Spatial and Temporal Distribution and Driving Factors of Ecosystem Carbon Sink in Northwest China
-
摘要:
西北地区气候干旱、降水稀少,能源丰富,生态环境脆弱敏感,是双碳目标战略实现的难点和关键区域,其生态系统碳汇功能及其驱动因素研究具有非常重要的意义。笔者在分析近40年间碳汇用地演化的基础上,揭示了碳汇的时空变化规律,深入探讨了碳汇变化与地形地貌、温度和降水等主要驱动因素的关系。结果表明:①西北地区碳汇用地类型整体变化不大,但局部有一定的变化。②2020年生态碳汇量约为5 826.44万tC/a,其中林地占主导地位,其次为草地、水域、耕地、湿地、未利用地;碳汇量从大到小依次为新疆、陕西、甘肃、青海、内蒙古(西北片区)、宁夏;碳汇强度大小依次为陕西、甘肃、宁夏、新疆、青海、内蒙古(西北片区);40年来碳汇量变化整体呈波动上升趋势,个别区域在某一时期有所下降。③碳汇驱动因素主要有地形地貌、降雨和气温,地形地貌决定了生态系统碳汇强度,碳汇强度与降水呈强正相关性,与气温呈现正相关。
Abstract:Northwest China is a difficult and key area for the realization of the dual carbon target strategy due to its arid climate, scarce precipitation, abundant energy and fragile and sensitive ecological environment. The study on its ecosystem carbon sink function and its driving factors is of great significance. Based on the analysis of the evolution of carbon sink land in the past 40 years, this paper reveals the temporal and spatial change law of carbon sink, and deeply explores the relationship between carbon sequestration change and major driving factors such as topography, temperature, and precipitation.The results show that: ① The overall change of land types for carbon sink in northwest China is small, but there are some changes in some parts. ② In 2020, the ecological carbon sinks will be about 58264400 tC/a, of which forest land will dominate, followed by grassland, water area, farmland, wetland and unused land; From large to small, the carbon sinks is Xinjiang, Shaanxi, Gansu, Qinghai, Inner Mongolia (northwest area), Ningxia; The carbon sink intensity is in order of Shaanxi, Gansu, Ningxia, Xinjiang, Qinghai, Inner Mongolia (northwest region). Over the past 40 years, the change of carbon sinks has shown an overall upward trend,and declined in some regions in a certain period. ③ The driving factors of carbon sink mainly include landform, rainfall and temperature. The landform determines the intensity of ecological carbon sink. The intensity of carbon sink is strongly positively correlated with rainfall and positively correlated with temperature.
-
Key words:
- ecosystem /
- carbon sink /
- temporal and spatial changes /
- drivers /
- Northwest China
-

-
表 1 主要参数列表
Table 1. List of main parameters
参数 定义 取值 单位 来源 FCSR 林地固碳速率 0.28~1.36 tC/hm2·a 陆地GEP核算技术指南 β 林地土壤固碳系数 0.646 / 陆地GEP核算技术指南 GSR 草地土壤固碳速率 0.02~0.06 tC/hm2·a 陆地GEP核算技术指南 
湿地的固碳速率 0.3026~0.6711 tC/hm2·a 陆地GEP核算技术指南 
水域的固碳速率 0.303 tC/hm2·a 张赫等,2020 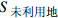
未利用地固碳速率 0.0005 tC/hm2·a 张赫等,2020 PR 秸秆还田推广实行率 0.8%~33.2% / 张国等,2017 NSC 土壤有机碳的变化 0.06 / 陆地GEP核算技术指南 H 土壤厚度 20 cm 陆地GEP核算技术指南 NF 化学氮肥施用量 / t 各省统计年鉴 CF 复合肥施用量 / t 各省统计年鉴 
作物j在当年的产量 / t 各省统计年鉴 
作物j的草谷比 见表2 / 农业农村部办公厅 表 2 不同作物的草谷比
Table 2. Ratio of grass to grain of different crops
作物 草谷比 作物 草谷比 水稻 0.623 油料 2.0 麦类 1.366 棉花 8.1 玉米 2.0 豆类 1.57 薯类 0.5 麻类 8.10 烟叶 1.0 其它谷物 0.85 表 3 40年间西北地区生态系统碳汇量及占比
Table 3. Carbon sink amount and proportion of ecosystem in Northwest China in 40 years
年份 碳汇量(104 tC/a)及占比 碳汇强度(tC/hm2) 林地 草地 耕地 湿地 水域 未利用地 合计 1980 2953.84 433.05 177.17 90.40 293.69 8.34 3956.50 0.105 74.66% 10.95% 4.48% 2.28% 7.42% 0.21% 100.00% 1990 2980.04 433.42 188.55 90.54 282.87 8.33 3983.73 0.106 74.81% 10.88% 4.73% 2.27% 7.10% 0.21% 100.00% 2000 2971.03 428.09 208.04 92.34 302.70 8.35 4010.57 0.107 74.08% 10.67% 5.19% 2.30% 7.55% 0.21% 100.00% 2010 3923.06 424.95 262.92 91.62 292.55 8.38 5003.49 0.133 78.41% 8.49% 5.25% 1.83% 5.85% 0.17% 100.00% 2015 5072.23 423.64 314.07 89.46 295.36 8.32 6203.08 0.165 81.77% 6.83% 5.06% 1.44% 4.76% 0.13% 100.00% 2020 4734.70 435.97 299.90 87.40 260.22 8.25 5826.44 0.155 81.26% 7.48% 5.15% 1.50% 4.47% 0.14% 100.00% 表 4 生态碳汇类型在地貌类型中的分布指数
Table 4. Distribution index of ecological carbon sink types in landform types
类型 平原 台地 丘陵 低山 中山 高山 林地 0.3 0.4 0.4 1.6 4.4 1.3 草地 0.8 0.9 0.8 1.5 1.5 1.5 耕地 1.7 1.3 0.7 1.0 1.2 0.1 水域 2.5 0.9 0.3 0.5 0.1 0.4 未利用地 1.0 1.1 1.4 0.6 0.3 0.8 -
[1] 党学亚,张俊,常亮,等. 西北地区水文地质调查与水资源安全[J]. 西北地质,2022,55(3):81–95.
DANG Xueya, ZHANG Jun, CHANG Liang, et al. Hydrogeoloicao Survey ang Water Resources Security in Northwest China[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2022, 55(3): 81-95.
[2] 冯晶红,刘瑛,肖衡林,等. 三峡库区消落带典型植物光合固碳能力及影响因素[J]. 水土保持研究,2020,27(1):305–311.
FENG Jinghong, LIU Ying, XIAO Henglin, et al. Photosynthesis and carbon sequestration characteristics of typical plants and their influencing factors in thereservoirpiparian region of Three Gorges Reservoir [J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation. 2020.27(1): 305-311.
[3] 巩杰,张影,钱彩云. 甘肃白龙江流域净生态系统生产力时空变化[J]. 生态学报,2017,37(15):5121–5128.
GONG Jie, ZHANG Ying, QIAN Caiyun. Temporal and spatial distribution of net ecosystem productivity in the Bailongjiang Watershed of Gansu Province[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(15): 5121-5128.
[4] 关晋宏,杜盛,程积民,等. 甘肃省森林碳储量现状与固碳速率[J]. 植物生态学报,2016,40(4):304–317.
GUAN Jinhong, DU Sheng, CHENG Jimin, et al. Current stocks and rate of sequestration of forest carbon in Gansu Province [J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology. 2016.40(4): 304-317.
[5] 郭丰杰,李婷,季民. 2000-2019年青海湖面积时序特征分析及预测[J]. 科学技术与工程,2022,22(2):740–748.
GUO Fengjie, LI Ting, JI Min, et al. Time series analysis and prediction of Qinghai Lake area from 2000 to 2019[J]. Science Technology and Engineering. 2022.22( 2): 740-748.
[6] 洪增林, 成星, 张瑜, 等. 黄土高原碳汇系统研究展望[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(3): 39−50.
HONG Zenglin, CHENG Xing, ZHANG Yu, et al. Key Issues of Earth System Science in the Study of Carbon Sinks in the Loess Plateau[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(3): 39−50.
[7] 胡雷,王长庭,王根绪,等. 青海省森林生态系统植被固碳现状研究[J]. 西南农业学报,2015,28(2):826–832.
HU Lei, WANG Changting, WANG Genxu, et al. Carbon sequestration of ecosystem vegetation in Qinghai Province [J]. Southwest China Journal of Agriculture Sciences, 2015.28(2): 826-832.
[8] 计文化, 王永和, 杨博, 等. 西北地区地质、资源、环境与社会经济概貌[J]. 西北地质, 2022, 55(3): 15−27.
JI Wenhua, WANG Yonghe, YANG Bo, et al. Overview of Geology, Resources, Environment and Social Economy in Northwest China[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2022, 55(3): 15−27.
[9] 李磊,兰安军,钟九生. 黔中水利枢纽工程区植被覆盖变化及其对地形与地貌的响应[J]. 水土保持研究,2022,29(4):176–183.
LI Lei, LAN Anjun, ZHONG Jiusheng. Change in vegetation cover and their response to topography and geomorphology in Qianzhong Water Conservancy Hub engineering areas[J]. Research of Soiland Water conservation. 2022.29(4): 176−183.
[10] 李文明, 李健强, 徐永, 等. 西北生态地质调查研究进展与展望[J]. 西北地质, 2022, 55(3): 108−119.
LI Wenming, LI Jianqiang, XU Yong, et al. Progress and Prospects of Ecological Geological Survey in Northwest China[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2022, 55(3): 108−119.
[11] 李姝,喻阳华,袁志敏,等. 碳汇研究综述[J]. 安徽农业科学,2015,43(34):136–139.
LI Shu, YU Yanghua, YUAN Zhimin, et al. Review on carbin sink[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2015.43(34): 136-139.
[12] 刘应帅,余瑞,郑彬彬,等. 海南岛森林植被NEP季节性时空变化规律及气候驱动因素分析[J]. 热带生物学报,2022,13(2):166–176.
LIU Yingshuai, YU Rui, ZHENG Binbin, et al. Analysis of seasonal spatial and temporal variation patterns of forestvegetation NEP and climate drivers in Hainan Island[J]. Journal of tropicao billogy, 2022.13(2): 166−176.
[13] 马丽娜, 张飞云, 翟玉鑫, 等. 1980-2020新疆土地利用变化下生态系统服务价值时空演变分析[J/OL]. 干旱区地理, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detali/65.1103.X.20220818.1615.003.html.
MA Lina, ZHANG Feiyun, ZHAI Yuxin, et al. Temporal and spatial evolution of ecosystem service value under land use change in Xinjiang from 1980 to 2020[J/OL]. Arid Land Geography, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detali/65.1103.X.20220818.1615.003.html.
[14] 潘竟虎,文岩. 中国西北干旱区植被碳汇估算及其时空格局[J]. 生态学报,2015,35(23):7718–7728.
PAN Jinghu, WEN Yan. Estimation and spatial-temporal characteristics of carbon sink in the arid region of northwest China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35( 23): 7718-7728.
[15] 彭文甫,周介铭,徐新良,等. 基于土地利用变化的四川省碳排放与碳足迹效应及时空格局[J]. 生态学报,2016,37(22):7244–31.
PENG Wenfu, ZHOU Jieming, XU Xinliang, et al. Change of land use changes on the temporal and spatial patterns of carbon emissions and carbon footpringts in the Sichuan Province of Western China from 1990 to 2010 [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021.37(1): 25-31.
[16] 王国强, 李婷, 陈隽璐, 等. 中国西北地区超基性岩封存CO2潜力研究[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(1): 186−193.
WANG Guoqiang, LI Ting, CHEN Junlu, et al. Assessment of Carbon Dioxide Sequestration Potential of Ultramafic Rocks in Northwest China[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(1): 186−193.
[17] 王志强,李雪薇. 新疆土地利用类型转变的碳强度变化规律分析[J]. 中国农机化学报,2022,43(5):165–203.
WANG Zhiqiang, LI Xuewei. Analysis on the change rule of carbon intensity in the transformation of land use types in Xinjiang [J]. China Agricultural Machinery Chemistry Journal, 2022.43(5): 165-203.
[18] 魏媛,简小玉. 基于碳达峰中和的贵州省土地利用碳排放演变及预测研究[J]. 生态经济,2022,38(4):108–114.
WEI Yuan, JIAN Xiaoyu. Research Evolution of Carbon Emissions from Land Use in Guizhou Province Based on Carbon Peak and Carbon Neutrality and the According Predictiongs[J]. Ecological economy, 2022.38(4): 108-114.
[19] 谢立军,白中科,杨博宇,等. 碳中和背景下国内外陆地生态系统碳汇评估方法研究进展[J]. 地学前缘,2023,30(02):447-462.
XIE Lijun, BAI Zhongke, YANG Boyu, et al. Research progress on carbon sink assessment methods of terrestrial ecosystems at home and abroad under the background of carbon neutrality[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2020.2. 78.
[20] 徐丽萍,李彭辉,李忠勤,等. 新疆山地冰川变化及影响研究进展[J]. 水科学进展,2020,31(6):946–959.
XU Liping, LI Penghui, LI Zhongqin, et al. Advances in research on changes and effects of glaciers in Xinjiang mountains [J]. Advaces in water science, 2020.31(6): 946-959.
[21] 徐友宁, 张江华, 何芳, 等. 西北地区矿山地质环境调查与防治研究[J]. 西北地质, 2022, 55(3): 129−139.
XU Youning, ZHANG Jianghua, HE Fang, et al. Investigation and Preventive Research of Mine Geological Environment in Northwest China[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2022, 55(3): 129−139.
[22] 严慈,侯兰功. 基于灰色理论的陕西省土地利用变化及其碳排放研究[J]. 西安理工大学学报,2021,37(1):25–31.
YAN Ci, HOU Langgong. Study on land use change and carbon emission in Shaanxi Province based on grey theory [J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Technology. 2021.37(1): 25-31.
[23] 杨静媛,张明,多玲花,等. 江西省土地利用碳排放空间格局及碳平衡分区[J]. 环境科学研究,2022,35(10):2312–2321.
YANG Jingyuan, ZHANG Ming, DUO Linghua, et al. Spatial Pattern of Land Use Carbon Emissions and Carbon Balance Zoning in Jiangxi Province[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2022.05. 04.
[24] 杨文学,张小平. 甘肃省土地利用碳排放变化及影响因素分解[J]. 安微农业科学,2016,44(33):49–53.
YANG Wenwen, ZHANG Xiaoping. Carbon emissions effect of Land-Use and influencing factors decomposition emiddion in Gansu Province [J]. Journal of Anhui Agri. 2016.44(33): 49-53.
[25] 张国,逯非,赵红,等. 我国农作物秸秆资源化利用现状及农户对秸秆还田的认知态度[J]. 农业环境科学学报,2017,36(5):981–988.
ZHANG Guo, LU Fei, ZHAO Hong, et al. Residue usage farmers' recognition and attitude toward residue retention in China's croplands [J]. Journal of Agro- Environmental Science, 2017.36(5): 981-988.
[26] 张赫,彭千芮,王睿,等. 中国县域碳汇时空格局及影响因素[J]. 生态学报,2020,40(24):8988–8998.
ZHANG He, PENG Qianrui, WANG Rui, et al. Spatiotemporl patterns and factors influencing county carbon sinks in china [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020.40(24): 8988-8998.
[27] 张杰,陈海,刘迪,等. 基于县域尺度土地利用碳排放的时空分异及影响因素研究[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版),2022,52(1):21–31.
ZHANG Jie, CHEN Hai, LIU Di, et al. The spatial and temporal variation and influencing factors of land use carbon emissions at county scale[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 52(1): 21-31.
-




 下载:
下载:





