Theory and Method for Urban–Rural Integration, Evaluation and Cooperative Detection of Ground and Underground Space: Example from the Urban Geological Survey of Guanzhong Plain
-
摘要:
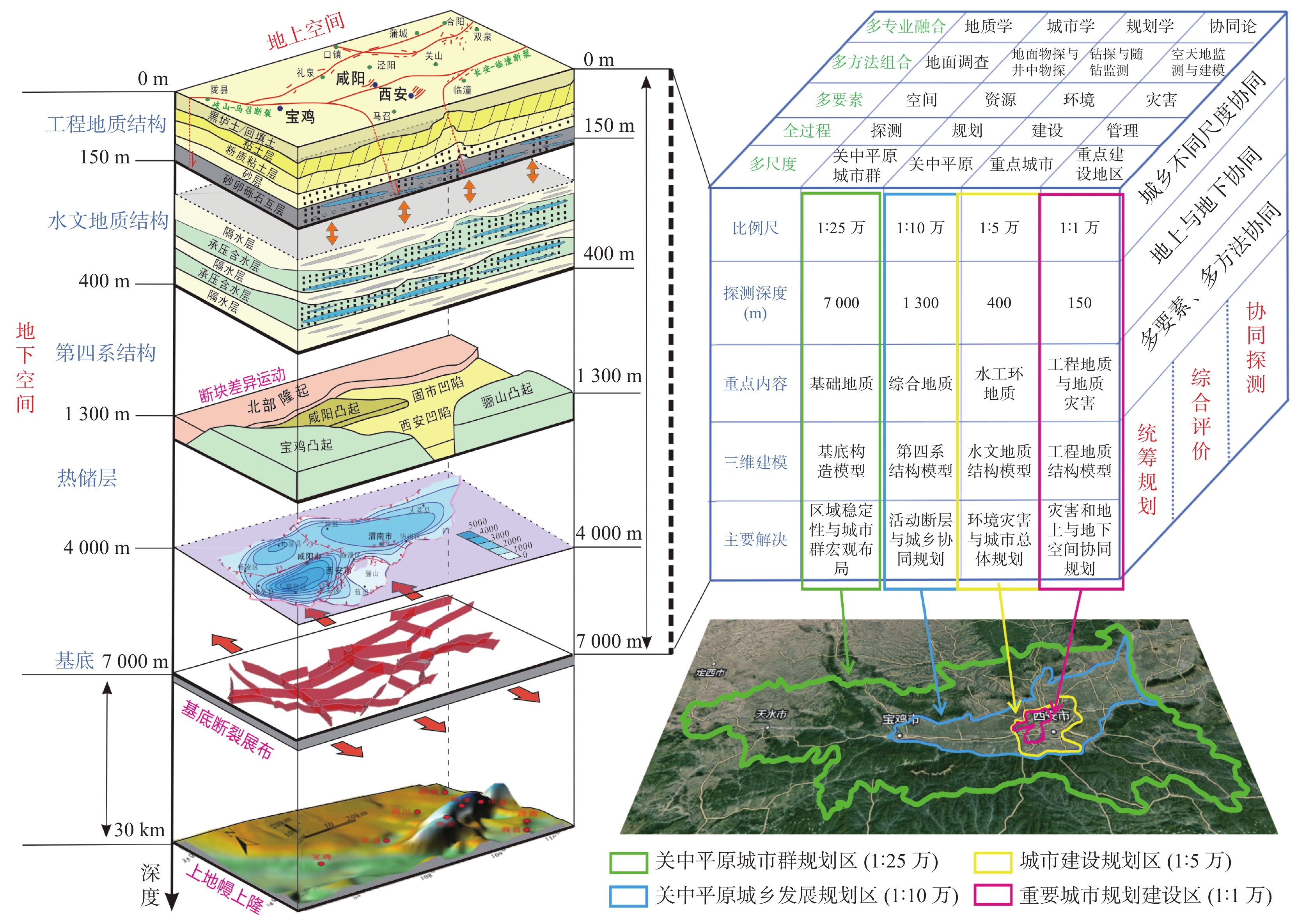
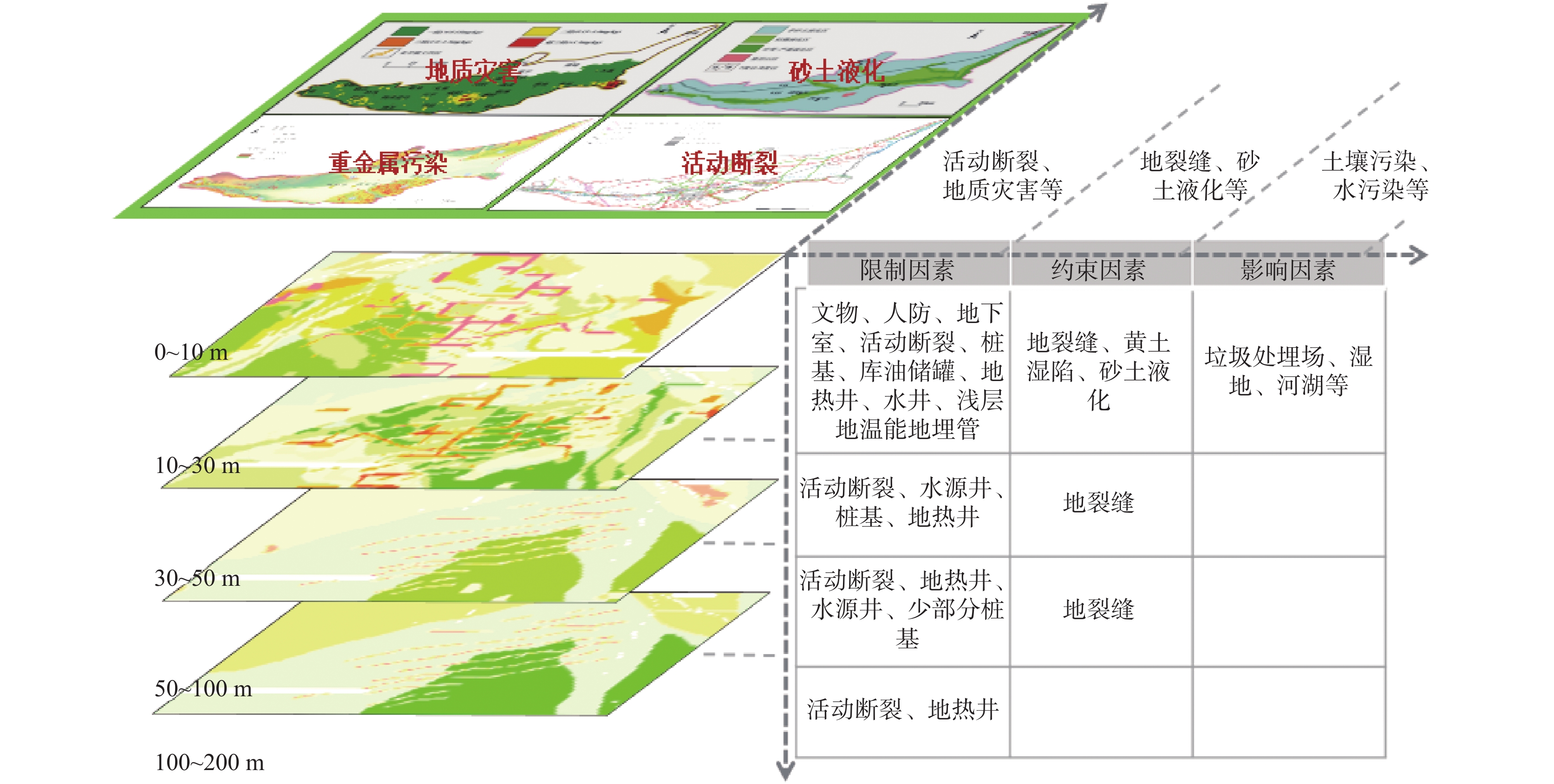
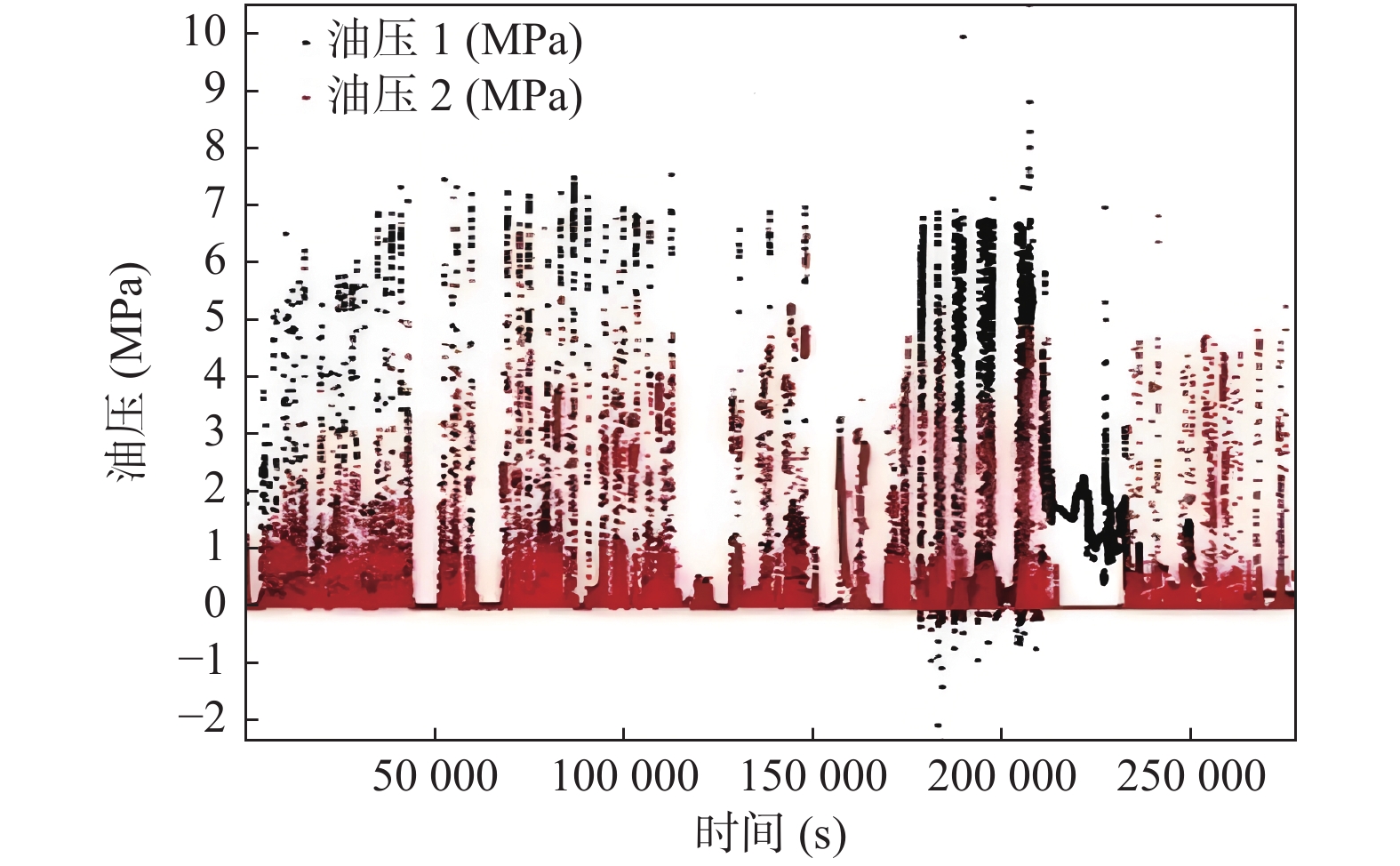
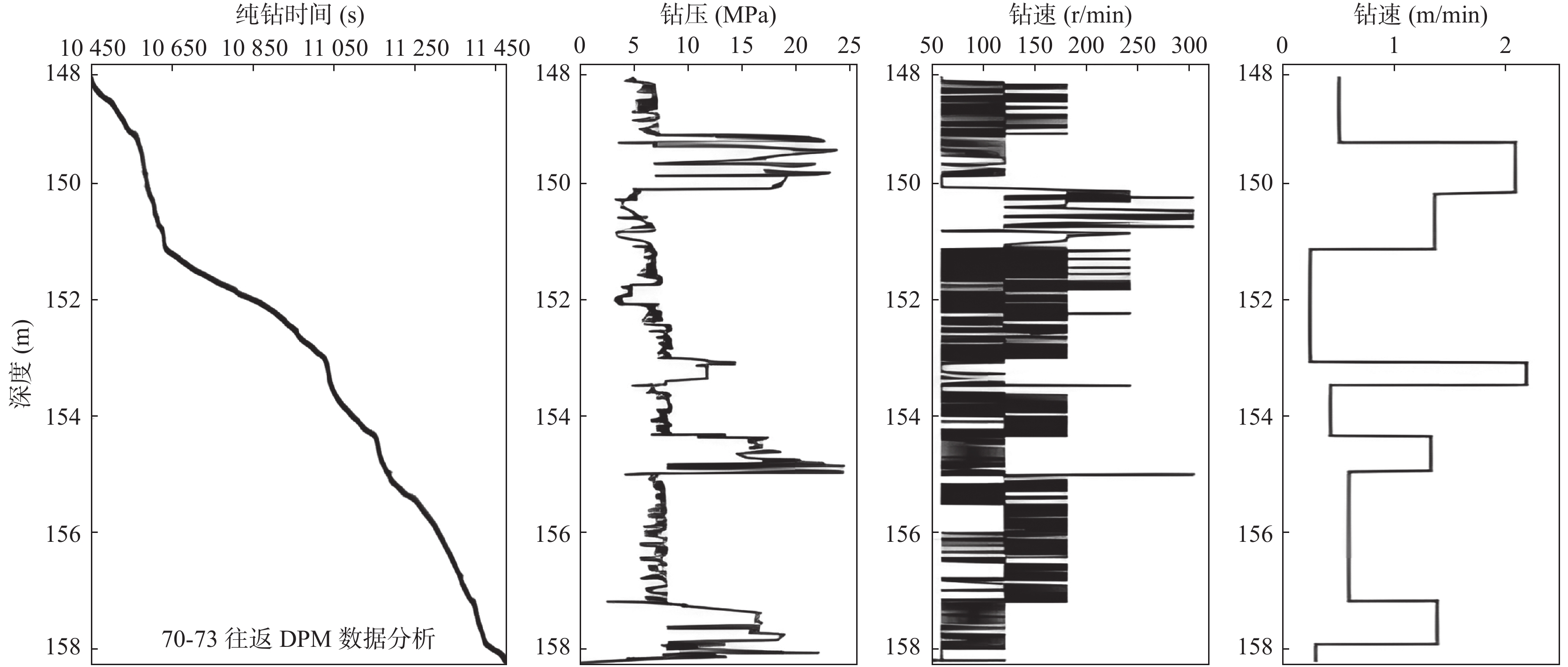
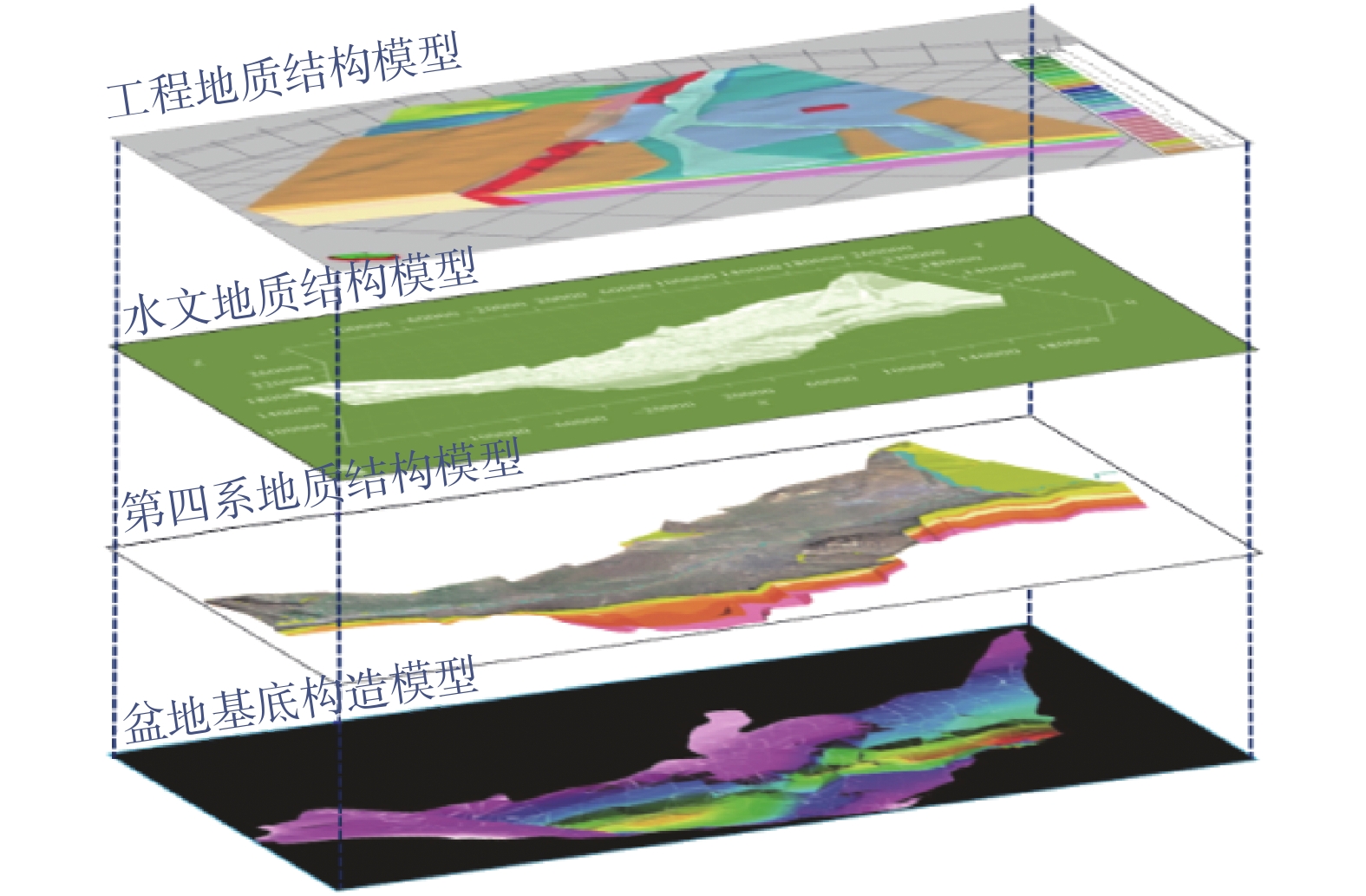
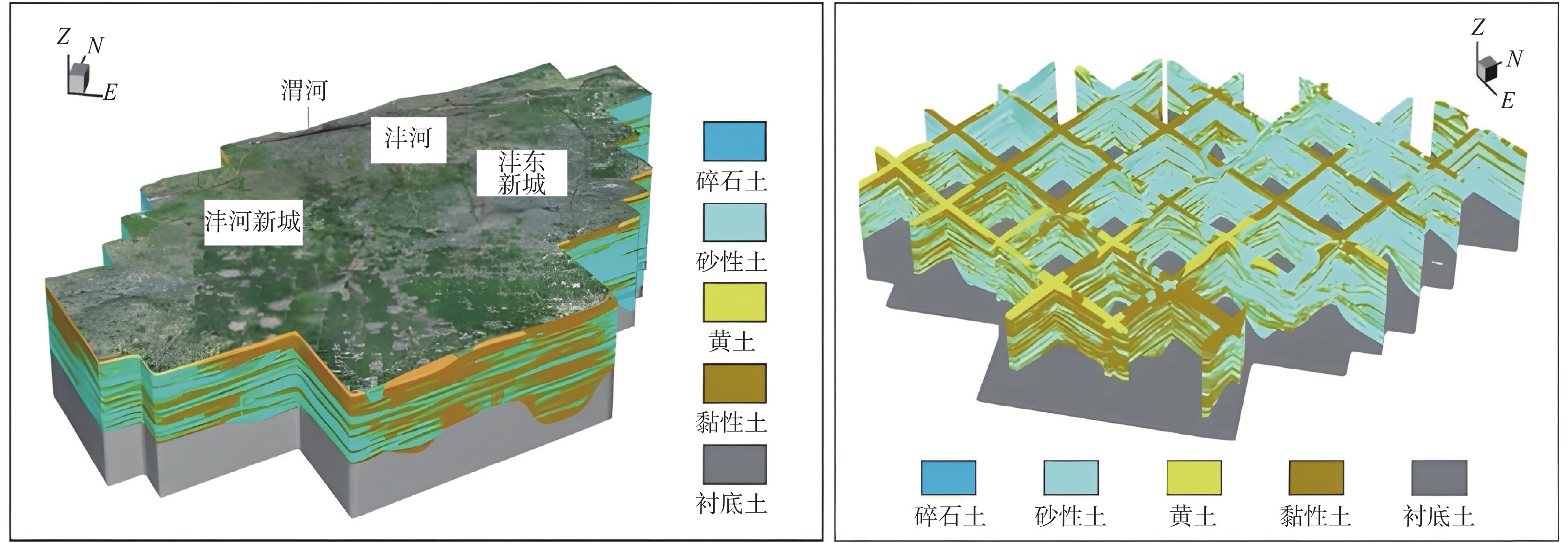
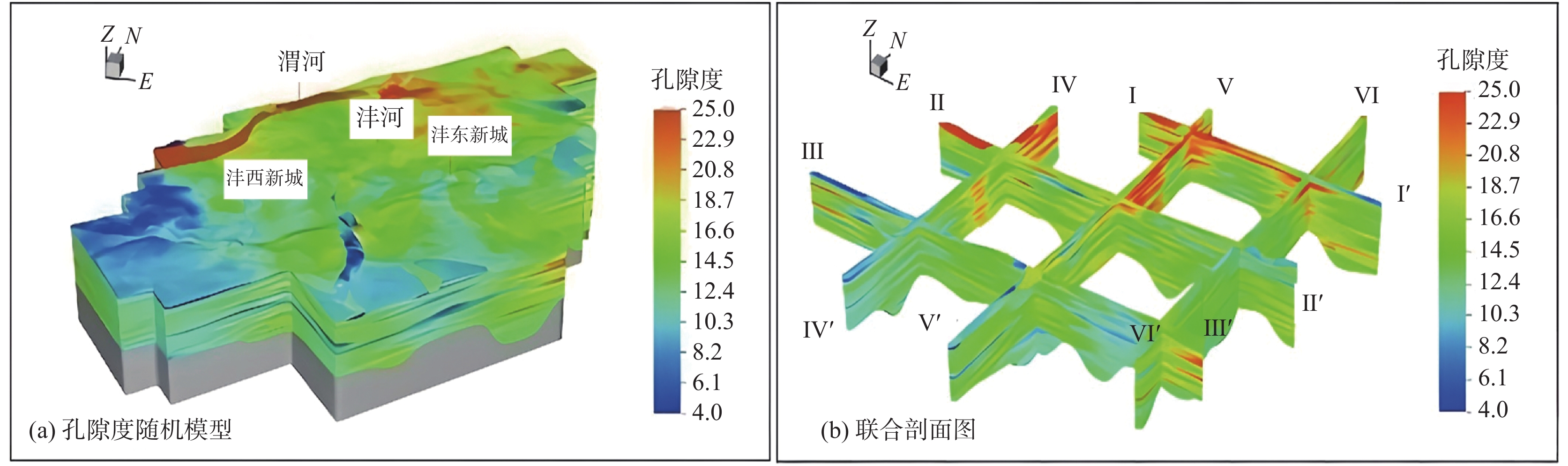
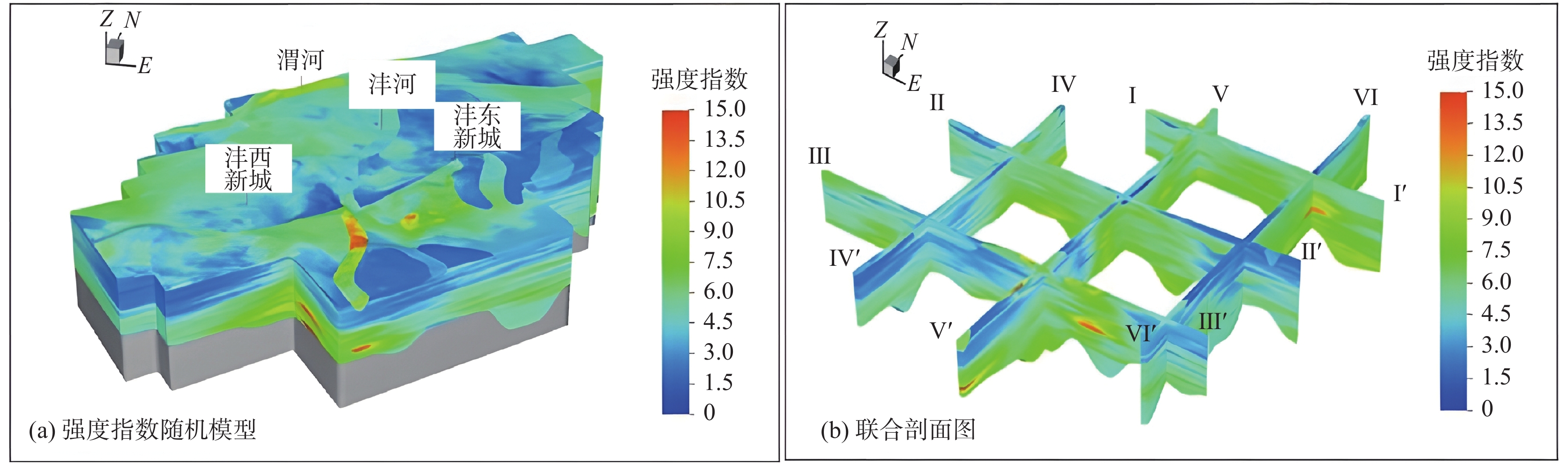
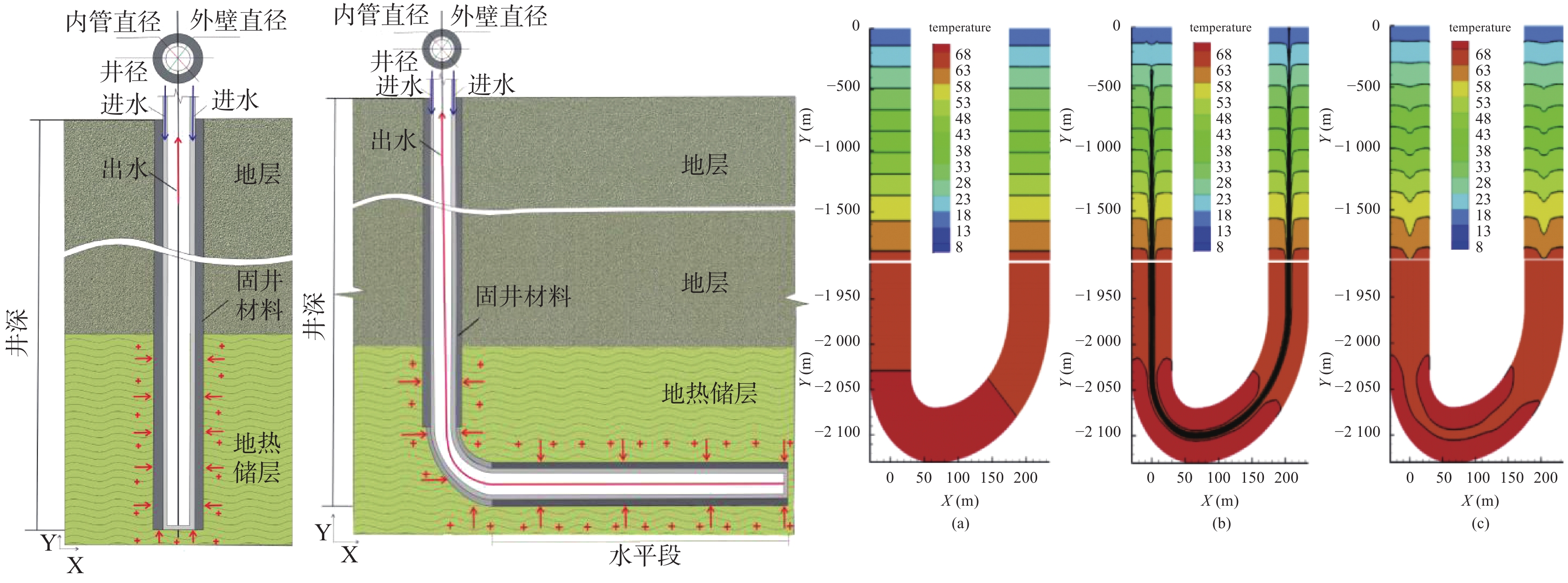
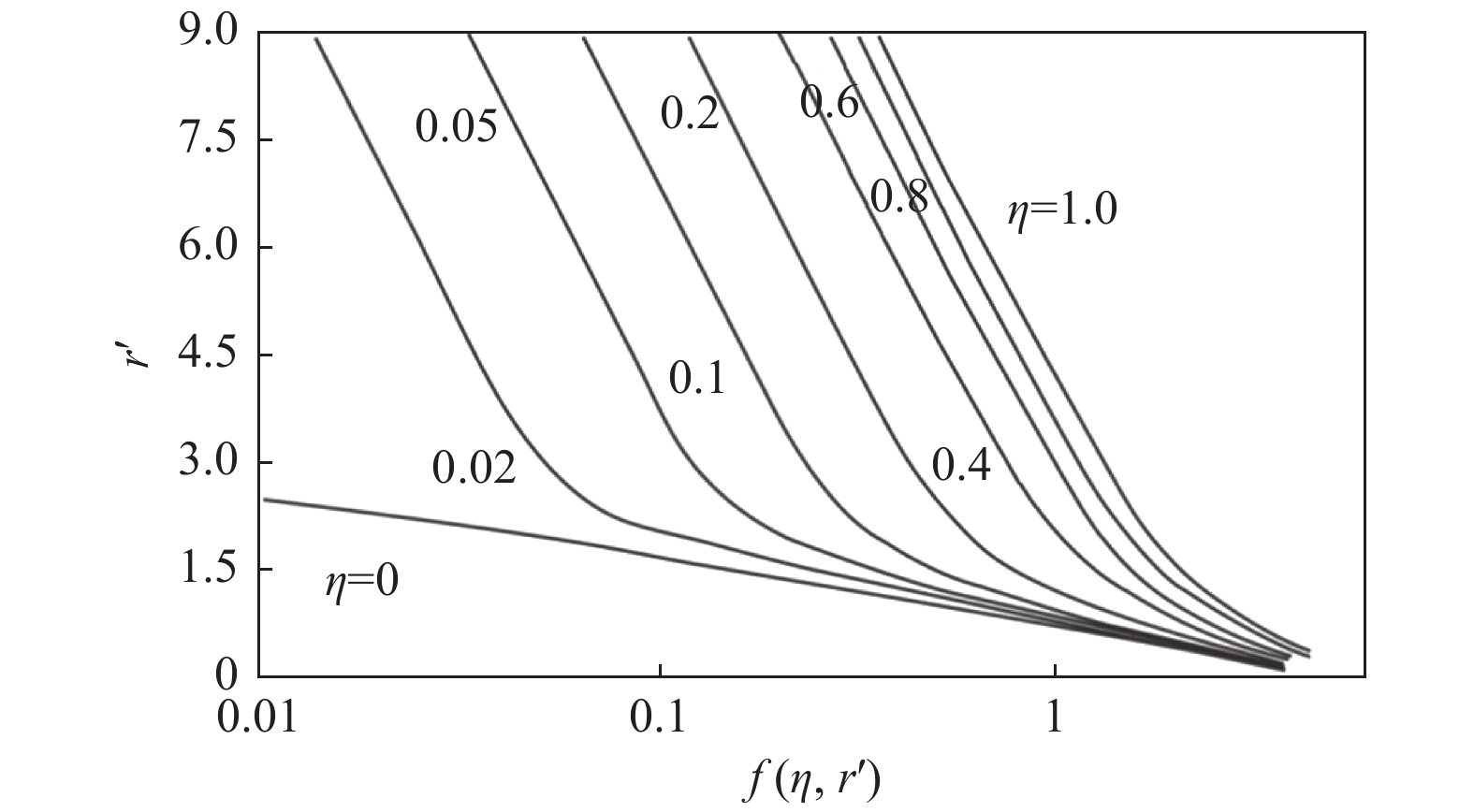
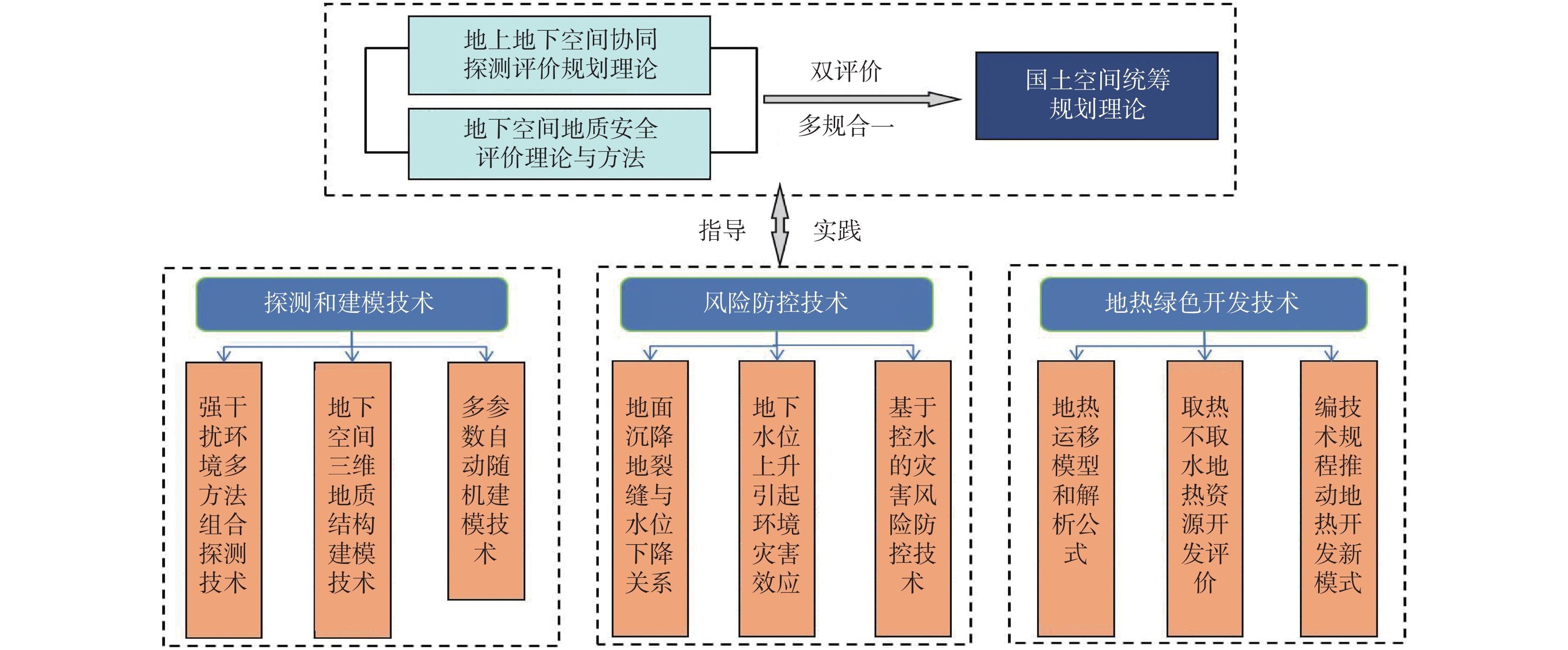
城乡融合、地上与地下空间协同探测、评价、规划是节约集约利用空间与自然资源,增强城市韧性,促进人与自然和谐共生现代化建设的重要途径。针对中国新型城镇化与乡村振兴协同发展面临着“多规合一”的国土空间规划、地上与地下空间协调集约利用等新的重大科技问题,以关中平原城市群为研究对象,基于地球系统科学和地球关键带理论,汲取系统论、协同论、信息论等理论,提出了城乡融合、地上与地下空间协同探测、综合评价、统筹规划的新时期城市地质理论,以及城市强干扰环境下地下空间精细化探测和建模关键技术、基于地下水位控制的地上与地下空间风险防控技术、“取热不取水”的地下空间地热能绿色开发新技术,并在多个城市得到成功应用。
Abstract:The collaborative detection and evaluation planning of ground and underground space is an important way to enhance the comprehensive carrying capacity of the city and promote the high–quality development of the city. In view of the new major scientific and technological problems such as "multi–plan integration" territorial spatial planning, coordinated and intensive utilization of ground and underground space aimed at the coordinated development of new urbanization and rural revitalization in China, taking Guanzhong plain urban agglomeration as the research area, based on the theories of the earth system science, the earth key belt, system, synergy and information, this paper puts forward the urban geological theory in the new period of urban–rural integration, coordinated detection, comprehensive evaluation and overall planning of ground and underground space; breaks through the key technologies of fine detection and modeling of underground space under the strong urban interference environment; proposes the risk prevention and control technology of ground and underground space based on groundwater; reveal the heat conduction law of geothermal fluid–exchanger in underground space, and raise the new green development technology of geothermal energy in underground space of "taking heat but not taking water". Which will provide the technique support for the urban planning, construction and operation management, land space planning, natural resource management, etc. And the theroies and the technologies have been successfully applied in many cities.
-
Key words:
- urban geology /
- underground space /
- new urbanization /
- rural revitalization /
- Guanzhong plain
-

-
[1] 董英,刘洁,王化齐. 西北地区城市地质调查与城市规划建设[J]. 西北地质,2022,55(03):200–209.
DONG Ying, LIU Jie, WANG Huaqi. Urban Geological Survey and Urban Planning and Construction in Northwest China[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2022, 55(03): 200-209.
[2] 董英,张茂省,李宁,等. 城市地下空间开发利用的地质安全评价内容与方法[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(05):161–168.
DONG Ying, ZHANG Maosheng, LI Ning, et al. . Methods and contents of geological safety evaluation for urbanunderground space development and utilization[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(05): 161-168.
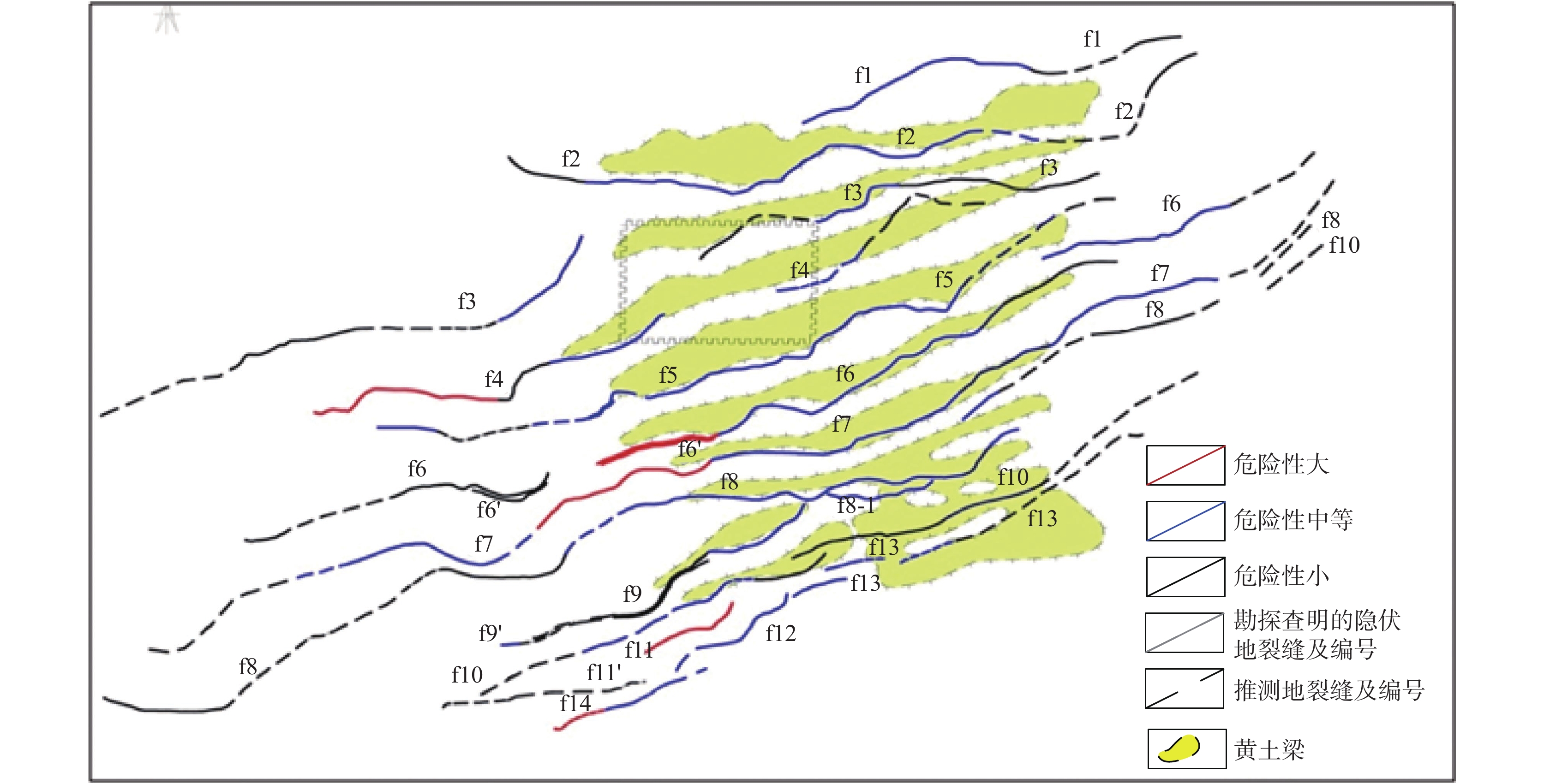
[3] 黄强兵,彭建兵,范文,等. 西安地铁二号线沿线地裂缝未来位错量估算及工程分级[J]. 工程地质学报,2007,15(04):469–474.
HUANG Qiangbing, PENG Jianbing, FANwen, et al. Estimation of the maximum displacement of ground fissuresalong Xi'an metro line 2anditsengineeringclassification. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2007(04): 469-474.
[4] 马琰,连皓,雷振东,等. 西咸城乡融合发展试验区融合发展路径与策略[J]. 规划师,2021,37(09):61–67.
Ma Yan, Lian Hao, Lei Zhendong, et al. . Development Path and Strategy of Xi’an-Xianyang Urban-rural Integration Pilot Area[J]. Planners, 2021, 37(09): 61-67.
[5] 彭建兵, 苏生瑞, 张骏. 渭河盆地活动断裂与地质灾害[M]. 西安: 西北大学出版社, 1992
[6] 彭建兵,范文,李喜安,等. 汾渭盆地地裂缝成因研究中的若干关键问题[J]. 工程地质学报,2007,(04):433–440.
PENG Jianbing, FAN Wen, LI Xi'an, et al. Some Key Questionsin the Formation of Ground Fissuresin the Fen-Wei Basin[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2007(04): 433-440.
[7] 王亚辉,张茂省,师云超,等. 基于综合物探的城市地下空间探测与建模[J]. 西北地质,2019,52(02):83–94.
WANG Yahui, ZHANG Maosheng, SHI Yunchao, et al. . Precise Detection and Modeling of Urban Underground Space Based onIntegrated Geophysical Exploration[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2019, 52(02): 83-94.
[8] 张家明. 西安地裂缝研究[M]. 西安: 西北大学出版社, 1990, 68−88
[9] 张茂省, 董英, 刘江, 等. 关中平原城市地质[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2021
[10] 张茂省,董英,刘洁. 论新型城镇化中的城市地质工作[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2014,50(05):581–587.
ZHANG Maosheng, DONG Ying, LIU Jie. Discussion of urban geological work in new urbanlization[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences), 2014, 50(05): 581-587.
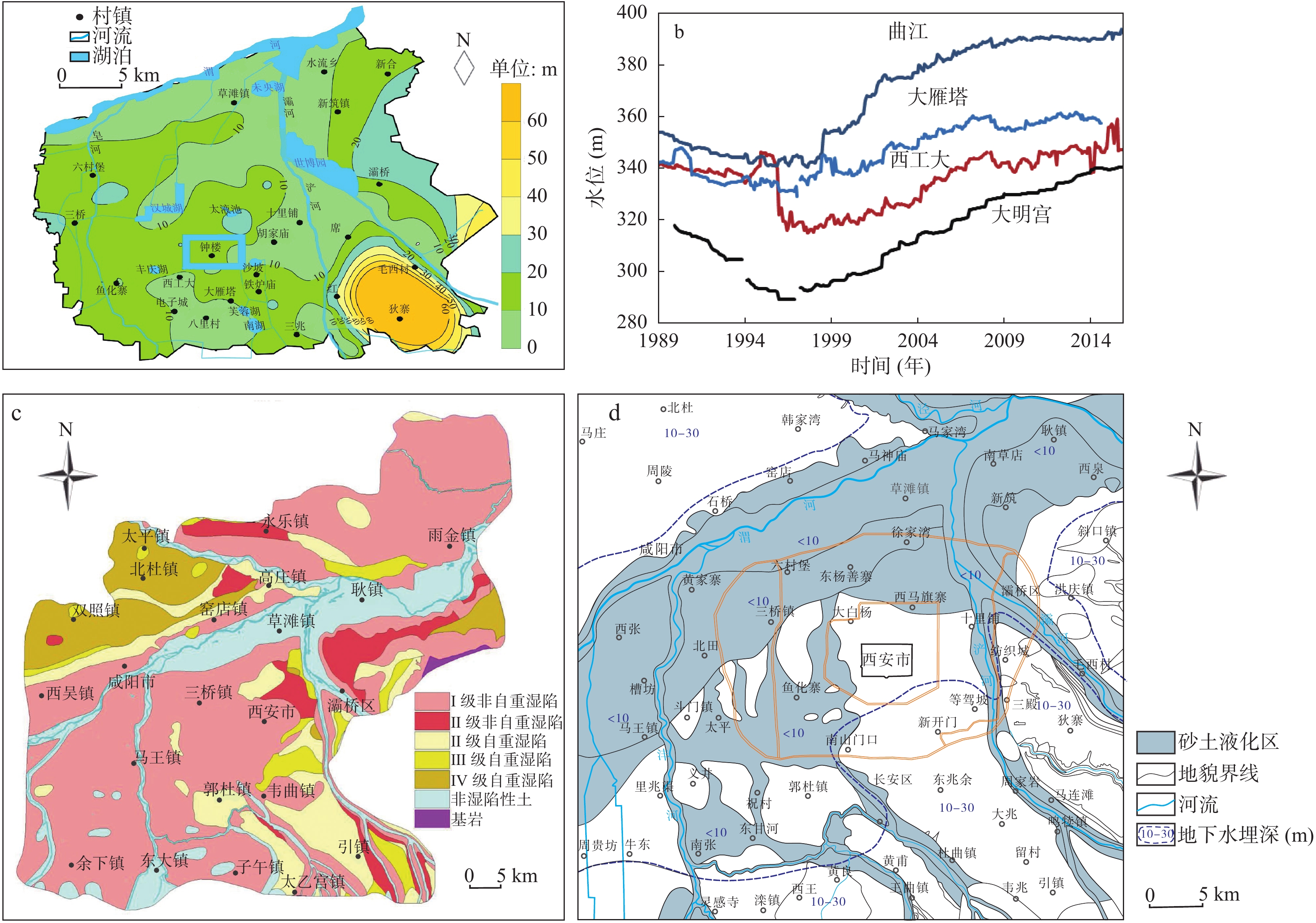
[11] 张茂省,董英,张新社,等. 地面沉降预测及其风险防控对策—以大西安西咸新区为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2013,24(04):115–118+126.
ZHANG Maosheng, DONG Ying, ZHANG Xinshe, et al. Prediction of land subsidence and Its mitigation methods-a case studyin the new urban district of Xi'an-Xianyang. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2013, 24(04): 115-118+126.
[12] 张茂省,王化齐,王尧,等. 中国城市地质调查进展与展望[J]. 西北地质,2018,51(04):1–9.
ZHANG Maosheng, WANG Huaqi, DONG Ying, et al. . Progress and Prospect of Urban Geological Survey in China[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2018, 51(04): 1-9.
-



 下载:
下载: