Analysis on Geochemical Characteristics and Difference of Formation Water in He 8th Member in Northern and Southern Tianhuan Depression
-
摘要:
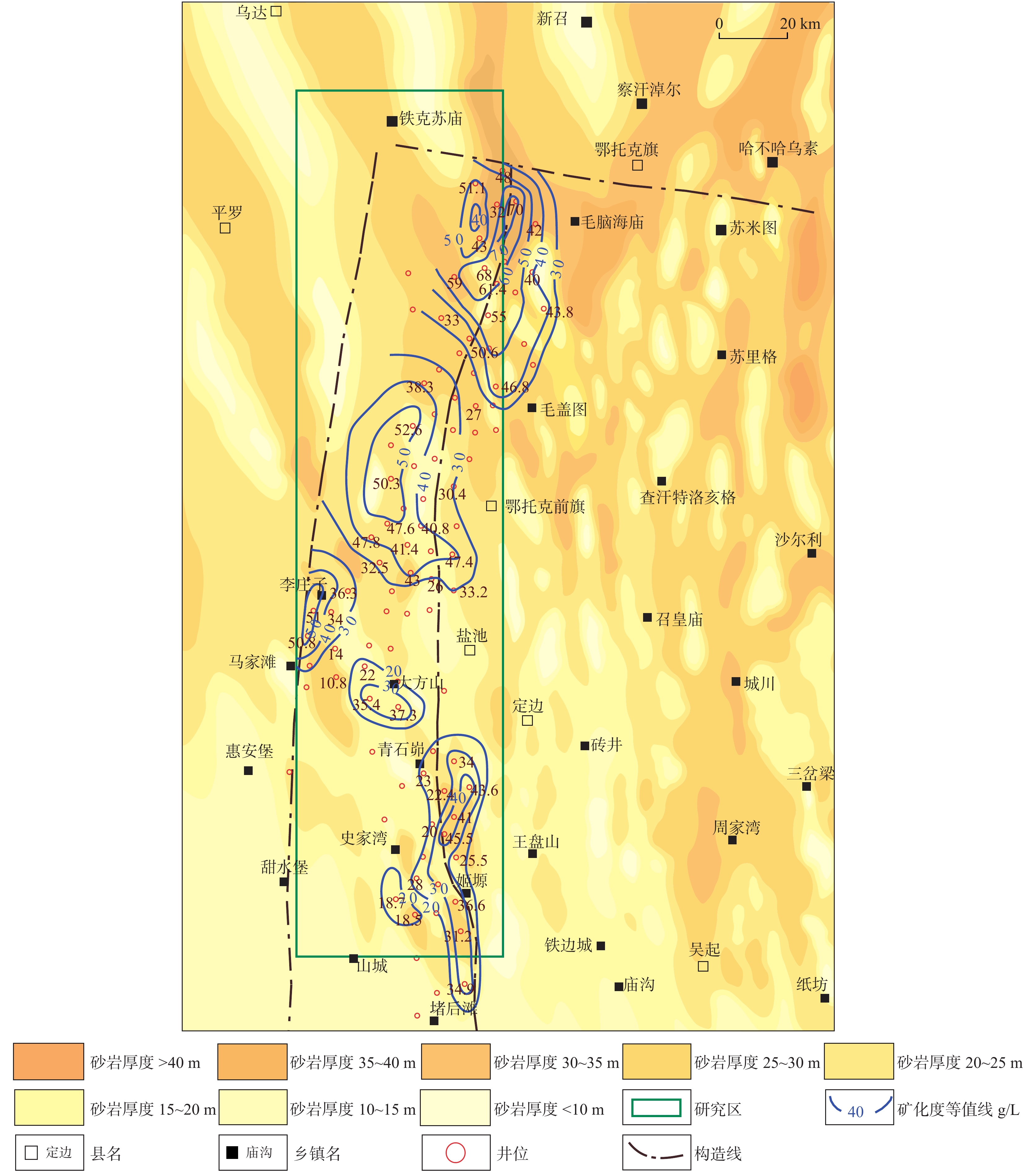
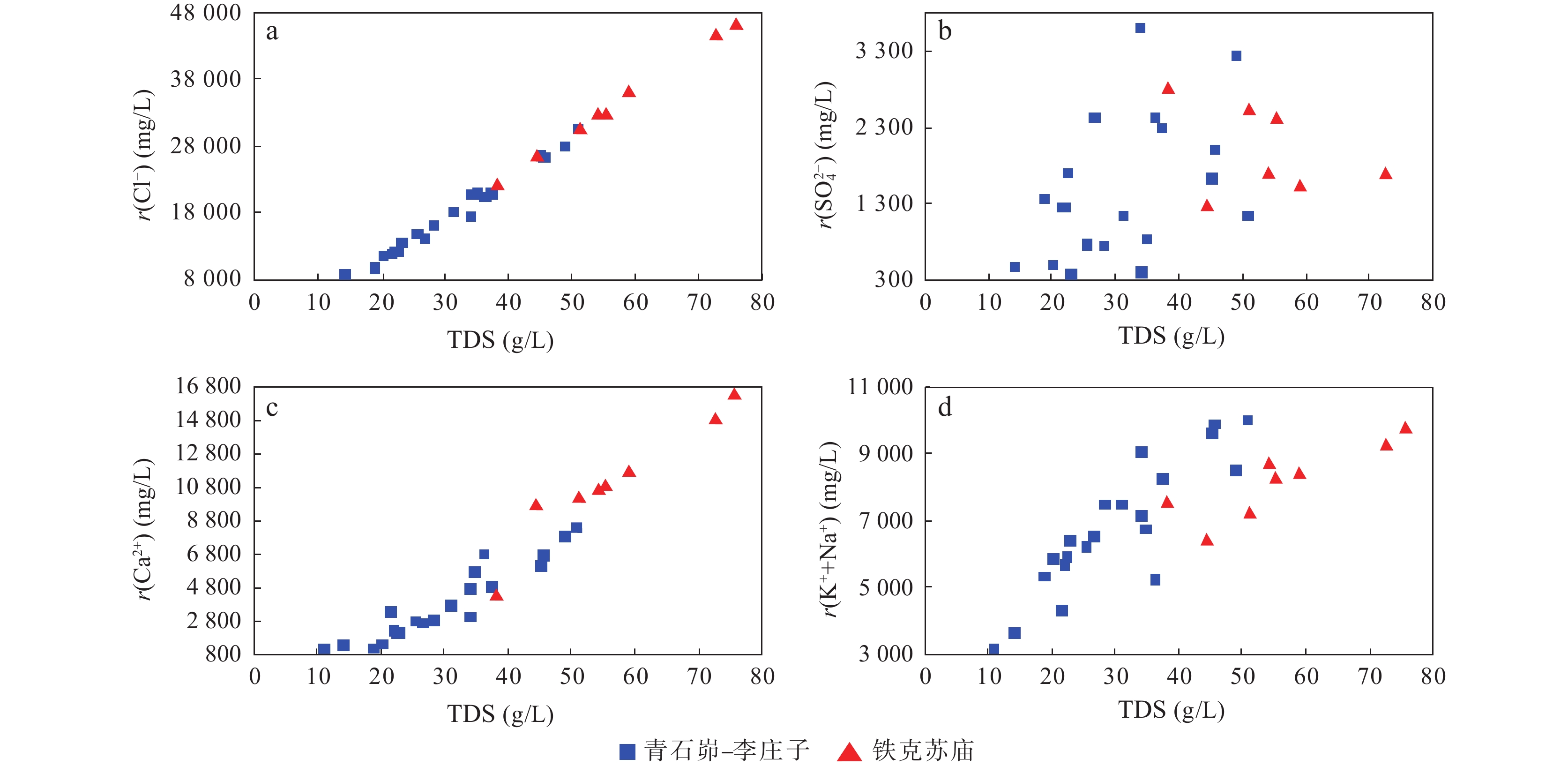
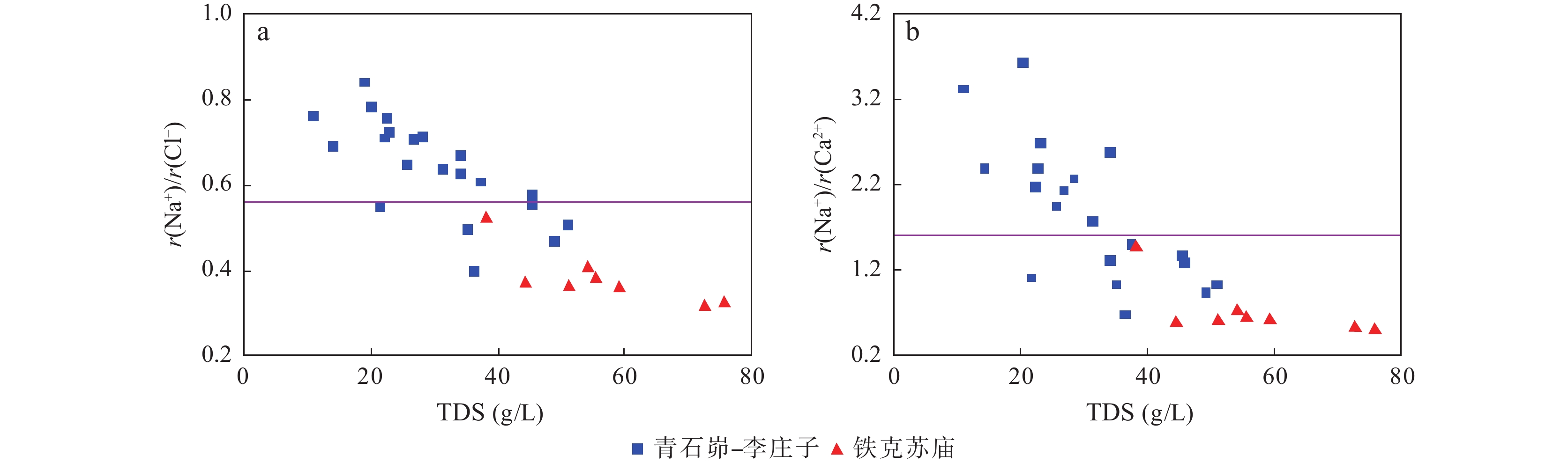
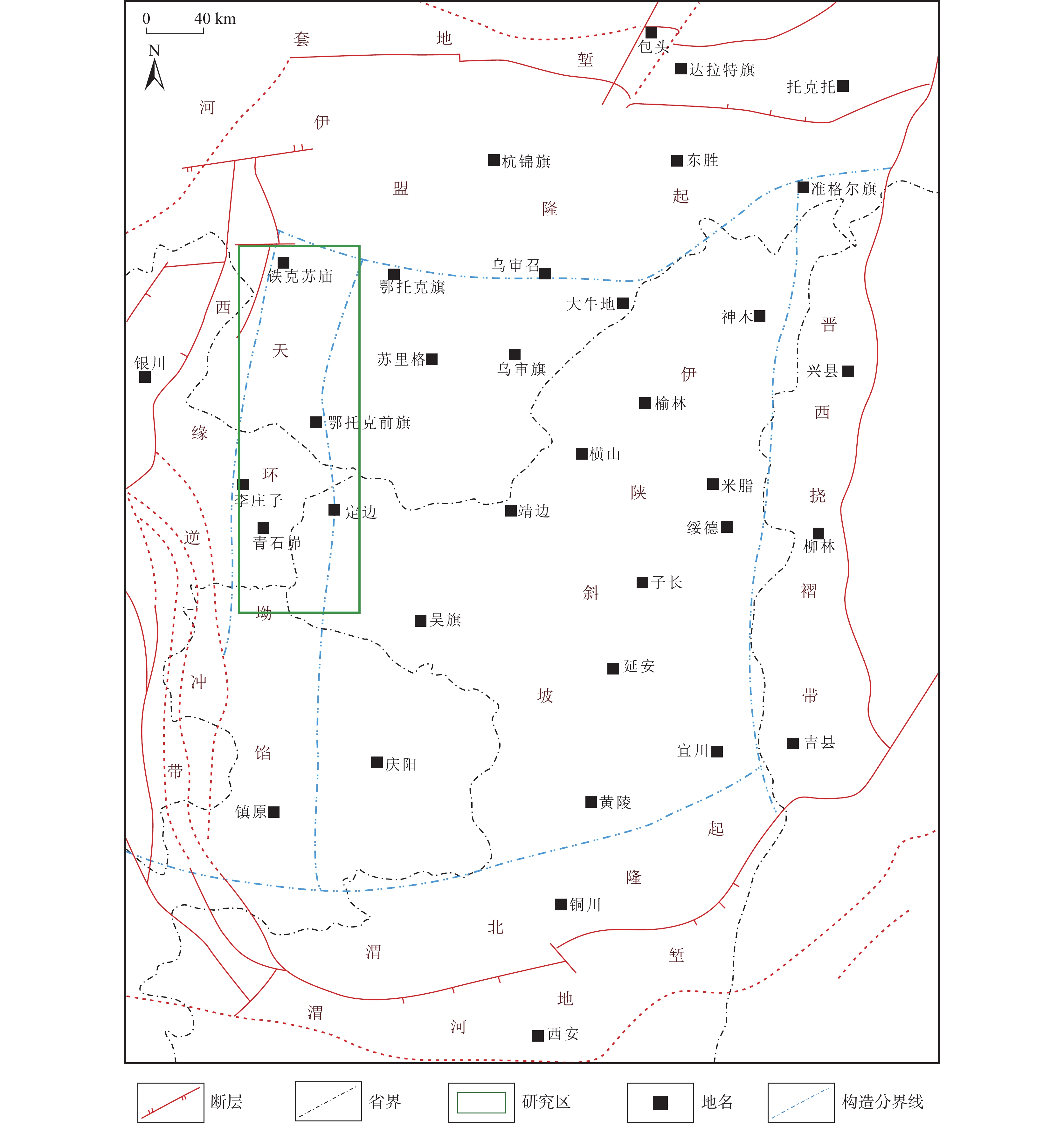
通过对鄂尔多斯盆地天环坳陷中二叠统下石盒子组盒8段地层水样品测试结果的统计分析,分别对区内南北部的地球化学特征进行研究,对比其差异性,分析天然气运聚和保存条件,为勘探部署提供支持。研究显示,天环坳陷中二叠统下石盒子组盒8段为偏酸性、氯化钙型地层水,区内矿化度、Cl-含量和浓度都显示为北高南低,反映了北部铁克苏庙地区地层水封闭条件优于南部青石峁–李庄子区域,更有利于气藏的聚集和保存。南北部地层水地化特征参数与气藏形成条件有较好的对应性。北部地区为Ⅳ型、Ⅴ型原始地层水,地层水的钠氯系数低、脱硫系数低、钠钙系数低、变质系数高,具有油气伴生水的特征,地层封闭性较好,利于气藏的聚集和保存;而南部地区为Ⅱ型、Ⅲ型、Ⅳ型地层水,显示较差的封闭条件,地层水与外界有沟通,不利于气藏的运聚和保存。
Abstract:Based on the statistics and analysis of the test results of formation water samples of He 8th Member of Tianhuan depression, Ordos basin, the geochemical characteristics of the northern and southern parts of the area are studied, and the differences were compared. The results show that the formation water of He 8th member of Tianhuan Depression is acidic and CaCl2 water type, and the mineralization degree, Cl− content and concentration in the area are higher in the north than in the south. It reflects that the sealing condition of formation water in the Tiekesumiao area in the north is better than that in Qingshimao - Lizhuangzi area in the south, which is more conducive to the accumulation and preservation of gas reservoirs. The Geo-chemical characteristic parameters of formation water in the north and south have good correspondence with the formation conditions of the gas reservoir. The formation water in the northern area is characterized by low sodium-chloride coefficient, low desulfurization coefficient, low sodium-calcium coefficient and high metamorphic coefficient. The formation water is of Ⅳ-type and Ⅴ-type original formation water, which is favorable for the accumulation and preservation of gas reservoirs. In the southern area, the formation water of Ⅱ-type, Ⅲ-type and Ⅳ-type shows poor sealing conditions, and the formation water communicates with the outside world, which is not conducive to the accumulation and preservation of gas reservoirs.
-
Key words:
- formation water /
- geochemical characteristics /
- difference /
- He 8th Member /
- Tianhuan depression
-

-
表 1 研究区下石盒子组(P2x)盒8段南北部地层水主要化学离子含量
Table 1. Content of main chemical ions in formation water in the northern and southern part in He 8th Member of Xiashihezi Formation (P2x) in the study area
地区 主要离子含量(mg/L) 矿化度(mg/L) K++Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− SO42− HCO3− 铁克苏庙 
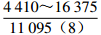
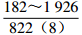
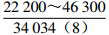
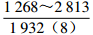
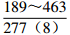
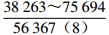
青石峁–李庄子 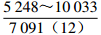
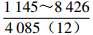
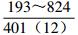
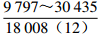
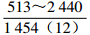
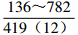
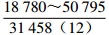
注:表中数据格式为 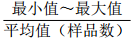 。
。表 2 研究区下石盒子组(P2x)盒8段地层水地球化学参数及分类
Table 2. Formation water geochemical parameters and classification of He 8th member of Xiashihezi formation in the study area
地区 钠氯系数
r(Na+)/r(Cl−)脱硫系数
2×100×r(SO42−)/r(Cl−)钠钙系数
r(Na+)/r(Ca2+)变质系数
1/2×r(Cl−)-r(Na+)/r(Mg2+)水型 铁克苏庙 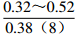
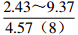
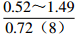
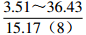
CaCl2 青石峁-李庄子 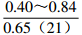
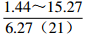
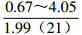
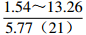
CaCl2 注:表中数据格式为 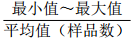 。
。表 3 博亚尔斯基对氯化钙型地层水的详细分类
Table 3. Classification of the calcium chloride type water
序号 Na/Cl 水型 石油地质意义 1 >0.85 Ⅰ 表现出水的运动速度相当大的水动力活跃的特点,这个地带保存条件差,保存油气藏的前景不大 2 0.75~0.85 Ⅱ 具有沉积盆地的积极水动力带和较稳定的静水带之间过渡带的特点,一般认为是烃类保存条件较差的地区 3 0.65~0.75 Ⅲ 水动力条件平缓,有利于保存油气,认为是保存烃类较好的有利环境 4 0.50~0.65 Ⅳ 具有烃类聚集与外界隔绝;并且有残余水存在的特点是烃类保存的有利地带。 5 <0.50 Ⅴ 具有古代残余海水的特点,在溶解固体的的浓度和溶解组分的比率上,在原始沉积时就被高度变质。这是烃类聚集最有希望的区域。需具备的附加条件有:①碘化物>1 mg/L;②溴化物>300 mg/L;③Cl−/Br<350;④SO42−×100/Cl−<1 -
[1] 陈朝兵, 杨友运, 邵金辉, 等. 鄂尔多斯东北部致密砂岩气藏地层水成因及分布规律[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(2): 313-325 doi: 10.11743/ogg20190210
CHEN Zhaobing, YANG Youyun, SHAO Jinhui, et al. Origin and distribution of formation water in tight sandstone reservoirs in the northeastern Ordos Basin [J]. Oil and Gas Geology, 2019, 40(2): 313-325. doi: 10.11743/ogg20190210
[2] 窦伟坦, 刘新社, 王涛. 鄂尔多斯盆地苏里格气田地层水成因及气水分布规律[J]. 石油学报, 2010, 31(5): 767-773 doi: 10.7623/syxb201005011
DOU Weitan, LIU Xinshe, WANG Tao. The origin of formation water and the regularity of gas and water distribution for the Sulige gas field, Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2010, 31(5): 767-773. doi: 10.7623/syxb201005011
[3] 雷易璇. 关于地层水特征及其地质意义概述[J]. 化学工程与装备, 2018, (04): 129-139
LEI Yixuan. The characteristics of formation water and its geological significance are summarized [J]. Chemical Engineering and Equipment, 2018, (04): 129-139.
[4] 李贤庆, 侯读杰, 柳常青, 等. 鄂尔多斯中部气田下古生界水化学特征及天然气藏富集区判识[J]. 天然气工业, 2002, 22(4): 10-14 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2002.04.003
LI Xianqing, HOU Dujie, LIU Changqing, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of Lower Paleozoic formation water and idendification of natural gas enrichment area in central gas fields in Ordos[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2002, 22(4): 10-14. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2002.04.003
[5] 梁积伟, 李荣西, 陈玉良, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地苏里格气田西部盒8段地层水地球化学特征及成因[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2013, 34(5): 625-630
LIANG Jiwei, LI Rongxi, CHEN Yuliang, et al. Geochemical behaviors and genesis of formation water in 8th member of Xiashihezi formation in western Sulige gas field, Ordos Basin[J]. Oil and Gas Geology, 2013, 34(5): 625-630.
[6] 柳广弟. 石油地质学(4版)[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2009
LIU Guangdi. Petroleum geology(4th ed.) [M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2009.
[7] 楼章华, 尚长健, 姚根顺, 等. 桂中坳陷及周缘海相地层油气保存条件[J]. 石油学报, 2011, 32(3): 432-441
LOU Zhanghua, SHANG Changjian, YAO Genshun, et al. Hydrocarbon preservation conditions in marine strata of the Guizhong depression and its margin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2011, 32( 3): 432-441.
[8] 楼章华, 朱蓉. 中国南方海相地层水文地质地球化学特征与油气保存条件[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2006, 27(5): 584-593 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2006.05.002
LOU Zhanghua, ZHU Rong. Hydrogeological and hydrogeochemical characteristics and hydrocarbon Preservation conditions in marine strata in southern China[J]. Oil and Gas Geology, 2006, 27(5): 584-593. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2006.05.002
[9] 孟旺才, 李云, 付国民, 等. 榆林北部气田山2段地层水化学特征与天然气聚集关系[J]. 西北地质, 2018, 51(2): 203-208
MENG Wangcai, LI Yun, FU Guomin, et al. Relationship between chemical characteristics of formation water and natural gas accumulation within Shan 2Member of Shanxi formation in North Yulin gas field[J]. Northwestern Geology. 2018, 51(2): 203-208.
[10] 钱诗友, 曾溅辉. 东营凹陷沙河街组地层水化学特征及其石油地质意义[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2009, 20(4): 603-609
QIAN Shiyou, ZENG Jianhui. Chemical characteristics of Shahejie Formation formation water and their petroleum geological significance, Dongying sag[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2009, 20(4): 603-609.
[11] 王怀长, 任德生, 侯云东, 等. 天环凹陷北部上古生界气水分布主控因素分析[J]. 特种油气藏, 2018, 25(6): 32-36
WANG Huaichang, REN Desheng, HOU Yundong, et al. Min-Controlling factor analysis of the Upper Gas-Water distribution in Norther Tianhuan depression[J]. Special Oil Gas Reservoirs, 2018, 25(6): 32-36.
[12] 王建麾, 李仲东, 过敏, 等. 杭锦旗地区上古生界地层水成因[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2009, 30(1): 65-67
WANG Jianhui, LI Zhongdong, GUO Min, et al. Origin of formation water of Upper Paleozoic in Hangjinqi area in Ordos Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2009, 30(1): 65-67.
[13] 王晓梅, 赵靖舟, 刘新社, 等. 苏里格气田西区致密砂岩储层地层水分布特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2012, 33(5): 802-810 doi: 10.11743/ogg20120519
WANG Xiaomei, ZHAO Jingzhou, LIU Xinshe, et al. Distribution of formation water in tight sandstone reservoirs of western Sulige gas field, Ordos Basin[J]. Oil and Gas Geology, 2012, 33(5): 802-810. doi: 10.11743/ogg20120519
[14] 王运所, 许化政, 王传刚, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地上古生界地层水分布与矿化度特征[J]. 石油学报, 2010, 31(5): 748-761 doi: 10.7623/syxb201005008
WANG Yunzheng, XU Huazheng, WANG Chuangang, et al. Characteristics of the salinity and distribution of the Neopaleozoic form ation water in Ordos Basin [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2010, 31(5): 748-761. doi: 10.7623/syxb201005008
[15] 王泽明, 鲁宝菊, 段传丽, 等. 苏里格气田苏20区块气水分布规律[J]. 天然气工业, 2010, 30(12): 37-40 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2010.12.009
WANG Zeming, LU Baoju, DUAN Chuanli, et al. Gas-water distribution pattern in Block 20 of the Sulige gas field[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2010, 30(12): 37-40. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2010.12.009
[16] 吴浩, 纪友亮, 周勇, 等. 南堡凹陷南部古近系深层优质储层成因[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2019, 48(3): 553-569 doi: 10.13247/j.cnki.jcumt.000952
WU Hao, JI Youliang, ZHOU Yong, et al. Origin of the Paleogene deep burial high-quality reservoirs in the southern Nanpu sag[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2019, 48(3): 553-569. doi: 10.13247/j.cnki.jcumt.000952
[17] 徐轩, 胡勇, 邵龙义, 等. 低渗致密砂岩储层充注模拟实验及含气性变化规律: 以鄂尔多斯盆地苏里格气藏为例[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2017, 46(6): 1323-1331
XU Xuan, HU Yong, SHAO Longyi, et al. Experimental simulation of gas accumulation mechanism in sandstone reservoir: A case study of Sulige gas field, Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2017, 46(6): 1323-1331.
[18] 杨振, 朱世发, 贾业, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地天环坳陷北部山1-盒8段地层水地球化学特征及成因[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2020, 20(7): 2634-2642 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.07.016
YANG Zhen, ZHU Shifa, JIA Ye, et al. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of formation water in Shan 1st to He 8th member in northern Tianhuan depression, Ordos basin[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2020, 20(7): 2634-2642. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.07.016
[19] 杨振. 鄂尔多斯盆地天环北部山1与盒8段气水分布规律研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学, 2020
YANG Zhen. Study on the distribution regulation of gas and water in the north Tianhuan depression, Ordos Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2020.
[20] 张帆, 王广才, 张茂省, 等. 产出水识别及受污染地下水水化学和氢氧稳定同位素特征[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(3): 98−108.
ZHANG Fan, WANG Guangcai, ZHANG Maosheng, et al. Identification of Produced Water and Characteristics of Hydrochemistry and Stable Hydrogen−Oxygen Isotopes of Contaminated Groundwater[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(3): 98−108.
[21] 张志升, 王小军, 冯立军, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地华庆地区延长组长8高阻水层成因分析与识别[J]. 西北地质, 2020, 53(2): 245-251 doi: 10.19751/j.cnki.61-1149/p.2020.02.016
ZHANG Zhisheng, WANG Xiaojun, FENG Lijun, et al. Genetic analysis and identification of Yanchang 8 high-resistivity water layer in Huaqing Area, Ordos Basin[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2020, 53(2): 245-251. doi: 10.19751/j.cnki.61-1149/p.2020.02.016
[22] 郑萌, 梁积伟, 冯振伟, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地中部寒武纪岩相古地理研究[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(6): 352−368.
ZHENG Meng, LIANG Jiwei, FENG Zhenwei, et al. Lithofacies Paleogeography of the Cambrian in the Central Ordos Basin[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(6): 352−368.
[23] 朱剑兵, 陈丽华, 纪友亮, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西缘逆冲带上古生界孔隙发育影响因素[J]. 石油学报, 2006, 27(3): 37-41 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2006.03.008
ZHU Jianbing, CHEN Lihua, JI Youliang, et al. Influence factors on the development of Upper Paleozoic pores in the thrust belt of the western margin of the Ordos Basin [J]. Acta Petroleum Sinica, 2006, 27(3): 37-41. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2006.03.008
-



 下载:
下载: