Early-Middle Triassic Adakitic and A-type Granite in Middle Segment of Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Petrogenesis and Tectonic Implications
-
摘要:
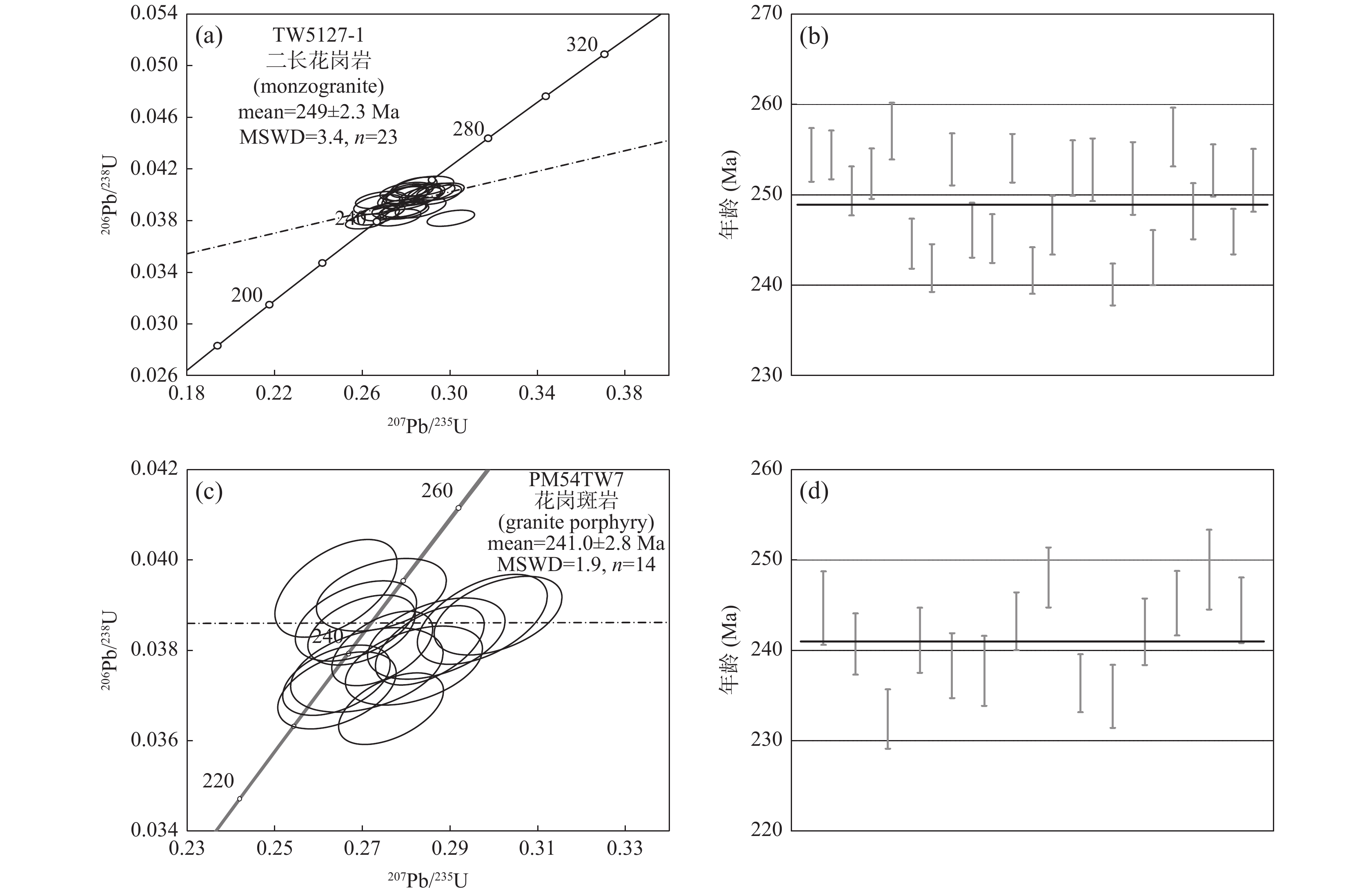
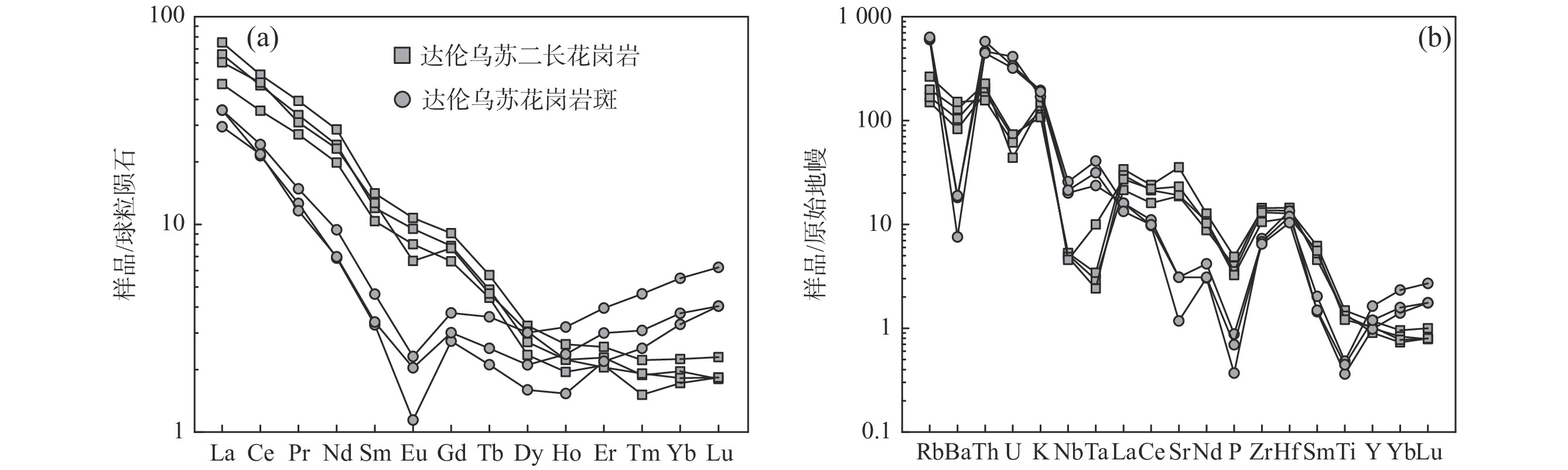
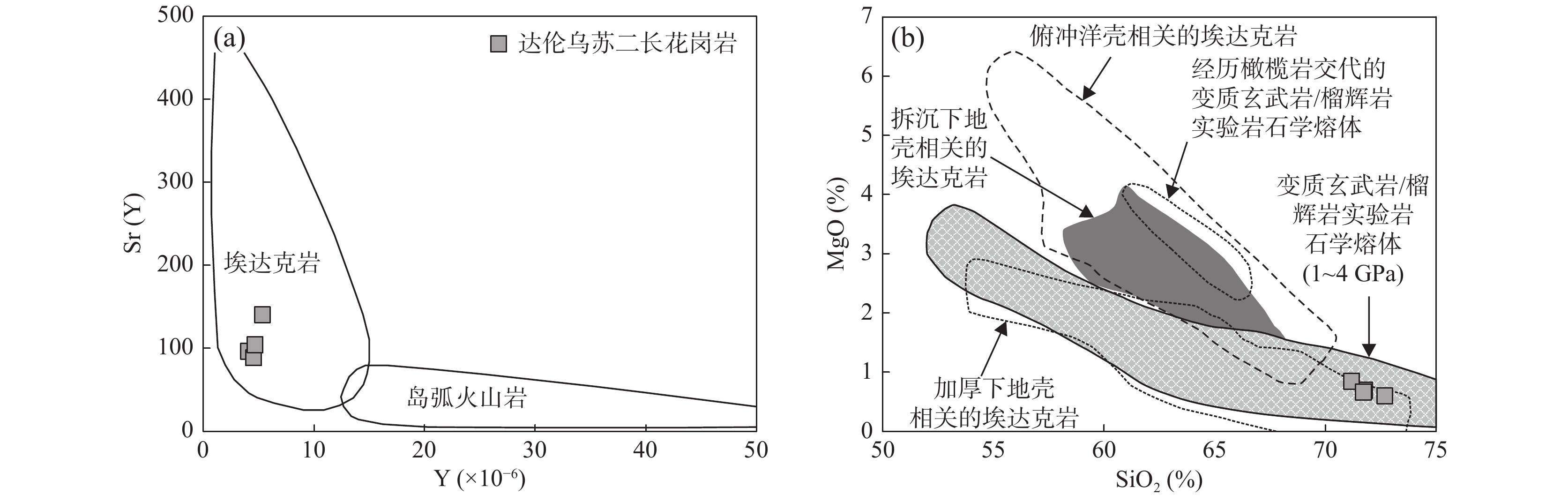
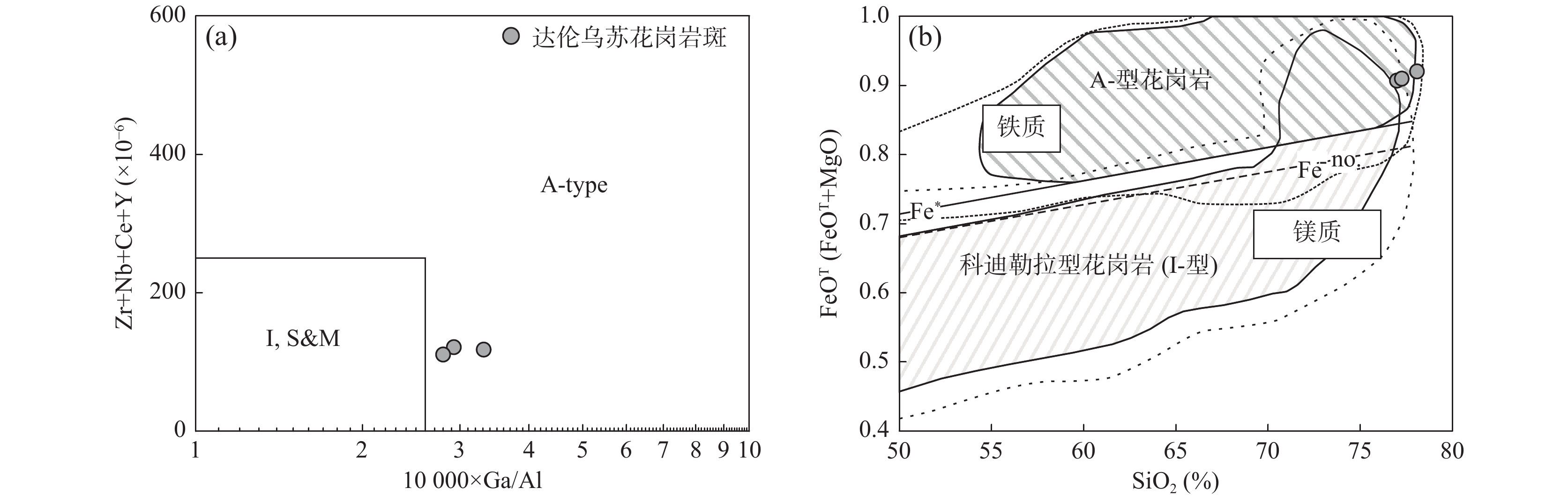
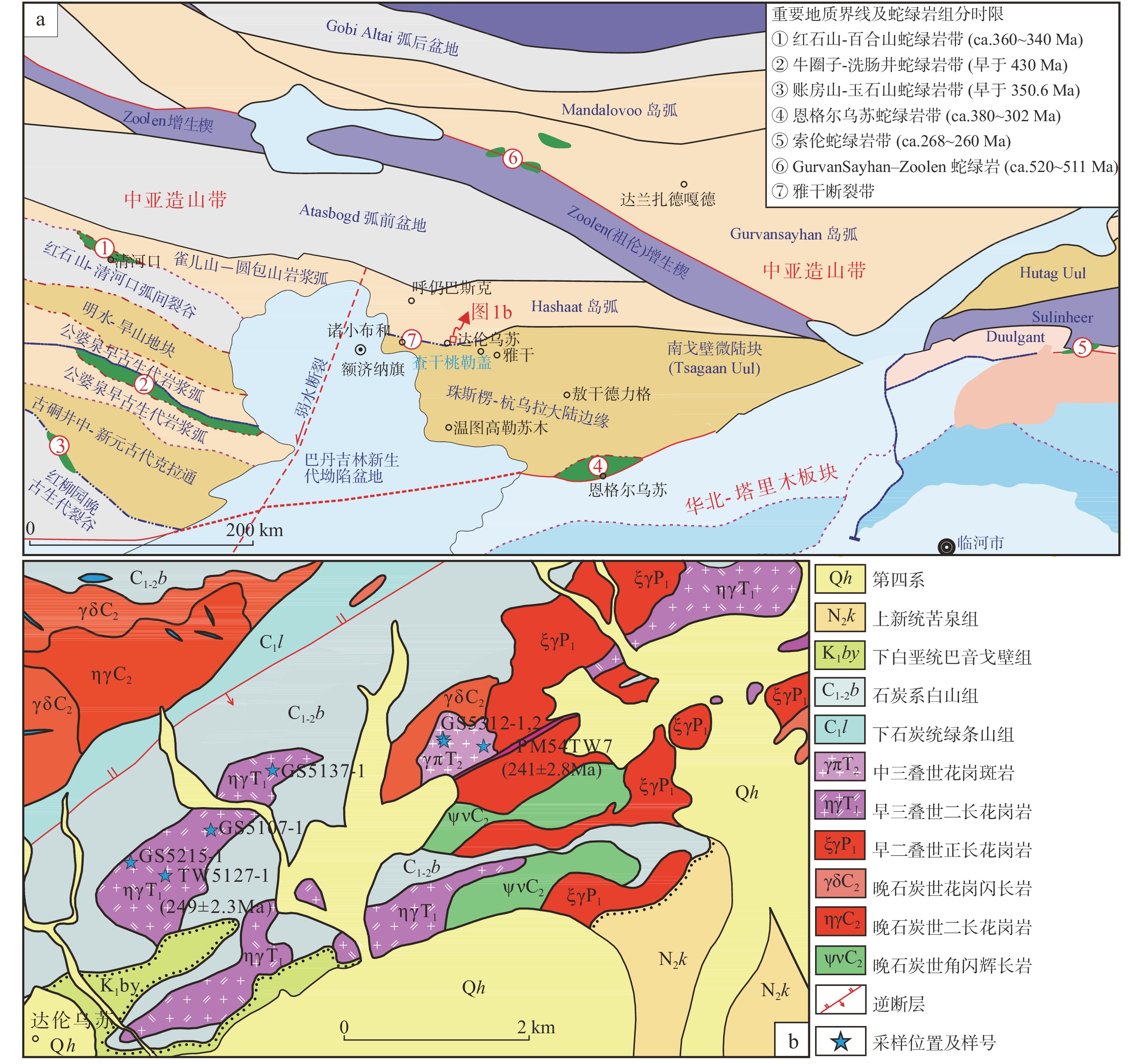
中亚造山带增生过程中发育的典型岩浆作用是研究其演化过程的关键。中亚造山带中段南缘达伦乌苏二长花岗岩、花岗斑岩系统的岩石学、地球化学和年代学研究表明,达伦乌苏二长花岗岩具有明显高Sr、低Y、Yb含量,高Sr/Y值(88.55~140.34),无明显Eu异常(δEu值为0.68~0.98),具埃达克岩地球化学特征。花岗斑岩富SiO2,贫CaO和MgO,具高的FeOT/(FeOT+MgO)和10000×Ga/Al值,高Zr、Nb、Ta 含量,富集Pb、Hf、 Rb、K和Th,相对亏损Ba、Sr、P和Ti,属于典型的A型花岗岩。二者的锆石U-Pb年龄分别为(249.0±2.3)Ma和(241.0±2.8)Ma。结合区域地质资料,埃达克岩指示了古亚洲洋闭合后陆壳碰撞加厚的背景,而A型花岗岩指示了碰撞后伸展构造背景。两种典型的岩浆作用记录了早—中三叠世中亚造山带中段南缘由增生造山到造山后期伸展的转换过程。
Abstract:Typical igneous rocks during the accretionary orogeny process in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt (CAOB) play a key role in understanding its tectonic evolution. We present new LA-ICP-MS in-situ zircon U-Pb and bulk geochemical data for the Dalunwusu monzogranite and granite porphyry suites which are located in Southernmost CAOB. The Dalunwusu monzogranites, have a crystallization age of (249.0±2.3) Ma, exhibit adakite-like geochemical characteristics, such as high Sr content and low Yb and Y contents, coupled with high Sr/Y values (88.55~140.34) and show a weakly negative Eu anomalies (δEu=0.68~0.98). Geochemical compositions indicate the Dalunwusu monzogranites derived from partial melting of mafic granulite in the lower thickened crust. The Dalunwusu granite porphyrys, have a crystallization age of (241.0±2.8) Ma, show typical geochemical features of A-type granites, which are characterized by having high SiO2, low CaO and MgO content, high FeOT/(FeOT+MgO) and 10000×Ga/Al values. Moreover, the granite porphyrys show trace element features of A-type granites including rich in Zr, Nb, Ta abundances, and high values for Pb, Hf, Rb, K and Th, and low values for Ba, Sr, P, and Ti. Taking into account available data of the regional geological background, we may suggest that the adakites were products through partial melting of the thickened lower crust after the closure of the Paleo-Asian Ocean, and the A-type granite porphyry were likely produced at the tectonic setting of post-collisional phase with crustal extension and thinning. These two typical igneous rocks reflect the shift of geodynamic setting, from an earlier accretionary orogen environment to a later extensional setting during early- middle Triassic.
-
Key words:
- central Asian Orogenic belt /
- zircon U-Pb age /
- triassic /
- adakite /
- A-type granite /
- Alxa
-

-
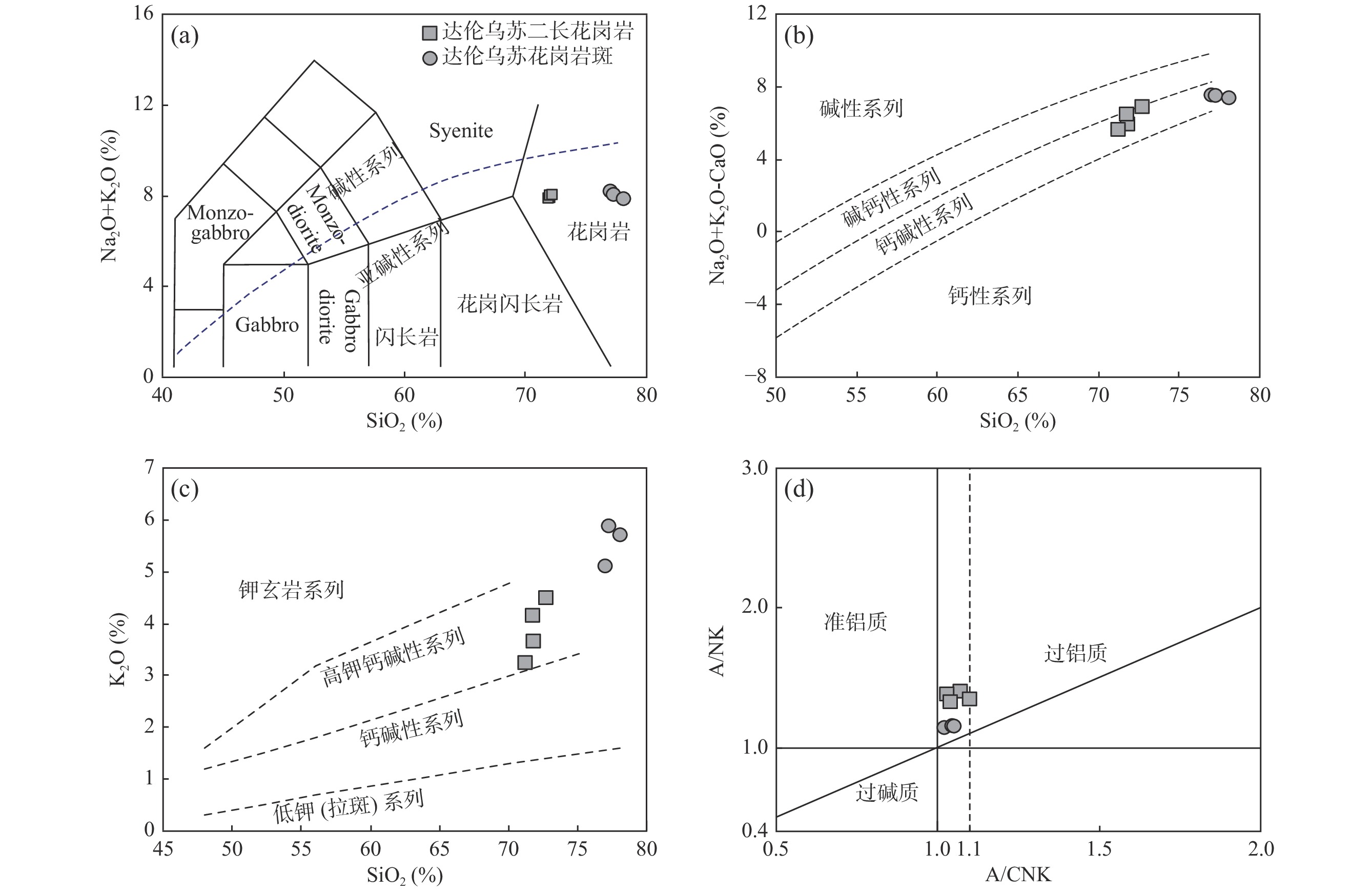
图 5 达伦乌苏早三叠世二长花岗岩和花岗斑岩TAS图解(a)(据Middemost, 1994)、SiO2-(Na2O+ K2O- CaO)(b)、SiO2- K2O(c)和A/NK-A/CNK图解(d)(据Miniar et al., 1989)
Figure 5.
图 8 达伦乌苏中三叠世花岗斑岩岩石类型及构造环境判别图解(a据Whalen et al., 1987; b据Forst et al., 2001)
Figure 8.
表 1 达伦乌苏早三叠世二长花岗岩和中三叠世花岗斑岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb 测年结果
Table 1. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating results for the Dalunwusu early-middle triassic monzogranite and granite porphyry
样品号 含量(10−6) Th/U 同位素比值 年龄(Ma) Pb Th U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 208Pb/232Th 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ TW5127-1,二长花岗岩 spot-01 32.8 326.9 674.0 0.49 0.05049 0.00147 0.28031 0.00805 0.04026 0.00048 0.01271 0.00033 217 67 251 6 254 3 spot-02 45.2 455.1 918.5 0.50 0.05321 0.00132 0.29573 0.00716 0.04026 0.00044 0.01333 0.00032 345 57 263 6 254 3 spot-03 28.3 258.8 604.2 0.43 0.04913 0.00141 0.26853 0.00759 0.03961 0.00044 0.01198 0.00027 154 67 242 6 250 3 spot-04 53.0 553.6 1104.3 0.50 0.05191 0.00116 0.28680 0.00654 0.03992 0.00045 0.01226 0.00028 280 52 256 5 252 3 spot-06 36.8 315.5 771.4 0.41 0.05038 0.00249 0.28842 0.00889 0.04069 0.00050 0.01441 0.00045 213 115 257 7 257 3 spot-07 52.9 653.7 1115.6 0.59 0.05049 0.00128 0.26964 0.00651 0.03867 0.00044 0.01216 0.00026 217 55 242 5 245 3 spot-08 53.5 681.0 1150.5 0.59 0.05180 0.00184 0.27615 0.00703 0.03824 0.00042 0.01142 0.00027 276 86 248 6 242 3 spot-09 59.7 588.7 1247.8 0.47 0.05236 0.00134 0.29155 0.00711 0.04018 0.00047 0.01260 0.00030 302 62 260 6 254 3 spot-10 26.7 259.7 576.7 0.45 0.05159 0.00165 0.27715 0.00837 0.03891 0.00049 0.01281 0.00035 333 74 248 7 246 3 spot-11 32.9 282.6 723.8 0.39 0.05188 0.00138 0.27909 0.00744 0.03876 0.00043 0.01279 0.00035 280 61 250 6 245 3 spot-12 61.6 743.3 1250.5 0.59 0.05035 0.00115 0.28021 0.00614 0.04020 0.00044 0.01272 0.00025 209 49 251 5 254 3 spot-13 58.5 935.0 1168.0 0.80 0.05662 0.00127 0.30055 0.00718 0.03820 0.00042 0.01236 0.00024 476 48 267 6 242 3 spot-14 33.1 398.4 699.9 0.57 0.05294 0.00130 0.28662 0.00766 0.03900 0.00053 0.01247 0.00031 328 28 256 6 247 3 spot-16 50.1 789.2 954.3 0.83 0.05336 0.00124 0.29522 0.00668 0.04002 0.00049 0.01279 0.00029 343 47 263 5 253 3 spot-18 32.2 366.7 644.9 0.57 0.05154 0.00161 0.28431 0.00892 0.03999 0.00056 0.01268 0.00033 265 77 254 7 253 3 spot-22 43.9 763.0 844.2 0.90 0.04963 0.00120 0.26183 0.00619 0.03795 0.00037 0.01184 0.00022 176 56 236 5 240 2 spot-24 25.9 240.0 545.8 0.44 0.05098 0.00152 0.28251 0.00887 0.03984 0.00065 0.01215 0.00041 239 70 253 7 252 4 spot-25 34.6 491.3 697.3 0.70 0.04986 0.00133 0.26655 0.00691 0.03842 0.00049 0.01198 0.00030 187 63 240 6 243 3 spot-27 35.5 383.4 718.5 0.53 0.05046 0.00134 0.28351 0.00710 0.04058 0.00052 0.01273 0.00031 217 61 253 6 256 3 spot-29 37.2 350.4 796.3 0.44 0.04926 0.00147 0.26735 0.00737 0.03925 0.00050 0.01164 0.00028 167 70 241 6 248 3 spot-30 39.0 658.3 726.7 0.91 0.05058 0.00132 0.28010 0.00692 0.03998 0.00046 0.01233 0.00027 220 59 251 5 253 3 spot-31 51.3 747.0 1026.8 0.73 0.05171 0.00134 0.27898 0.00669 0.03889 0.00040 0.01207 0.00026 272 59 250 5 246 3 spot-32 45.1 528.0 924.9 0.57 0.05077 0.00151 0.27851 0.00752 0.03980 0.00056 0.01234 0.00031 232 66 249 6 252 3 PM54TW7,花岗斑岩 spot-01 28.7 427.2 572.8 0.75 0.05527 0.00186 0.29714 0.00979 0.03869 0.00065 0.01221 0.00040 433 76 264 8 245 4 spot-02 48.7 619.9 1002.1 0.62 0.05177 0.00152 0.27438 0.00762 0.03805 0.00054 0.01167 0.00033 276 69 246 6 241 3 spot-03 33.9 406.8 725.1 0.56 0.05418 0.00204 0.27645 0.00792 0.03671 0.00053 0.01233 0.00037 389 81 248 6 232 3 spot-05 42.4 786.6 831.7 0.95 0.05388 0.00157 0.28522 0.00820 0.03811 0.00058 0.01118 0.00030 365 67 255 6 241 4 spot-09 24.3 284.9 523.6 0.54 0.05405 0.00210 0.28162 0.01030 0.03766 0.00058 0.01145 0.00037 372 87 252 8 238 4 spot-10 55.3 781.8 1085.9 0.72 0.05242 0.00438 0.27090 0.01148 0.03757 0.00062 0.01364 0.00049 306 191 243 9 238 4 spot-13 38.0 550.1 770.3 0.71 0.05064 0.00156 0.26967 0.00809 0.03845 0.00051 0.01204 0.00035 233 72 242 6 243 3 spot-14 36.8 470.6 743.6 0.63 0.05036 0.00182 0.27417 0.00974 0.03923 0.00053 0.01244 0.00038 213 88 246 8 248 3 spot-15 34.4 538.8 723.4 0.74 0.05096 0.00156 0.26393 0.00810 0.03735 0.00051 0.01168 0.00031 239 72 238 7 236 3 spot-16 25.8 435.0 524.3 0.83 0.05166 0.00184 0.26403 0.00885 0.03711 0.00056 0.01228 0.00033 333 81 238 7 235 3 spot-21 27.5 373.2 569.7 0.66 0.05394 0.00206 0.28668 0.01036 0.03826 0.00059 0.01193 0.00044 369 87 256 8 242 4 spot-22 39.5 549.3 782.3 0.70 0.05610 0.00259 0.30074 0.00964 0.03877 0.00057 0.01394 0.00045 457 102 267 8 245 4 spot-23 33.4 588.1 646.7 0.91 0.04870 0.00181 0.26388 0.00917 0.03937 0.00071 0.01205 0.00040 132 87 238 7 249 4 spot-27 33.8 463.5 682.4 0.68 0.05041 0.00173 0.26837 0.00914 0.03865 0.00059 0.01287 0.00044 213 84 241 7 244 4 表 2 达伦乌苏早三叠世二长花岗岩和中三叠世花岗斑岩主、微量分析测试结果
Table 2. Major (%) and trace element (10−6) analysis results for the Dalunwusu early- middle Triassic monzogranite and granite porphyry
GS5215-1 GS5137-1 GS5107-1 TW5127-1 PM54TW7 GS5312-1 GS5312-2 岩体 早三叠世二长花岗岩 中三叠世紫红色花岗斑岩 SiO2 71.80 71.21 71.74 72.71 77.00 77.25 78.08 TiO2 0.30 0.32 0.29 0.26 0.08 0.10 0.10 Al2O3 15.12 15.05 14.84 14.98 12.27 11.62 11.35 Fe2O3 1.40 1.16 1.12 1.36 1.01 0.94 1.02 FeO 0.90 1.47 1.31 0.32 0.49 1.13 0.80 CaO 1.85 2.07 1.72 1.39 0.72 0.60 0.54 MgO 0.69 0.84 0.66 0.60 0.14 0.19 0.15 K2O 3.66 3.25 4.16 4.50 5.11 5.89 5.71 Na2O 4.14 4.47 4.05 3.79 3.15 2.23 2.22 MnO 0.04 0.04 0.03 0.02 0.02 0.03 0.02 P2O5 0.09 0.11 0.08 0.07 0.01 0.02 0.02 LOI 1.28 0.60 0.82 0.91 0.33 0.25 0.27 TOTAL 99.70 99.66 99.69 100.13 99.88 99.78 99.81 K2O/Na2O 0.89 0.73 1.03 1.19 1.62 2.64 2.58 FeOT 2.16 2.52 2.33 1.55 1.40 1.97 1.72 A/CNK 1.07 1.03 1.04 1.10 1.02 1.04 1.05 A/NK 1.40 1.38 1.33 1.35 1.14 1.16 1.15 Mg# 40.24 41.22 37.47 44.75 17.69 17.19 15.34 R1 2388 2316 2295 2392 2771 2918 3027 R2 529 558 508 472 324 302 287 Ga 19.6 19.4 19.8 19.7 21.5 18 16.8 Rb 95.5 107 126 168 383 388 403 Sr 395 748 402 487 24.8 65.4 65.2 Y 4.1 5.33 4.54 4.68 4.47 7.42 5.43 Zr 161 153 146 118 81.7 76 72.5 Nb 3.63 3.78 3.46 3.25 14.3 18.4 15.2 Ba 579 727 901 1056 52.9 127 132 La 14.7 23.3 20.4 18.7 11 11 9.16 Ce 28.5 42.5 37.8 38.9 17.3 19.6 17.6 Pr 3.31 4.8 4.1 3.78 1.54 1.81 1.42 Nd 11.9 17.2 14.5 13.9 4.13 5.65 4.19 Sm 2.02 2.75 2.34 2.47 0.64 0.9 0.66 Eu 0.59 0.79 0.7 0.49 0.084 0.17 0.15 Gd 1.72 2.35 2.04 1.99 0.71 0.97 0.78 Tb 0.21 0.27 0.23 0.22 0.1 0.17 0.12 Dy 0.78 1.08 0.9 1.01 0.53 1 0.7 Ho 0.14 0.19 0.16 0.16 0.11 0.23 0.17 Er 0.44 0.54 0.48 0.43 0.46 0.83 0.63 Tm 0.049 0.072 0.061 0.062 0.082 0.15 0.1 Yb 0.36 0.47 0.41 0.38 0.69 1.15 0.78 Lu 0.059 0.074 0.058 0.059 0.13 0.2 0.13 Hf 4.46 4.19 3.93 3.57 4.15 3.68 3.21 Ta 0.12 0.14 0.099 0.41 0.97 1.67 1.29 Pb 23.7 27.2 22.8 26.4 51.2 31.7 31.9 Th 15.7 17.4 19.3 13.3 39.4 49 38 U 1.45 1.54 0.92 1.29 8.67 7.06 6.72 δEu 0.97 0.95 0.98 0.68 0.38 0.56 0.64 ΣREE 64.78 96.39 84.18 82.55 37.51 43.83 36.59 (La/Yb)N 29.30 35.58 35.71 35.31 11.44 6.86 8.43 (La/Sm)N 4.70 5.48 5.63 4.89 11.11 7.90 8.97 10000×Ga/Al 2.45 2.43 2.52 2.48 3.31 2.93 2.80 -
[1] 陈井胜, 刘正宏, 刘永江, 等. 中亚造山带东段构造演化研究进展: 前言[J]. 岩石学报, 2022, 38(08): 2175-2180 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2022.08.01
CHEN Jingsheng, LIU Zhenghong, LIU Yongjiang, et al. Recent Progress in the evolution of eastern segment of the Central Asia Orogenic Belt[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2022, 38(8): 2175-2180. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2022.08.01
[2] 董玉, 王锶淼, 于倩, 等. 中国东北地区晚古生代构造-岩浆演化历史[J]. 岩石学报, 2022, 38(8): 2249-2268 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2022.08.04
DONG Yu, WANG Simiao, YU Qian, et al. Late Paleozoic tectonic-magmatic evolution history of the northeastern China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2022, 38(8): 2249-2268. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2022.08.04
[3] 付超,李俊建,张帅,等.中蒙边界地区侵入岩时空分布特征及对构造演化的启示[J].华北地质, 2023, 46(1): 1−19.
FU Chao, LI Junjian, ZHANG Shuai, et al. The temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of intrusive rocks in the border area between China and Mongolia and its implications for tectonic evolution[J]. North China Geology, 2023, 46(1): 1−19.
[4] 贾小辉, 王强, 唐功建. A型花岗岩的研究进展及意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2009, 33(3), 465-480 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2009.03.017
JIA Xiaohui, WANG Qiang, TANG Gongjian. A-type Granites: Research Progress and Implications[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 33(3), 2009, 465-480. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2009.03.017
[5] 雷聪聪, 薄海军, 丁海生, 等. 内蒙古自治区雅干地区白山组火山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其构造环境[J]. 地质通报, 2023,42(12):2096-2108.
LEI Congcong, BO Haijun, DING Haisheng, et al. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating and tectonic setting of volcanic rocks of Baishan Formation in Yagan area, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region[J]. Geological Bulletin, 2023,42(12):2096-2108.
[6] 李凤春, 侯明兰, 栾日坚, 等. 电感耦合等离子体质谱仪与激光器联用测量条件优化及其在锆石U-Pb定年中的应用[J]. 岩矿测试, 2016, 35(1): 17-23.
LI Fengchun, HOU Minglan, LUAN Rijian, et al. Optimization of Analytical Conditions for LA-ICP-MS and Its Application to Zircon U-Pb Dating[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis. 2016, 35(1): 17-23
[7] 刘桂萍, 郭瑞清, 魏震, 等. 新疆库鲁克塔格地区古生代花岗质侵入岩全岩Sr-Nd和锆石Hf同位素地球化学特征及其意义[J]. 西北地质, 2021, 54(03): 39-50
LIU Guiping, GUO Ruiqing, WEI Zhen. Geochemical Characteristics and Significance of the Whole Rock Sr-Nd and Zircon Hf Isotopic in the Paleozoic Granite-plutons in Kuruktag, Xinjiang. Northwestern Geology, 2021, 54(03): 39-50.
[8] 刘基, 王丕军, 薄海军. 内蒙古额济纳旗内乔仑恩格次黑云母二长花岗斑岩中锆石的特征及其指示意义[J]. 西北地质, 2020, 53(03): 41-55
LIU Ji, Wang Pijun Bo Haijun. Characteristics and Implications of Zircon in Qiaolun'en'geci Biotite Monzogranite Porphyry in Ejina County, Inner Mongolia[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2020, 53(03): 41-55.
[9] 马军, 雷聪聪, 王文宝, 等. 阿拉善地块北缘雅干地块诸小布和糜棱岩化花岗岩地球化学特征、锆石U-Pb年龄及构造背景研究[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2021, 40(06): 1357-1368 doi: 10.19658/j.issn.1007-2802.2021.40.086
MA Jun, LEI Congcong, WANG Wenbao, et al. A Study on Geochemistry, Zircon U-Pb Dating and Tectonic Setting of the Zhuxiaobuhe Mylonitized Granite in the Yagan Area of Northern Margin of the Alxa Terrain[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2021, 40(06): 1357-1368. doi: 10.19658/j.issn.1007-2802.2021.40.086
[10] 邵积东. 内蒙古地质构造单元划分及存在的有关问题[J]. 西部资源, 2016, 3: 84-87/150. doi: 10.16631/j.cnki.cn15-1331/p.2016.03.030
SHAO Jidong. Division of geological tectonic units of Inner Mongolia and related problems[J]. Westrn Resources, 2016. 3: 84-87/150. doi: 10.16631/j.cnki.cn15-1331/p.2016.03.030
[11] 邵济安, 唐克东, 何国琦. 内蒙古早二叠世构造古地理的再造[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(7): 1858–1866
SHAO Jian, TANG Kedong, HE Guoqi. Early Permian tectono-palaeogeographic reconstruction of Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(7): 1858–1866.
[12] 舍建忠, 贾健, 金成, 等. 西准噶尔谢米斯台山中段晚石炭世A型花岗岩地球化学特征及岩石成因[J]. 地质通报, 2023, 42(7): 1051−1068.
SHE Jianzhong, JIA Jian, JIN Cheng, et al. Geochemical characteristics and petrogenesis of Late Carboniferous A-type granites in the middle section of Xiemisitai Mountain, West Junggar[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2023, 42(7): 1051−1068.
[13] 宋博, 张慧元, 魏东涛, 等. 中亚造山带南缘中-新元古代地壳的揭示——来自北山—阿拉善北部钻遇碱性花岗岩的年代学和Hf 同位素示踪研究[J]. 地球学报, 2021, 42(1): 9-20 doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2020.071901
SONG Bo, ZHANG Huiyuan, WEI Dongtao, et al. Revelation of the Meso–Neoproterozoic Crust on the Southern Margin of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Chronology and Hf Isotope Tracer from Drilling-intersected Alkaline Granites, Northern Beishan-Alxa[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2021, 42(1): 9-20. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2020.071901
[14] 王丕军. 额济纳旗乔仑恩格次花岗岩特征及构造环境研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2018
WANG Pijun. Characteristics and Tectonic Environment of Qiaolunengeci Granite in Ejina County[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2018.
[15] 王廷印, 王金荣, 王士政, 等. 华北板块和塔里木板块之关系[J]. 地质学报, 1993, 67(4): 287-300 doi: 10.19762/j.cnki.dizhixuebao.1993.04.001
WANG Tingyin, WANG Jinrong, WANG Shizheng, et al. Relationships between the North China and Tarim Plates[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1993, 67(4): 287-300. doi: 10.19762/j.cnki.dizhixuebao.1993.04.001
[16] 王元元, 杨小强, 阿种明, 等. 新疆西准噶尔沙勒克腾地区花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其对后碰撞构造环境的约束[J]. 地质通报, 2023, 42(4): 600−615.
WANG Yuanyuan, YANG Xiaoqiang, A Zhongming, et al. Zircon U-Pb age, geochemistry of granites in Shaleketeng area, West Junggar, Xinjiang and its constraints on the post-collision tectonic environment[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2023, 42(4): 600−615.
[17] 王振义, 李钢柱, 丁海生, 等. 内蒙古额济纳旗雅干地区北山岩群的厘定及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 2022, 47(4): 1177-1193 doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1000-2383.2022.4.dqkx202204003
WANG Zhenyi, LI Gangzhu, DING Haisheng, et al. Determination and Geological Significance of Beishan Group in Yagan Area, Ejiana, Inner Mongolia[J]. Earth Science, 2022, 47(4): 1177-1193. doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1000-2383.2022.4.dqkx202204003
[18] 吴泰然, 何国琦. 内蒙古阿拉善地块北缘的构造单元划分及各单元的基本特征[J]. 地质学报, 1993, 67(2): 97-108. doi: 10.19762/j.cnki.dizhixuebao.1993.02.001
WU Tairan, HE Guoqi. Tectonic units and their fundamental characteristics on the northern margin of the Alxa Block[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1993, 67(2), 97-108. doi: 10.19762/j.cnki.dizhixuebao.1993.02.001
[19] 谢春林, 杨建国, 王立社, 等. 甘肃北山地区古亚洲南缘古生代岛弧带位置的讨论[J]. 地质学报, 2009, 83(11): 1584-1599 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2009.11.004
XIE Chunlin, YANG Jianguo, WANG Lishe, et al. Disscussion on the Location of Paleozoic Island Arc Zone on the South Margin of Paleo-Asian Ocean in the Beishan Area of Gansu Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2009, 83(11): 1584-1599. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2009.11.004
[20] 辛后田, 牛文超, 田健, 等. 内蒙古北山造山带时空结构与古亚洲洋演化[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(9): 1297-1316
XIN Houtian, NIU Wenchao, TIAN Jian, et al. Spatio-temporal structure of Beishan orogenic belt and evolution of Paleo-Asian Ocean, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2020, 39(9): 1297-1316.
[21] 熊万宇康, 赵梦琪, 于淼, 等. 造山带洋陆转换过程与岩浆作用: 以东昆仑都兰地区古生代花岗岩为例[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(6): 113−139.
XIONG Wanyukang, ZHAO Mengqi, YU Miao, et al. Ocean−Continent Transition Process and Magmatism in Orogenic Belts: A Case Study of Paleozoic Granites in the Dulan Area of East Kunlun[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(6): 113−139.
[22] 杨玉柱, 袁万明. A型花岗岩的鉴别标志[J]. 河北地质学院学报, 1993, 16(2): 150-158
YANG Yuzhu, YUAN Wanming. Discriminating Marks of A-type Granitoids[J]. Journal of Hebei College of Geology, 1993, 16(2): 150-158.
[23] 张旗, 焦守涛. 埃达克岩来自高压背景-一个科学的, 可靠的, 有预见性的科学发现[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(6): 1675-1683 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.06.02
ZHANG Qi, JIAO Shoutao. Adakite comes from a high-pressure background: A scientific, reliable, predictable scientific discovery[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2020, 36(6): 1675-1683. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.06.02
[24] 张旗, 冉皞, 李承东. A型花岗岩的实质是什么?[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2012, 31(4): 621-626 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2012.04.014
ZHANG Qi, RAN Hao, LI Chengdong. A-type granite: what is the essence? [J]. Acta Petrologica Et Mineralogica, 2012, 31(4): 621-626. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2012.04.014
[25] 张旗, 王焰, 刘伟, 等. 埃达克岩的特征及其意义[J]. 地质通报, 2002, 21(7): 431-435 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2002.07.012
ZHANG Qi, WANG Yan, LIU Wei, et al. Adakite: Its characteristics and implications[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2002, 21(7): 431-435. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2002.07.012
[26] 张旗, 王焰, 王元龙. 埃达克岩与构造环境[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2003, 27(2): 101-108 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2003.02.001
ZHANG Qi, WANG Yan, WANG Yuanlong. On the relationship between adakite and its tectonic setting[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2003, 27(2): 101-108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2003.02.001
[27] 张永玲, 张治国, 刘希军, 等. 内蒙朝克山辉长岩中单斜辉石矿物化学特征及地质意义[J]. 西北地质, 2024, 57(1): 122−138.
ZHANG Yongling, ZHANG Zhiguo, LIU Xijun, et al. Mineralogical Chemistry Characteristics and Geological Significance of the Clinopyroxene from Chaokeshan Gabbro, Inner Mongolia[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2024, 57(1): 122−138.
[28] 郑荣国, 吴泰然, 张文, 等. 阿拉善地块北缘雅干花岗岩体地球化学、地质年代学及其对区域构造演化制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(08): 2665-2675
ZHENG Rongguo, WU Tairan, ZHANG Wen, et al. 2013. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Yagan granite in the northern margin of the Alxa block: Constraints on the tectonic evolution of the southern Altaids[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(8): 2665-2675.
[29] Badarch G, Cunningham W D, Windley BF. A new terrane subdivision for Mongolia: implications for the Phanerozoic crustal growth of Central Asia[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2002, 21(1): 87~110. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(02)00017-2
[30] Boynton W V, Geochemistry of the rare earth elements: meteorite studies[A]. In Henderson P (ed.). Rare earth element geochemistry[M]. Amsterdam, Elsevier, 1984: 63−114.
[31] Charvet J, SHU Liangshu, Laurent-Charvet S. Paleozoic structural and geodynamic evolution of eastern Tianshan (NW China): welding of the Tarim and Junggar plates[J]. Episodes, 2007, 30: 162-186.
[32] Defant M J, Drummond M S. Derivation of Some ModernArc Magmas by Melting of Young Subducted Lithosphere[J]. Nature, 1990, 347(6294): 662-665. doi: 10.1038/347662a0
[33] DU Long, LONG Xiaoping, YUAN Chao, et al. Petrogenesis of Late Paleozoic diorites and A-type granites in the central Eastern Tianshan, NW China: Response to post-collisional extension triggered by slab breakoff[J]. Lithos, 2018, 318: 47-59.
[34] Eby G N. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids: petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 1992, 20(7): 641-644. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0641:CSOTAT>2.3.CO;2
[35] Eizenhöfer P R, ZHAO Guochun. Solonker Suture in East Asia and its bearing on the final closure of the eastern segment of the Palaeo-Asian Ocean[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2018, 186: 153-172. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.09.010
[36] Forst B R, Barnes C G, Collins W J, et al. A Geochemitic Classification For Granitic Rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2001. 42(11): 2033-2042. doi: 10.1093/petrology/42.11.2033
[37] FU Dong, HUANG Bo, Kusky T M, et al. A middle Permian ophiolitic mélange belt in the Solonker suture zone, western Inner Mongolia, China: Implications for the evolution of the Paleo-Asian Ocean[J]. Tectonics, 2018, 37: 1292-1320. doi: 10.1029/2017TC004947
[38] JIAN Ping, Kröner A, Jahn B M, et al. Zircon dating of Neoproterozoic and Cambrian ophiolites in West Mongolia and implications for the timing of orogenic processes in the central part of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2014, 133: 62-93. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.02.006
[39] Jian Ping, LIU Dunyi, Kröner A, et al. Time scale of an early to mid-Paleozoic orogenic cycle of the long-lived Central Asian Orogenic Belt, Inner Mongolia of China: Implications for continental growth[J]. Lithos, 2008, 101: 233-259. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2007.07.005
[40] LI HaoDong, ZHOU JianBo, Wilde S A. Nature and development of the South Tianshan-Solonker suture zone[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2022, 223: 104189
[41] LI Jinyi. Permian geodynamic setting of Northeast China and adjacent regions: closure of the Paleo-Asian Ocean and subduction of the Paleo-Pacific Plate[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2006, 26(3-4): 207-224. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2005.09.001
[42] Li Shan, Chung S L, Wilde S A, et al. Early‐Middle Triassic high Sr/Y granitoids in the southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Implications for ocean closure in accretionary orogens. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth[J], 2017, 122(3): 2291-2309.
[43] LI Shan, WANG Tao, Wilde S A, et al. Geochronology, petrogenesis and tectonic implications of Triassic granitoids from Beishan, NW China[J]. Lithos, 2012, 134-135: 123-145. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2011.12.005
[44] Li Shan, Wang Tao, Wilde S A, et al. Evolution, source and tectonic significance of Early Mesozoic granitoid magmatism in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt (central segment). Earth-Science Reviews[J], 2013, 126: 206−234.
[45] LIU Min, LAI Shaocong, ZHANG Da, et al. Middle Permian high Sr/Y monzogranites in central Inner Mongolia: reworking of the juvenile lower crust of Bainaimiao arc belt during slab break-off of the Palaeo-Asian oceanic lithosphere[J]. International Geology Review, 2019, 61(17): 2083-2099. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2019.1579057
[46] LIU Qian, ZHAO Guochun, HAN Yigui, et al. Early Paleozoic subduction processes of the Paleo-Asian Ocean: insights from geochronology and geochemistry of Paleozoic plutons in the Alxa Terrane[J]. Lithos, 2016, 262: 546-560. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2016.07.041
[47] LIU Qian, ZHAO Guochun, HAN Yigui, et al. Timing of the final closure of the Paleo-Asian Ocean in the Alxa Terrane: Constraints from geochronology and geochemistry of Late Carboniferous to Permian gabbros and diorites[J]. Lithos, 2017, 274-275: 19-30. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2016.12.029
[48] LIU Qian, ZHAO Guochun, HAN Yigui, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of Paleozoic to Mesozoic granitoids in western Inner Mongolia, China: implications for the tectonic evolution of the southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. The Journal of Geology, 2018, 126(4): 451-471. doi: 10.1086/697690
[49] LIU Yongsheng, WANG Xiaohong, WANG Dongbing, et al. Triassic high-Mg adakitic andesites from Linxi, Inner Mongolia: insights into the fate of the Paleo-Asian ocean crust and fossil slab-derived melt-peridotite interaction[J]. Chemical Geology, 2012, 328: 89-108. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.03.019
[50] LU Jia, ZHANG Chen, LIU Dongdong. Geochronological, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic studies of the A-type granites and adakitic granodiorites in Western Junggar: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J]. Minerals, 2020, 10(397): 1-25.
[51] Ludwing K R. Isoplot 3.00: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[CP]. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Center. 2003.
[52] LUAN JinPeng, TANG Jie, et al. Accretion kinematics and driving mechanism of the eastern Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Insights from seismic tomography and middle Permian-Middle Triassic magmatism in central Jilin Province[J]. Gondwana Research, 2022, 101: 114-131. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2021.08.002
[53] Middemost E A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994, 37(3-4): 215-224. doi: 10.1016/0012-8252(94)90029-9
[54] Miniar P D, Piccoli P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101(5): 635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
[55] Rapp R P, Watson E B. Dehydration Melting of Metabasalt at 8-32 kbar: Implications for Continental Growth and Crust Mantle Recycling[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1995, 36(4): 891-931. doi: 10.1093/petrology/36.4.891
[56] Şengör A M C, Natal'in B A, Burtman V S. Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Palaeozoic crustal growth in Eurasia[J]. Nature, 1993, 364(6435): 299-307. doi: 10.1038/364299a0
[57] SHI Guanghai, MIAO Laicheng, ZHANG Fuqing, et al. Emplacement age and tectonic implications of the Xilinhot A-type granite in Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49(7): 723-729. doi: 10.1007/BF03184272
[58] SHI Yuruo, Anderson J L, LI Linlin, et al. Zircon ages and Hf isotopic compositions of Permian and Triassic A-type granites from central Inner Mongolia and their significance for late Palaeozoic and early Mesozoic evolution of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. International Geology Review, 2016, 58(8): 967-982. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2016.1138333
[59] SONG Dongfang, XIAO Wenjiao, Windley B F, et al. Carboniferous to Early Triassic magmatism and accretion in Alxa(NW China): implications for accretionary orogenesis of the southern Altaids[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2020, 177: 997-1012. doi: 10.1144/jgs2020-046
[60] SUN S S, Mcdonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
[61] WANG Qiang, XU JiFeng, et al. Petrogenesis of Adakitic Porphyries in an Extensional Tectonic Setting, Dexing, SouthChina: Implications for the Genesis of Porphyry Copper Mineralization[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2006, 47(1): 119-144. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egi070
[62] WANG Tao, TONG Ying, XIAO Wenjiao, et al. Rollback, scissor-like closure of the Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean and formation of an orocline: magmatic migration based on a large archive of age data[J]. National science review, 2022, 9(5), nwab210. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwab210
[63] WANG Tao, ZHENG Yadong, Gehrels G E, et al. Geochronological evidence for existence of South Mongolian microcontinent—A zircon U-Pb age of grantoid gneisses from the Yagan-Onch Hayrhan metamorphic core complex[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2001, 46(23): 2005-2008. doi: 10.1007/BF02901917
[64] WANG Wenlong, TENG Xuejian, LIU Yang, et al. From subduction to post‐collision: Early Permian‐middle Triassic magmatic records from Langshan Belt, Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Geological Journal, 2020, 55(3): 2167-2184. doi: 10.1002/gj.3790
[65] Whalen J B, Currie K L, Chappell B W. A-type granites: geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95: 407-419. doi: 10.1007/BF00402202
[66] Windley B F, Alexeiev D, XIAO Wenjiao, et al. Tectonic models for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2007, 164(1): 31-47. doi: 10.1144/0016-76492006-022
[67] Wu Fuyuan, Sun Deyou, Li Huimin , et al, A-type granites in Northeastern China: age and geochemical constraints on their petrogenesis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 187, 143−173.
[68] XIAO Wenjiao, Windley BF, HAN Chunming, et al. Late Paleozoic to early Triassic multiple roll-back and oroclinal bending of the Mongolia collage in Central Asia[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2018, 186: 94-128. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.09.020
[69] XIAO Wenjiao, Windley BF, HAO Jie, et al. Accretion leading to collision and the Permian Solonker suture, Inner Mongolia, China: Termination of the central Asian orogenic belt[J]. Tectonics, 2003, 22(6): 1069.
[70] XU Bei, Charvet J, CHEN Yan, et al. Middle Paleozoic convergent orogenic belts in western Inner Mongolia (China): framework, kinematics, geochronology and implications for tectonic evolution of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 23(4): 1342-1364. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.05.015
[71] YAN Quanshu, Metcalfe I, SHI Xuefa, et al. Early Cretaceous granitic rocks from the southern Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China: implications for lithospheric extension[J]. International Geology Review, 2019, 61(7): 821-838. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2018.1474388
[72] ZHANG Wen, Pease V, MENG Qingpeng, et al. Discovery of a Neoproterozoic granite in the Northern Alxa region, NW China: its age, petrogenesis and tectonic significance[J]. Geological Magazine, 2016, 153(03): 512-523. doi: 10.1017/S0016756815000631
[73] ZHENG Jiahao, MAO Jingwen, CHAI Fengmei, et al. Petrogenesis of Permian A-type granitoids in the Cihai iron ore district, Eastern Tianshan, NW China: Constraints on the timing of iron mineralization and implications for a non-plume tectonic setting[J]. Lithos, 2016, 260: 371-383. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2016.05.012
[74] ZHENG Rongguo, LI Jinyi, ZHANG Jin, et al. Permian oceanic slab subduction in the southmost of Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Evidence from adakite and high-Mg diorite in the southern Beishan[J]. Lithos, 2020, 358: 105406.
[75] ZHENG Rongguo, LI Jinyi, ZHANG Jin, et al. A prolonged subduction-accretion in the southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Insights from anatomy and tectonic affinity for the Beishan complex[J]. Gondwana Research, 2021, 95: 88-112. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2021.02.022
[76] ZHENG Rongguo, WU Tairan, ZHANG Wen, et al. Late Paleozoic subduction system in the northern margin of the Alxa block, Altaids: geochronological and geochemical evidences from ophiolites[J]. Gondwana Research, 2014, 25(2): 842-858. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2013.05.011
-



 下载:
下载: