Application of Multi–source Remote Sensing Technology on Investigation of Geological Disasters Induced by Rainfall in Mian County
-
摘要:
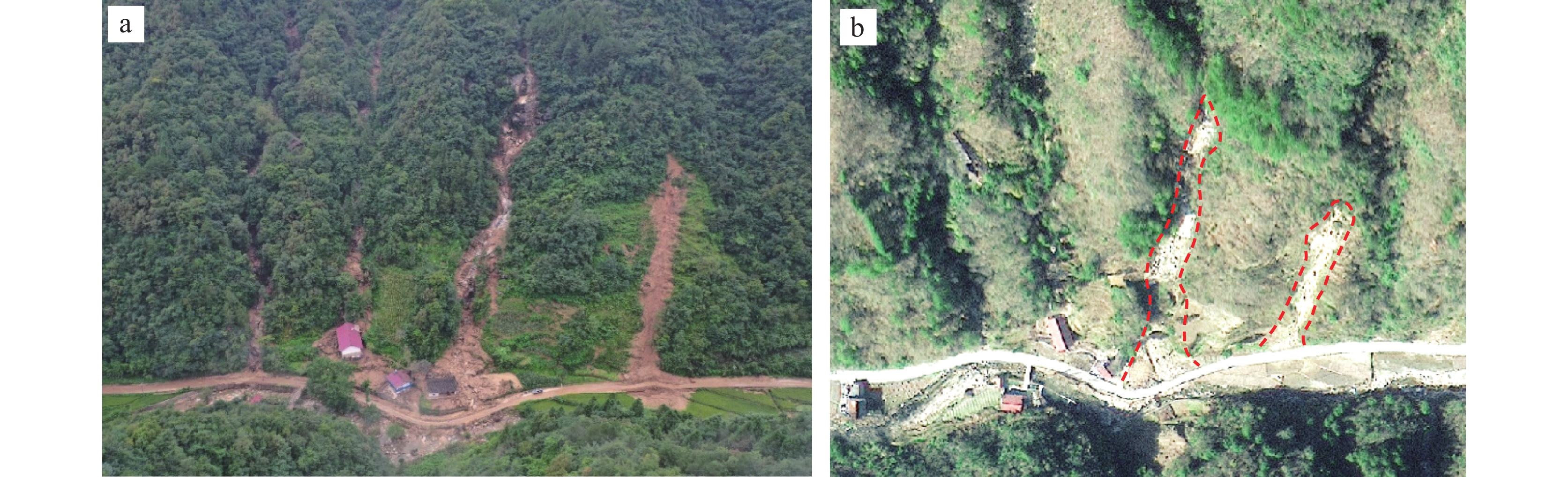
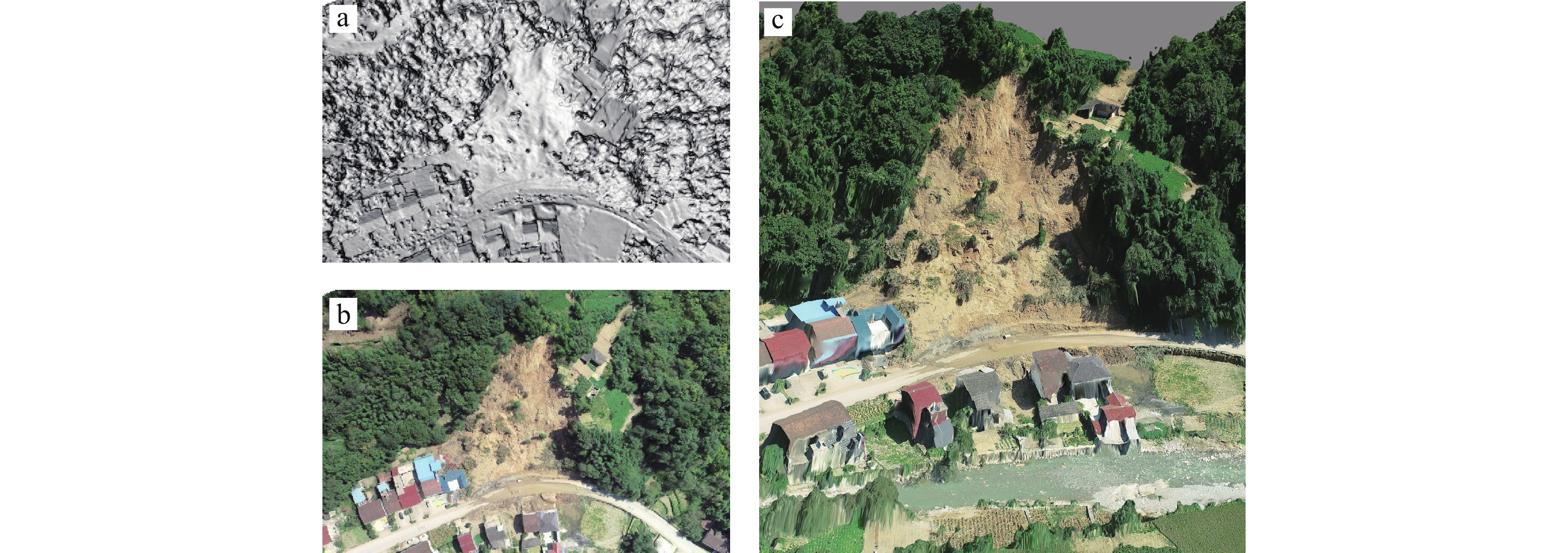
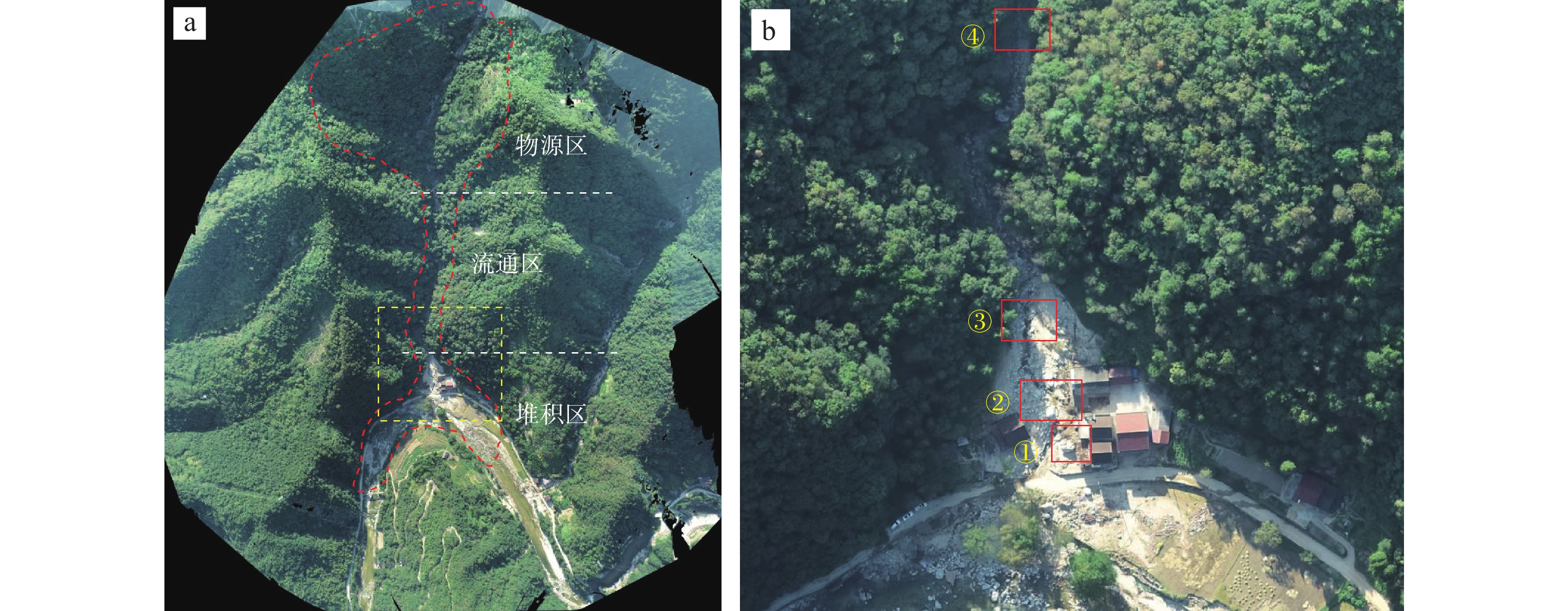
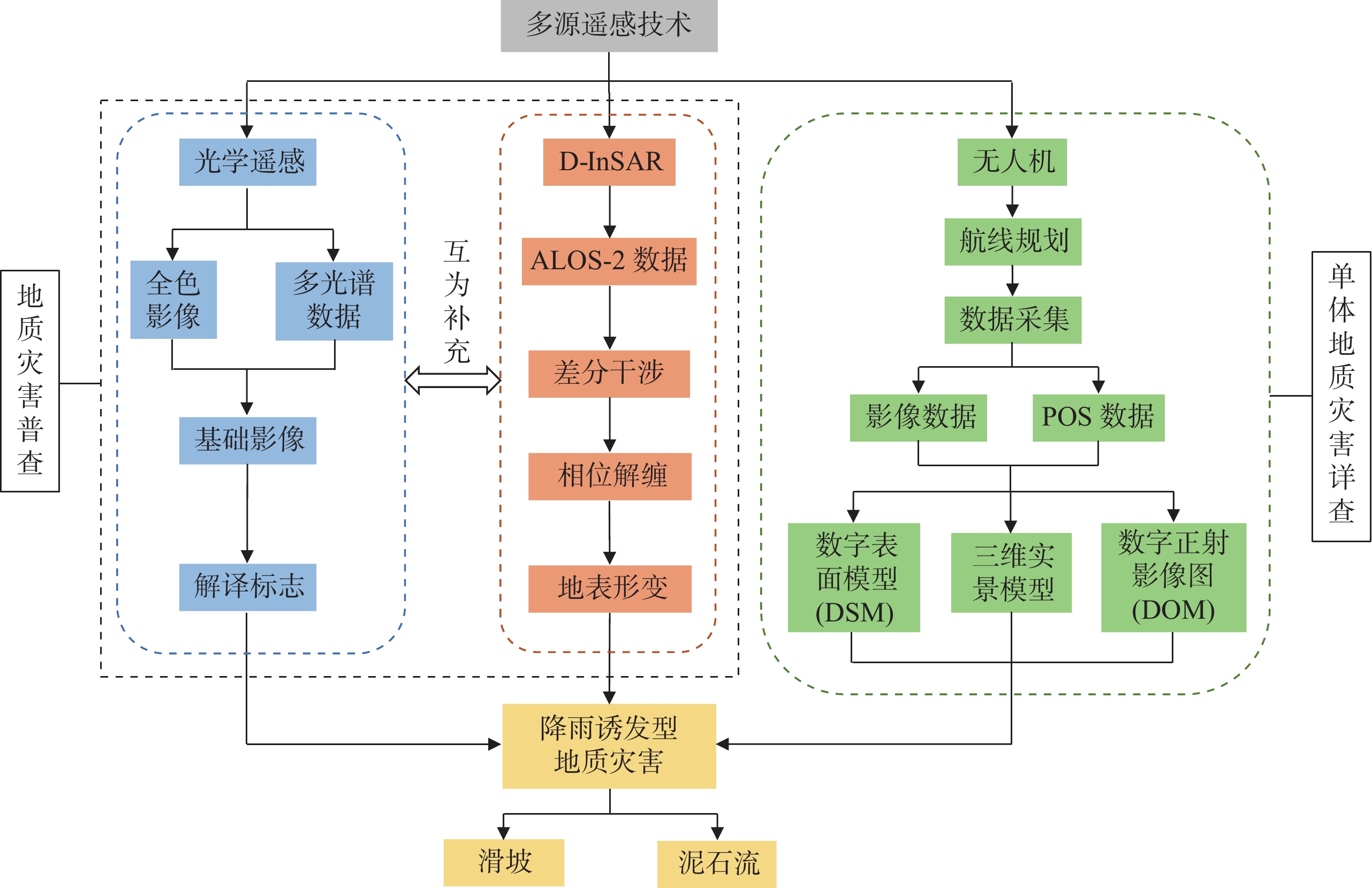
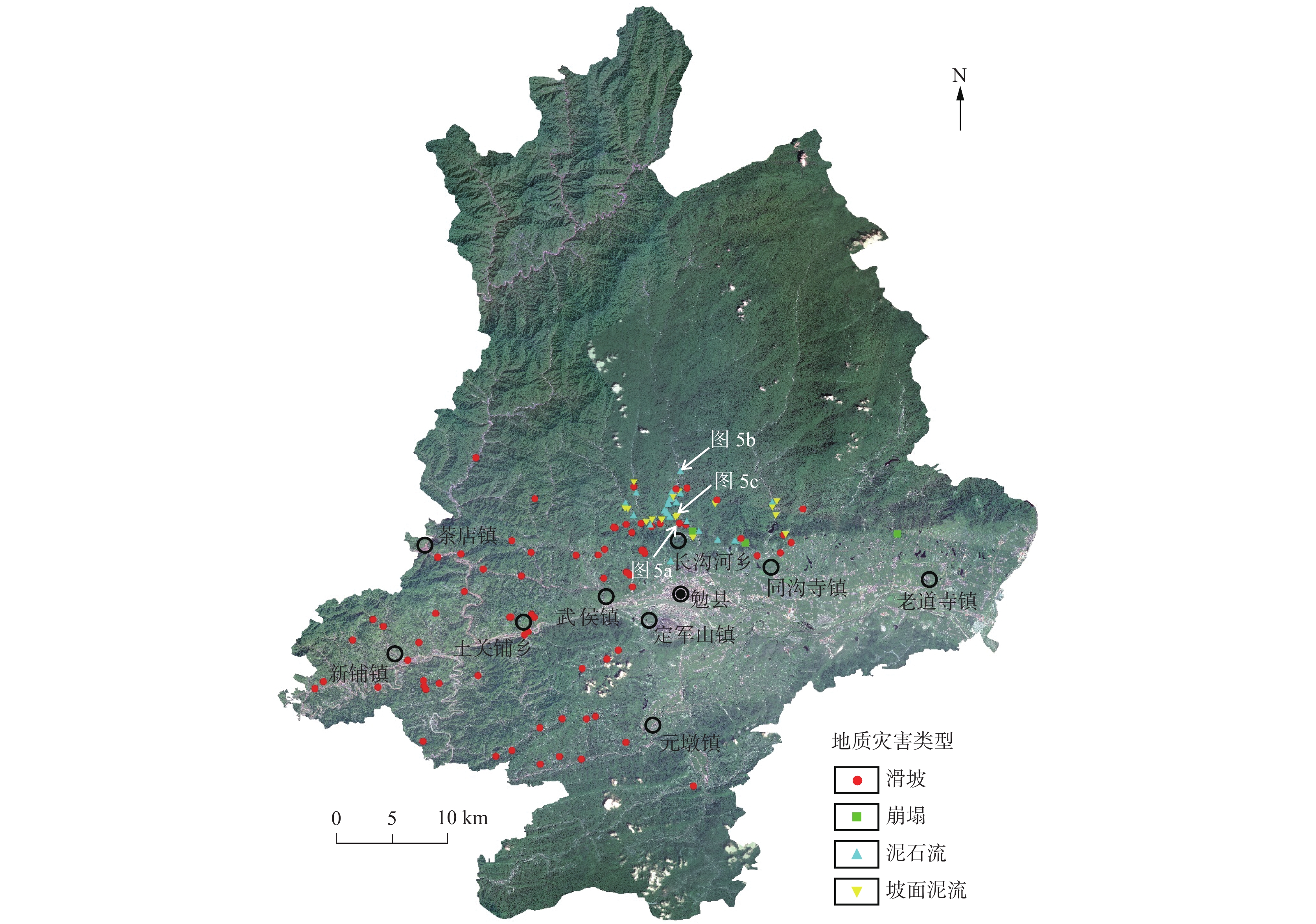
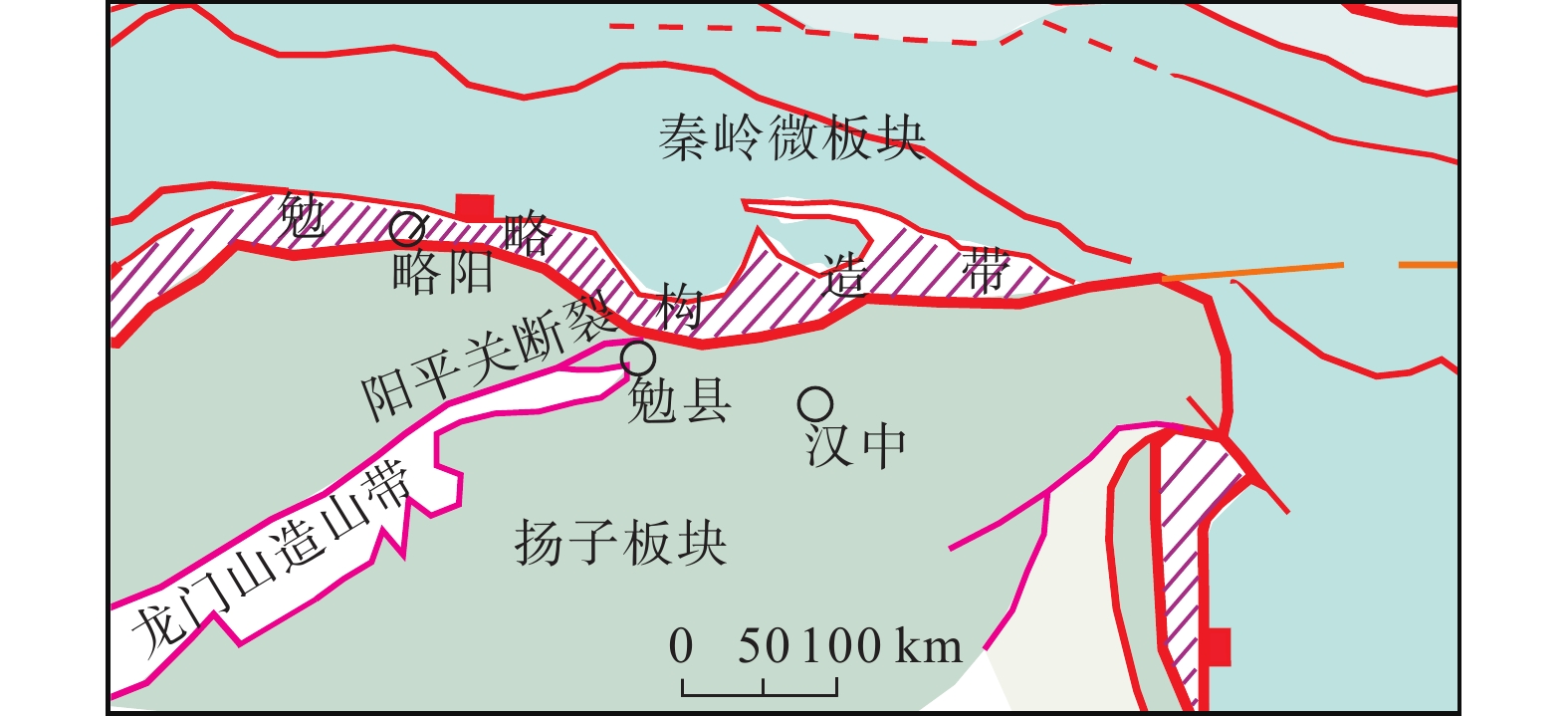
陕南秦巴山区地形地貌、地质构造和气候条件复杂,易发和频发滑坡、泥石流等地质灾害。由于该区地形高差大且植被覆盖率高,传统的人工地面调查排查在地质灾害的调查识别中难度较大,需借助先进的地质灾害监测识别技术方法。笔者综合采用光学遥感、合成孔径雷达干涉测量(Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar, InSAR)和无人机航测等多种技术手段,对陕南勉县“8.22”强降雨诱发的地质灾害进行应急调查与识别分析,探索多源遥感技术对降雨诱发型地质灾害的识别能力与有效性。研究表明,多源遥感技术在强降雨诱发区域性地质灾害的识别和应急调查中能够发挥重要作用,可大大减少现场工作时间,并能提供全方位、多角度和可视化的高精度遥感成果;光学遥感、InSAR、无人机航测等技术具有各自的优势和识别范畴,仅靠单一的技术手段难以完全有效地解决灾害隐患识别问题,建立一套多源遥感技术相互融合、优势互补的综合调查识别体系,是强降雨条件下区域性地质灾害快速调查识别与评价的有效途径。
Abstract:Qinba Mountain Area in southern of Shaanxi province has characteristics of complex terrain and geomorphology, geological structure and climate conditions, and is prone to occurrence of landslide, debris flow and other geological disasters. Due to the large topographic elevation difference and high vegetation coverage in this area, the traditional artificial field investigation is difficult in the identification and investigation of geological disasters, and thus the advanced geological disaster monitoring and identification methods are needed. In this study, a variety of technical methods including optical remote sensing, InSAR and unmanned aerial vehicle photography are used to identify and analyze the hidden dangers of geological disasters induced by “8.22” heavy rainfall in Mian County, southern Shaanxi province, and to explore the identification ability and effectiveness of multi–source remote sensing technology for rainfall–induced geological disasters. The research shows that multi–source remote sensing technology can play an important role in the identification and emergency investigation of regionally geological disasters caused by heavy rainfall. Moreover, the multi–source remote sensing technology can greatly save the working time in field, and provide high–precision remote sensing results with virtue of all aspects, multi–angle and visuality. Optical remote sensing, InSAR, and unmanned aerial vehicle photography have their own advantages and identification categories. It is difficult to completely and effectively solve the problem in hazard identification only by means of a single technical approach. Establishing a multi–source remote sensing–based comprehensive identification system with characteristics of mutual integration and complementary advantage is an effective way to the rapid identification and evaluation of regional geological disasters under heavy rainfall conditions.
-
Key words:
- geological disaster /
- optical remote sensing /
- InSAR technology /
- unmanned aerial vehicle /
- Mian County
-

-
[1] 蔡杰华, 张路, 董杰, 等. 九寨沟震后滑坡隐患雷达遥感早期识别与形变监测[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2020, 45(11): 1707-1716
CAI Jiehua, ZHANG Lu, DONG Jie, et al. Detection and monitoring of post-earthquake landslides in Jiuzhaigou using radar remote sensing[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2020, 45(11): 1707-1716.
[2] 戴可人, 铁永波, 许强, 等. 高山峡谷区滑坡灾害隐患InSAR早期识别—以雅砻江中段为例[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(3): 554-568
DAI Keren, TIE Yongbo, XU Qiang, et al. Early Identification of Potential Landslide Geohazards in Alpine-canyon Terrain Based on SAR Interferometry—a Case Study of the Middle Section of Yalong River[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(3): 554-568.
[3] 丁辉, 张茂省, 朱卫红, 等. 黄土滑坡高分辨率遥感影像识别——以陕西省延安市地区为例[J]. 西北地质, 2019, 52(03): 231-239.
DING Hui, ZHANG Maosheng, ZHU Weihong, et al. High resolution remote sensing for the identification of loess landslides: example from Yan’an City[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2019, 52(03): 231-239.
[4] 董秀军. 三维空间影像技术在地质工程中的综合应用研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2015
DONG Xiujun. Research of comprehensive application of three-dimensional image technology in geological engineering[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2015.
[5] 韩海辉, 李健强, 易欢, 等. 遥感技在西北地质调查中的应用及展望[J]. 西北地质, 2022, 55(3): 155-169
HAN Haihui, LI Jianqiang, YI Huan, et al. Application and prospect of remote sensing technology in geological survey of northwast China[J]. Northweatern Geology, 2022, 55(3): 155-169.
[6] 黄洁慧, 谢谟文, 王立伟. 基于差分干涉合成孔径雷达技术的米林滑坡形变监测[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2019, 19(25): 7-12
HUANG Jiehui, XIE Mowen, WANG Liwei. The deformation monitoring of Milin landslide based on D-InSAR technology[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2019, 19(25): 7-12.
[7] 黄玉华, 武文英, 冯卫, 等. 秦岭山区南秦河流域崩滑地质灾害发育特征及主控因素[J]. 地质通报, 2015, 34(11): 2116-2122
HUANG Yuhua, WU Wenying, FENG Wei, et al. Characteristics of main controlling factors of landslide in Nanqin River, Qinling Mountains[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2015, 34(11): 2116-2122.
[8] 梁京涛. 高烈度地震区典型地质灾害遥感早期识别及震后演化特征研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2018
LIANG Jingtao. Study on the early remote sensing identification and evolution characteristics of typical geological disaster in high intensity earthquake zone[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2018.
[9] 李万林, 周英帅. 基于D-InSAR技术的地质灾害和监测预警[J]. 测绘工程, 2021, 30(1): 66-70
LI Wanlin, ZHOU Yingshuai. Early warning and monitoring of geohazards based on D-InSAR technology[J]. Engineering of Surveying and Mapping, 2021, 30(1): 66-70.
[10] 李振洪, 宋闯, 余琛, 等. 卫星雷达遥感在滑坡灾害探测和监测中的应用: 挑战与对策[J]. 武汉大学学报∙信息科学版, 2019, 44(7): 967-979
LI Zhenhong, SONG Chuang, YU Chen, et al. Application of satellite radar remote sensing to landslide detection and monitoring: challenges and solutions[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(7): 967-979.
[11] 李志忠, 孙萍萍, 陈霄燕, 等. 基于卫星遥感技术的绿色发展指标—以中国西部地区为例[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2022a, 44(2): 143-155
LI Zhizhong, SUN Pingping, CHEN Xiaoyan, et al. Green development index based on satellite remote sensing technology – a case study in the western China[J]. Journal of earth sciences and environment, 2022a, 44 (2): 143-155.
[12] 李志忠, 卫征, 陈霄燕, 等. 新型对地观测技术与地球健康体检[J]. 西北地质, 2022b, 55(02): 56-70
LI Zhizhong, WEI Zheng, CHEN Xiaoyan, et al. New earth observation technology and earth health examination[J]. Northweatern Geology, 2022b, 55(02): 56-70.
[13] 李志忠, 杨日红, 党福星, 等. 高光谱遥感卫星技术及其地质应用[J]. 地质通报, 2009, 28(2-3): 270-277
LI Zhizhong, YANG Rihong, DANG Fuxing, et al. The hyperspectral remote sensing technology and its application[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2009, 28(2-3): 270-277.
[14] 刘星洪, 姚鑫, 於开炳, 等. 川藏高速巴塘—芒康段地质灾害遥感综合早期识别研究[J]. 工程科学与技术, 2020, 52(6): 49-60
LIU Xinghong, YAO Xin, YU Kaibing, et al. Remote sensing integrated identification of geological hazards in the Batang - Mangkang section of Sichuan – Xizang highway[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 2020, 52(6): 49-60.
[15] 陆会燕, 李为乐, 许强, 等. 光学遥感与InSAR结合的金沙江白格滑坡上下游滑坡隐患早期识别[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2019, 44(9): 1342-1354.
LU Huiyan, LI Weile, XU Qiang, et al. Early Detection of Landslides in the Upstream and Downstream Areas of the Baige Landslide, the Jinsha River Based on Optical Remote Sensing and InSAR Technologies[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(9): 251-261.
[16] 陆松年, 陈志宏, 李怀坤, 等. 秦岭造山带中—新元古代(早期)地质演化[J]. 地质通报, 2004, 23(2): 107-112
LU Songnian, CHEN Zhihong, LI Huaikun, et al. Late Mesoproterozoic-early Neoproterozoic evolution of the Qinling orogeny[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2004, 23(2): 107-112.
[17] 宁奎斌, 李永红, 何倩, 等. 2000~2016年陕西省地质灾害时空分布规律及变化趋势[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2018, 29(1): 93-101
NING Kuibin, LI Yonghong, HE Qian, et al. The spatial and temporal distribution and trend of geological disaster in Shaanxi Province from 2000 to 2016[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2018, 29(1): 93-101.
[18] 苏晓军, 张毅, 贾俊, 等. 基于InSAR技术的秦岭南部略阳县潜在滑坡灾害识别研究[J]. 山地学报, 2021, 39(1): 59-70
SU Xiaojun, ZHANG Yi, JIA Jun, et al. InSAR-based monitoring and identification of potential landslides in Lueyang County, the Southern Qinling Mountains, China[J]. Mountain Research, 2021, 39(1): 59-70.
[19] 王东升, 王宗起, 庞绪勇, 等. 陕西勉略宁地区铜厂湾金矿床辉绿岩年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2021, 40(1): 1-18
WANG Dongsheng, WANG Zongqi, PANG Xuyong, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of diabase veins from Tongchangwan gold deposit in Mianluening area of Shaanxi Province and its tectonic significance[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2021, 40(1): 1-18.
[20] 王绚, 范宣梅, 杨帆, 等. 植被茂密山区地质灾害遥感解译方法研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2020, 45(11): 1771-1781
WANG Xuan, FAN Xuanmei, YANG Fan, et al. Remote Sensing Interpretation Method of Geological Hazards in Lush Mountainous Area[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2020, 45(11): 1771-1781.
[21] 王志一, 徐素宁, 王娜, 等. 高分辨率光学和SAR遥感影像在地震地质灾害调查中的应用——以九寨沟M7.0级地震为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2018, 29(5): 81-88
WANG Zhiyi, XU Suning, WANG Na, et al. Application of the high resolution optical and SAR remote sensing data images induced by the Jiuzhaigou M7.0 earthquake geological hazards survey[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2018, 29(5): 81-88.
[22] 许强. 对地质灾害隐患早期识别相关问题的认识与思考[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2020, 45(11): 1651-1659
XU Qiang. Understanding and consideration of related issues in early identification of potential geohazards[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2020, 45(11): 1651-1659.
[23] 许强, 董秀军, 李为乐. 基于天-空-地一体化的重大地质灾害隐患早期识别与监测预警[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2019, 44(7): 957-966
XU Qiang, DONG Xiujun, LI Weile. Integrated space-air-ground early detection, monitoring and warning system for potential catastrophic geohazards[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(7): 957-966.
[24] 杨燕, 杜甘霖, 曹起铜. 无人机航测技术在地质灾害应急测绘中的研究与应用—以9.28丽水山体滑坡应急测绘为例[J]. 测绘通报, 2017, (增刊1): 119-122
YANG Yan, DU Ganlin, CAO Qitong. Application of UAV aerial surveying technology in geological disaster emergency mapping[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2017, (sup. 1): 119-122.
[25] 姚鑫, 凌盛, 李凌婧, 等. 中巴经济走廊喀喇昆仑山区段蠕滑滑坡InSAR识别研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2016, 24(增刊1): 1283-1289
YAO Xin, LING Sheng, LI Lingjing, et al. Study of slow-moving landslide recognition by InSAR in the Karakoram Mountain section of China-Pakistan economic corridor[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2016, 24(sup. 1): 1283-1289.
[26] 叶伟林, 宿星, 魏万鸿, 等. 无人机航测系统在滑坡应急中的应用[J]. 测绘通报, 2017, (9): 70-74 doi: 10.13474/j.cnki.11-2246.2017.0290
YE Weilin, SU Xing, WEI Wanhong, et al. Application of UAV aerial photograph system in emergency rescue and relief for landslide[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2017, (9): 70-74. doi: 10.13474/j.cnki.11-2246.2017.0290
[27] 张茂省, 贾俊, 王毅, 等. 基于人工智能(AI)的地质灾害防控体系建设[J]. 西北地质, 2019, 52(02): 103-116.
ZHANG Maosheng, JIA Jun WANG Yi, et al. Construction of geological disaster prevention and control system based on AI[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2019, 52(02): 103-116.
[28] 张茂省, 雷学武, 校培喜, 等. 遥感技术在黄土高原区地质灾害详细调查中的应用[J]. 西北地质, 2007, 162(03): 92-97.
ZHANG Maosheng, LEI Xuewu, XIAO Peixi, et al. Application of remote sensing in detailed survey of geological hazards in Loess Plateau[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2007, 162(03): 92-97.
[29] Dai Keren, Xu Qiang, Li Zhenhong, et al. Post-disaster assessment of 2017 catastrophic Xinmo landslide (China) by spaceborne SAR interferometry[J]. Landslides, 2019, 16: 1189-1199. doi: 10.1007/s10346-019-01152-4
[30] Dong Jie, Liao Mingsheng, Xu Qiang, et al. Detection and displacement characterization of landslides using multi-temporal satellite SAR interferometry: A case study of Danba County in the Dadu River Basin[J]. Engineering Geology, 2018, 240: 95-109. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.04.015
[31] Hu Sheng, Qiu Haijun, Pei Yanqian, et al. Digital terrain analysis of a landslide on the loess tableland using high-resolution topography data[J]. Landslides, 2019, 16: 617-632. doi: 10.1007/s10346-018-1103-0
[32] Li Minghua, Zhang Lu, Dong Jie, et al. Characterization of pre- and post-failure displacements of the Huangnibazi landslide in Li County with multi-source satellite observations[J]. Engineering Geology, 2019, 257: 105140. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.05.017
[33] Meng Qingkai, Li Weile, Raspini Federico, et al. Time-series analysis of the evolution of large-scale loess landslides using InSAR and UAV photogrammetry techniques: a case study in Hongheyan, Gansu Province, Northwest China[J]. Landslides, 2021, 18: 251-261. doi: 10.1007/s10346-020-01490-8
[34] Tang C, Zhu J, Li WL, et al. Rainfall-triggered debris flows following the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2009, 68(2): 187-194. doi: 10.1007/s10064-009-0201-6
[35] Xu Qiang, Peng Dalei, Zhang Shuai, et al. Successful implementations of a real-time and intelligent early warning system for loess landslides on the Heifangtai terrace, China[J]. Engineering Geology, 2020, 278: 105817. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105817
-



 下载:
下载: