Key Issues of Earth System Science in the Study of Carbon Sinks in the Loess Plateau
-
摘要:
全球温度升高1.2 ℃,应对气候变化已经到了刻不容缓的地步。2019年9月,中国政府承诺中国在2030年碳达峰,在2060年碳中和,这是一份巨大担当,也是一个巨大的挑战。碳中和的达成需要节能减排,还需要负排放技术和增加生态、地质碳汇。能源结构的调整和CCUS等负排放技术的发展需要几十年的时间,亟需要调查和研究生态和地质碳汇的现状并且增加碳汇潜力。全球范围的碳汇清查主要依靠“自上而下”和“自下而上”的估算方法,而国家级别的区域碳汇清查目前还是一个难点。黄土高原是最早起步进行退耕还林还草生态工程的地区,也是生态脆弱区。目前,黄土高原区域的碳汇调查和研究尚属于起步阶段。基于国家“双碳”战略需要和黄土高原生态文明建设,笔者从地球系统科学角度,回溯黄土高原的碳汇调查研究成果,总结黄土高原区域碳汇评估的方法体系,包含有机碳汇系统和无机碳汇系统。其中,有机碳汇系统包含有机质碳储量子系统和生态碳汇子系统的研究;无机碳汇系统主要包含碳酸盐碳汇系统和硅酸盐碳汇系统。在此基础上,从地球系统科学角度提出黄土高原碳汇调查研究建议。
Abstract:With the global temperature rising by 1.2 ℃, it is urgent to deal with climate change. In September 2019, the Chinese government promised that China will reach its carbon peak in 2030 and become carbon neutral in 2060, which is a huge responsibility and a huge challenge. The achievement of carbon neutrality requires energy conservation and emission reduction, as well as negative emission technologies and an increase in ecological and geological carbon sinks. The adjustment of the energy structure and the development of negative emission technologies such as CCUS will take decades. There is an urgent need to investigate and study the current status of ecological and geological carbon sinks and increase the potential of carbon sinks. The global carbon sink inventory mainly relies on the "top–down" and "bottom–up" estimation methods, while the national–level regional carbon sink inventory is still a difficult problem. The Loess Plateau is the first area where the ecological project of returning farmland to forests and grasslands started, and it is also an ecologically fragile area. The current investigation and research on carbon sinks in the Loess Plateau is still in its infancy. Based on the needs of the national carbon neutral strategy and the construction of ecological civilization on the Loess Plateau, this paper begins to review the research results of carbon sinks on the Loess Plateau from the perspective of earth system science. Firstly, the method system of carbon sink assessment in the Loess Plateau is summarized, and then it is further summarized that the carbon sink system of the Loess Plateau mainly includes organic carbon sink system and inorganic carbon sink system. Among them, the organic carbon sink system includes the research on the organic carbon storage sub-system and the ecological carbon sink system. The inorganic carbon sink system mainly includes carbonate carbon sink system and silicate carbon sink system. Finally, from the perspective of earth system science, the suggestions are given for the investigation and research of carbon sinks in the Loess Plateau.
-

-
图 2 基于流域(地下水系统+地表水系统)H2O–CaCO3–CO2–水生光合生物相互作用的碳酸盐风化碳汇模式图(Liu et al.,2018)
Figure 2.
表 1 无机碳汇估算方法汇总表
Table 1. Summary table of methods for estimating carbon sinks
估算方法 计算公式 适用场景 参考文献 正演模型 排除大气、外源酸和微量碳酸盐矿物影响之后,计算花岗岩和玄武岩的风化阳离子浓度总和(K+2Ca+Na+2Mg),并结合每个流域的径流深q(mm),分别计算出花岗岩和玄武岩风化的阳离子通量 适用于流域尺度的硅酸盐化学风化研究 (Yang et al.,2022) 反演模型 [ΦCO2]sil=(2Ca2+sil+2Mg2+sil+Na+sil+K+sil) ×径流量/流域面积
[ΦCO2]carb=(Ca2+carb+Mg2+carb) ×径流量/流域面积
[ΦCO2]sil和[ΦCO2]carb分别为硅酸盐和碳酸盐化学风化消耗的CO2速率适用于流域尺度的硅酸盐化学风化研究 (Wu et al.,2013) 水化学径流法 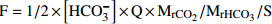
式中:F为岩溶碳汇强度(t/(km2·a)),[HCO3−]为水体中所含HCO3−的的浓度(g/l),1/2指径流中一半碳来自大气,Q为流域径流量(l/s),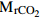 和
和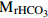 分别为CO2和HCO3−的相对分子质量,S为流域面积(km2)
分别为CO2和HCO3−的相对分子质量,S为流域面积(km2)明确的流域边界、地下水为全排型,至少有一个完整的水文年的流量和HCO3−浓度数据。同时要扣除硝酸和硫酸等外源酸对地下水中HCO3−的贡献 (刘再华,2000) Galy模型法 将河流中水化学离子组分归因于不同岩石端元的溶解,根据河水中元素比值关系,估算不同岩石风化对河水溶质的贡献。硅酸盐风化组成的地下水,离子比值为一定值(Mg2+/K+=0.5,Ca2+/Na+=0.2)
若仅考虑碳酸(H2CO3)对碳酸盐岩(CaCO3)的风化溶蚀,地下水中TDS来源于碳酸盐岩溶蚀生成的量表示如下:
TDS碳酸盐岩=[Ca2+]碳酸盐岩+[Mg2+]碳酸盐岩+1/2[HCO3−]
若考虑硫酸(H2SO4)和碳酸(H2CO3)共同参与了碳酸盐岩(CaCO3)的风化溶蚀,地下水中TDS来源于碳酸盐岩溶蚀生成的量表示如下:
TDS碳酸盐岩=[Ca2+]碳酸盐岩+[Mg2+]碳酸盐岩+1/4[HCO3−]碳酸+[HSO4−]硫酸
硅酸盐风化速率计算如下:
TDS硅酸盐眼=[Na+]硅酸盐岩+[K+]硅酸盐岩+[Ca2+]硅酸盐岩+[Mg2+]硅酸盐岩+
[SiO2]硅酸盐岩
来源于硅酸盐岩风化消耗的大气/土壤CO2计算公式如下:
CO2硅酸盐岩=[HCO3−]硅酸盐岩=[Na+]硅酸盐岩+[K+]硅酸盐岩+
2[Ca2+]硅酸盐岩+2[Mg2+]硅酸盐岩适用于中小流域尺度的岩石风化碳汇,估算不同岩溶风化对地表河水的贡献 (Galy et al.,1999;覃小群等,2015) 溶蚀试片法 E=(W1-W2)×1000×T−1×365×S−1,式中,E为试片溶蚀速率(mg·cm−2·a−1),W1为埋放前的试片重量(g),W2为回收后的试片重量(g),S为试片溶蚀表面积,T为试片埋放的时间(d) 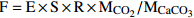 ,式中,F为岩溶作用吸收的CO2的汇(1010g/a),E为岩石试片的溶蚀速率(mg·cm−2·a−1),S为岩溶区面积(km2),R为岩石试片的碳酸盐岩纯度,
,式中,F为岩溶作用吸收的CO2的汇(1010g/a),E为岩石试片的溶蚀速率(mg·cm−2·a−1),S为岩溶区面积(km2),R为岩石试片的碳酸盐岩纯度,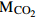 和
和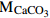 分别为CO2和CaCO3的相对分子质量
分别为CO2和CaCO3的相对分子质量广泛用于岩溶碳汇研究中,在西南岩溶区应用较为广泛,在黄土区估算量偏低 (黄奇波等,2015a,2015b) -
[1] 蔡兆男, 成里京, 李婷婷等. 碳中和目标下的若干地球系统科学和技术问题分析[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2021, 36(5): 602-613
Cai Zhaonan, Cheng Lijing, Li Tingting et al. Key Scientific and Technical Issues in Earth System Science Towards Achieving Carbon Neutrality in China [J]. Proceedings of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2021, 36(5): 602-613.
[2] 陈骏, 安芷生, 王洪涛等. 黄土高原中部S1古土壤次生碳酸盐稳定同位素组成与成因初探[J]. 科学通报, 1996, 41 (14): 1297-1300 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1996.14.013
Chen Jun, An Zhisheng, Wang Hongtao et al. Stable isotopic composition and genesis of S1 paleosol secondary carbonates in the central Loess Plateau [J]. Chinese Journal, 1996, 41 (14): 1297-1300. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1996.14.013
[3] 陈秀玲, 张文开, 肖宝玉. 黄土中碳酸盐的研究进展[J]. 新疆有色金属, 2008, 31 (4): 3
Chen Xiuling, Zhang Wenkai, Xiao Baoyu. Research progress of carbonate in loess [J]. Xinjiang Nonferrous Metals, 2008, 31 (4): 3.
[4] 程淑兰, 欧阳华, 牛海山等. 荒漠化重建地区土壤有机碳时空动态特征——以陕西省榆林市为例[J]. 地理学报, 2004, 59(4): 505-513
Cheng Shulan, Ouyang Hua, Niu Haishan et al. Temporal-spatial Dynamic Analysis of Soil Organic Carbon in Inversed Desertification Area: a case study in Yulin County, Shaanxi Province [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2004, 59(4): 505-513.
[5] 邓蕾. 黄土高原生态系统碳固持对植被恢复的响应机制[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2014
DENG Lei. Response mechanism of ecosystem carbon sequestration to vegetation restoration in the Loess Plateau [D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2014.
[6] 丁仲礼. 中国碳中和框架路线图研究[R]. 2021.
DING Zhongli. Research on China's carbon neutral Framework roadmap [R]. 2021.
[7] 董刚. 中国东北松嫩草甸草原碳水通量及水分利用效率研究[D].沈阳; 东北师范大学, 2011
DONG Gang. Carbon and water flux and water use efficiency in Songnen Meadow Steppe of Northeast China [D]. Shenyang: Northeast Normal University, 2011.
[8] 方精云, 郭兆迪, 朴世龙等. 1981~ 2000 年中国陆地植被碳汇的估算[J]. 中国科学: D 辑, 2007, 37(6): 804-812
Fang Jingyun, Guo Zhaodi, Piao Shilong et al. Estimation of carbon sinks of terrestrial vegetation in China from 1981 to 2000 [J]. Science in China: Series D, 2007, 37(6): 804-812.
[9] 高海东, 李占斌, 李鹏等. 基于土壤侵蚀控制度的黄土高原水土流失治理潜力研究[J]. 地理学报, 2015, 70(9): 1503-1515
Gao Haidong, Li Zhanbin, Li Peng et al. Potential of soil erosion control based on soil erosion control degree in the Loess Plateau [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2015, 70(9): 1503-1515.
[10] 韩冰, 王效科, 逯非等. 中国农田土壤生态系统固碳现状和潜力[J]. 生态学报, 2008, 28(2): 612-619
Han Bin, Wang Xiaoke, Lu Fei et al. Current status and potential of carbon sequestration in farmland soil ecosystems in China [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2008, 28(2): 612-619.
[11] 黄奇波, 覃小群, 刘朋雨等. 半干旱区岩溶碳汇原位监测方法适宜性研究[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2015a, 45 (1): 240-246
Huang Qibo, Qin Xiaoqun, Liu Pengyu et al. Applicability of Karst Carbon Sinks Calculation Methods in Semi-Arid Climate Envrionment [J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Sciece Edition, 2015a, 45(1): 240-246.
[12] 黄奇波, 覃小群, 刘朋雨. 不同岩性试片溶蚀速率差异及意义[J]. 地球与环境, 2015b, 43 (4): 7
Huang Qibo, Qin Xiaoqun, Liu Pengyu et al. Dissolution Rate and It’s Significance of Different Lithological Tables [J]. Earth and Envrionment, 2015b, 43 (4): 7.
[13] 黄奇波. 北方半干旱岩溶区岩溶碳汇过程及效应研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2019
HUANG Qibo. Study on the Carbon sequestration Process and Its Effect in the Semi-arid Karst Area of Northern China [D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2019.
[14] 贾旖旎. 基于DEM的黄土高原流域边界剖面谱研究[D]. 南京: 南京师范大学, 2010
JIA Yini. Study on boundary profile spectrum of Loess Plateau Watershed based on DEM [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Normal University, 2010.
[15] 蒋定生, 黄国俊. 黄土高原土壤入渗速率的研究[J]. 土壤学报, 1986, (4): 299-305
Jiang Dingsheng, Huang Guojun. Study on soil infiltration rate in Loess Plateau [J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 1986, (4): 299-305.
[16] 乐小芳,陈佳淳,苗璐
[17] 李妙宇. 黄土高原生态系统碳储量现状及固碳潜力评估[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院教育部水土保持与生态环境研究中心), 2021.
LI Miaoyu. Assessment of carbon storage status and carbon sequestration potential in Loess Plateau ecosystems [D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Research Center for Soil, Water and Soil Conservation and Ecological Environment, Ministry of Education, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2021.
[18] 李巧玲, 阎欣, 吴秀芝等. 荒漠草原沙漠化对土壤无机碳和有机碳的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2019, 33(1): 98-103 doi: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2019.01.017
Li Qiaoling, Yan Xin, Wu Xiuzhi et al. Effects of desertification on soil inorganic carbon and organic carbon in desert steppe [J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 33(1): 98-103. doi: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2019.01.017
[19] 李婷, 吕一河, 任艳姣等. 黄土高原植被恢复成效及影响因素[J]. 生态学报, 2020.40(23), 8593-8605
Li Ting, Lv Yihe, Ren Yanjiao et al. Effect and influencing factors of vegetation restoration on the Loess Plateau [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020.40(23), 8593-8605.
[20] 李旭东. 黄土高原草地与农田系统土壤呼吸及碳平衡 [D].兰州: 兰州大学, 2011.
LI Xudong. Soil respiration and carbon balance in grassland and cropland systems on the Loess Plateau [D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2011.
[21] 梁二, 蔡典雄, 张丁辰等. 中国陆地土壤有机碳储量估算及其不确定性分析[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2010. (06), 75-79
Liang Er, Cai DianXiong, Zhang Dingchen et al. Terrestrial soil organic carbon storage in China: Estimates and uncertainty[J]. Soil and Fertilizer in China, 2010. (06), 75-79.
[22] 刘嘉麒, 钟华, 刘东生. 渭南黄土中温室气体组分的初步研究[J]. 科学通报, 1996, 41 (24): 4 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1996.24.015
Liu Jiaqi, Zhong Hua, Liu Tungsheng. Preliminary study on greenhouse gases in Weinan Loess [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1996, 41 (24): 4. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1996.24.015
[23] 刘强, 刘嘉麒, 刘东生. 北京斋堂黄土剖面主要温室气体组分初步研究[J]. 地质地球化学, 2000, 28 (02): 82-86
Liu Qiang, Liu Jiaqi, Liu Dongsheng. Primary research on major greenhouse gases in Zhaitang Loess section, Beijing [J]. Geology and Geochemistry, 2000, 28 (02): 82-86.
[24] 刘迎春, 高显连, 付超等. 基于森林资源清查数据估算中国森林生物量固碳潜力[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(11), 4002-4010.
Liu Yingchun, Gao Xianlian , Fuchao et al. Estimation of carbon sequestration potential of forest biomass in China based on National Forest Resources Inventory [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39( 11) : 4002-4010.
[25] 刘再华. 大气CO2两个重要的汇[J]. 科学通报, 2000, 45 (21): 4
Liu Zaihua. Two important sinks of atmospheric CO2 [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2000, 45 (21): 4.
[26] 苗甜, 金雅琪, 王磊等. 黄土碳酸盐古气候意义及其研究展望[J]. 盐湖研究, 2021, 29 (4): 10
Miao Tian, Jin Yaqi, Wang Lei et al. Paleoclimate significance of loess carbonate and its research prospect [J]. Salt Lake Research, 2021, 29 (4): 10.
[27] 潘根兴, & 赵其国. 我国农田土壤碳库演变研究: 全球变化和国家粮食安全[J]. 地球科学进展, 2005, 20(4): 384 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2005.04.003
Pan Genxing, & Zhao Qiguo. Study on the evolution of farmland soil carbon pool in China: global change and national food security [J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2005, 20(4): 384. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2005.04.003
[28] 朴世龙, 岳超, 丁金枝, 等. 试论陆地生态系统碳汇在“碳中和”目标中的作用[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学. 2022a, 52(07):1419−1426.
PIAO Shilong, YUE Chao, DING Jinzhi,et al. Perspectives on the role of terrestrial ecosystems in the ‘carbon neutrality’ strategy [J]. Science China Earth Sciences. 2022a, 52(07):1419−1426.
[29] 朴世龙, 何悦, 王旭辉, 等. 中国陆地生态系统碳汇估算: 方法、进展、展望[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2022b, 52(06):1010−1020. doi: 10.1360/SSTe-2021-0197
PIAO Shilong, HE Yue, WANG Xuhui , et al. Estimation of China’s terrestrial ecosystem carbon sink: Methods, progress and prospects[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2022b,52(06):1010−1020. doi: 10.1360/SSTe-2021-0197
[30] 齐丽彬, 樊军, 邵明安等. 黄土高原水蚀风蚀交错带不同土地利用类型土壤呼吸季节变化及其环境驱动[J]. 生态学报, 2008, 28 (11): 9
Qi Libin, Fan Jun, Shao Ming 'an et al. Seasonal variation of soil respiration and its environmental drivers in Different land use types in the water Erosion and wind Erosion ecotone of the Loess Plateau [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2008, 28 (11): 9.
[31] 秦小光, 李长生, 蔡炳贵. 气候变化对黄土碳库效应影响的敏感性研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2001, (02): 153-161
Qin Xiaoguang, Li Changsheng, Cai Bing-gui. Study on the sensitivity of climate change to Loess carbon pool effect [J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2001, (02): 153-161.
[32] 邵明玉, 张连凯, 刘朋雨等. 黄土区典型小流域矿物化学风化及碳汇效应[J]. 地球与环境, 2019, 47 (5): 11
Shao Mingyu, Zhang Liankai, Liu Pengyu et. Mineral Dissolution and Carbon Sink Effect in a Typical Small Watershed of the Loess Area[J]. Earth and Environment, 2019, 47 (5): 11.
[33] 宋超. 陕西省典型森林生态系统固碳速率及潜力研究[R]. 中国科学院研究生院 (教育部水土保持与生态环境研究中心), 2015.
SONG Chao. Study on carbon sequestration rate and potential of typical forest ecosystems in Shaanxi Province[R]. Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Research Center for Soil and Water Conservation and Ecological Environment, Ministry of Education), 2015.
[34] 覃小群, 蒋忠诚, 张连凯等. 珠江流域碳酸盐岩与硅酸盐岩风化对大气CO2汇的效应[J]. 地质通报, 2015, 34 (9): 9
Qin Xiaoqun, Jiang Zhongcheng, Zhang Liankai et al. Effects of weathering of carbonate and silicate rocks on atmospheric CO2 sinks in the Pearl River Basin [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2015, 34 (9): 9.
[35] 腾志宏, 张银玲. 黄土高原地下水资源与水质初步评价[J]. 西北大学学报: 自然科学版, 2000, 30(1): 60–64.
TENG Zhihong, ZHANG Yinling. Water resource and water quality evaluation of underground water in Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2000, 30(1): 60–64.
[36] 涂夏明, 曹军骥, 韩永明等. 黄土高原表土有机碳和无机碳的空间分布及碳储量[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2012, 26 (2): 5
Tu xiaming, Cao Junji, Han Yongming et al. Storage and spatial distribution of organic and inorganic carbon in the topsoil of Loess Plateau [J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2012, 26 (2): 5.
[37] 王国强, 李婷, 陈隽璐, 等. 中国西北地区超基性岩封存CO2潜力研究[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(1): 186-193.
WANG Guoqiang, LI Ting, CHEN Junlu, et al. Assessment of Carbon Dioxide Sequestration Potential of Ultramafic Rocks in Northwest China[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(1): 186-193.
[38] 文启忠. 中国黄土地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989
WEN Qizhong. Loess Geochemistry in China [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1989.
[39] 吴卫华, 郑洪波, 杨杰东等. 硅酸盐风化与全球碳循环研究回顾及新进展[J]. 高校地质学报, 2012, 018 (002): 215-224 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2012.02.003
Wu Weihua, Zheng hongbo, Yang Jiedong et. Review and new progress of silicate weathering and global carbon cycle [J]. Geological Journal of Chinese Universities, 2012, 018 (002): 215-224. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2012.02.003
[40] 熊平生, 谢世友. 中国全球变化研究优势领域及进展[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 2008, 24 (3): 5
Xiong Pingsheng, Xie Shiyou. Research advances on global change in China [J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 2008, 24 (3): 5.
[41] 杨黎芳, 李贵桐, 李保国. 土壤发生性碳酸盐碳稳定性同位素模型及其应用[J]. 地球科学进展, 2006, (09): 97-105 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2006.09.012
Yang Lifang, Li Guitong, Li Baoguo. Stable isotope model of soil-derived carbonate carbon and its application [J]. Advance in Earth Science, 2006, (09): 97-105. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2006.09.012
[42] 杨艳芬,王兵,王国梁,等
YANG Yanfen, WANG Bing, WANG Guoliang, et al
[43] 于贵瑞, 王绍强, 陈泮勤等. 碳同位素技术在土壤碳循环研究中的应用[J]. 地球科学进展, 2005, 20 (5): 10
Yu Guirui, Wang Shaoqiang, Chen Panqin et al. Isotope tracer approaches in soil organic carbon cycle research [J]. Advances in earth science, 2005, 20 (5): 10.
[44] 张龙军, 王宝森, 薛明, 等. 黄河流域硅酸盐风化的讨论(2)——流域耗水量对化学风化消耗大气CO2的贡献 [J]. 中国海洋大学学报: 自然科学版, 2011, 41 (4): 109-115.
ZHANG Longjun, WANG Baosen, XUE Ming, et al. Discussion on silicate weathering in the Huanghe River drainage basin(2): the contribution of water consumption to CO2 consumption by silicate weathering [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2011, 41 (4): 109-115.
[45] 张晴, 李力. 我国净生态系统碳交换量 (NEE) 的时空变化特征研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2009, 37(7): 3108-3109
Zhang Qing, Li Li. Spatial-temporal variation characteristics of net ecosystem carbon exchange volume (NEE) in China [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2009, 37(7): 3108-3109
[46] 张崧. 黄土高原中部60万年来黄土—古土壤序列有机碳同位素研究[D. 北京: 中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所, 2008
ZHANG Song. Study on the Sequence of organic carbon Isotopes in the Paleosol of the Central Loess Plateau during the past 600 000 years [D]. Beijing: Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2008.
[47] An Zhisheng. The history and variability of the East Asian paleomonsoon climate [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2000, 19(1-5): 171-187. doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(99)00060-8
[48] Avitabile V. , Herold M. , Heuvelink G. B. , Lewis et al. An integrated pan‐tropical biomass map using multiple reference datasets [J]. Global change biology, 2016, 22(4): 1406-1420. doi: 10.1111/gcb.13139
[49] Beck J. W. , Zhou Weijian, Li Cheng et al. A 550, 000-year record of East Asian monsoon rainfall from 10Be in loess [J]. science, 2018, 360(6391): 877-881. doi: 10.1126/science.aam5825
[50] Cerling T E, Quade J. Stable carbon and oxygen isotopes in soil carbonates [M]. Climate Change in Continental Isotopic Records, 1993.
[51] Deng L. , Shangguan Z. P. , & Sweeney S. “Grain for Green” driven land use change and carbon sequestration on the Loess Plateau, China [J]. Scientific reports, 2014, 4(1): 1-8.
[52] Ding Zhongli, Liu Tungsheng, Rutter N. et al. Ice-volume forcing of East Asian winter monsoon variations in the past 800, 000 years [J]. Quaternary Research, 1995, 44(2): 149-159. doi: 10.1006/qres.1995.1059
[53] Fan S. , Gloor M. , Mahlman J et al. A large terrestrial carbon sink in North America implied by atmospheric and oceanic carbon dioxide data and models [J]. Science, 1998, 282(5388): 442-446. doi: 10.1126/science.282.5388.442
[54] Feng X. , Fu B. , Lu N et al. How ecological restoration alters ecosystem services: an analysis of carbon sequestration in China's Loess Plateau [J]. Scientific reports, 2013, 3(1): 1-5.
[55] Friedlingstein P. , O'sullivan M. , Jones M. W et al. Global carbon budget 2020 [J]. Earth System Science Data, 2020, 12(4): 3269-3340. doi: 10.5194/essd-12-3269-2020
[56] Galdo I D, Six J, Peressotti A, et al. Assessing the impact of land‐use change on soil C sequestration in agricultural soils by means of organic matter fractionation and stable C isotopes [J]. Global Change Biology, 2003, 9 (8): 1204-1213. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2486.2003.00657.x
[57] Galy A, France-Lanord C. Weathering processes in the Ganges–Brahmaputra basin and the riverine alkalinity budget [J].Chemical Geology, 1999, 159 (1-4): 0-60.
[58] Guo Zhengtang, Biscaye P. , Wei L et al. Summer monsoon variations over the last 1.2 Ma from the weathering of loess‐soil sequences in China [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2000, 27(12): 1751-1754. doi: 10.1029/1999GL008419
[59] He N. , Wen D. , Zhu J et al. Vegetation carbon sequestration in Chinese forests from 2010 to 2050 [J]. Global change biology, 2017, 23(4): 1575-1584. doi: 10.1111/gcb.13479
[60] IPCC. AR6 Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis[R], 2021.
[61] Kato T, Tang Y, Gu S, et al. Temperature and biomass influences on interannual changes in CO2 exchange in an alpine meadow on the Qinghai‐Xizang Plateau[J]. Global Change Biology, 2006, 12(7): 1285-1298.
[62] Khademi H. Submicroscopy and stable isotope geochemistry of carbonates and associated palygorskite in Iranian Aridisols [J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 2010, 50 (2): 207-216.
[63] Li Z P, Han F X, Su Y, et al. Assessment of soil organic and carbonate carbon storage in China [J]. Geoderma, 2007, 138 (1-2): 119-126. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2006.11.007
[64] Li J. , Li M. , Dong L et al. Plant productivity and microbial composition drive soil carbon and nitrogen sequestrations following cropland abandonment [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 744: 140802. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140802
[65] Liu Z, Macpherson G L, Groves C, et al. Large and active CO2 uptake by coupled carbonate weathering [J]. Earth Science Reviews, 2018: 42-49.
[66] Maher K, Chamberlain C P. Hydrologic regulation of chemical weathering and the geologic carbon cycle [J]. Science, 2014, 343 (6178): 1502-1504. doi: 10.1126/science.1250770
[67] Pan Y. , Birdsey R. A. , Fang J. et al. A large and persistent carbon sink in the world’s forests [J]. Science, 2011, 333(6045): 988-993. doi: 10.1126/science.1201609
[68] Sun Y. , Kutzbach J. , An Z. et al. Astronomical and glacial forcing of East Asian summer monsoon variability [J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2015, 115: 132-142. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2015.03.009
[69] Wang X, Wang J, Xu M, et al. Carbon accumulation in arid croplands of northwest China: pedogenic carbonate exceeding organic carbon [J]. Scientific reports, 2015, 5: 11439. doi: 10.1038/srep11439
[70] Wang J, Feng L, Palmer P I, et al. Large Chinese land carbon sink estimated from atmospheric carbon dioxide data[J]. Nature, 2020, 586(7831): 720-723.
[71] Wu W, Zheng H, Yang J, et al. Chemical weathering, atmospheric CO2 consumption, and the controlling factors in a subtropical metamorphic-hosted watershed [J]. Chemical Geology, 2013, 356: 141-150. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.08.014
[72] Xiao J, Jin Z. D. , Zhang, F. Spatial characteristics and controlling factors of chemical weathering of loess in the dry season in the middle Loess Plateau, China [J]. Hydrological Processes, 2016, 30: 4855-4869. doi: 10.1002/hyp.10959
[73] Yang L, Zhang F, Hu Y, et al. Seasonal Variations of Chemical Weathering and CO2 Consumption Processes in the Headwater (Datong River Basin) of the Yellow River Draining the Xizang Plateau [J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2022, 10:
[74] Yang Shiling, Ding Zhongli, Li Yangyang et al. Warming-induced northwestward migration of the East Asian monsoon rain belt from the Last Glacial Maximum to the mid-Holocene [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2015, 112(43): 13178-13183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1504688112
[75] Yi Z, Fu S, Yi W, et al. Partitioning soil respiration of subtropical forests with different successional stages in south China [J]. Forest Ecology & Management, 2007, 243 (2-3): 178-186.
[76] Yu Guirui, Zhu X. J. , Fu Y. L. et al. Spatial patterns and climate drivers of carbon fluxes in terrestrial ecosystems of China [J]. Global Change Biology, 2013, 19(3): 798-810. doi: 10.1111/gcb.12079
[77] Zhang L, Xiaoqun B, Bullet Q, et al. Estimation of carbon sink fluxes in the Pearl River basin (China) based on a water–rock–gas–organism interaction model [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2015, 74 (2): 945-952. doi: 10.1007/s12665-014-3788-2
[78] Zhang F, Jin Z, Li F, et al. Controls on seasonal variations of silicate weathering and CO2 consumption in, two river catchments on the NE Xizang Plateau [J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 62: 547-560. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.11.004
[79] Zhang Zeke, Li Gaojun, Cai Yanjun et al. Millennial‐Scale Monsoon Variability Modulated by Low‐Latitude Insolation During the Last Glaciation [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2022, 49(1), e2021GL096773.
[80] Zhu Y. , Jia X. , Shao M. et al. Loess thickness variations across the Loess Plateau of China [J]. Surveys in Geophysics, 2018, 39(4): 715-727. doi: 10.1007/s10712-018-9462-6
-




 下载:
下载:
