Soil Nutrient Characteristics and Main Controlling Factors in the Oasis Zone of the Northeastern Margin of Tarim Basin
-
摘要:
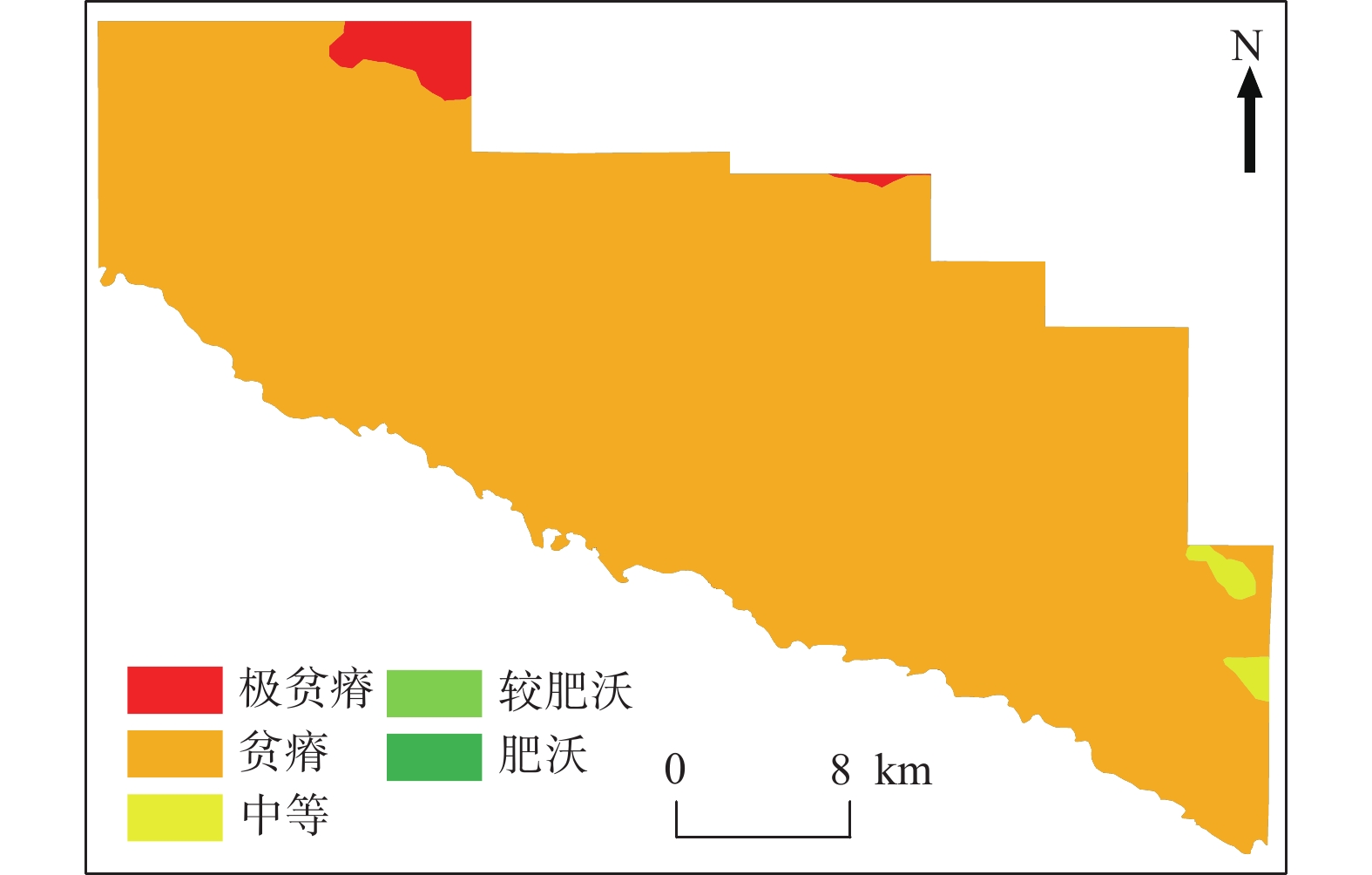
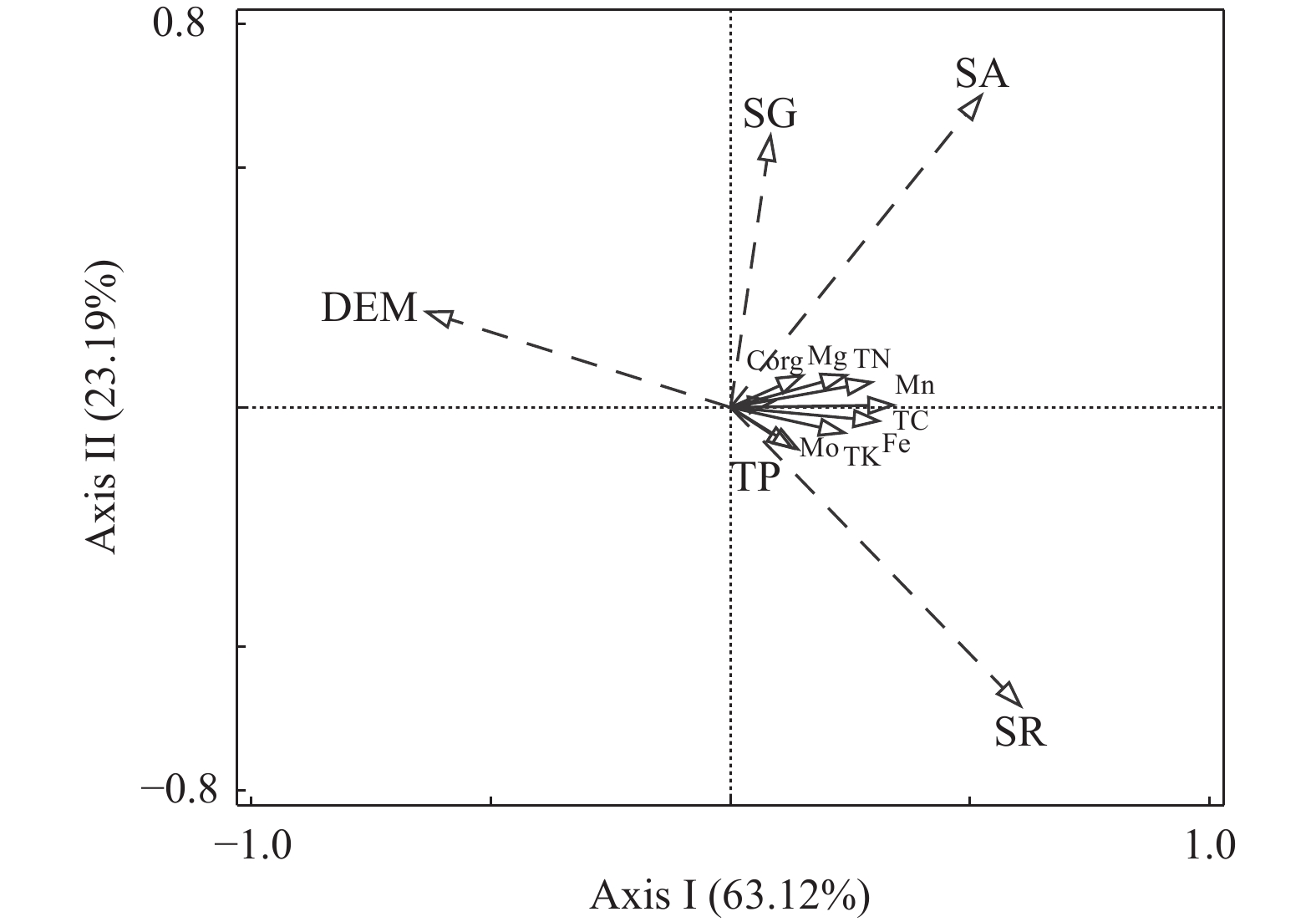
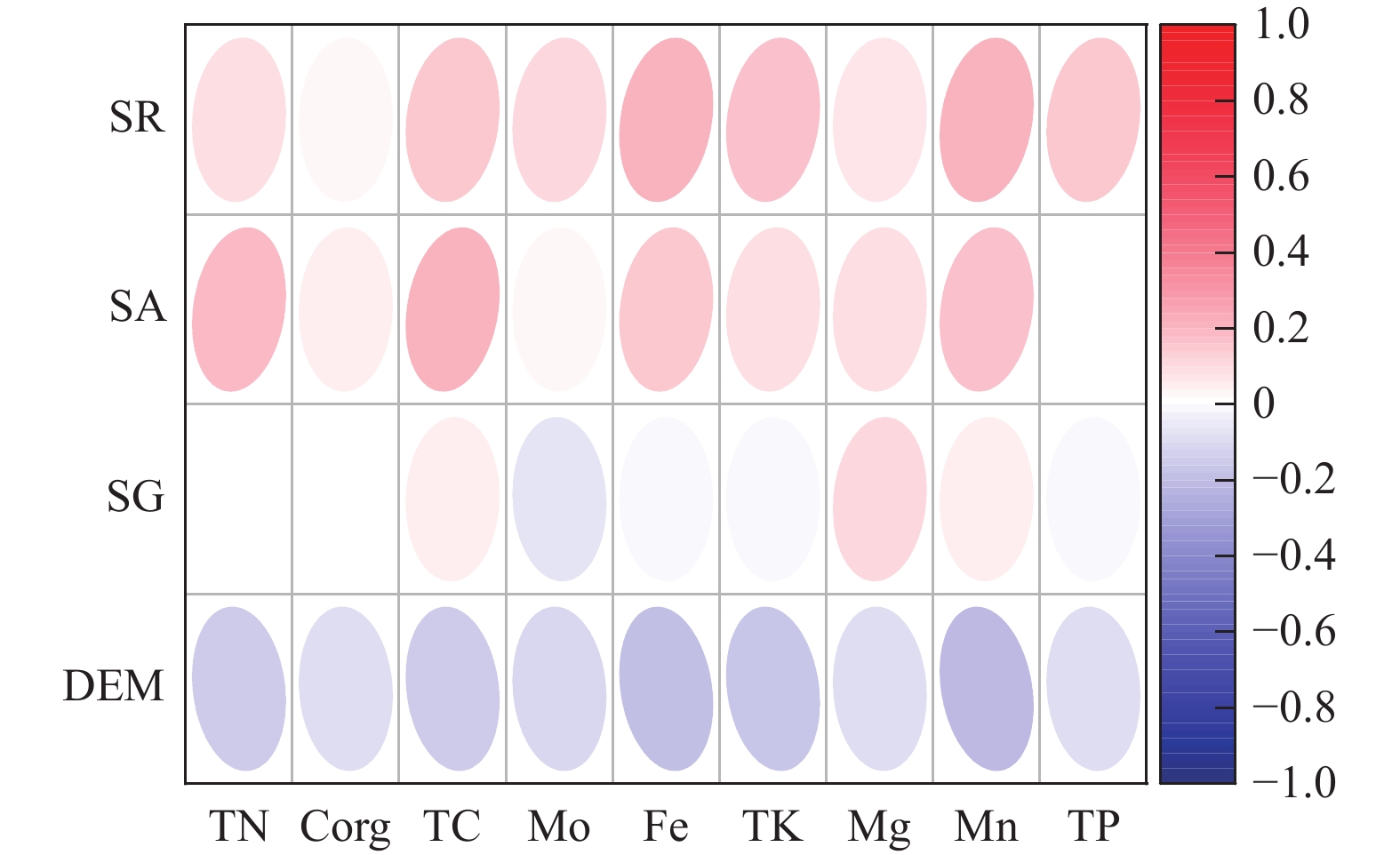
土壤健康关系人民生产生活水平,关乎国家粮食安全,是重要的战略资源。为摸清塔里木盆地东北缘典型绿洲区土壤养分特征,采集研究区土壤表层样品140件,测定主要养分元素含量,分析其生态化学计量特征、空间分布规律及影响养分富集的主控因素。结果表明:① 研究区Fe、Mn含量高值分布面积最广,Mg含量高值分布范围最小;分析土壤生态化学计量特征,发现缺氮少磷是限制区内植物正常生长的主控因素。②从数量上来看,研究区贫瘠、极贫瘠级别的土地面积占总面积的99.14%,仅0.86%的土地处于中等级别水平。从空间分布上来看,中等肥力的土地分布在区内东南部,呈孤岛状;极贫瘠的土地主要分布在绿洲–荒漠的过渡带上。③研究区4种土地利用方式中,耕地的土壤养分含量较高;土壤养分元素的含量与坡向、地表粗糙度呈正相关关系,与海拔呈负相关关系。同时,土壤养分的丰缺与长期连作、作物施肥、灌溉技术等人为影响也有着密切的关系。
Abstract:Soil health is related to people’s production, living standards, and national food security and is an important strategic resource. To understand the nutrient characteristics of soils in typical oasis areas on the northeast edge of the Tarim basin. A total of 140 soil surface samples were collected from the study area to determine the content of major nutrient elements and analyze their ecological chemometric characteristics, spatial distribution patterns, and the main controlling factors affecting nutrient enrichment. The results showed that: ① High values of Fe and Mn were most widely distributed in the study area, while high values of Mg were the least widely distributed. Analysis of the ecological stoichiometric characteristics of the soil showed that the lack of nitrogen and phosphorus was the main controlling factor limiting the normal growth of plants in the area. ② In terms of quantity, 99.14% of the total land area in the study area is infertile or very infertile, and only 0.86% of the land is at the medium−grade level. In terms of spatial distribution, the moderately fertile land is distributed in the south−eastern part of the district in the form of islands, and the very barren land is mainly distributed in the oasis−desert transition zone. ③ Among the four types of land use, the soil nutrient content of the arable land is higher. Meanwhile, the content of nutrient elements is positively correlated with slope orientation and surface roughness and negatively correlated with altitude. At the same time, the abundance of soil nutrients is also closely related to long−term continuous cropping, crop fertilization, irrigation techniques, and other anthropogenic influences.
-
Key words:
- soil /
- nutrients /
- Tarim Basin /
- oasis zone /
- dominant control factors
-

-
表 1 描述统计相关参数表(n=140)
Table 1. Describes the statistically related parameters (n=140)
元素 最小值 最大值 均值 标准偏差 偏度 峰度 变异系数(%) 正态分布 TN 0.01 0.13 0.04 0.02 1.12 2.18 0.47 平方差 Corg 0.06 1.83 0.43 0.29 1.50 3.65 0.68 平方差 TC 1.15 3.45 2.45 0.47 0.00 −0.66 0.19 平方差 Mo 0.37 2.04 0.82 0.30 1.29 2.37 0.37 对数 Fe 1.70 5.06 3.10 0.67 0.48 −0.44 0.22 平方差 TK 1.23 2.79 2.20 0.22 −0.37 2.88 0.10 平方差 Mg 1.38 4.49 2.77 0.62 0.34 −0.28 0.22 平方差 Mn 261.63 732.43 480.49 93.39 0.42 −0.32 0.19 对数 TP 336.08 869.40 557.23 109.32 0.56 0.26 0.20 对数 注:TN、Corg、TC、TK、Fe、Mg含量为%;Mo、Mn、TP含量为10–6。 表 2 第二次全国土壤普查土壤养分分级标准表
Table 2. Soil nutrient classification standards for the second national soil survey
一级 二级 三级 四级 五级 六级 TN >40 1.5~2 1~1.5 0.75~1 0.5~0.75 <0.5 TP >1 0.8~1 0.6~0.8 0.4~0.6 0.2~0.4 <0.2 TK >25 20~25 15~20 10~15 5~10 <5 有机质 >40 30~40 20~30 10~20 6~10 <6 注:元素含量均为‰。 表 3 半方差函数相关参数表
Table 3. Related parameters of the half-variance function
元素 块金值
C0基台值
C0+C块金比
C0/C0+C变程
R决定系数
R2残差
RSS模型 TN 1.21E-04 2.04E-03 0.941 4170.00 0.74 2.49E-09 指数模型 Corg 0.0025 0.0445 0.944 4770.00 0.70 1.07E-04 指数模型 TC 0.0016 0.0237 0.933 4800.00 0.21 1.43E-05 球状模型 Mo 0.0079 0.1108 0.929 3420.00 0.27 1.72E-04 指数模型 Fe 0.0052 0.034 0.848 2390.23 0.49 8.81E-06 高斯模型 TK 7.80E-04 5.72E-03 0.864 4710.00 0.79 7.61E-08 指数模型 Mg 0.0043 0.0354 0.880 2760.00 0.21 6.25E-05 指数模型 Mn 0.0008 0.0368 0.978 2720.00 0.54 6.57E-06 球状模型 TP 0.0022 0.0382 0.942 2810.00 0.35 2.86E-05 球状模型 表 4 土壤养分元素的权重表
Table 4. Weights of soil nutrient elements
元素 TN Corg TC Mo Fe TK Mg Mn TP 权重 0.1995 0.2254 0.0537 0.1622 0.0885 0.0219 0.0799 0.0715 0.0974 表 5 肥力等级及面积占比表
Table 5. Fertility grade and area ratio
土壤肥力等级 肥沃F1 较肥沃F2 中等F3 贫瘠F4 极贫瘠F5 IFI ≥0.8 0.6~0.8 0.4~0.6 0.2~0.4 ≤0.2 面积占比 0 0 0.86% 89.64% 9.50% 表 6 不同土地利用方式间土壤生态化学计量特征表
Table 6. Soil ecological stoichiometry of different land use methods
生态化学计量比 耕地 园地 林地 荒地 wC∶wN 69.20±15.20ab 65.17±10.85a 74.31±12.32b 68.73±10.32a wC∶wP 42.99±5.70a 45.20±7.09ab 46.06±7.22b 44.32±5.90a wN∶wP 0.71±0.11a 0.73±0.11b 0.72±0.08ab 0.71±0.11a 注:表中数据为平均值±标准差,不同小写字母表示不同土地利用方式土壤生态化学计量特征差异显著。 -
[1] 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析(第三版)[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2008
BAO Shidan. Soil agrochemical analysis (3rd ed. ) [M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2008.
[2] 陈金萍, 李奕, 李祥余, 等. 不同农业土地利用方式对土壤养分含量分布影响及养分等级评价[J]. 萍乡学院学报, 2022, 39(3): 111-116
CHEN Jinping, LI Yi, LI Xiangyu, et al. Effects of different agricultural land use practices on soil nutrient content distribution and evaluation of nutrient classes[J]. Journal of Pingxiang College, 2022, 39(3): 111-116.
[3] 陈彦. 绿洲农田土壤养分时空变异及精确分区管理研究[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2008
CHEN Yan. Research on spatial and temporal variability of soil nutrients in oasis farmland and precise zoning management[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2008.
[4] 冯博, 周皓, 徐阳, 等. 矿区农地重金属污染风险评价——基于改进的模糊综合评价法[J]. 有色金属工程, 2022, 12(2): 138-145 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2022.02.019
FENG Bo, ZHOU Hao, XU Yang, et al. Evaluation of heavy metal pollution risk in agricultural land in mining areas--based on improved fuzzy integrated evaluation method[J]. Nonferrous Metals, 2022, 12(2): 138-145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2022.02.019
[5] 郭雯雯, 毕淑琪, 李冰, 等. 不同土地利用参数下CALPUFF模型的敏感性分析[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2022, 44(6): 705-709
GUO Wenwen, BI Shuqi, LI Bing, et al. Sensitivity analysis of CALPUFF model under different land use parameters[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2022, 44(6): 705-709.
[6] 贺思楠, 吕刚, 王锋柏, 等. 辽西北风沙地土壤养分空间变异性与土地利用的关系[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2022, 53(2): 213-220. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1700.2022.02.010
HE Sinan, LV Gang, WANG Fengbai, et al. Relationship between spatial variability of soil nutrients and land use in a wind-sand landscape in northwest Liaoning Province[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2022, 53(2): 213-220. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1700.2022.02.010
[7] 黄彩变, 严军, 鞠景枫, 等. 塔里木盆地南缘新垦农田土壤性状变化及其与小麦产量的关系[J]. 水土保持学报, 2020, 34(2): 245-252 doi: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2020.02.035
HANG Caibian, YAN Jun, JU Jingfeng, et al. Changes in soil properties and their relationship with wheat yield in newly reclaimed farmland on the southern edge of the Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 34(2): 245-252. doi: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2020.02.035
[8] 黄锦学, 熊德成, 刘小飞, 等. 增温对土壤有机碳矿化的影响研究综述[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(1): 12-24
HUANG Jinxue, XIONG Decheng, LIU Xiaofei, et al. Effects of warming on soil organic carbon mineralization: A review[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(1): 12-24.
[9] 贾佳瑜, 刘小芳, 赵勇钢, 等. 汾河流域下游农田土壤重金属空间分布特征与污染评价[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2021, 35(8): 132-137 doi: 10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2021.224
JIA Jiayu, LIU Xiaofang, ZHAO Yonggang, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics and pollution evaluation of heavy metals in agricultural soils in the downstream of Fen River Basin[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2021, 35(8): 132-137. doi: 10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2021.224
[10] 贾鲁净, 杨联安, 封涌涛, 等. 宝鸡市农耕区土壤养分空间变异及其影响因素分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2022, 36(12): 135-143
JIA Lujing, YANG Lianan, FENG Yongtao, et al. Spatial variability of soil nutrients and its influencing factors in the farming area of Baoji[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2022, 36(12): 135-143.
[11] 李丹维, 王紫泉, 田海霞, 等. 太白山不同海拔土壤碳、氮、磷含量及生态化学计量特征[J]. 土壤学报, 2017, 54(1): 160-170 doi: 10.11766/trxb201604140096
LI Danwei, WANG Ziquan, TIAN Haixia, et al. Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus contents and ecological stoichiometry of soils at different altitudes in the Taibai Mountains[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2017, 54(1): 160-170. doi: 10.11766/trxb201604140096
[12] 李红林, 贡璐, 朱美玲, 等. 塔里木盆地北缘绿洲土壤化学计量特征[J]. 土壤学报, 2015, 52(6): 1345-1355 doi: 10.11766/trxb201411220585
LI Honglin, GONG Lu, ZHU Meiling, et al. Soil chemometric characteristics of oases on the northern edge of the Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2015, 52(6): 1345-1355. doi: 10.11766/trxb201411220585
[13] 李美娟, 陈国宏, 陈衍泰. 综合评价中指标标准化方法研究[C]. 2004年中国管理科学学术会议, 2004
LI Meijuan, CHEN Guohong, CHEN Yantai. Research on standardization methods of indicators in comprehensive evaluation[C]. 2004 Chinese Management Science Conference, 2004.
[14] 廖启林, 华明, 张为, 等. 人为活动对江苏土壤元素含量分布的影响[J]. 地质学刊, 2012, 36(2): 147-156 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2012.02.147
LIAO Qilin, HUA Ming, ZHANG Wei, et al. Influence of anthropogenic activities on the distribution of soil elemental content in Jiangsu[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2012, 36(2): 147-156. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2012.02.147
[15] 刘寒双, 崔纪菡, 刘猛, 等. 有机肥替代部分化肥对谷子产量、土壤养分及酶活性的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2022(7): 71-81 doi: 10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.21183
LIU Hanshang, CUI Jihan, LIU Meng, et al. Effects of organic fertilizers on grain yield, soil nutrients and enzyme activities by replacing some chemical fertilizers[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2022(7): 71-81. doi: 10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.21183
[16] 刘庆, 王静, 史衍玺, 等. 基于GIS的农田土壤重金属空间分布研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2007(2): 109-113 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6094.2007.02.029
LIU Qing, WANG Jing, SHI Yanxi, et al. Spatial distribution of heavy metals in agricultural soils based on GIS[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2007(2): 109-113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6094.2007.02.029
[17] 鲁泽让, 夏梓泰, 芦美, 等. 周年轮作休耕对土壤AMF群落和团聚体稳定性的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2023: 1-14
LU Zerang, XIA Zitai, LU Mei, et al. Effects of annual crop rotation fallow on the stability of soil AMF communities and aggregates[J]. Environmental Science, 2023: 1-14.
[18] 李青, 薛珍. 塔里木河流域居民生态认知与支付行为空间异质性研究——基于上中下游2133个居民调查数据[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2018, 32(1): 14-21 doi: 10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2018.003
LI Qing, XUE Zhen. Spatial heterogeneity of ecological cognition and payment decision behavior in the Tarim River Basin-Based on the survey data of 2133 residents[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2018, 32(1): 14-21. doi: 10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2018.003
[19] 马倩倩, 董博, 许旺旺, 等. 干旱区耕地质量等级评价及土壤养分与盐渍化的分析研究——以民勤绿洲为例[J]. 干旱区地理, 2021, 44(2): 514-524 doi: 10.12118/j.issn.10006060.2021.02.22
MA Qianqian, DONG Bo, XU Wangwang, et al. Evaluation of arable land quality rating and analysis of soil nutrients and salinization in arid areas: the case of Minqin Oasis[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2021, 44(2): 514-524. doi: 10.12118/j.issn.10006060.2021.02.22
[20] 能子礼超, 勾琴, 刘盛余, 等. 模糊数学法综合评价土壤重金属污染程度研究[J]. 能源与环保, 2020, 42(7): 39-43
NENG ZI Lichao, GOU Qin, LIU Shengyu, et al. Fuzzy mathematical method for comprehensive evaluation of soil heavy metal pollution[J]. China Energy and Environmental Protection, 2020, 42(7): 39-43.
[21] 宋铮, 余庭龙, 朱春云, 等. 高寒丘陵区不同退耕年限人工林形质评价[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2020, 35(6): 52-59 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2020.06.07
SONG Zheng, YU Tinglong, ZHU Chunyun, et al. Evaluation of the morphological quality of plantation forests in alpine hilly areas with different years of fallowing[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2020, 35(6): 52-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2020.06.07
[22] 陶睿, 王子芳, 高明, 等. 重庆市丰都县紫色土养分空间变异及土壤肥力评价[J]. 土壤, 2017, 49(1): 155-161 doi: 10.13758/j.cnki.tr.2017.01.023
TAO Rui, WANG Zifang, GAO Ming, et al. Spatial variation of nutrients and evaluation of soil fertility in purple soils of Fengdu County, Chongqing[J]. Soils, 2017, 49(1): 155-161. doi: 10.13758/j.cnki.tr.2017.01.023
[23] 陶于祥, 许凯丰, 易宗旺, 等. 基于半变异函数的城市热岛空间异质性分析[J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 40(10): 145-152 doi: 10.13718/j.cnki.xdzk.2018.10.023
TAO Yuxiang, XU Kaifeng, YI Zongwang, et al. Spatial heterogeneity analysis of urban heat island based on semi-variance function[J]. Journal of Southwest University(Natural Science Edition), 2018, 40(10): 145-152. doi: 10.13718/j.cnki.xdzk.2018.10.023
[24] 田鸽. 秦岭火地塘土壤养分空间分布特征及其影响因素[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2021
TIAN Ge. Spatial distribution characteristics of soil nutrients in Tierra del Fuego in the Qinling Mountains and its influencing factors[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2021.
[25] 田立文, 祁永春, 戴路, 等. 新疆南疆耕地土壤养分含量及其分布特征评价——以阿克苏地区为例[J]. 核农学报, 2020, 34(1): 214-223 doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2020.01.0214
TIAN Liwen, QI Yongchun, DAI Lu, et al. Evaluation of soil nutrient content and its distribution characteristics in arable land in South Xinjiang - an example from Aksu region[J]. Acta Agriculturae Nucleatae Sinica, 2020, 34(1): 214-223. doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2020.01.0214
[26] 王宇超, 李倩, 黎斌, 等. 秦岭南坡中段植物群落物种多样性与环境相关性分析[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学, 2016, 35(10): 2859-2866 doi: 10.13417/j.gab.035.002859
WANG Yuchao, LI Qian, LI Bin, et al. Analysis of species diversity and environmental relevance of plant communities on the southern slopes of the Qinling Mountains[J]. Genomics and Applied Biology, 2016, 35(10): 2859-2866. doi: 10.13417/j.gab.035.002859
[27] 魏新, 郑小锋, 张硕新. 秦岭火地塘不同海拔梯度森林土壤理化性质研究[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2014, 29(3): 9-14 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2014.03.02
WEI Xin, ZHENG Xiaofeng, ZHANG Shuoxin. Physicochemical properties of forest soils at different elevation gradients in Tierra del Fuego in the Qinling Mountains[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2014, 29(3): 9-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2014.03.02
[28] 信会男, 赖宁, 耿庆龙, 等. 基于GIS的塔额盆地农田土壤养分空间变异特征分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(7): 1776-1785 doi: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2022.07.025
XIN Huinan, LAI Ning, GENG Qinglong, et al. Analysis of spatial variability of soil nutrients in agricultural fields of the Ta'er Basin based on GIS[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(07): 1776-1785. doi: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2022.07.025
[29] 闫金凤, 陈曦, 罗格平, 等. 干旱区绿洲地下水水位时空变异性对土地覆被变化的响应[J]. 科学通报, 2006(S1): 42-48 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2006.z1.007
YAN Jinfeng, CHEN Xi, LUO Geping, et al. Response of spatial and temporal variability of groundwater levels to land cover change in an arid oasis[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2006(S1): 42-48. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2006.z1.007
[30] 杨阳, 李飒, 孙立强, 等. 半变异函数计算波动范围的方法研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(工学版), 2021, 54(7): 618-626 doi: 10.14188/j.1671-8844.2021-07-006
YANG Yang, LI Sa, SUN Liqiang, et al. Research on the method of calculating the fluctuation range by semi-variance function[J]. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University, 2021, 54(7): 618-626. doi: 10.14188/j.1671-8844.2021-07-006
[31] 张慧文, 马剑英, 张自文, 等. 地统计学在土壤科学中的应用[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 45(6): 14-20 doi: 10.13885/j.issn.0455-2059.2009.06.013
ZHANG Huiwen, MA Jianying, ZHANG Ziwen, et al. Application of geostatistics in soil science[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University(Natural Sciences), 2009, 45(6): 14-20. doi: 10.13885/j.issn.0455-2059.2009.06.013
[32] 张子璐, 左昕弘, 刘峰, 等. 渝西丘陵区土壤速效钾空间异质性及影响因素[J]. 土壤学报, 2020, 57(2): 307-315 doi: 10.11766/trxb201902250030
ZHANG Zilu, ZUO Xinhong, LIU Feng, et al. Spatial heterogeneity and influencing factors of soil fast-acting potassium in the hilly areas of western Chongqing[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2020, 57(02): 307-315 doi: 10.11766/trxb201902250030
[33] 赵敬坤, 陈松柏, 李忠意, 等. 模糊综合评价法判断重庆花椒种植区土壤肥力水平[J]. 中国农机化学报, 2021, 42(10): 206-212 doi: 10.13733/j.jcam.issn.2095-5553.2021.10.29
ZHAO Jingkun, CHEN Songbai, LI Zhongyi, et al. Fuzzy integrated evaluation method to determine soil fertility level in pepper growing areas of Chongqing[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2021, 42(10): 206-212. doi: 10.13733/j.jcam.issn.2095-5553.2021.10.29
[34] 朱平宗, 张光辉, 杨文利, 等. 红壤区林地浅沟不同植被类型土壤生态化学计量特征[J]. 水土保持研究, 2020, 27(6): 60-65 doi: 10.13869/j.cnki.rswc.2020.06.008
ZHU Pingzong, ZHANG Guanghui, YANG Wenli, et al. Soil ecological stoichiometry of different vegetation types in shallow furrows in red soil areas[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 27(06): 60-65. doi: 10.13869/j.cnki.rswc.2020.06.008
[35] 赵雯, 黄来明. 高寒山区不同土地利用类型土壤养分化学计量特征及影响因素[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(11): 4415-4427
ZHAO Wen, HUANG Laiming. Stoichiometric characteristics and influencing factors of soil nutrients under different land use types in an alpine mountain region[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(11): 4415-4427.
[36] Ali E N, Sang S L, Yasser M A, et al. Influence of soil properties and feedstocks on biochar potential for carbon mineralization and improvement of infertile soils[J]. Geoderma, 2018, 332: 100-108. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2018.06.017
[37] Ayoubi, Mehnatkesh, Jalalian, et al. Relationships between grain protein, Zn, Cu, Fe and Mn contents in wheat and soil and topographic attributes[J]. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 2014, 60(5): 625-638. doi: 10.1080/03650340.2013.825899
[38] Cory C C, Daniel L. C: N: P Stoichiometry in Soil: Is There a "Redfield Ratio" for the Microbial Biomass? [J]. Biogeochemistry, 2007, 85(3): 235-252. doi: 10.1007/s10533-007-9132-0
[39] Cheng W J, Xi H Y, Sindikubwabo C, et al. Ecosystem health assessment of desert nature reserve with entropy weight and fuzzy mathematics methods: A case study of Badain Jaran Desert[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2020, 119.
[40] Dai W, Li Y H, FU W J, et al. Spatial variability of soil nutrients in forest areas: A case study from subtropical China[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 2018, 181(6): 827-835. doi: 10.1002/jpln.201800134
[41] Khormali F, Ajami M, Ayoubi S, et al. Role of deforestation and hillslope position on soil quality attributes of loess-derived soils in Golestan province, Iran[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 2009, 134(3): 178-189.
[42] Li D X, Li Y N, Xie Y L, et al. Effects of ecological restoration on soil biogenic elements and their ecological stoichiometry in the Yellow River Delta, China[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2022.
[43] Li Q, Yang J Y, Guan W H, et al. Soil fertility evaluation and spatial distribution of grasslands in Qilian Mountains Nature Reserve of eastern Qinghai-Xizang Plateau[J]. Peerj, 2021, 9.
[44] Razan M, Shankar S, Dinesh K, et al. Soil Fertility Mapping and Assessment of the Spatial Distribution of Sarlahi District, Nepal[J]. American Journal of Agricultural Science, 2020, 7(1): 8-16.
[45] Sharma R, Sood K. Characterization of Spatial Variability of Soil Parameters in Apple Orchards of Himalayan Region Using Geostatistical Analysis[J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 2020, 51(8): 1065-1077. doi: 10.1080/00103624.2020.1744637
[46] Tian H Q, Chen G S, Zhang C, et al. Pattern and variation of C: N: P ratios in China's soils: a synthesis of observational data[J]. Biogeochemistry, 2010, 98(1/3): 139-151.
[47] Xiao J J, Ma H X, Lu C T. Study on Spatial Distribution of Soil Nutrients and Comprehensive Evaluation of Nutrients in Low Mountain-Hilly Region of Sichuan Province, China[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2013, 2301(295-298): 2544-2548.
[48] Zhang X X, Xu K, Zhang D J. Risk assessment of water resources utilization in Songliao Basin of Northeast China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2012, 67(5): 1319-1329. doi: 10.1007/s12665-012-1575-5
-



 下载:
下载: