78 0.0506 0.0015 0.1946 0.0059 0.0279 0.0006 223.1 67.2 180.5 5.0 177.3 3.8 98% H-D-3-026 384.09 364.24 15.02 0.95 0.0513 0.0017 0.1998 0.0068 0.0282 0.0006 255.5 75.6 184.9 5.7 179.4 3.9 97% H-D-3-027 427.61 348.41 16.21 0.81 0.0518 0.0017 0.1992 0.0066 0.0279 0.0006 276.5 72.9 184.5 5.6 177.4 3.8 96% H-D-3-028 1109.09 648.61 39.08 0.58 0.0495 0.0013 0.1887 0.0049 0.0276 0.0006 171.6 58.0 175.5 4.2 175.8 3.7 100% H-D-3-029 130.61 73.88 4.72 0.57 0.0467 0.0030 0.1832 0.0115 0.0284 0.0007 35.4 144.9 170.8 9.9 180.7 4.2 94% H-D-3-030 707.68 276.05 24.24 0.39 0.0507 0.0014 0.1979 0.0057 0.0283 0.0006 227.7 63.8 183.3 4.8 179.9 3.9 98% 表 3 绥化村花岗岩(S-SH-1)与阿城区花岗岩(H-D-3)花岗岩微量与稀土元素(10–6)
Table 3. Trace and rare earth elements of Suihuacun granite (S-SH-1) and Acheng granite (H-D-3) (10–6)
元素 SH1 SH2 SH3 SH4 SH5 SH平 H1 H2 H3 H4 H5 H平 Ti 2.52 3.23 2.78 5.15 1.75 3.09 9.94 5.85 2.95 5.52 9.92 6.84 Fe 10.17 13.58 41.84 17.72 17.56 20.17 3.65 4.12 2.12 2.69 2.29 2.97 Zr 4898.00 4898.00 4898.00 4898.00 4898.00 4898.00 4898.00 4898.00 4898.00 4898.00 4898.00 4898.00 Nb 4.31 4.52 4.19 4.28 4.85 4.43 1.16 4.29 5.89 1.00 2.49 2.97 Hf 139.88 146.23 142.79 143.53 147.32 143.95 109.15 129.19 142.22 116.40 118.78 123.15 Ta 1.91 1.94 1.70 1.99 2.24 1.96 0.44 1.37 1.93 0.35 0.90 1.00 Pb 21.39 24.10 19.66 21.32 26.93 22.68 9.27 33.06 30.29 9.64 16.21 19.70 Th 332.24 366.37 289.23 324.97 448.71 352.30 232.46 865.63 543.12 206.93 348.41 439.31 U 610.16 693.84 565.66 622.87 739.51 646.41 239.30 891.02 843.67 249.08 427.61 530.14 Y 9.41 9.64 9.00 9.64 10.37 9.61 10.68 18.00 19.43 10.97 13.58 14.53 La 13.87 11.96 27.79 9.55 17.39 16.11 5.80 11.12 15.82 2.32 2.18 7.45 Ce 77.35 59.24 95.88 58.60 82.09 74.63 28.43 58.08 66.51 27.36 30.62 42.20 Pr 4.07 3.28 9.02 2.94 5.11 4.88 1.78 3.37 2.28 0.81 0.73 1.79 Nd 15.58 14.37 34.55 13.17 20.03 19.54 9.74 17.12 8.04 6.11 5.23 9.25 Sm 4.75 4.75 7.83 4.70 6.33 5.67 6.18 9.71 5.53 5.82 5.82 6.61 Eu 0.41 0.34 0.55 0.48 0.61 0.48 1.67 1.82 1.07 1.53 1.46 1.51 Gd 0.16 0.16 0.17 0.15 0.18 0.16 0.26 0.40 0.32 0.28 0.28 0.31 Tb 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.06 0.05 0.08 0.13 0.12 0.08 0.09 0.10 Dy 0.71 0.73 0.69 0.72 0.78 0.73 0.94 1.52 1.52 0.95 1.13 1.21 Ho 0.28 0.30 0.28 0.29 0.32 0.29 0.35 0.56 0.60 0.35 0.43 0.46 Er 1.54 1.56 1.47 1.56 1.69 1.56 1.69 2.71 3.01 1.73 2.12 2.25 Tm 0.36 0.35 0.34 0.36 0.39 0.36 0.36 0.57 0.65 0.37 0.47 0.48 Yb 3.55 3.45 3.30 3.58 3.89 3.56 3.56 5.21 6.21 3.60 4.53 4.62 Lu 0.74 0.73 0.70 0.76 0.83 0.75 0.77 1.08 1.29 0.76 0.94 0.97 ∑REE 123.42 101.28 182.63 96.92 139.70 128.79 61.59 113.38 112.95 52.08 56.02 79.21 LREE 116.03 93.94 175.62 89.44 131.56 121.32 53.60 101.22 99.25 43.95 46.04 68.81 HREE 7.39 7.34 7.01 7.48 8.14 7.47 7.99 12.16 13.70 8.13 9.99 10.40 LREE/HREE 15.70 12.80 25.07 11.96 16.16 16.34 6.71 8.32 7.24 5.41 4.61 6.46 δEu 1.46 1.18 1.46 1.75 1.76 1.52 4.03 2.84 2.45 3.64 3.49 3.29 δCe 2.52 2.32 1.48 2.71 2.14 2.23 2.17 2.33 2.72 4.90 5.97 3.62 La/Yb 2.80 2.48 6.03 1.91 3.21 3.29 1.17 1.53 1.83 0.46 0.35 1.07 La/Sm 1.89 1.63 2.29 1.31 1.77 1.78 0.61 0.74 1.85 0.26 0.24 0.74 Gd/Yb 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.03 0.04 0.04 0.06 0.06 0.04 0.07 0.05 0.06 -
[1] 曹怀仁, 胡建芳, 彭平安, 等. 松辽盆地青山口组二段下部湖泊水体环境变化[J]. 地学前缘, 2017, 24(01): 205-215
CAO Huairen, HU Jianfang, PENG Ping’an, et al. Environmental change of lake water in the lower part of Qingshankou Formation II in Songliao Basin [J]. Geoscience Front, 2017, 24 (01): 205-215.
[2] 程顺波, 付建明, 徐德明, 等. 湖南雪花顶花岗岩及其包体的地质地球化学特征和成因分析[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2009, 33(04): 588-597 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2009.04.013
CHENG Shunbo, FU Jianming, XU Deming, et al. Geological and geochemical characteristics and genetic analysis of Xuehuading granite and its xenoliths in Hunan [J]. Geotectonics and Metallogeny, 2009, 33 (04): 588-597. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2009.04.013
[3] 冯光英, 牛晓露, 刘飞, 等. 张广才岭地块早侏罗世晚期花岗闪长岩及其闪长质包体的岩石成因及构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(10): 2598-2616 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.10.014
FENG Guangying, NIU Xiaolu, LIU Fei, et al. Petrogenesis and tectonic significance of late Early Jurassic granodiorites and dioritic inclusions in the Zhangguangcailing block [J]. Journal of Geology, 2019, 93 (10): 2598-2616. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.10.014
[4] 付秀丽, 蒙启安, 文政, 等. 松辽盆地白云岩沉积环境及成因机理[J]. 沉积学报, 2024, 42(1): 113−129.
FU Xiuli, MENG Qi’an, WEN Zheng, et al. Sedimentary environment and genetic mechanism of dolomite in Songliao Basin [J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2024, 42(1):113−129
[5] 句高, 梁一鸿, 孙晓, 等. 张广才岭南段两个侏罗纪花岗岩体的地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 世界地质, 2018, 37(02): 374-384
GU Gao, LIANG Yihong, SUN Xiao, et al. Geochemical characteristics and geological significance of two Jurassic granites in the southern section of the Zhangguangcai Ridge [J]. World Geology, 2018, 37 (02): 374-384
[6] 李冰, 杨红霞. 电感耦合等离子体质谱原理和应用[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2005.
[7] 李蓉, 孙德有, 苟军, 等. 张广才岭北部苇河花岗岩基的地球化学特征与岩石成因[J]. 世界地质, 2012, 31(03): 462-470
LI Rong, SUN Deyou, GOU Jun, et al. Geochemical characteristics and petrogenesis of the Weihe granite batholith in the north of Zhang Guangcai Ling [J]. World Geology, 2012, 31 (03): 462-470
[8] 李宗怀, 韩宝福, 李辛子, 等. 新疆准噶尔地区花岗岩中微粒闪长质包体特征及后碰撞花岗质岩浆起源和演化[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2004,24(3): 214-226 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2004.03.003
LI Zonghuai, HAN Baofu, LI Xinzi, et al. Characteristics of micro-diorite xenoliths and origin and evolution of post-collisional granitic magma in granites in Junggar, Xinjiang [J]. Journal of Rock Mineralogy, 2004,23 (3): 214-226 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2004.03.003
[9] 刘大明, 肖渊甫, 李宁, 等. 松潘—甘孜造山带北部达日泽龙花岗岩体地球化学、年代学及构造意义[J]. 矿物学报, 2022, 42(03): 270-284.
LIU Daming, XIAO Yuanfu, LI Ning, et al. Geochemistry, chronology and tectonic significance of the Darizelong granite body in the northern Songpan-Ganzi orogenic belt [J]. Journal of Minerals, 2022, 42 (03): 270-284.
[10] 刘颖, 刘海臣, 李献华. 用ICP-MS准确测定岩石样品中的40余种微量元素[J]. 地球化学, 1996(06): 552-558 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1996.06.004
LIU Ying, LIU Haichen, LI Xianhua. Accurate determination of more than 40 trace elements in rock samples by ICP-MS [J]. Geochemistry, 1996 (06): 552-558. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1996.06.004
[11] 骆念岗, 高莲凤, 张璟, 等. 大兴安岭北段宜里地区早侏罗世二长花岗岩U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地质论评, 2021, 67(06): 1649-1669
LUO Niangang, GAO Lianfeng, ZHANG Jing, et al. U-Pb age, geochemical characteristics and tectonic significance of the early Jurassic monzogranite in the Yili area of the northern section of the Great Hinggan Mountains [J]. Geological Review, 2021, 67 (06): 1649-1669.
[12] 孟恩, 许文良, 杨德彬, 等. 满洲里地区灵泉盆地中生代火山岩的锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(04): 1209-1226
MENG En, XU Wenliang, YANG Debin, et al. Zircon U-Pb chronology, geochemistry and geological significance of the Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the Lingquan Basin in the Manzhouli region [J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2011, 27 (04): 1209-1226
[13] 钱烨, 赵昌吉, 张涛, 等. 吉林中部早侏罗世A型花岗岩的地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 黑龙江科技大学学报, 2021, 31(05): 562-568+577 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-7262.2021.05.005
QIAN Ye, ZHAO Changji, ZHANG Tao, et al. Geochemical characteristics and geological significance of the early Jurassic A-type granite in central Jilin [J]. Journal of Heilongjiang University of Science and Technology, 2021, 31 (05): 562-568+577 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-7262.2021.05.005
[14] 任永健, 程烁, 张明明, 等. 黑龙江张家湾地区中侏罗世A型花岗岩地球化学特征及构造环境分析[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(05): 1067-1076
REN Yongjian, CHENG Shuo, ZHANG Mingming, et al. Geochemical characteristics and tectonic environment analysis of the Middle Jurassic A-type granite in Zhangjiawan area, Heilongjiang Province [J]. Modern Geology, 2020, 34 (05): 1067-1076.
[15] 任永健. 张广才岭南部早—中侏罗世花岗质岩浆作用及构造演化[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(11): 2813-2831
REN Yongjian. Early to Middle Jurassic granitic magmatism and tectonic evolution in the south of Zhang Guangcai Ling [J]. Journal of Geology, 2019, 93 (11): 2813-2831.
[16] 邵济安, 刘福田, 陈辉, 等. 大兴安岭—燕山晚中生代岩浆活动与俯冲作用关系[J]. 地质学报, 2001(01): 56-63
SHAO Ji'an, LIU Futian, CHEN Hui, et al. The relationship between late Mesozoic magmatism and subduction in the Greater Khingan-Yanshan Mountains [J]. Journal of Geology, 2001 (01): 56-63
[17] 舒良树. 普通地质学(第三版)[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2010.
[18] 隋振民, 葛文春, 吴福元, 等. 大兴安岭东北部侏罗纪花岗质岩石的锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2007(02): 461-480
SUI Zhenmin, GE Wenchun, WU Fuyuan, et al. Zircon U-Pb age, geochemical characteristics and genesis of Jurassic granitic rocks in the northeast of the Great Hinggan Mountains [J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007 (02): 461-480
[19] 孙德有, 吴福元, 高山, 等. 吉林中部晚三叠世和早侏罗世两期铝质A型花岗岩的厘定及对吉黑东部构造格局的制约[J]. 地学前缘, 2005(02): 263-275
SUN Deyou, WU Fuyuan, GAO Shan, et al. Determination of the late Triassic and early Jurassic aluminous A-type granites in central Jilin and their constraints on the tectonic framework in the eastern part of Jilin and Heihe [J]. Geologic Front, 2005 (02): 263-275
[20] 唐杰, 许文良, 王枫, 等. 古太平洋板块在欧亚大陆下的俯冲历史: 东北亚陆缘中生代-古近纪岩浆记录[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2018, 48(05): 549-583
TANG Jie, XU Wenliang, WANG Feng, et al. The subduction history of the ancient Pacific plate under the Eurasian continent: the Mesozoic-Paleogene magmatic record of the northeastern Asian continental margin [J]. Chinese Science: Earth Science, 2018, 48 (05): 549-583
[21] 王得权, 王建国, 杨帅, 等. 陕西秋树坪金矿似斑状奥长花岗岩脉锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 矿物岩石, 2022, 42(01): 90-97
WANG Dequan, WANG Jianguo, YANG Shuai, et al. Zircon U-Pb age, geochemical characteristics and geological significance of porphyry anorthite vein in Qiushuping gold deposit, Shaanxi [J]. Mineral and Rock, 2022, 42 (01): 90-97.
[22] 吴元保, 郑永飞. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J]. 科学通报, 2004(16): 1589-1604 doi: 10.1360/csb2004-49-16-1589
WU Yuanbao, ZHENG Yongfei. Zircon genetic mineralogy and its constraints on U-Pb age interpretation [J]. Science Bulletin, 2004 (16): 1589-1604 doi: 10.1360/csb2004-49-16-1589
[23] 肖庆辉, 邱瑞照, 邢作云, 等. 花岗岩成因研究前沿的认识[J]. 地质论评, 2007(S1): 17-27
XIAO Qinghui, QIU Ruizhao, XING Zuoyun, et al. Understanding of the frontier of granite genesis research [J]. Geological Review, 2007 (S1): 17-27.
[24] 杨雅军, 杨晓平, 江斌, 等. 大兴安岭中生代火山岩地层时空分布与蒙古—鄂霍茨克洋、古太平洋板块俯冲作用响应[J]. 地学前缘, 2022, 29(02): 115-131
YANG Yajun, YANG Xiaoping, JIANG Bin, et al. The spatial and temporal distribution of Mesozoic volcanic rock strata in the Great Khingan Mountains and the response to the subduction of the Mongolia-Okhotsk Ocean and the Paleo-Pacific Plate [J]. Geologic Front, 2022, 29 (02): 115-131.
[25] 杨长江, 王亚春. 小兴安岭东南部伊春中生代花岗岩的锆石U-Pb测年及其地质意义[J]. 吉林地质, 2010, 29(04): 1-5+31 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2427.2010.04.001
YANG Changjiang, WANG Yachun. Zircon U-Pb dating of the Yichun Mesozoic granite in the southeast of the Xiaoxing'an Mountains and its geological significance [J]. Jilin Geology, 2010, 29 (04): 1-5+31 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2427.2010.04.001
[26] 俞胜, 贾轩, 姚皓骞, 等. 西秦岭白龙江地区志留系迭部组岩石地球化学特征及碎屑锆石原位U–Pb年代学研究[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(5): 245−261.
YU Sheng, JIA Xuan, YAO Haoqian, et al. Geochemistry Characteristics and Detrital Zircon In–Site U–Pb Geochronology of Silurian Diebu Formation in Bailongjiang Area, West Qinling Mountains[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(5): 245−261.
[27] 袁洪林, 吴福元, 高山, 等. 东北地区新生代侵入体的锆石激光探针U-Pb年龄测定与稀土元素成分分析[J]. 科学通报, 2003(14): 1511-1520 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2003.14.008
YUAN Honglin, WU Fuyuan, GAO Shan, et al. Zircon laser probe U-Pb dating and rare earth element composition analysis of Cenozoic intrusions in Northeast China [J]. Science Bulletin, 2003 (14): 1511-1520 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2003.14.008
[28] 张健, 张海华, 贺君玲, 等. 东北地区氦气成藏条件与资源前景分析[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(1): 117−128.
ZHANG Jian, ZHANG Haihua, HE Junling, et al. Analysis of Helium Accumulation Conditions and Resource Prospect in Northeast China[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(1): 117−128.
[29] 张旗, 金惟俊, 王元龙, 等. 大洋岩石圈拆沉与大陆下地壳拆沉: 不同的机制及意义——兼评“下地壳+岩石圈地幔拆沉模式”[J]. 岩石学报, 2006(11): 2631-2638 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2006.11.002
ZHANG Qi, JIN Weijun, WANG Yuanlong, et al. Ocean lithospheric delamination and continental lower crust delamination: different mechanisms and significance-also comment on "lower crust+lithospheric mantle delamination model" [J]. Journal of Rock, 2006 (11): 2631-2638 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2006.11.002
[30] 赵越, 刘敬党, 张国宾, 等. 张广才岭南部帽儿山岩体二长花岗岩年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2021, 51(04): 1098-1118
ZHAO Yue, LIU Jingdang, ZHANG Guobin, et al. Chronology, geochemical characteristics and tectonic significance of the monzogranite of the Maoershan pluton in the southern part of Zhang Guangcai Ling [J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2021, 51 (04): 1098-1118.
[31] Allègre C. J., Minster J. F. Quantitative models of trace element behavior in magmatic processes[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1978, 38(1). doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(78)90123-1
[32] Champion D C, Chappell B W. Petrogenesis of felsic I-ype granites: An example from northern Queensland[J]. Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh Earth Science, 1992, 83: 115- 126. doi: 10.1017/S026359330000780X
[33] Defant M J, Drummond M S. Derivation of some morden arc magmas by of young subducted lithosphere[J]. Nature, 1990, 47: 62-665
[34] Dong Yu, Ge Wenchun, Yang Hao. Geochronology and geochemistry of Early Cretaceous volcanic rocks from the Baiyingaolao Formation in the central Great Xing’an Range, NE China, and its tectonic implications[J]. Lithos, 2014, 205: 168-184. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2014.07.004
[35] Fan Weiming, Guo Feng, Wang Yuejun, et al. Late Mesozoic calc-alkaline volcanism of post-orogenic extension in the northern Da Hinggan Mountains, Northeastern China[J]. Journal of Volcanology & Geothermal Rsearch, 2003, 121(1): 115-135.
[36] Feng Zhiqiang, Jia Jie, Liu Yongjiang, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Carboniferous magmatism in the northern Great Xing’an Rang, NE China: Constraints on the timing of amalgamation of Xing’an and Songnen blocks[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 113: 411-426. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.12.017
[37] Kravchinsky V A, Cogne J P, Harbert W P. Evolution of the Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean as constrained by new palaeomagnetic data from the Mongol-Okhotsk suture zone, Siberia[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2002, 148(1): 34-57. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-246x.2002.01557.x
[38] Meng Qingren. What drove late Mesozoic extension of the northern China-Mongolia tract[J]. Tectonophysics, 2003, 369(3): 155-174.
[39] Möller A, O’Brien P J, Kennedy A, et al. Linking growth epi‐sodes of zircon and metamorphic textures to zircon chemistry: An example from the ultrahigh-temperature granulites of Rogaland(SW Norway) [J]. Geological Society, London, SpecialPublications, 2003, 220: 65-82. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2003.220.01.04
[40] Paterno R, Castillo. An Overview Of Adakite Petrogenesis[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2006(03): 258-268.
[41] Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4): 956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
[42] Richards J P. Magmatic to hydrothermal metal fluxes in convergent and collided margins[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2011, 40(1): 1-26. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2011.05.006
[43] Daniela Rubatto, Dieter Gebauer. Use of Cathodoluminescence for U-Pb Zircon Dating by Ion Microprobe: some Examples from the Western Alps[J]. Cathodoluminescence in Geosciences, 2000, 373-400
[44] Rudnick R L, Gao S. Composition of the continental crust[J]. Treatise on Geochemistry, 2003, 33: 1-64.
[45] Rudnick R L. Making continental crust[J]. Nature, 1995, 378(6557): 571-578. doi: 10.1038/378571a0
[46] Sengor A M C, Natalin B A, Burtman V S. Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Palaeozoic crustal growth in Eurasia[J]. Nature, 1993, 364( 6435): 299-307. doi: 10.1038/364299a0
[47] Shi Lu, Zheng Changqing, Yao Wengui, et al. Geochronological framework and tectonic setting of the granitic magmatism in the Chaihe-Moguqi region, central Great Xing’an Range, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 113: 443-453. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.12.013
[48] Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders A D and Norry M J(eds). Magmatism in ocean basins[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
[49] Taylor S R, McLennan S M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution[D]. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1985, 1−312.
[50] Tomurtogoo O, Windley B F, Kroner A. Zircon age and occurrence of the Adaatsag ophiolite and Muron shear zone, central Mongolia: constraints on the evolution of the Mongol-Okhotsk ocean, suture and orogen[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2005, 162(1): 125-134. doi: 10.1144/0016-764903-146
[51] Valley J W, Lackey J S, Cavosie A J. Billion Years of Crustal Maturation: Oxygen Isotope Ratios of Magmatie Zircon[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2005, 150(6): 561-580. doi: 10.1007/s00410-005-0025-8
[52] Wang Fei, Zhou Xinhua, Zhang Lianchang, et al. Late Mesozoic volcanism in the Great Xing'an Range (NE China): Timing and implications for the dynamic setting of NE Asia[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006, 251(1): 179-198.
[53] Wu Fu Y, Sun De Y, Ge W C, et al. Geochronology of the Phanerozoic granitoids in northeastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 41: 1-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.11.014
[54] Wu Fuyuan, Yang Jinhui, Lo Chinghua. The Heilongjiang Group: A Jurassic accretionary complex in the Jiamusi Massif at the western Pacific margin of northeastern China[J]. Island Arc, 2010, 16 (1): 156-172.
[55] Xu Wenliang, Wang Feng, Pei Fuping, et al. Mesozoic tectonic regimes and regional ore-forming background in NE China: Constraints from spatial and temporal variations of Mesozoic volcanic rock associations[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013, 29(2): 339-353.
[56] Ying Jiheng, Zhou Xinhua, Zhang Lianchang, et al. Geochronological framework of Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the Great Xing’an Range, NE China, and their geodynamic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2010, 39(6): 786-793. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.04.035
[57] Zhang Jiheng, Ge Wenchun, Wu Fuyuan, et al. Large-scale Early Cretaceous volcanic events in the northern Great Xing’an Range, Northeastern China[J]. Lithos, 2008, 102(1-2): 138-157. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2007.08.011
[58] Zhou Jianbo, Wilde S A, Zhang Xingzhou. The onset of Pacific margin accretion in NE China: Evidence from the Heilongjiang highpressure metamorphic belt[J]. Tectonophysics, 2009, 478 (3): 230-246.
-



 下载:
下载: