Characteristics and Causes of Groundwater Environment Changes in the Middle Reaches of the Mainstream of the Heihe River in Recent 40 Years
-
摘要:
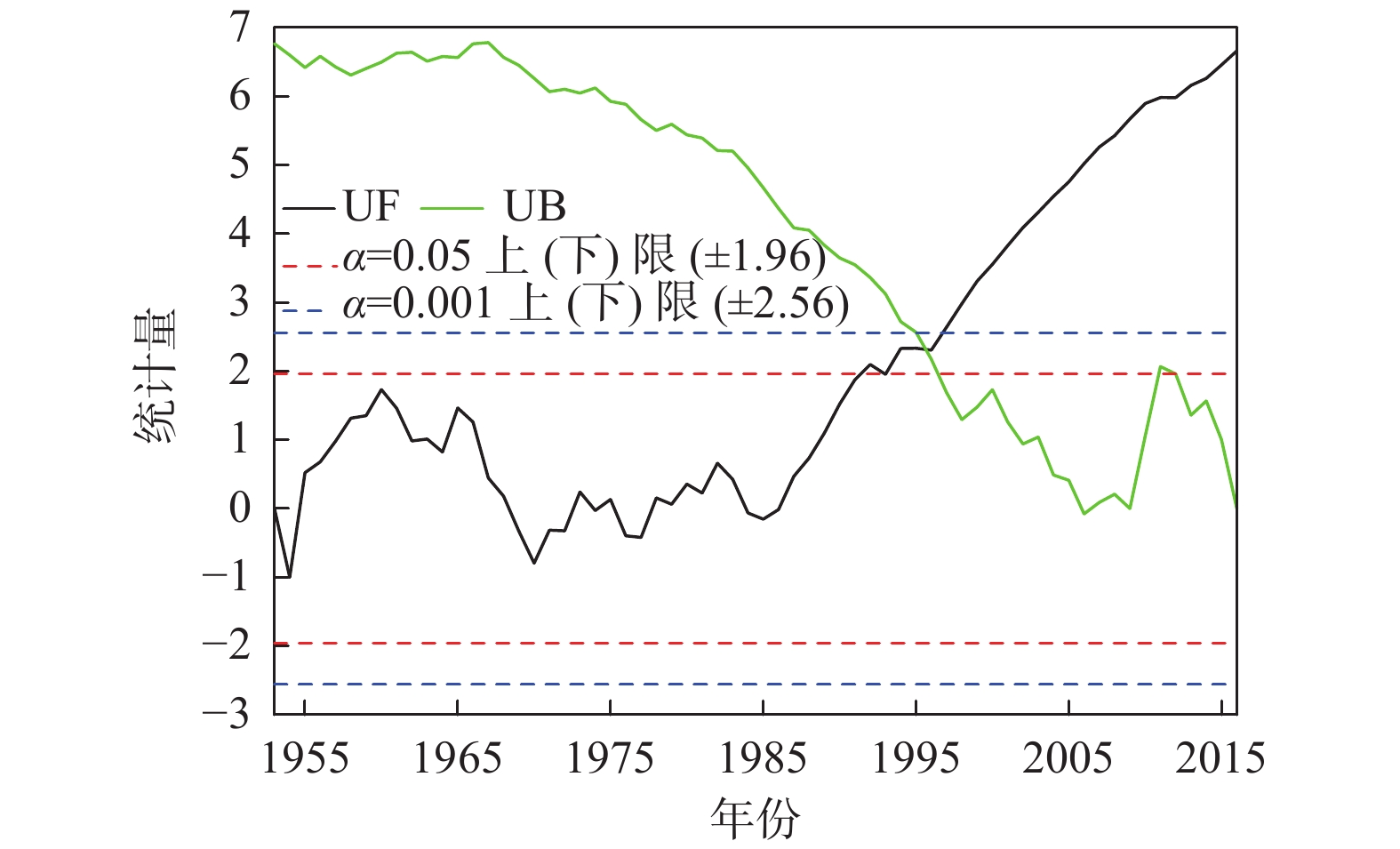
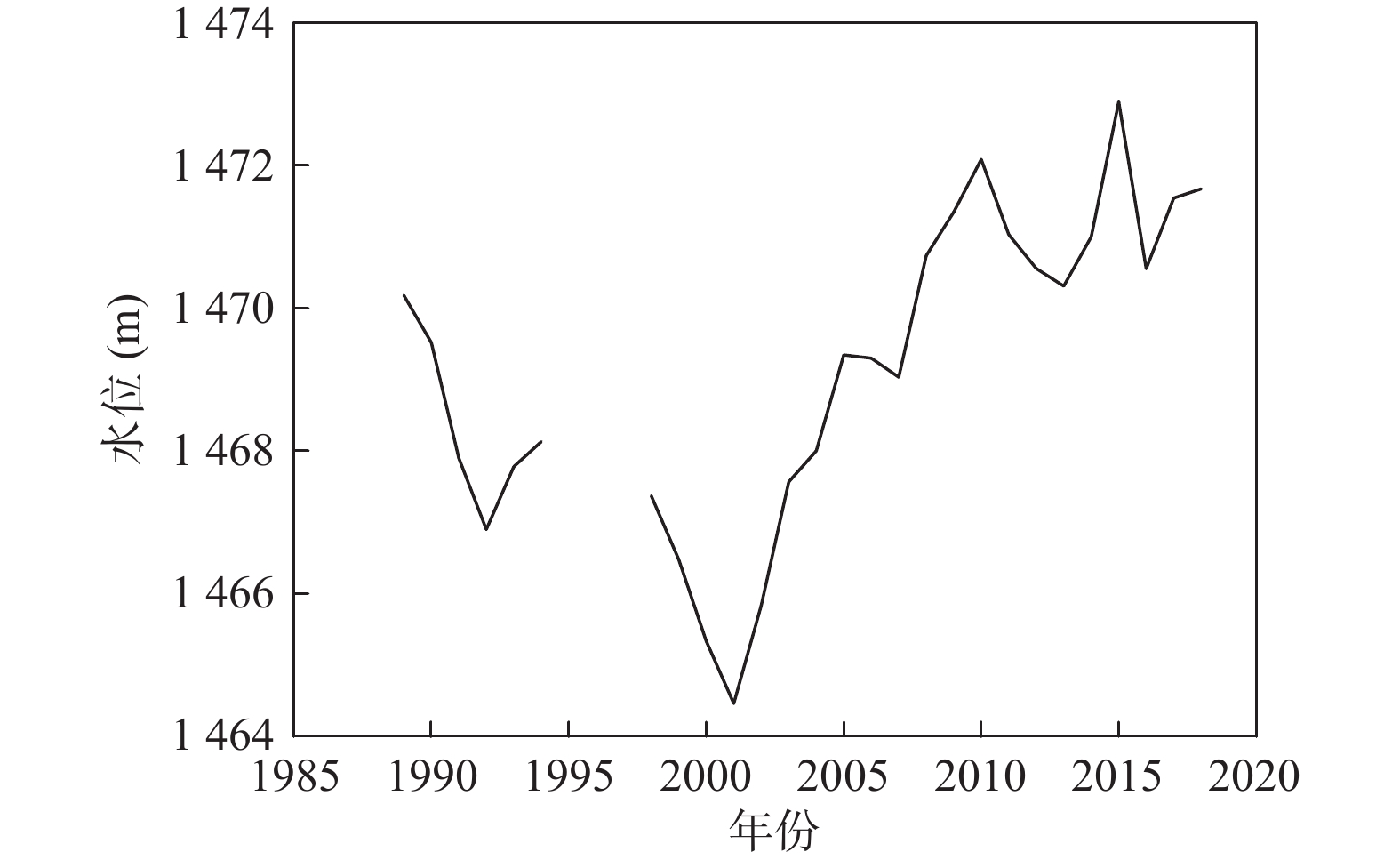
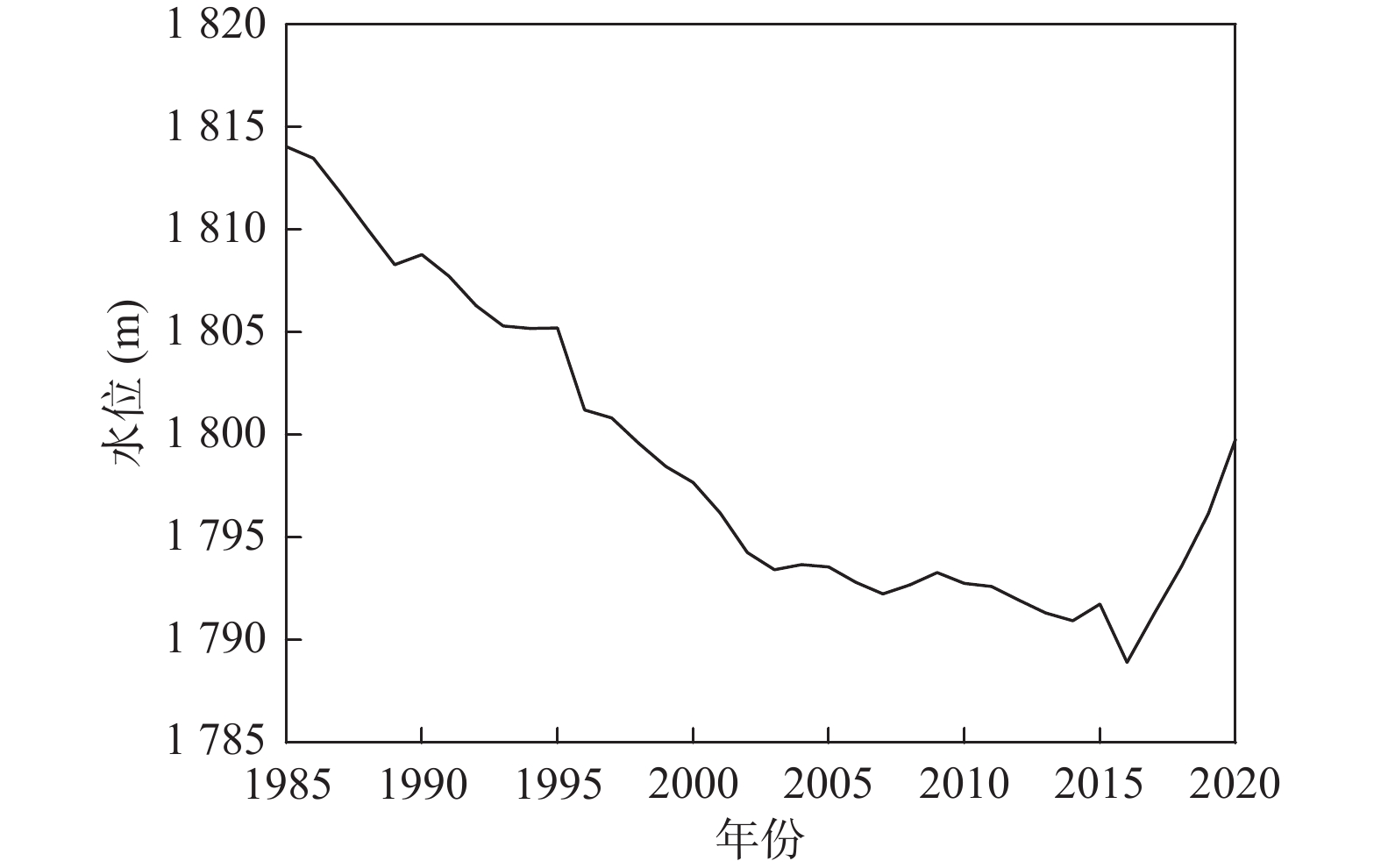
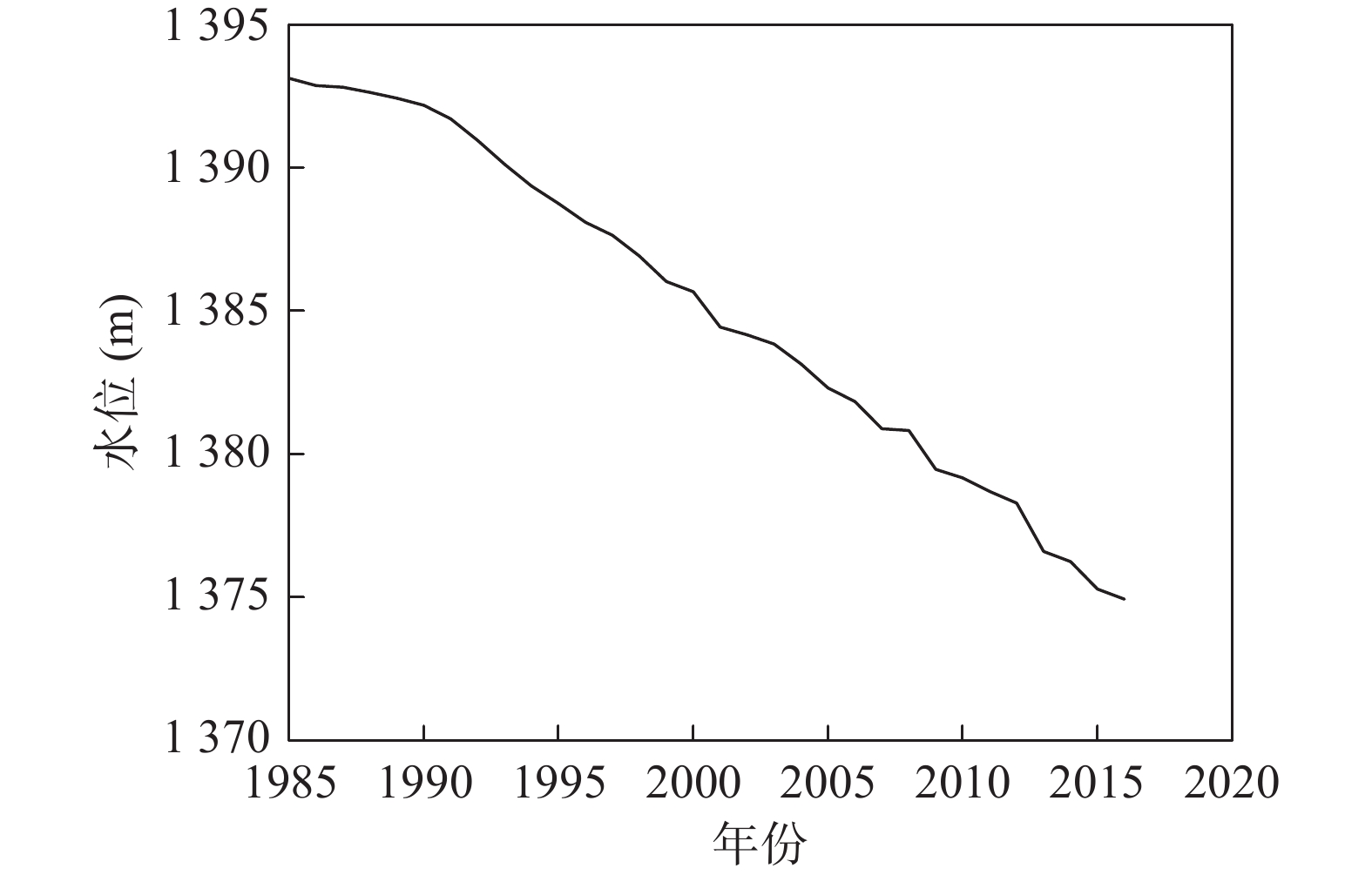
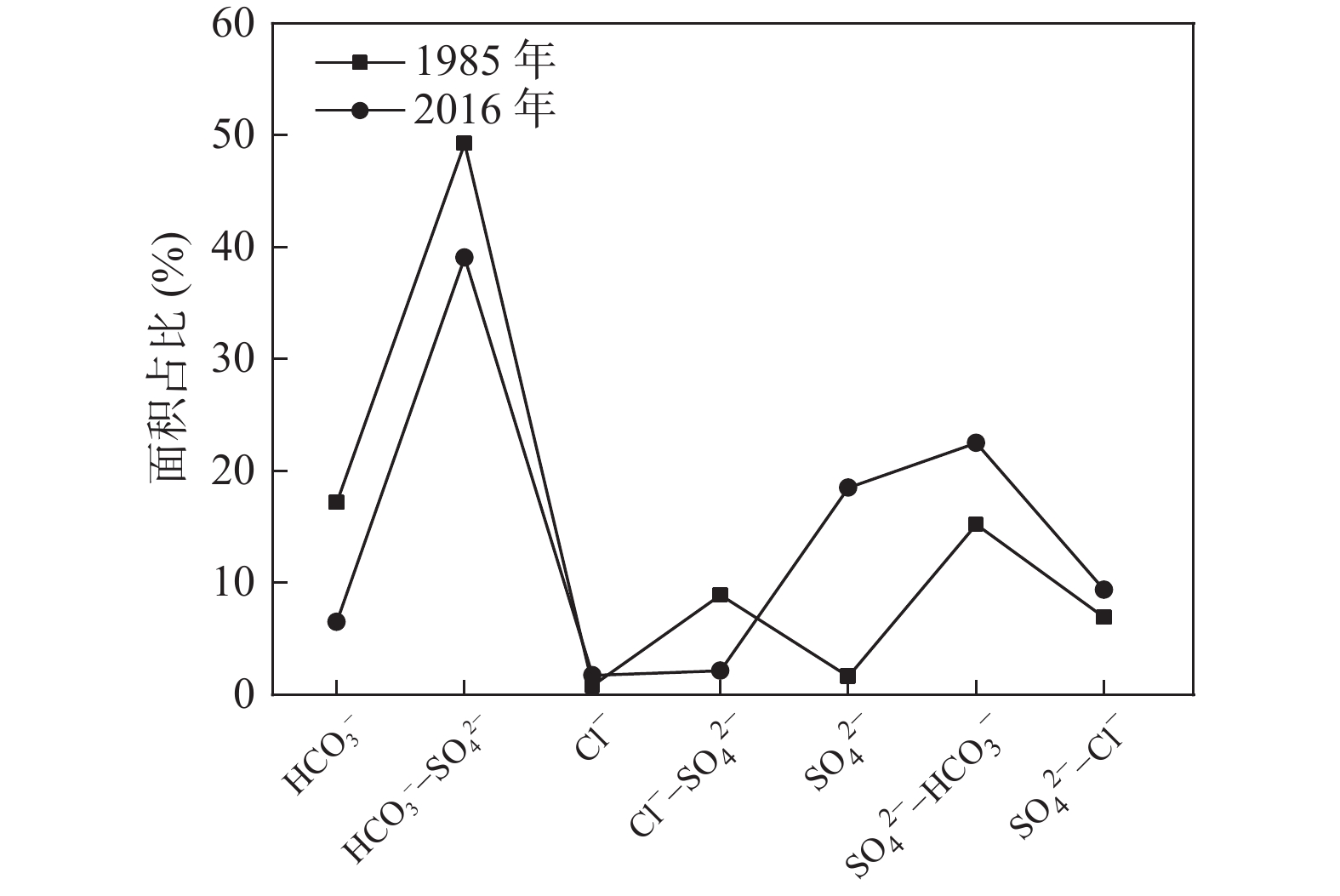
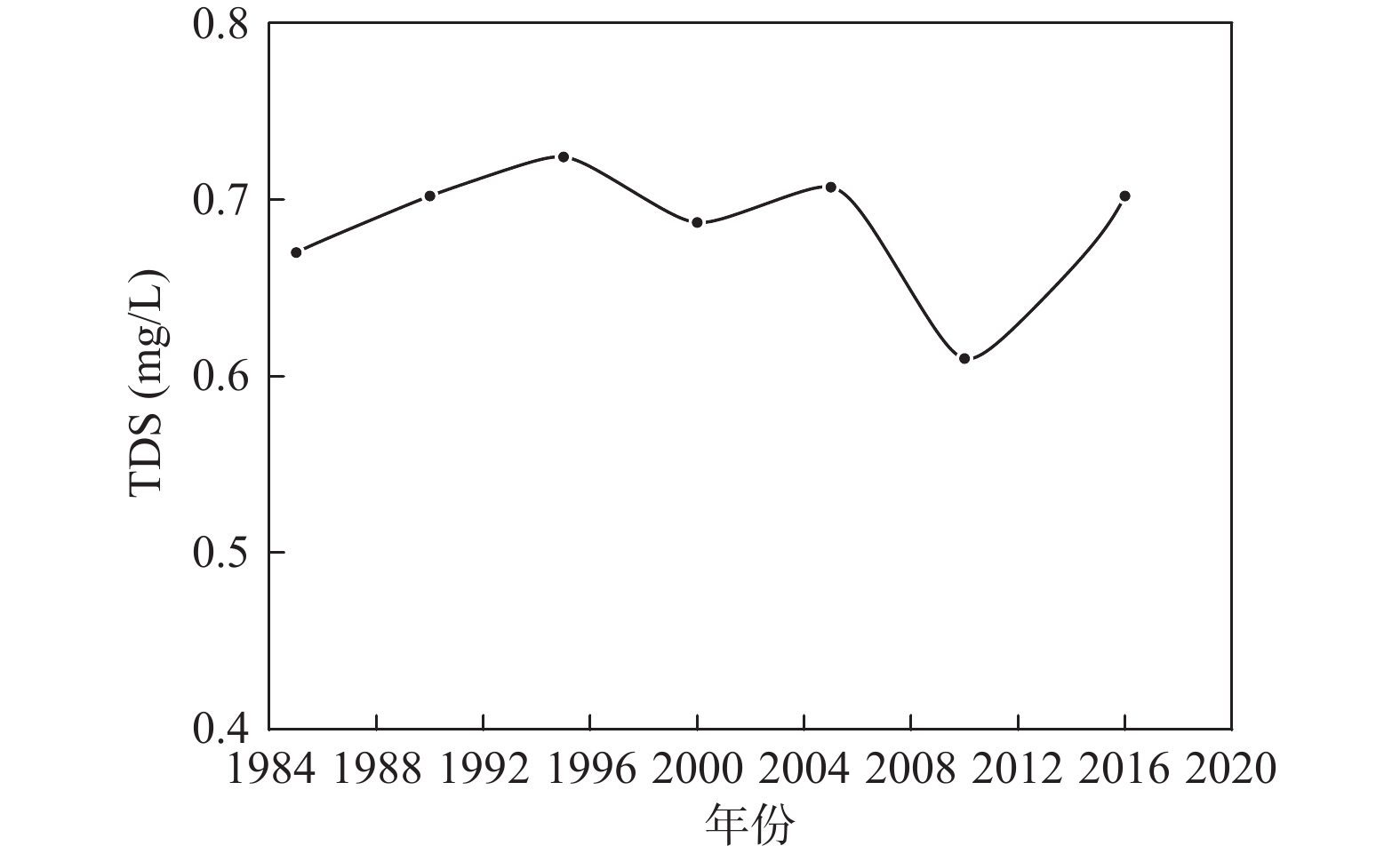
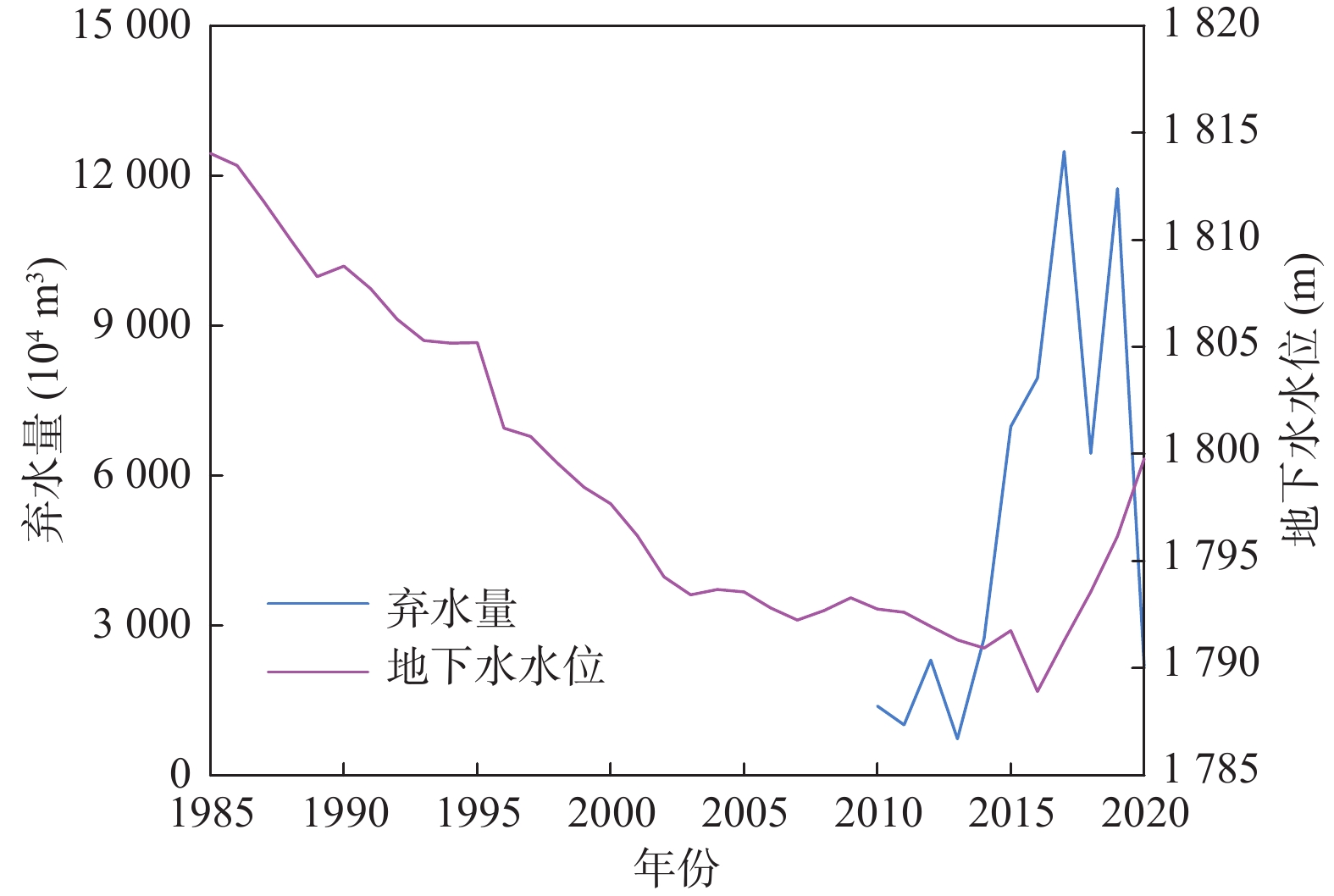
长期的监测结果表明自20世纪80年代以来黑河中游张掖地区地下水环境发生显著变化。笔者应用时间序列分析、相关性分析和遥感解译等方法分析近40年来该地区地下水水位、地下水水化学、黑河出山径流量、气象要素、绿洲面积演变规律,识别地下水环境对气候变化及人类活动的响应规律。结果表明,研究区中部区域地下水水位变化与出山径流量相关性显著,与张掖地区降水量相关性差,气候变化通过影响黑河上游径流量进而对研究区中部地下水水位产生影响,研究区降水变化对地下水水位影响微弱;研究区西部、东部地下水水位变化受人类活动影响显著,东部山前区受河流弃水量持续增大影响,近年来地下水水位显著回升,西部明花乡至骆驼城一带井灌区由于地下水大量开采,地下水水位仍处于持续下降状态;研究区南部山前带河流两侧一定范围内地下水水化学特征多年保持稳定,其余地区地下水水化学特征变化显著。
Abstract:The long–term monitoring results have shown significant changes in the groundwater environment in the middle reaches of the Heihe River in Zhangye area since the 1980s. Time series analysis, correlation analysis and remote sensing interpretation were applied to analyze the evolution of groundwater level, groundwater hydrochemistry, mountain runoff of Heihe river, meteorological elements, and oasis area in this area in recent 40 years, and to identify the response of groundwater environment to climate change and human activities. The results demonstrate that groundwater level changes in the central part of the study area are significantly correlated with the runoff from the mountain, and poorly correlated with the precipitation in Zhangye area. Climate change affects the groundwater level in the central part of the study area by affecting the runoff in the upper reaches of Heihe river. Rainfall change in the study area has a weak impact on the groundwater level. The change of groundwater level in the west and east of the study area is significantly affected by human activities. Affected by the continuous increase of surplus water, the groundwater level in the eastern pre–mountain area has risen significantly in recent years, while the groundwater level in the well irrigation area from Minghua township to Camel City in the west is still in a state of continuous decline due to the massive exploitation of groundwater. The groundwater chemical characteristics in a certain range on both sides of the river in the southern pre–mountain area have remained stable for many years, while significant changes have been observed in other areas.
-
Key words:
- climate change /
- human activities /
- groundwater environment /
- groundwater level
-

-
[1] 党学亚, 张俊, 常亮, 等. 西北地区水文地质调查与水资源安全[J]. 西北地质, 2022, 55(3): 81−95.
DANG Xueya, ZHANG Jun, CHANG Liang, et al. Hydrogeological Survey and Water Resources Security in Northwest China[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2022, 55(3): 81-95.
[2] 李文明, 李健强, 徐永, 等. 西北生态地质调查研究进展与展望[J]. 西北地质, 2022, 55(3): 108−119.
LI Wenming, LI Jianqiang, XU Yong, et al. Progress and Prospects of Ecological Geological Survey in Northwest China[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2022, 55(3): 108−119.
[3] 李文鹏, 康卫东, 刘振英, 等. 西北典型内流盆地水资源调控与优化利用模式——以黑河流域为例[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2010, 1−362
LI Wenpeng, KANG Weidong, LIU Zhenying, et al. Water resources regulation and optimal allocation in arid inland basins of Northwest China: the case of the Heihe River Basin[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2010, 1−362.
[4] 李卓仑, 王乃昂, 李育, 等. 近50年来黑河出山径流对气候变化的响应[J]. 水土保持通报, 2012, 32(02): 7-11+16. DOI: 10.13961/j. cnki. stbctb. 2012.02. 006. DOI:10.13961/j.cnki.stbctb.2012.02.006.
LI Zhuolun, WANG Naiang, Li Yu, et al, Variations of Runoff in Responding to Climate Change in Mountainous Areas of Heihe River During Last 50 Years[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2012, 32(02): 7-11+16. doi: 10.13961/j.cnki.stbctb.2012.02.006
[5] 廉耀康, 柳小龙, 周润田, 等. 黑河出山口径流与源区降水特征及匹配度分析[J]. 人民黄河, 2019, 41(07): 14-17 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2019.07.004
LIAN Yaokang, LIU Xiaolong, ZHOU Runtian, et al. Matching Degree and Characteristics of Runoff from Mountainous Watershed and Precipitation in the Source Areas of Heihe River[J]. YELLOW RIVER, 2019, 41(07): 14-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2019.07.004
[6] 连英立. 张掖盆地地下水对气候变化响应特征与机制研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2011, 1−165
LIAN Yingli. Variation characteristics and mechanism of groundwater response to climate Change in Zhangye Basin[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2011, 1−165.
[7] 刘得俊. 格尔木流域地下水水位对气候变化和人类活动的响应[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 2016, 14(A1): 23-25+49
LIU Dejun. Response of Groundwater to Climate Change and Human Activities in Golmud Basin[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology. 2016, 16(1): 23-25+49.
[8] 米丽娜, 肖洪浪, 田军仓, 等. 张掖盆地地下水资源时空分异特征及影响因素[J]. 水文, 2016, 36(06): 81-88
MI lina, XIAO Honglang, TIAN Juncang, et al. Temporal spatial variations of the groundwater level and its mechanism analysis for middle part of the Zhangye basin [J]. JOURNAL OF CHINA HYDROLOGY, 2016, 36(06): 81-88.
[9] 牛最荣. 气候变化对祁连山区水文循环的影响研究[M]. 兰州: 甘肃人民出版社, 2013.
NIU Zuirong. Effects of Climate Change on Hydrological Cycle in Qilian Mountains[M]. Lanzhou: Gansu People's Publishing House, 2013.
[10] 钱云平, Andrew L H, 张春岚, 等. 应用222Rn研究黑河流域地表水与地下水转换关系[J]. 人民黄河, 2005(12): 58-59+61 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2005.12.026
QIAN Yunping, Andrew L H, ZHANG Chunlan, et al. Applying 222Rn to Study the Conversion Relationship Between Surface Water and Groundwater in Heihe River Basin[J], YELLOW RIVER, 2005(12): 58-59+61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2005.12.026
[11] 王浩, 段磊, 王文科. 秦岭北麓地下水位动态特征与影响因素[J]. 西北地质, 2020, 53(2): 280−288.
WANG Hao, DUAN Lei, WANG Wenke. Dynamic Features of Groundwater Level in Northern Qinling and Its Influence Factors[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2020, 53(2): 280−288.
[12] 闫云霞, 王随继, 颜明, 等. 张掖盆地中部地下水位的时空变化及机理探讨[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2014, 28(11): 90-97. DOI: 10.13448/j. cnki. jalre. 2014.11. 016.
YAN Yunxia, WANG Suiji, YAN Ming, et al. Temporal spatial variations of the groundwater level and its mechanism analysis for middle part of the Zhangye basin [J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2014, 28(11): 90-97. DOI:10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2014.11.016.
[13] 张楠. 气候变化和人类活动影响下伊舒盆地地下水环境演化研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2017
ZHANG Nan, Research on Groundwater Environmental Evolution of Yishu Basin under the Impact of Climate Change and Human Activities[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2017, 1−213.
[14] 张震域, 赵沛, 畅祥生, 等. 额济纳绿洲1992-2015年地下水埋深变化分析[J]. 人民黄河, 2019, 41(07): 33-37
ZHANG Zhenyue, ZHAO Pei, CHANG Xiangsheng, et al, Analysis of Groundwater Depth Change in Ejina Oasis from 1992 to 2015[J]. YELLOW RIVER, 2019, 41(7): 33-37.
[15] Elias G. Bekele, H. Vernon Knapp. Watershed Modeling to Assessing Impacts of Potential Climate Change on Water Supply Availability[J]. Water Resources Management, 2010, 24(13): 3299-3320. doi: 10.1007/s11269-010-9607-y
[16] Green T R , Taniguchi M , Kooi H, et al. Beneath the surface of global change: Impacts of climate change on groundwater[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2011, 405(3): 532-560.
[17] Wang Jiawei, Huang Jinting, FangTuo, et al. Relationship of underground water level and climate in Northwest China's inland basins under the global climate change: Taking the Golmud River Catchment as an example[J]. China Geology, 2021, 4(03): 402-409.
-




 下载:
下载: