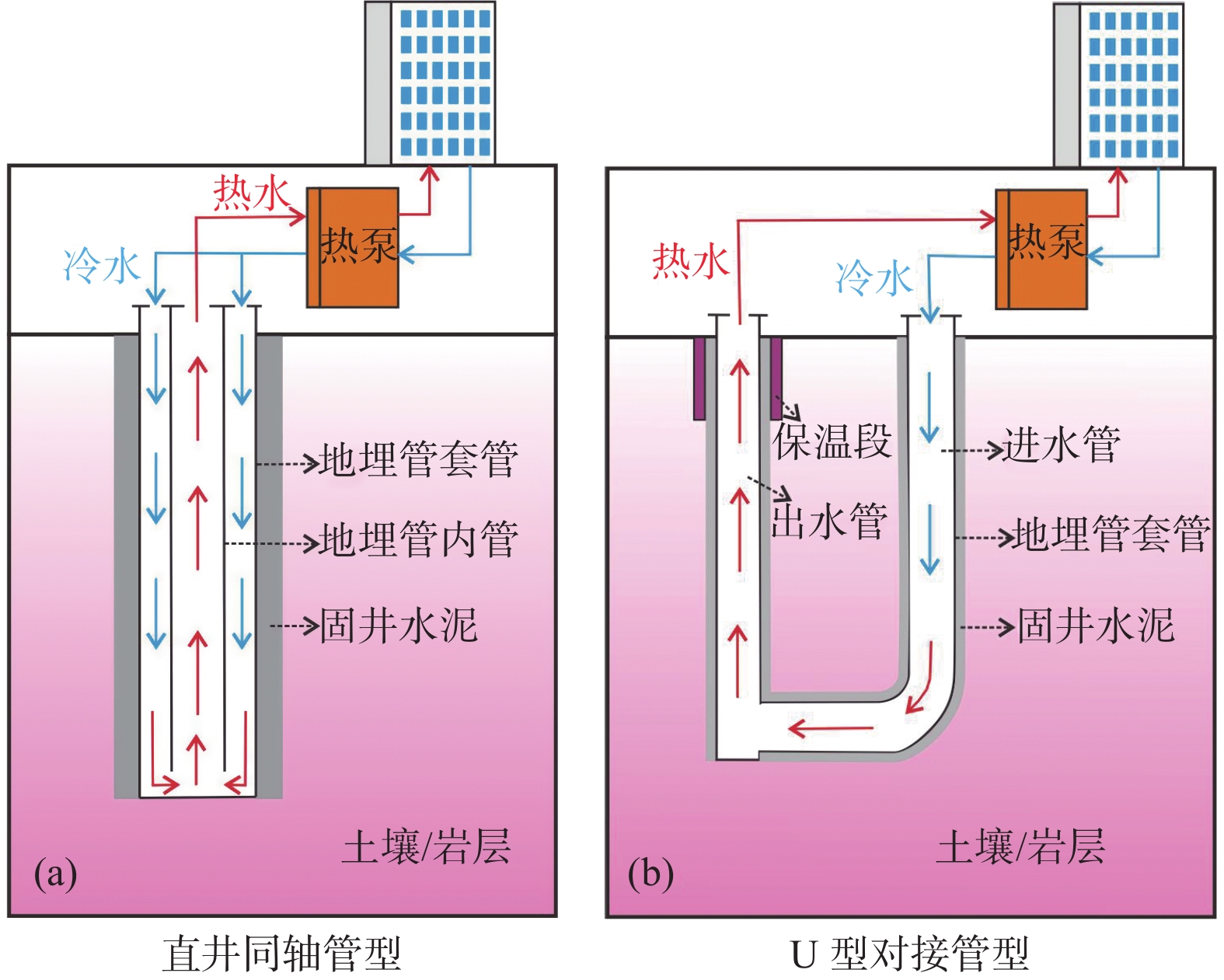
Development Potential and Environmental Benefit Analysis of Geothermal Medium–Deep Buried Pipe Heating System in Capital Cities in Northwest China
-
摘要:
笔者回顾并对比分析了西北省会城市供热现状及环境空气质量,指出传统采暖方式是影响该区环境空气质量的主要因素之一,而地热清洁能源的使用将有助于改善环境空气质量。传统热水井取热方式受地质条件制约较大,近年来一种取热不取水的新型地热开发利用技术——中深层地埋管供热系统应运而生,发展迅速。但是,以往的研究多集中于地面供热系统及管井换热能力的研究,对于地热资源储量及承载力的研究较少。在分析该技术适用范围的基础上,总结西北五省省会城市的地热资源条件,采用适当的方法结合城市建设范围估算地热可采资源量,分析在城市中推广使用中深层地埋管供热系统的前景及环境效益,并提出后续研究方向。
-
关键词:
- 地热资源 /
- 中深层地埋管供热系统 /
- 环境空气质量 /
- 西北省会城市
Abstract:In this paper, the current situation of heating and ambient air quality in the capital city of Northwest China has been reviewed and comparatively analyzed. The results suggest that the traditional heating method is one of the main factors affecting the ambient air quality in the region, while the use of geothermal clean energy will help improve the ambient air quality. In recent years, a new type of geothermal development and utilization technology “medium–deep buried pipe heating system” has emerged and is developing rapidly. But most of the previous studies have focused on the research of surface heating system and heat transfer capacity of pipe wells, and less on the research of geothermal resource storage and bearing capacity. In this paper, on the basis of analyzing the scope of application of this technology, the geothermal resource conditions in the capital cities of five northwestern provinces has been summarized, an appropriate method has been adopted to estimate the recoverable resources of geothermal resources in combination with the scope of urban construction, the prospects and environmental benefits of promoting the use of medium–deep buried pipe heating systems in cities has been analyzed, and the direction of subsequent research has been proposed.
-

-
表 1 西北省会城市供热现状表
Table 1. Heating status of capital cities in Northwest China
城市 供暖期 供 热 现 状 西安 4个月 城市中心区、城北、城东南、城东北、高陵建制区、草堂、泾渭工业园以及阎良航空产业基地为燃气锅炉集中供热,面积约为1.07亿m2;城西、高新开发区、沣东新城、大兴新区部分区域依托热电联产燃煤锅炉集中供热,供热面积约为0.32亿m2;西咸新区沣西区块主要以中深层地埋管地源热泵供热系统分散供热,全市中深层地埋管供热系统供暖面积达0.15亿m2,其他为散烧燃气锅炉供暖 兰州 5个月 供热热源有煤及天然气,总供暖面积为1.07亿m2 西宁 6个月 市区集中供热主要依靠热电联产燃煤锅炉,规划供热建筑面积约为0.13亿m2,实际集中供热面积为0.08亿m2,分散供热热源以天然气为主 银川 6个月 主城区供热面积达1.2亿m2,热源以热电联产为主、分散燃气锅炉为辅,其中热电联产集中供热面积约为0.7亿m2 乌鲁木齐 6个月 总供热面积为2.42亿m2,其中:燃气锅炉供热面积为1.18亿m2,热电联产供热面积为0.8亿m2,壁挂炉供热面积为0.34亿m2,电供暖总面积为0.06亿m2,农村地区散煤燃烧供热面积为0.04亿m2 表 2 各城市大气污染因子年均浓度值(μg/m3)
Table 2. Annual average concentration of air pollution factors in each city (μg/m3)
城市 污染因子 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 《环境空气质量标准》
(GB 3095-2012)标准值西安 PM10 130 122 102 91 82 70 PM2.5 73 63 58 51 41 35 兰州 PM10 111 103 79 76 72 70 PM2.5 49 47 36 34 32 35 西宁 PM10 100 91 59 61 58 70 PM2.5 39 45 34 35 32 35 银川 PM10 / 101 74 72 63 70 PM2.5 / 38 33 36 27 35 乌鲁木齐 PM10 106 / 86 83 65 70 PM2.5 70 54 50 47 39 35 注:西安市2017、2019年数据来自《西安市大气污染特征及颗粒物来源分析》,其他数据均来自各市年度(月)环境质量报告。 表 3 不同地埋管影响半径内可获得的地热资源更新量(W)
Table 3. Renewable amount of geothermal resources within the influence radius of different buried pipes
地埋管影响半径(m) 地温梯度(℃/100 m) 2.5 3 3.5 4 10 17.84 21.41 24.98 28.55 20 71.37 85.65 99.92 114.20 30 160.59 192.70 224.82 256.94 表 4 西安凹陷地层特征表
Table 4. Stratigraphic characteristics of Xi’an depression
地 层 特 征 新生界 第四系 全新统(Qh) 现代河流冲积、洪积层和山前洪积坡积,岩性一般为砂、砂砾卵石、砂质黏土 上更新统 (Qp3) 秦岭山前洪积扇为洪积相沉积,岩性为砂质黏土及砾石、漂石等,分选极差,厚度为8~30 m;渭河及其较大支流的二级阶地下部为冲积相沉积,岩性为粘质砂土,砂质黏土及砂、砂砾卵石层,二级阶地以上各地貌单元上部覆盖有风积黄土 中更新统 (Qp2) 浅灰褐色较疏松无层理的黄土,夹多层红褐色古土壤 下更新统 (Qp1) 河湖相交替沉积,主要为黄色沉积泥质岩 新近系 张家坡组( N2z) 河湖相沉积,岩性为灰绿色泥岩、含砂泥岩夹疏松的砂泥岩,厚度为300~900 m 蓝田灞河组(N2lb) 河流相沉积,上段为黄棕、浅灰绿色泥岩,中段为紫褐、黄棕色砂质泥岩与砂砾岩互层,下段为浅紫褐色泥岩、浅棕黄色砂岩,厚度为100~900 m 寇家村组( N1k) 为湿热条件下的河湖相沉积,岩性以棕红、桔黄色泥岩、砂质泥岩为主,夹灰白色、棕黄色砂岩,底部发育砾岩或砂砾岩。厚度为0~142 m 冷水沟组( N1ls) 为湿热条件下的河湖相沉积,棕红色砂质泥岩与灰黄、灰绿色砂岩互层及底部砾岩夹杂色泥岩,厚度为1 342 m 古近系 白鹿塬组( E3b) 河流相沉积,以灰白色块状砂岩为主,夹(或互)紫红色泥岩,底部发育砂砾岩或含砾粗砂岩,厚度为500 m 红河组( E2h) 湖泊、河流相沉积,以大套紫红色泥岩为主,夹灰黄色和灰绿色砂岩、粉砂岩,厚度为2 100~2 800 m 表 5 西安市地热可采资源量估算表
Table 5. Estimate of recoverable geothermal resources in Xi’an
地温梯度
分区
(℃/100 m)单位面积
可采资源量
(1013 kcal/km2)分区
面积
(km2)分区可采
资源量
(1016 kcal)相当于
标煤
(108 t)2.5~3 1.03 54 0.06 0.79 3~3.5 3.09 1029 3.18 45.42 3.5-4 5.15 250 1.28 18.36 合计 1333 4.52 64.56 表 6 兰州盆地地层特征表(杨俊仓,2011)
Table 6. Stratigraphic characteristics of Lanzhou Basin
地 层 特 征 新生界 第四系 全新统(Q4 ) 近代冲洪积层,主要分布在黄河河漫滩及一二级阶地 上更新统(Q3 ) 马兰黄土及冲洪积砂砾卵石层 中更新统(Q2 ) 离石黄土及冲洪积砂土夹砾卵石层,在兰州分布较广 下更新统(Q1 ) 出露于雷坛河、五泉山一带及南北两山地区的高阶地上,为山前洪积相堆积 新近系 临夏组(N2l) 河流相碎屑岩、泥岩互层,厚度约为300 m 咸水河组(N1x) 河湖相、山麓相砂质泥岩、砂岩、泥岩、黏土岩,厚度大于782 m 古近系 野狐城组(E3y) 湖相泥岩夹石膏,厚度为434 m 西柳沟组(E1-2x) 山麓相橘红色碎屑岩,下部为厚层砾岩,中上部为砂岩及砂砾岩,厚度为953 m 中生界 白垩系 河口组(K1) 河湖相红色碎屑岩。该群的岩性和厚度变化较大,厚度为600~1 600 m,盆地边缘岩石粗厚度薄,盆地中心岩石变细,厚度增加,岩性多为黏土岩、砂岩及砾岩 侏罗系 享堂组(J3x) 河湖相碎屑岩,厚度为122 m 窑街群(J1-2yj) 河湖—沼泽相的含煤沉积,厚度为166 m 古生界 奥陶系 雾宿山群(O2-3WX) 浅海相中—基性火山岩、碎屑岩和硅质岩,岩石普遍遭受低级或轻度变质,与中生界呈断层或不整合接触,厚度大于1 090 m 元古界 皋兰群(Chgl) 海相泥、砂质沉积地层,经受了多起区域变质和岩浆活动及构造复合作用,岩石变质程度较深,破碎严重,总厚度大于7 713 m 兴隆山群(Chx) 海相火山硅质岩,岩层总厚度大于3 759 m,与马衔山群呈断层接触 马衔山群(Ptm) 浅海陆源沉积建造,岩层总厚度大于2 416 m 表 7 兰州市地热可采资源量估算表
Table 7. Estimation of recoverable geothermal resources in Lanzhou
地温梯度
分区
(℃/100 m)单位面积
可采资源量
(1013 kcal/km2)面积
(km2)分区可采
资源量
(1016 kcal)相当于
标煤
(108 t)2.5~3 1.03 108 0.11 1.59 3~3.5 3.09 128 0.40 5.66 3.5~4 5.15 206 1.06 15.11 >4 2.06 227 0.47 6.69 合计 669 2.03 29.05 表 8 西宁市地热可采资源量估算表
Table 8. Estimate of recoverable geothermal resources in Xining
地温梯度
分区
(℃/100 m)单位面积
可采资源量
(1012 kcal/km2)面积
(km2)分区可采
资源量
(1014 kcal)相当于
标煤
(107 t)2.5~3 1.08 62 0.67 0.96 3~3.5 3.24 22 0.71 1.02 3.5~4 5.40 21 1.13 1.62 4~4.5 7.56 25 1.89 2.70 >4.5 9.72 22 2.14 3.05 合计 152 6.54 9.35 表 9 城市建筑供暖形式分析表
Table 9. Analysis table of urban building heating
城市 城市
人口
(万人)估算建
筑面积
(108 m2)集中供
热面积
(108 m2)估算分散
供热面积
(108 m2)年供热总
热耗相当
于耗标煤
(104 t)西安 928 3.49 1.52 1.97 1 326 兰州 438.43 1.65 1.07 0.58 937 西宁 119.83 0.45 0.13 0.32 256 表 10 每10万m2供暖面积采暖期减排污染物量
Table 10. Emission reduction during heating period per 100 000 m2 heating area
城市 替代热源 减排污染物(t) 粉尘 SO2 NO2 CO2 西安 燃气锅炉 1.2 3 12 4482 兰州 燃气锅炉 1.8 4.5 18.1 6776 西宁 燃气锅炉 2.4 6.1 24.4 9109 表 11 地热供暖不同替代率下减碳降污总量表
Table 11. Total table of carbon reduction and pollution reduction under different substitution rates of geothermal heating
城市 15%替代率 35%替代率 75%替代率 100%替代率 粉尘(t) CO2(104 t) 粉尘(t) CO2(104 t) 粉尘(t) CO2(104 t) 粉尘(t) CO2(104 t) 西安 628 235 1465 547 3140 1173 4187 1564 兰州 445 168 1039 391 2225 838 2967 1117 西宁 162 62 378 144 / / / / -
[1] 冯兴军. 西安地热能开发利用的几点思考[J]. 陕西煤炭, 2017, 第4期: 8-12
FENG Xingjun. Some thoughts on the development and utilization of geothermal energy in Xi’an. Shaanxi Coal. 2017. Fouth: 8-12.
[2] 计文化, 王永和, 杨博, 等. 西北地区地质、资源、环境与社会经济概貌[J]. 西北地质, 2022, 55(3): 15-27 doi: 10.19751/j.cnki.61-1149/p.2022.03.002
JI Wenhua, WANG Yonghe, YANG Bo, et al. Overview of Geology, Resources, Environment and Economy in Northwest China[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2022, 55(3): 15-27. doi: 10.19751/j.cnki.61-1149/p.2022.03.002
[3] 柯婷婷, 余如洋, 许威, 等. 西安交通大学西咸校区中深层地热资源潜力评估[A]. 中国地球物理学会,中国地震学会,全国岩石学与地球动力学研讨会组委会,中国地质学会构造地质学与地球动力学专业委员会,中国地质学会区域地质与成矿专业委员会.2018年中国地球科学联合学术年会论文集(二十九)——专题59: 计算地球物理方法和应用、专题60: 地热资源成因新理论与综合探测新技术[C].中国和平音像电子出版社,2018:44−46.
[4] 李成英, 韩积斌, 黄鑫, 等. 西宁市海湖新区地下热水形成的机理[J]. 盐湖研究, 2017, 25(2): 13-20
Li Chengying, Han Jibing, Huang Xin, et al. Formation Mechanism of Groundwater Hot Water in Haihu New District of Xining City[J]. Journal of Salt Lake Researth, 2017, 25(2): 13-20.
[5] 穆根胥, 李锋, 闫文中, 等. 关中盆地地热资源赋存规律及开发利用关键技术[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2016
MU Genxu, LI Feng, YAN Wenzhong, et al. The Geothermal Resource Occrrence Rulesand Key Technologies for Development and Utilization in the Guanzhong Basin[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2016
[6] 秦大军, 庞忠和, Jeffrey V. Turner, 等. 西安地区地热水和渭北岩溶水同位素特征及相互关系. 2005.21(5): 1489-1500
Qin D J, Pang Z H, Turner J V, et al. Isotopes of geothermal water in Xi’an area and implications on its relation to karstie groundwater in North Mountains. Acta Petrologica Sinica. 2005.21(5): 1489-1500.
[7] 王贵玲, 杨轩, 马凌, 等. 地热能供热技术的应用现状及发展趋势. 华电技术[J]. 2021.43(11): 15-24
Wang Guiling, Yang Xuan, Ma Ling, et al. Status quo and prospects of geothermal energy in heat supply. Huadian Technology. 2021.43(11): 15-24
[8] 谢娜, 喻生波, 丁宏伟, 张明泉. 甘肃省地热资源赋存特征及潜力评价[J]. 中国地质, 2020.47(6): 1804-1812
Xie Na, Yu Shengbo, Ding Hongwei, et al. Occurrence Features of Geothermal Potential Assessment in Gansu Province[J]. Geology in China. 2020.47(6): 1804-1812
[9] 杨俊仓, 贾贵义, 魏洁. 兰州盆地地热资源及其潜力分析[J]. 甘肃科技, 2011.27(24): 49-51
Yang Juncang, Jia Guiyi, Wei Jie. Geothermal resources and their potential analysis in Lanzhou Basin. Gansu science and technology. 2011.27(24): 49-51.
[10] 余秋生, 周文生. 宁夏地热资源现状评价与区划成果报告[R]. 宁夏回族自治区地质调查院, 2015.
[11] 袁丽发, 谢宁, 徐海龙. 乌鲁木齐市甘泉堡-古海温泉区地热地质特征分析[J]. 地下水, 2021, 43(2): 59-66
Yuan Lifa, Xie Ning, Xu Hailong. Ganquanbao-Guhai Hot Spring Zone in Urumqi Analysis of geothermal geological characteristics[J]. Groundwater, 2021, 43(2): 59-66.
[12] 张丰雄, 杨家凯, 刘淑英, 等. 西宁地区地热资源分布规律探讨[J]. 科技资讯, 2006, 21: 138-139 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3791.2006.26.112
Zheng Fengxiong, Yang Jiakai, Liu Shuying, et al. Discussion on distribution law of geothermal resources in Xining area[J]. Science&Technology Information, 2006, 21: 138-139. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3791.2006.26.112
[13] 张森琦, 李长辉, 孙王勇, 等. 西宁盆地热储构造概念模型的建立. 地质通报. 2008.27(1): 126-136.
Zhang S Q, Li C H, Sun W Y, et al. Construction of the conceptual model of thermal reservoir structure of the Xining basin, China. Geological Bulletin of China, 2008, 27(1): 126- 136
[14] 赵振, 于漂罗, 陈惠娟, 等. 青海省西宁地热田成因分析及资源评价[J]. 中国地质, 2015, 42(3): 803-810 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2015.03.029
Zhao Zhen, Yu Piaoluo, Chen Huijuan, et al. Genetic analysis and resource evaluation of the Xining geothermal field in Qinghai Province[J]. Geology in China, 2015, 42(3): 803-810. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2015.03.029
[15] 周斌. 甘肃省主要城市地热资源特征及开发保护建议[J]. 地下水, 2011.33(1): 54-57 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2011.01.021
Zhou Bin. Characteristics of geothermal resources in major cities of Gansu Province and suggestions for development and protection [J]. Groundwater, 2011, 33(1): 54-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2011.01.021
[16] 祖浙江. 乌鲁木齐水磨沟地热资源类型及勘查方法[J]. 新疆地质, 2007, 25(3): 320-322 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2007.03.020
Zu Zhejiang. Types and exploration methods of geothermal resources in Shuimogou, Urumqi[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2007, 25(3): 320-322. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2007.03.020
[17] Du Dingshan, Li Yongqiang, Wang Kaipeng, et al. Experimengtal and numerical simulation research on heat tranfer performance of coaxial casing heat exchanger in 3500m-deep geothermal well in Weihe Basin[J]. Geothermics, 2023, 109: 102658
[18] HeYuting, Jia Min, Li Xiaogang, et al. Performance analysis of coaxial heat exchanger and heat-carrier fluid in medium-deep geothermal energy development[J]. Renewable Energy, 2021, 168: 938-959.
-



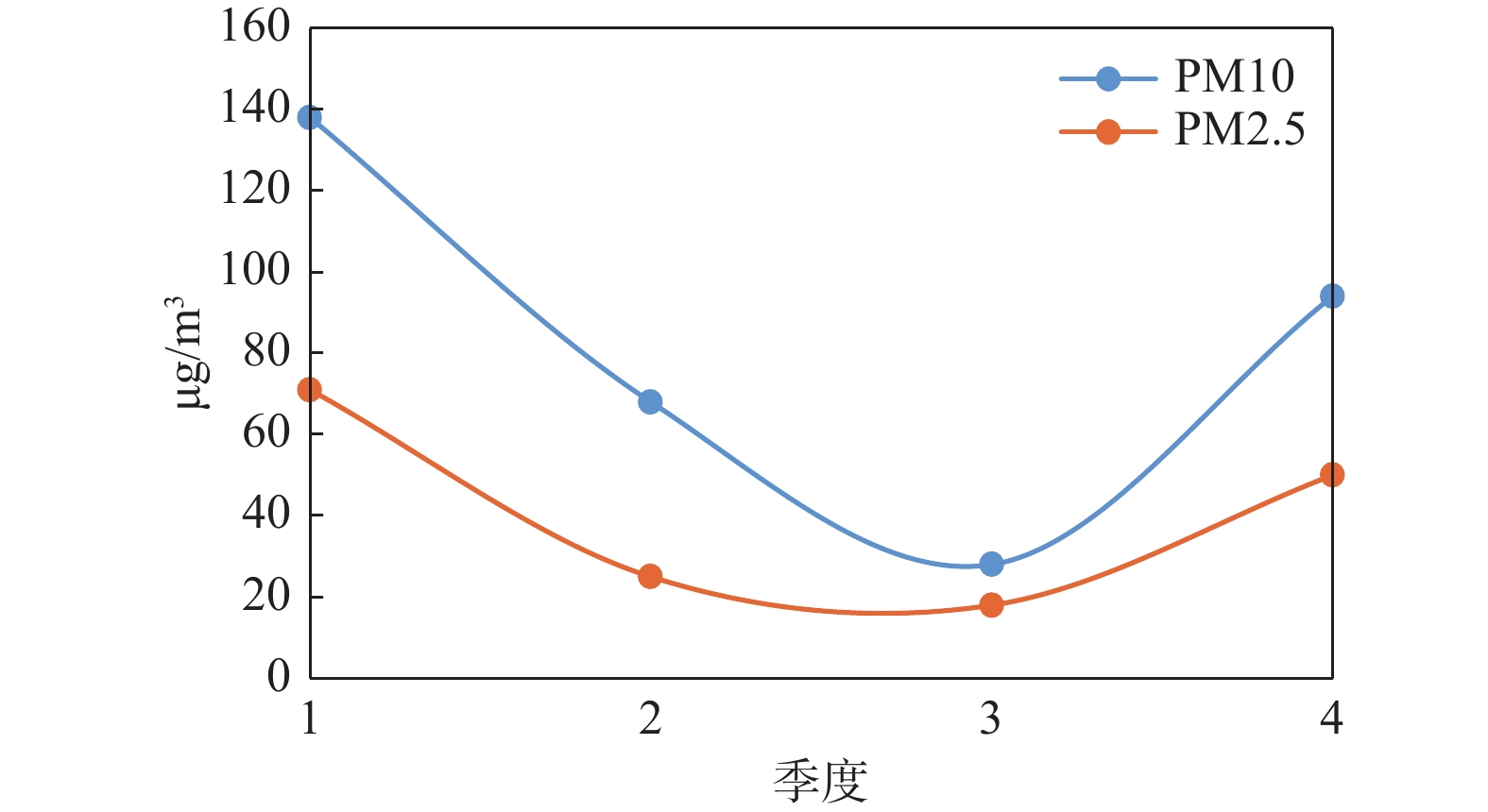
 下载:
下载: