Response of Ecosystem Carbon Fixation Value to Forest System Structure in Yulin City
-
摘要:
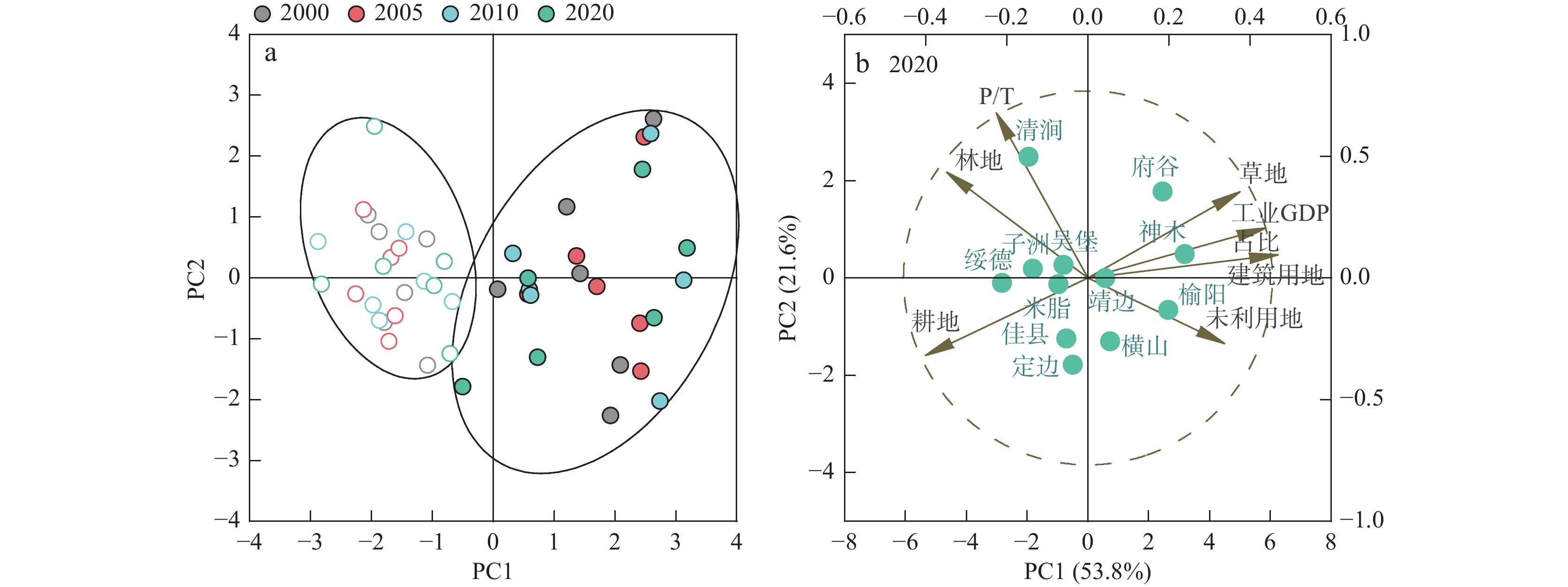
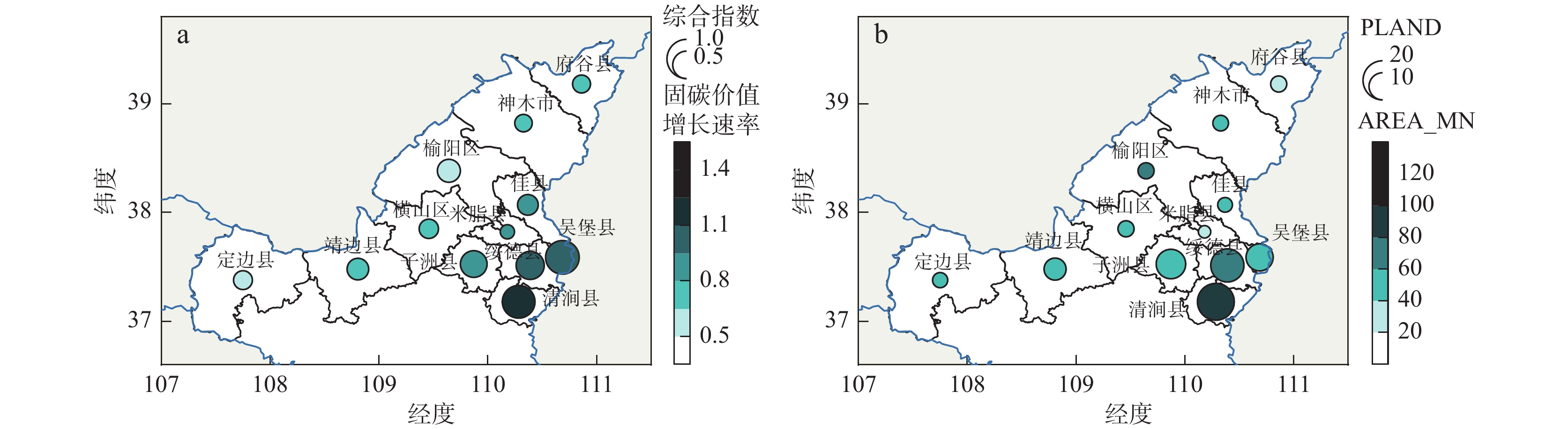
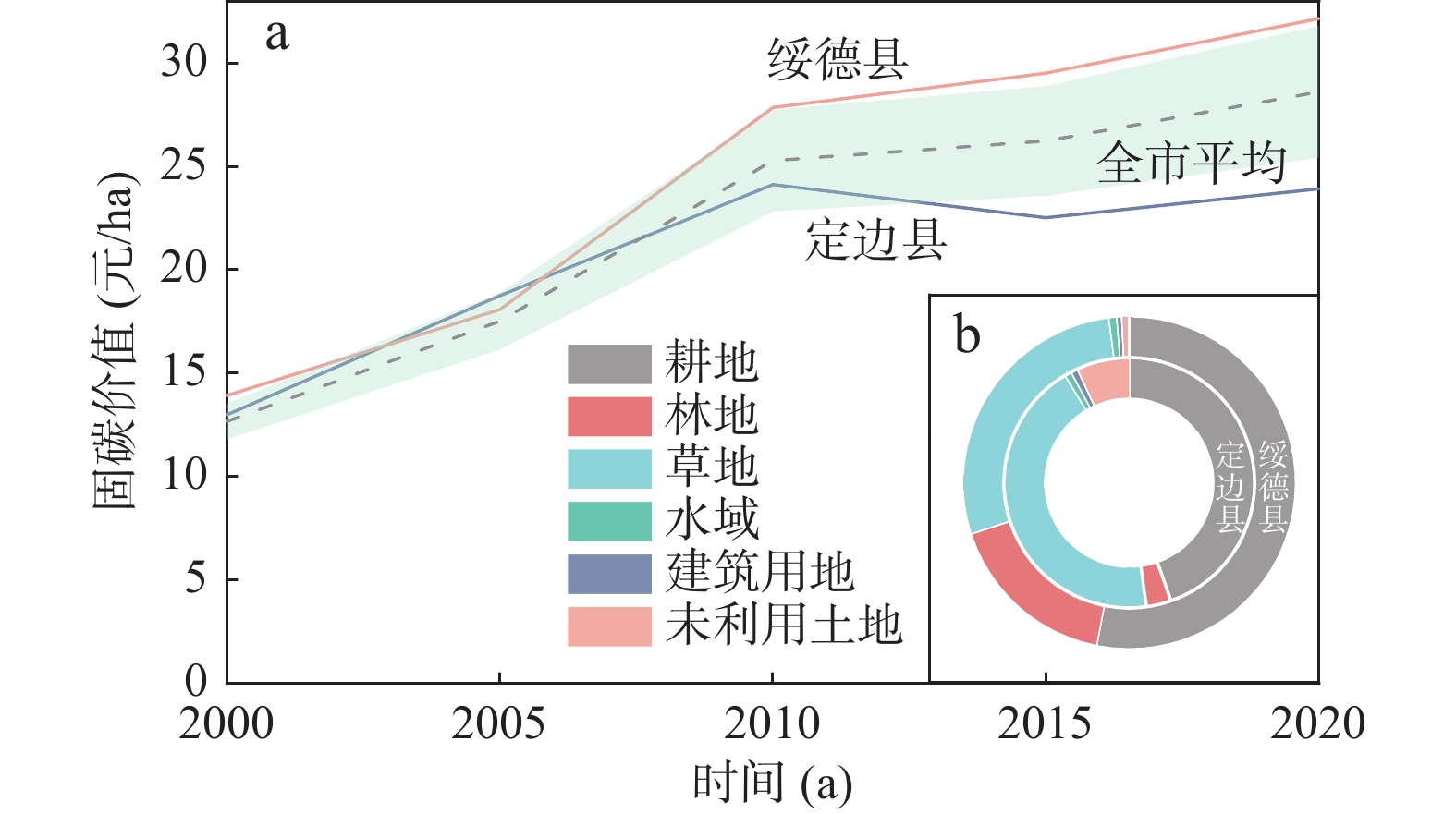
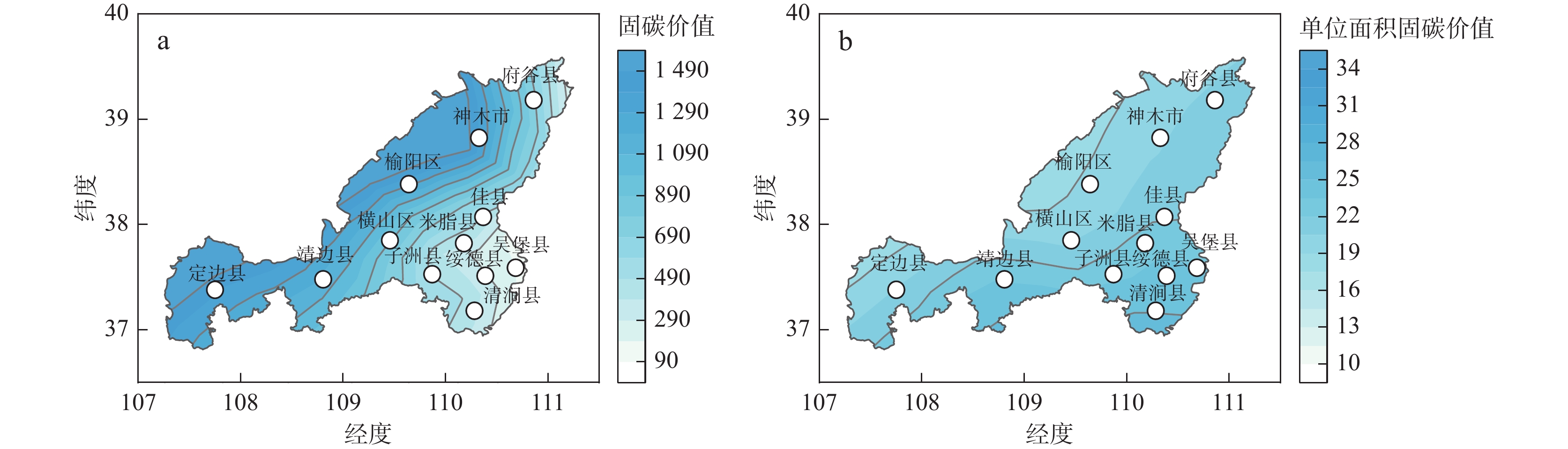
将生态资源纳入经济体系统筹管理是环境可持续发展的必然要求。对于生态脆弱地区,加强环境压力变化下的资源管理尤为重要。笔者从系统结构的角度理解生态系统固碳功能变化特征,在榆林地区结合景观结构指数对固碳功能进行空间分析。2000~2020年榆林市生态系统固碳服务价值持续增加,2000~2010年增长较快,2010~2020年增速减缓。在空间分布方面,单位面积固碳价值从东南向西北递减,东南部的增长速率也更快。工业活动是形成榆林市生态系统固碳价值西北、东南分划的主要因素,东南部区县受生态系统结构变化的影响更强。研究结果表明,在生态脆弱区实施生态建设和修复工程时,应综合考虑生态系统的结构性以提高地区生态系统潜在的功能性。
Abstract:It is an inevitable requirement of environmentally sustainable development to bring ecological resources into the overall management of the economic system. For ecologically fragile areas, it is particularly important to strengthen resource management under changing environmental pressures. This paper attempts to understand the change characteristics of carbon fixation function of ecosystem from the perspective of system structure, and carries out spatial analysis of carbon fixation function in Yulin area combined with landscape structure index. From 2000 to 2020, the carbon sequestration service value of Yulin’s ecosystem continued to increase, and the growth rate was fast in 2000~2010 and slowed down in 2010~2020. In terms of spatial distribution, the carbon sequestration value per unit area s decreases from southeast to northwest, and the growth rate in southeast is also faster. Industrial activities are the main factor to form the northwest and southeast division of carbon sequestration value of Yulin, and the southeast counties are more affected by the change of ecosystem structure. The results of the study suggest that we should comprehensively consider the structure of the ecosystem to improve the potential functionality of the regional ecosystem when implementing ecological construction and restoration projects in the ecological fragile areas in the future.
-
Key words:
- ecosystem services /
- carbon fixation value /
- system structure /
- ecologically fragile area
-

-
[1] 陈仲新, 张新时. 中国生态系统效益的价值[J]. 科学通报, 2000, 45(1): 17-22 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2000.01.004
CHEN Zhongxin, ZHANG Xinshi. The value of ecosystem benefits in China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2000, 45(1): 17-22. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2000.01.004
[2] 封建民, 文琦, 郭玲霞. 风沙过渡区土地利用变化对生态系统服务价值的影响——以榆林市为例[J]. 水土保持研究, 2018, 25(4): 304-308 doi: 10.13869/j.cnki.rswc.2018.04.045
FENG Jianmin, WEN Qi, GUO Lingxia. Effects of land use change on the ecosystem service value in ecotone of wind and sand[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 25(4): 304-308. doi: 10.13869/j.cnki.rswc.2018.04.045
[3] 国家市场监督管理总局, 国家标准化管理委员会. 生态系统评估、生态系统生产总值(GEP)核算技术规范[S]. 国家市场监督管理总局, 国家标准化管理委员会, 2020.
[4] 李登科, 王钊. 气候变化和人类活动对陕西省植被NPP影响的定量分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1071-1079 doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.06.001
LI Dengke, WANG Zhao. Quantitative analysis of the impact of climate change and human activities on vegetation NPP in Shaanxi Province[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2022, 31(6): 1071-1079. doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.06.001
[5] 李晶, 任志远. 基于GIS的陕北黄土高原土地生态系统固碳释氧价值评价[J]. 中国农业科学, 2011, 44(14): 2943-2950 doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2011.14.011
LI Jing, REN Zhiyuan. Research on the values of CO2 fixation and O2 release by landuse ecosystem in Loess Plateau in Northern Shaanxi province[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2011, 44(14): 2943-2950. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2011.14.011
[6] 欧阳志云, 王效科, 苗鸿. 中国陆地生态系统服务功能及其生态经济价值的初步研究[J]. 生态学报, 1999, 19(5): 607-613 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.1999.05.004
OUYANG Zhiyun, WANG Xiaoke, MIAO Hong. A primary study on Chinese terrestrial ecosystem services and their ecological-economic values[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 1999, 19(5): 607-613. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.1999.05.004
[7] 潘勇军, 王兵, 牛香. 让自然资本成为主流, 用生态GDP核算美丽中国. 温带林业研究[J]. 温带林业研究, 2018, 1(3): 10-18 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-4900.2018.03.003
PAN Yongjun, WANG Bin, NIU Xiang. Mainstreaming the economics of natural capital and accounting the eco-GDP of beautiful China[J]. Journal of Temperate Forestry Research, 2018, 1(3): 10-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-4900.2018.03.003
[8] 陕西省生态环境厅. 2021年陕西省生态环境状况公报[R]. 陕西省生态环境厅, 2022.
[9] 孙萍萍, 张茂省, 贾俊, 等. 中国西部黄土区地质灾害调查研究进展[J]. 西北地质, 2022, 55(3): 96-107
SUN Pingping, ZHANG Maosheng, Jia Jun, et al. Geo-hazards research and investigation in the Loess Regions of Western China[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2022, 55(3): 96-107.
[10] 王德丽, 殷淑燕, 王海燕, 等. 近50年陕北地区的气候变化 [J]. 干旱区研究, 2011, 28(2): 262-267. doi: 10.13866/j.azr.2011.02.022
WANG Deli, YIN Shuyan, WANG Haiyan, et al. Analysis on climate change in North Shaanxi Province [J]. Arid Zone Research, 2011, 28(2): 262-267. doi: 10.13866/j.azr.2011.02.022
[11] 谢高地, 张彩霞, 张雷明, 等. 基于单位面积价值当量因子的生态系统服务价值化方法改进[J]. 自然资源学报, 2015, 30(8): 1243-1254 doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.2015.08.001
XIE Gaodi, ZHANG Caixia, ZHANG Leiming, et al. Improvement of the evaluation method for ecosystem service value based on per unit area[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2015, 30(8): 1243-1254. doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.2015.08.001
[12] 杨文峰, 李星敏, 鲁渊平. 陕西省近50年气候变化及其对水资源的影响[J]. 陕西气象, 2002, 6: 1-6
YANG Wenfeng, LI Xingmin, LU Yuanping. Climate change and its impact on water resources in Shaanxi province in recent 50 years. Journal of Shaanxi Meteorology, 2002, 6: 1-6.
[13] 仲原, 王春梅, 庞国伟, 等. 黄土高原浅沟空间分异特征[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(5): 1798-1810
ZHONG Yuan, WANG Chunmei, PANG Guowei, et al. Spatial variation of ephemeral gully in the Loess Plateau[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(5): 1798-1810.
[14] Cortina J, Maestre FT, Vallejo R, et al. Ecosystem structure, function, and restoration success: are the related? [J] Journal for Nature Conservation, 2006, 14: 152-160. doi: 10.1016/j.jnc.2006.04.004
[15] Costanza R, d'Arge R, de Groot R, et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital [J]. Nature, 1997, 387: 253-260. doi: 10.1038/387253a0
[16] Elmqvist T, Folke C, Nyström M, et al. Response diversity, ecosystem change, and resilience[J]. The Ecological Society of America, 2003, 1(9): 488-494.
-



 下载:
下载: