Engineering Geological Characteristics of Xigeda Formation Claystone in Luding County, Western Sichuan
-
摘要:
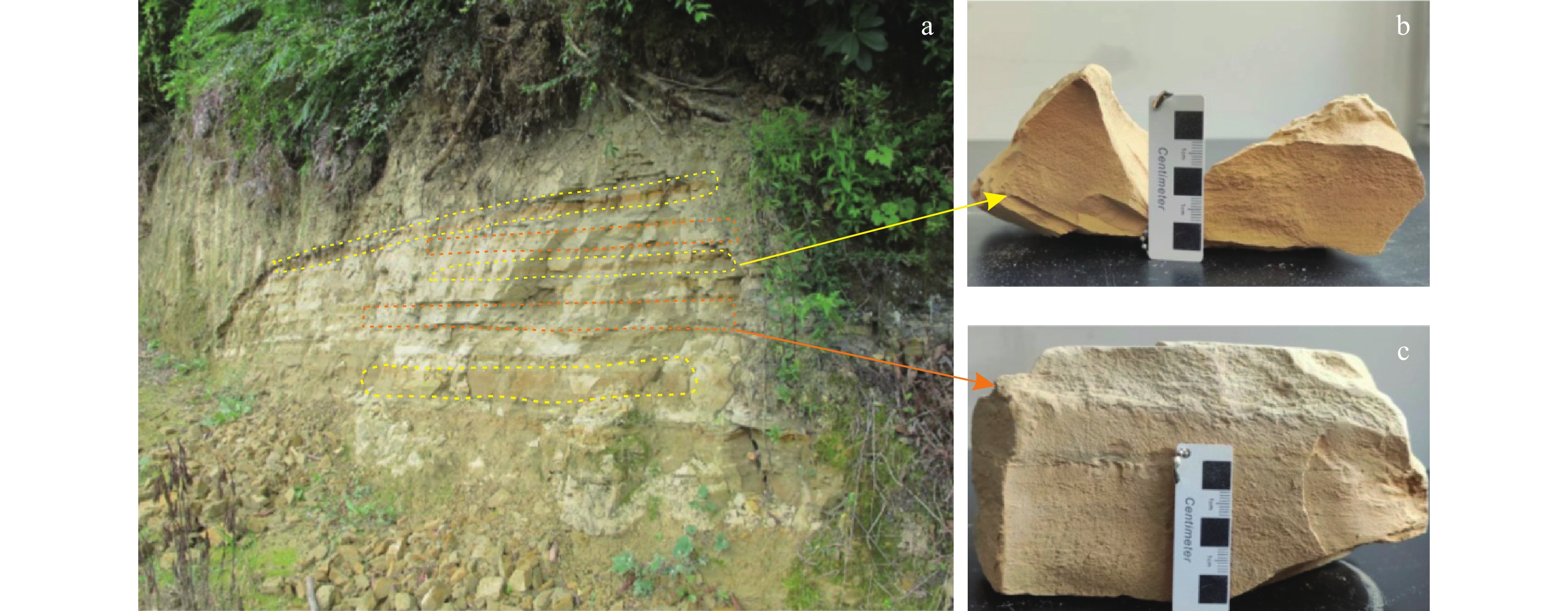
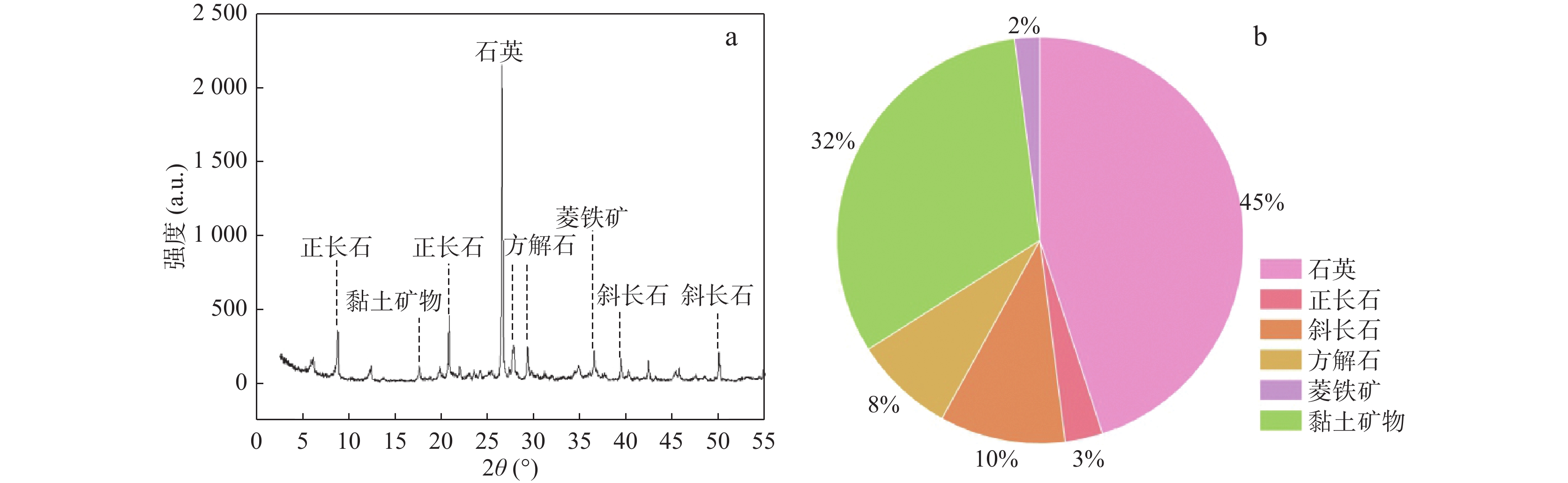
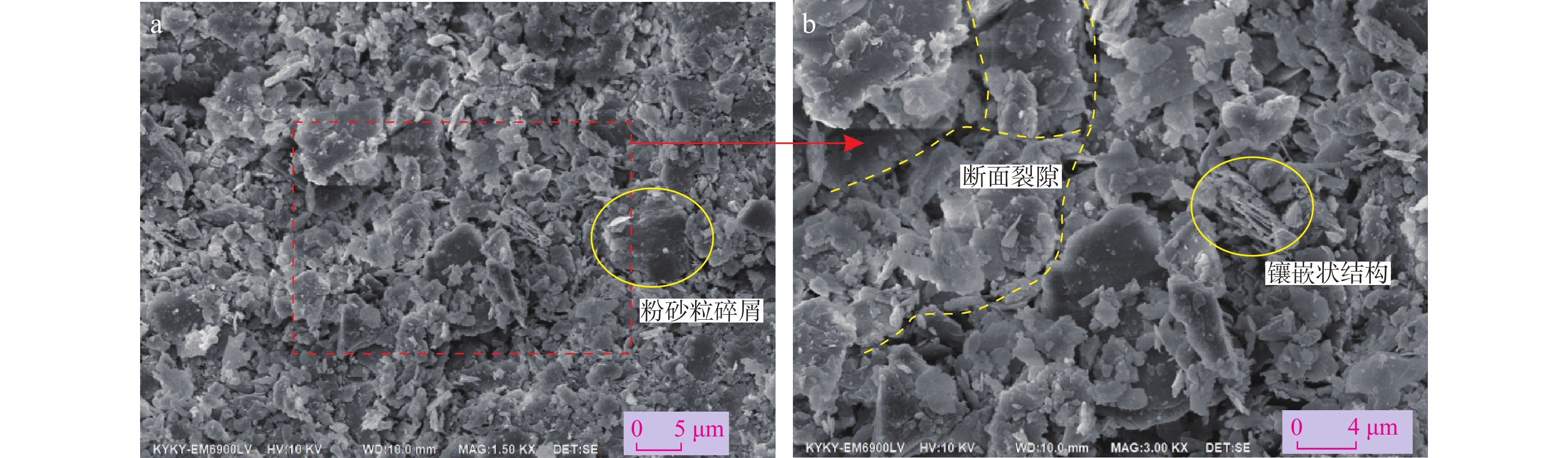
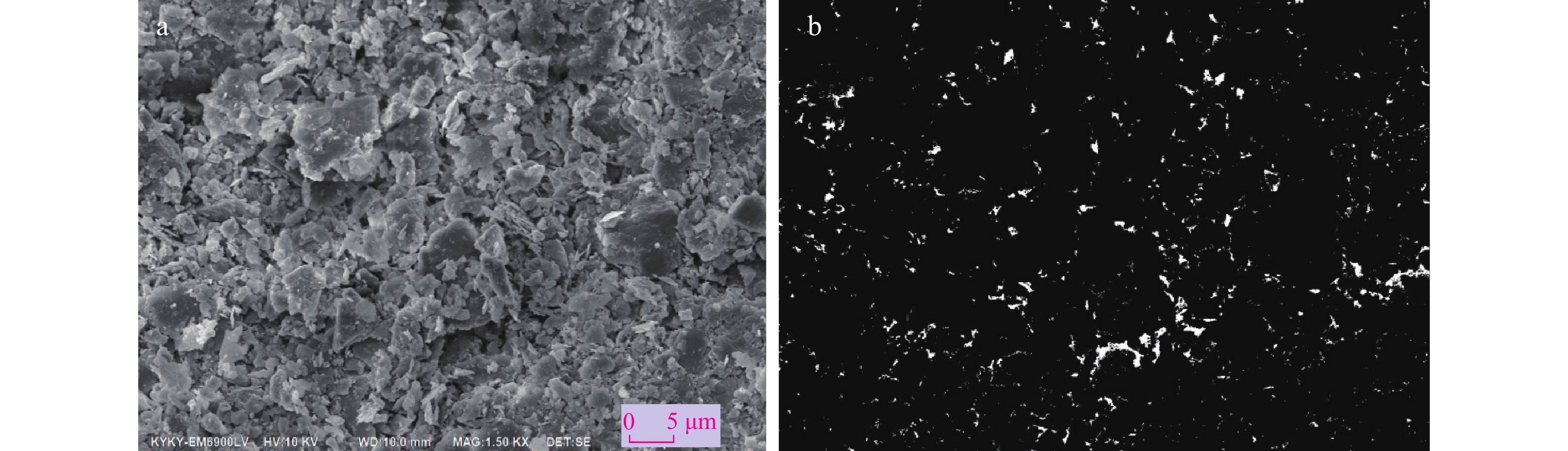
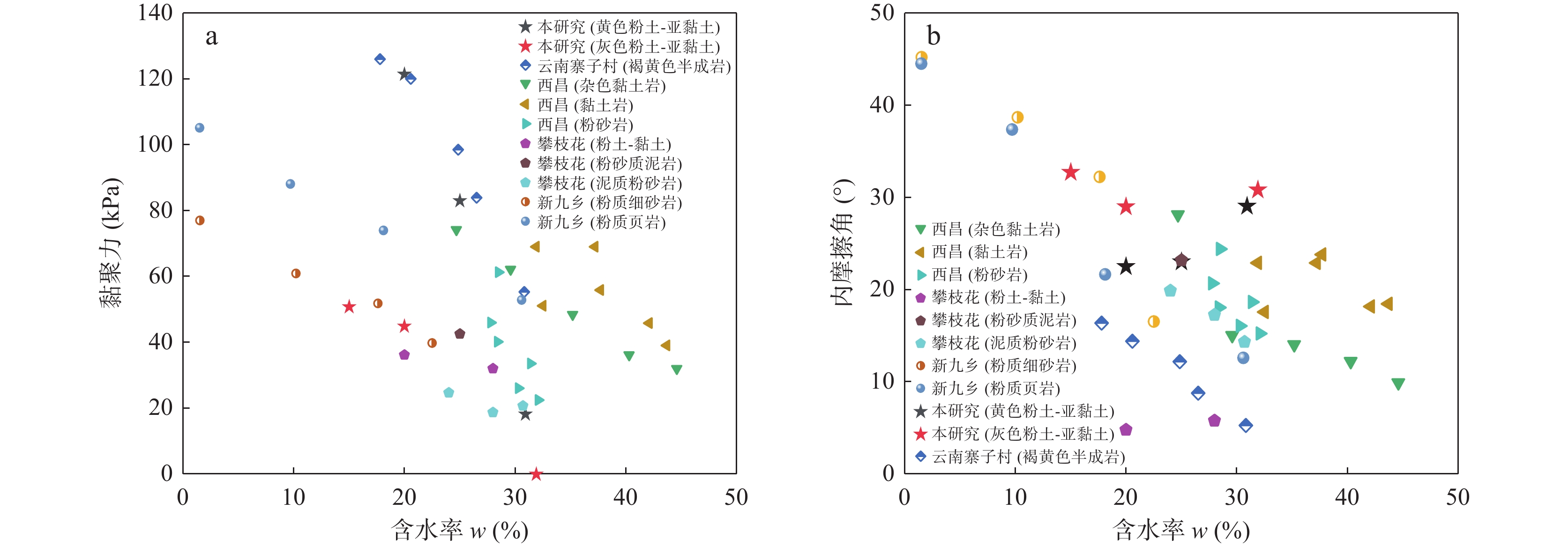
昔格达地层作为一类特殊的半成岩,具有“见风成粉,遇水成泥”的特性,是工程地质问题与地质灾害的良好孕生载体。以川西泸定海子坪昔格达地层黏土岩为研究对象,通过X射线衍射、电镜扫描、现场与室内岩土测试,分析了其物质组成、微观结构及力学特性,重点研究水作用下其物理力学性质的变化规律,并与其他地区昔格达地层工程地质特性进行比较分析。研究表明:①海子坪昔格达地层黏土岩主要成分为粉细砂、黏土等细粒物质,由薄层黄色和灰色的黏土岩互层产出,具有近水平层理构造。②黄色和灰色黏土岩的物质组成相同,但占比不同,黄色黏土岩的黏粒含量比灰色黏土岩高约12%,方解石含量少约10%,黄色黏土岩的结构更为致密,黏粒间胶结作用更强。③海子坪昔格达地层黏土岩现场实测渗透系数为3.62×10−4~7.34×10−4 cm/s,介于其他地区昔格达地层的黏土岩类–砂岩类之间,这与其天然节理发育、受扰动极易开裂的特性密切相关。④黄、灰色黏土岩的黏聚力均随含水率增加而降低,且含水率越高,降幅越大,内摩擦角与含水率的关系则表现有所不同。⑤不同地区昔格达地层的力学特性对含水率变化的敏感性具有明显差异,其中泸定海子坪昔格达地层黏土岩的水敏性最为显著。
Abstract:The Xigeda Formation is a special semi-diagenetic, which has the characteristics of "wind-induced powder, water-induced mud", and is a good carrier for engineering geological problems and geological hazards. In this study, the yellow and gray claystone of the Xigeda Formation in Haiziping Village, Luding County, western Sichuan was investigated. Its material composition, microstructure, and mechanical properties were analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), field and laboratory geotechnical tests. The variation law of its physical and mechanical properties under the action of water is emphasized, and the engineering geological characteristics of the Xigeda Formation are compared and analyzed with those in other regions. Based on the above research, some conclusions are as follows. ①The Xigeda Formation claystone in Haiziping Village is mainly composed of fine sand, clay, and additional fine-grained materials. It is produced by yellow and gray thin layers interbedding and has a horizontal lamination structure. ②Yellow and gray claystone have the same material composition, but material proportions are different. The clay content of yellow claystone is 12% higher than that of gray claystone, and the calcite content is 10% inferior. The microstructure of yellow claystone is denser and cemented with clay particles more strongly. ③The permeability coefficient measured on the site of Xigeda Formation claystone in Haiziping Village is 3.62~7.34×10−4 cm/s, which is between claystones and sandstones in Xigeda Formation in other regions. The characteristic of its permeability is closely related to the development of natural joints and the characteristic of cracks that is susceptible to disturbance. ④The cohesion of yellow and gray claystone decreased with the increase of moisture content, and the higher the moisture content, the greater the decline, but the relationship between internal friction angle and moisture content was different.⑤ The mechanical properties of the Xigeda Formation in different regions and lithology have obvious differences in sensitivity to moisture content changes, among which the mechanical property weakening by the water of the Xigeda Formation claystone in Haiziping Village, Luding County is the most significant.
-
Key words:
- Xigeda Formation /
- claystone /
- microstructure /
- engineering geological characteristics /
- Western Sichuan
-

-
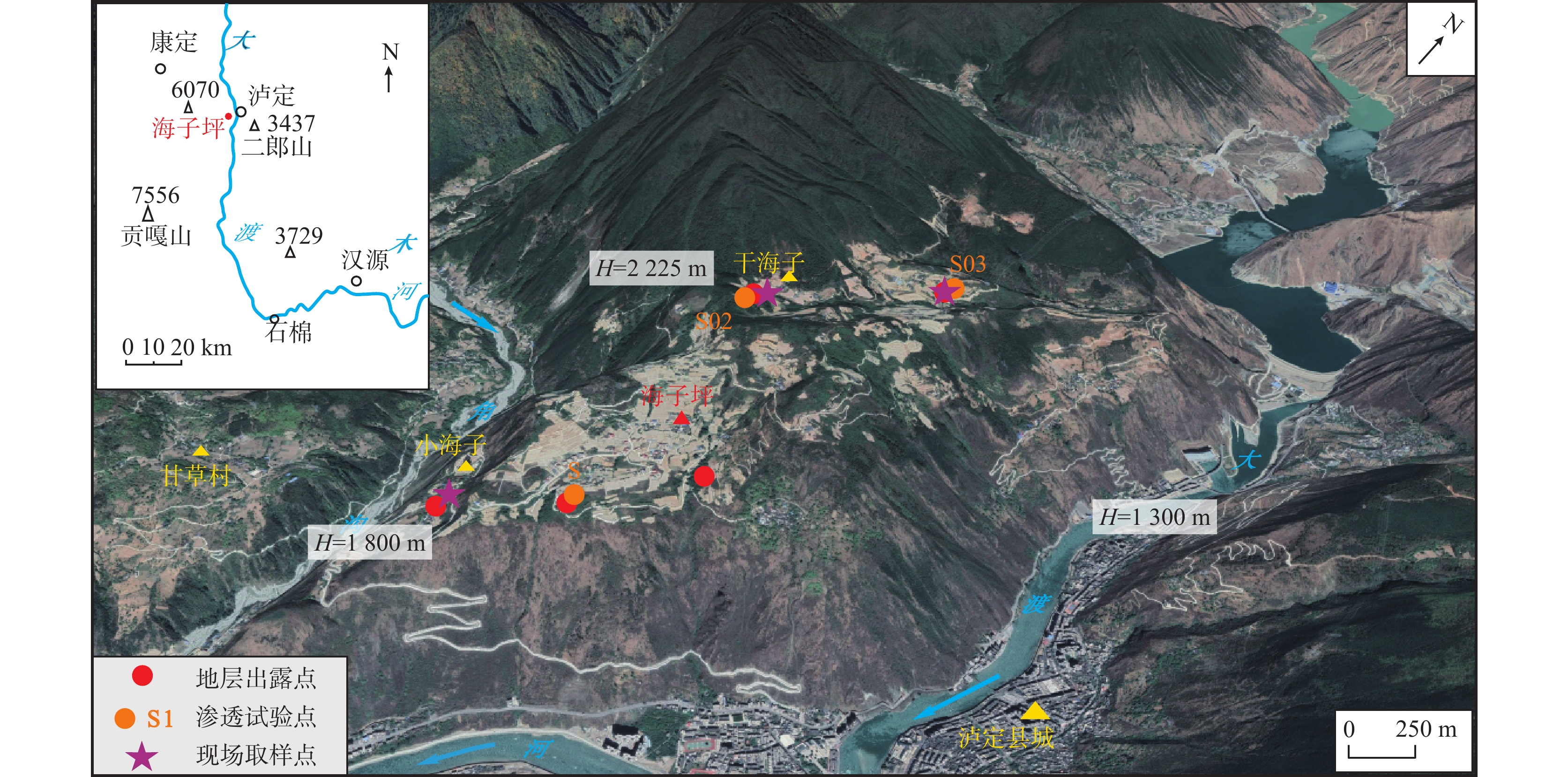
表 1 泸定海子坪昔格达地层测年方法及结果统计
Table 1. The dating methods and statistical results of the Xigeda formation in Haiziping village, Luding county
表 2 黄色和灰色黏土岩黏土矿物分析结果
Table 2. Test results of clay minerals of yellow and gray claystone samples
序号 样品类型 黏土矿物检测结果(%) 蒙脱石
S伊蒙混层
I/S伊利石
It高岭石
K绿泥石
CI/S混层比(%S) 1 黄色黏土岩 3 — 93 — 4 — 2 灰色黏土岩 5 — 89 — 6 — 表 3 黄色和灰色黏土岩各孔径级别对应的微观孔隙测量结果
Table 3. Measurement results of different pore sizes of yellow and gray claystone samples
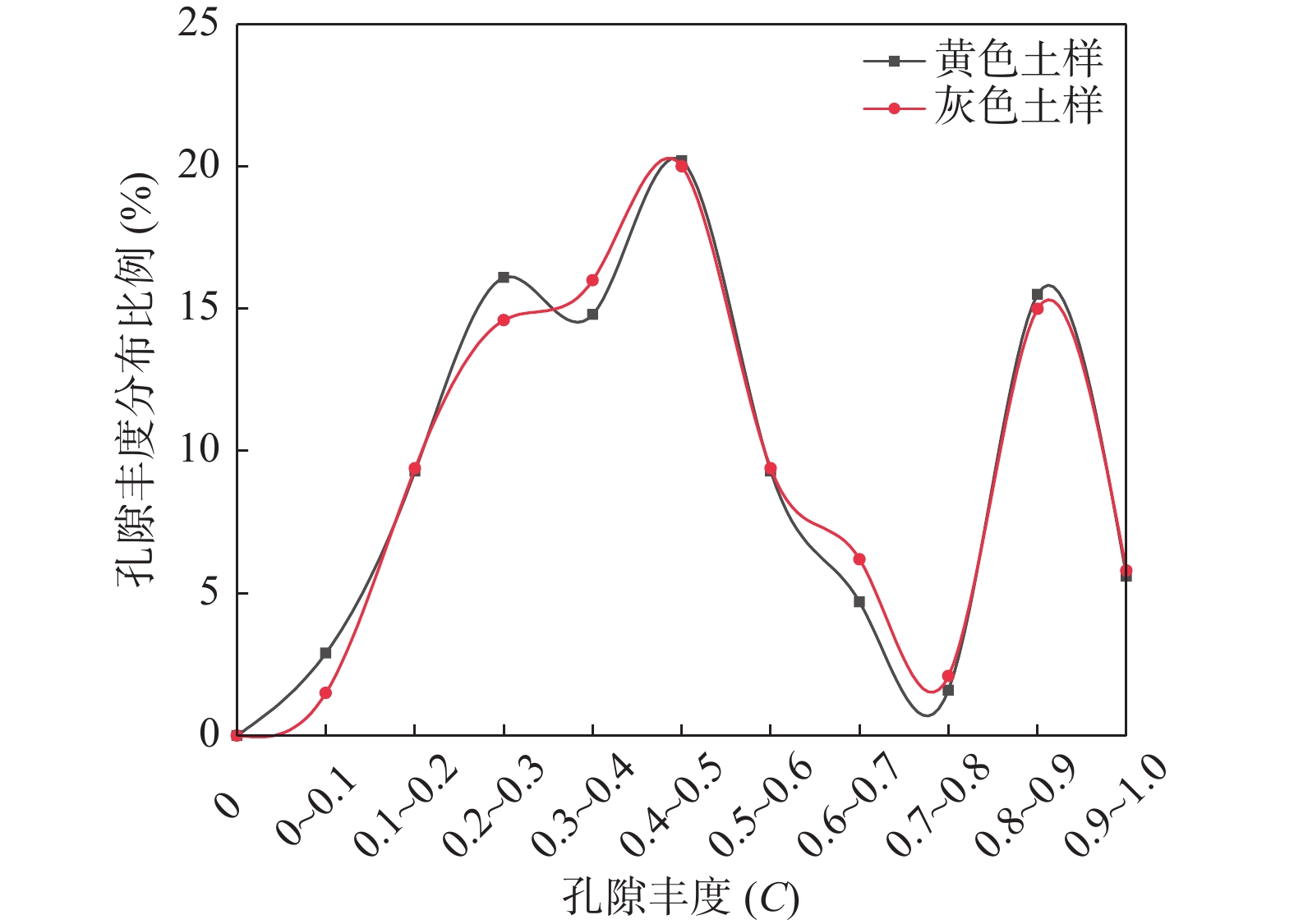
孔径级别(µm) 黄色黏土岩 灰色黏土岩 数量 N(个) 孔径d(µm) 面积A(µm2) 丰度(C) 数量 N(个) 孔径d(µm) 面积A(µm2) 丰度(C) <0.4 356 0.23 0.04 0.53 512 0.24 0.05 0.53 0.4~1 137 0.59 0.24 0.46 178 0.57 0.26 0.51 1~4 22 1.5 1.64 0.45 30 1.24 1.06 0.44 >4 0 0 0 0 1 4.11 5.99 0.52 注:C为B与L的比值,B表示孔隙的短轴长度,L表示孔隙长轴长度,A为平均孔隙面积。 表 4 黄色和灰色黏土岩基本物性指标
Table 4. Basic physical property indexes of yellow and gray claystone samples
土样
编号样品
类型含水率
(%)土粒
比重天然密度
(g/cm3)干密度
(g/cm3)孔隙比 液限
(%)塑限
(%)塑性
指数饱和含水
率(%)XGD-01 灰色黏土岩 3.7 2.69 1.86 1.76 0.569 36.4 25.9 10.5 30.93 XGD-02 黄色黏土岩 4.5 2.70 1.80 1.73 0.550 36.3 24.9 11.4 31.91 表 5 双环注水试验结果
Table 5. Results of double-ring water injection tests
试验点序号 渗透系数
(cm/s)平均渗透系数
(cm/s)透水性等级 S01 3.62×10−4 5.11×10−4 中等透水 S02 7.34×10−4 S03 4.36×10−4 表 6 不同地区昔格达地层渗透特性比较
Table 6. Comparison of permeability characteristics of Xigeda Formation in different regions
地区 试验对象 试验条件 渗透系数(cm/s) 透水性等级 数据来源 泸定海子坪 粉土-亚黏土 现场双环注水 3.62×10−4~7.34×10−4 中等透水 本研究 攀枝花格里坪 亚黏土 室内渗透 3.7×10−5~7.2×10−4 弱透水 宋为广等(2017) 粉砂岩 室内渗透 2.0×10−5~2.78×10−5 弱透水 左永振等(2016) 攀枝花粟子坪 亚黏土 室内渗透 2.8×10−7~3.3×10−7 极弱透水 李小泉(1996) 云南龙开口镇 黏土岩 室内渗透 10−8~10−7 极弱透水 张德强等(2021) 川南地区 泥岩 现场、室内渗透 1.7×10−5~5.25×10−5 弱透水 钟成等(2012) 砂岩 1.6×10−4 中等透水 西昌经久乡 黏土岩 室内渗透、
钻孔压水1.95×10−7~4.61×10−5 弱透水 杨碧(2010) 粉砂岩 1.47×10−4~6.54×10−4 中等透水 -
[1] 安少鹏, 韦立德, 刘文连, 等. 昔格达组粉砂岩与结构接触面力学特性试验研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2013, 21(05): 702-708 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2013.05.005
AN Shaopeng, WEI Lide, LIU Wenlian, et al. Experimental study on mechanical behavior of Xigeda Formation siltstone and structure interface[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2013, 21(05): 702-708. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2013.05.005
[2] 陈林, 朱剑. 昔格达滑坡破坏模式及稳定性评价[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护, 2015, 26(03): 11-16 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4362.2015.03.003
CHEN Lin, ZHU Jian. Deformation mechanism and stability assessment of Xigeda landslide[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation, 2015, 26(03): 11-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4362.2015.03.003
[3] 陈智梁, 孙志明, L. H. Royden, 等. 四川泸定昔格达组的堰塞湖成因及其意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2004, 24(06): 614-620 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2004.06.002
CHEN Zhiliang, SUN Zhiming, L. H. Royden, et al. Landslide blocked lake: origin of the Xigeda Formation in Luding, Sichuan and its significance[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2004, 24(06): 614-620. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2004.06.002
[4] 冯立, 张茂省, 张成航, 等. 四川虹口黑泥湾滑坡风险性评估[J]. 西北地质, 2014, 47(03): 165-176 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2014.03.022
FENG Li, ZHANG Maosheng, ZHANG Chenghang, et al. Risk Assessment of Landslide in Heiniwan, Hongkou County, Sichuan Province[J]. Northwest Geology, 2014, 47(03): 165-176. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2014.03.022
[5] GB/T 50123-2019, 土工试验方法标准[S].
GB/T 50123-2019, Standard for Geotechnical Test Methods[S].
[6] 蒋复初, 吴锡浩, 肖华国. 四川泸定昔格达组时代及其新构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 1999, 73(1): 1-6 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.1999.01.001
JIANG Fuchu, WU Xihao, XIAO Huaguo. The age of Xigeda Formation in Luding, Sichuan and its neotectonic significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1999, 73(1): 1-6. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.1999.01.001
[7] 黄绍槟, 吉随旺, 朱学雷, 等. 西攀路昔格达地层滑坡分析[J]. 公路交通科技, 2005, 22(6): 41-44
HUANG Shaobin, JI Suiwang, ZHU Xuelei, et al. Analysis on Xigeda landslide in Xipan expressway[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2005, 22(6): 41-44.
[8] 李绵绵, 赵法锁, 宋飞, 等. 双排抗滑桩的受力特性研究—以柳家坡2号滑坡治理工程为例[J]. 西北地质, 2019, 52(02): 181-189
LI Mianmian, ZHAO Fasuo, SONG Fei, et al. Force Characteristics of Double-row Anti-slide Pile in Liujiapo Landslide[J]. Northwest Geology, 2019, 52(02): 181-189.
[9] 李小泉. 粟子坪水电站厂基昔格达土的工程特性[J]. 广西水利水电, 1996, (01): 18-22+45 doi: 10.16014/j.cnki.1003-1510.1996.01.005
LI Xiaoquan. Engineering characteristics of Xigeda foundation soil in Suziping Hydropower plant[J]. Guangxi Water Resources & Hydropower Engineering, 1996, (01): 18-22+45. doi: 10.16014/j.cnki.1003-1510.1996.01.005
[10] 梁坤. 基于昔格达混合填料中砂泥配比变化的工程力学效应研究[D]. 绵阳: 西南科技大学, 2021
LIANG Kun. Research on engineering mechanics effect based on the variation of sand and mud ratio in Xigeda mixed filling[D]. Mianyang: Southwest University of Science and Technology, 2021.
[11] 刘惠军, 聂德新. 昔格达地层研究综述[J]. 地球科学进展, 2004, (S1): 80-82
LIU Huijun, NIE Dexin. The overview of the Xigeda Strata’ study[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2004, (S1): 80-82.
[12] 卢志鹏, 孔玉侠, 王慧娟, 等. 昔格达土的压缩特性和微观结构[J]. 南京工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 44(1): 114-122
LU Zhipeng, KONG Yuxia, WANG Huijuan, et al. Compressive characteristics and microstructure of Xigeda soil[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 44(1): 114-122.
[13] 罗璐. 四川泸定晚新生代昔格达组沉积记录及大渡河水系演化[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2021
LUO Lu. Sedimentary records of the Xigeda Formation in the late eenozoic and evolution of the Dadu river system in Luding, Sichuan[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2021.
[14] 罗运利, 刘东生. 昔格达组沉积环境演化与旋回地层学研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 1998, 4: 373 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1998.04.015
LUO Yunli, LIU Dongsheng. Study on sedimentary environment evolution and cyclostratigraphy of Xigeda Formation[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1998, 4: 373. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1998.04.015
[15] 孟庆会. 西昌昔格达地层粘土塑性指数形成机制[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2011
MENG Qinghui. Formation mechanism of clay plasticity index of Xigeda Clay in Xichang[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2011.
[16] 彭盛恩. 昔格达组粘土的工程地质特性研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 1986, 2: 16-18 doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.1986.02.006
PENG Shengen. Study on the engineering geological characteristics of the clay in the Xigeda Group[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 1986, 2: 16-18. doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.1986.02.006
[17] SL 345-2007, 水利水电工程注水试验规程[S].
SL 345-2007, Code of Water Injection Test for Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering[S].
[18] 施云云. 大渡河泸定段海子坪昔格达组的宇生核素等时线埋藏测年及地貌意义[D]. 南京: 南京师范大学, 2020
SHI Yunyun. Cosmogenic nuclides Isochronal burial dating and geomorphological significance of the Haiziping Xigeda Formation in Luding section of Dadu River[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Normal University, 2020.
[19] 宋德光, 吴瑞安, 马德芹, 等. 四川泸定昔格达组滑坡灾害运动过程模拟分析[J]. 地质通报, 2023, 42(12): 2185−2197.
SONG Deguang, WU Ruian, MA Deqin, et al. Simulation analysis of landslide disaster movement process in Xigeda Formation, Luding County, Sichuan Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2023, 42(12): 2185−2197.
[20] 宋为广, 杜妍平. 昔格达土用于坝体防渗料试验研究[J]. 山西建筑, 2017, 43(01): 228-229 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6825.2017.01.120
SONG Weiguang, DU Yanping. On dam anti-seepage material test with Xigeda soil[J]. Shan’xi Architecture, 2017, 43(01): 228-229. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6825.2017.01.120
[21] 铁永波, 张宪政, 龚凌枫, 等. 西南山区典型地质灾害链成灾模式研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 2022, 28(6): 1071-1080 doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.20222830
TIE Yongbo, ZHANG Xianzheng, GONG Linfeng, et al. Research on the pattern of typical geohazard chains in the southwest mountainous region, China [J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2022, 28(6): 1071-1080. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.20222830
[22] 王萍, 李建平, 王建存, 等. 四川昔格达组地层的石英Ti心ESR测年及与磁性地层剖面的对比[J]. 核技术, 2011, 34(02): 111-115
WANG Ping, LI Jianping, WANG Jiancun, et al. Quartz Ti-center in ESR dating of Xigeda Formation in Sichuan and contrast with magnetic stratigraphic profiles[J]. Nuclear Techniques, 2011, 34(02): 111-115.
[23] 王书兵, 赵志中, 乔彦松, 等. 泸定昔格达组时代认定与古环境[J]. 第四纪研究, 2006, 26(2): 257-264 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2006.02.014
WANG Shubing, ZHAO Zhizhong, QIAO Yansong, et al. Age and paleoenvironment of Xigeda Formation in Luding[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2006, 26(2): 257-264. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2006.02.014
[24] 王思敬, 黄鼎成. 攀西地区环境工程地质[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1990
WANG Sijing, HUANG Dingcheng. Environmental engineering geology in west of Sichuan[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1990.
[25] 文丽娜, 朱学雷, 白志勇, 等. 西攀高速公路新九地区昔格达地层岩土特性[J]. 公路, 2005, 7: 145-148 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0451-0712.2005.03.034
WEN Lina, ZHU Xuelei, BAI Zhiyong, et al. Characteristics rock and soil of Xigeda Strata in Xinjiu district of Xi-Pan Expressway [J]. Highway, 2005, 7: 145-148. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0451-0712.2005.03.034
[26] 吴俊峰, 王运生, 张桥, 等. 大渡河加郡-得妥河段大型滑坡地质灾害遥感调查[J]. 水土保持通报, 2011, 31(03): 113-116
WU Junfeng, WANG Yunsheng, ZHANG Qiao, et al. Investigation on Large-scale Landslides in Daduhe River Between Jiajun County and Detuo County Based on Remote Sensing[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2011, 31(03): 113-116.
[27] 徐奕梓, 樊晓一, 张友谊, 等. 四川省汉源县中海村滑坡动力学特征数值分析[J]. 中国地质调查, 2022, 9(4): 102-111 doi: 10.19388/j.zgdzdc.2022.04.12
XU Yizi, FAN Xiaoyi, ZHANG Youyi, et al. Numerical analysis on dynamic characteristics of Zhonghai Village landslide in HanyuanCounty of Sichuan Province[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2022, 9(4): 102-111. doi: 10.19388/j.zgdzdc.2022.04.12
[28] 徐则民, 刘文连. 昔格达地层研究中需要注意的若干关键问题[J]. 地学前缘, 2011, 18(5): 256-270
XU Zemin, LIU Wenlian. Some problems in the study of the genesis of Xigeda Formation[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2011, 18(5): 256-270.
[29] 杨碧, 范柱国, 刘文连, 等. 攀钢钒钛钢铁新基地昔格达地层岩土工程特性研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2010, 10(4): 973-976 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2010.04.027
YANG Bi, FAN Zhuguo, LIU Wenlian, et al. Engineering property of Xigeda strata of Panzhihua new steel V-Ti base[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2010, 10(4): 973-976. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2010.04.027
[30] 张德强, 孙兴伟, 魏尚朝, 等. 金沙江中游龙开口水电站昔格达黏土物理特性研究[J]. 人民长江, 2021, 52(S1): 104-107 doi: 10.16232/j.cnki.1001-4179.2021.S1.023
ZHANG Deqiang, SUN Xingwei, WEI Shangchao, et al. Study on physical properties of Xigeda clay at Longkaikou Hydropower Station in the middle reaches of Jinsha River[J]. Yangtze River, 2021, 52(S1): 104-107. doi: 10.16232/j.cnki.1001-4179.2021.S1.023
[31] 张威, 徐则民, 刘文连, 等. 含水率对西昌昔格达组粘土岩抗剪强度的影响研究[J]. 工程勘察, 2011, 39(05): 1-5
ZHANG Wei, XU Zemin, LIU Wenlian, et al. Study on the influence of water content to shear strength of Xigeda-strata clay rock in Xichang[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, 2011, 39(5): 1-5.
[32] 张文举. 攀西地区昔格达土工程力学特性试验研究[D]. 成都: 四川大学, 2003
ZHANG Wenju. Study on engineering dynamic properties of Xigeda soil in Panxi area[D]. Chengdu: Sichuan University, 2003.
[33] 钟成, 范德平. 川南昔格达岩组工程地质特性研究[J]. 四川水力发电, 2012, 31(01): 97-99 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2184.2012.01.027
ZHONG Cheng, FAN Deping. Study on engineering geological characteristics of Xigeda Formation in south Sichuan[J]. Sichuan Water Power, 2012, 31(01): 97-99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2184.2012.01.027
[34] 周罕, 曹平, 张科. 昔格达组黏土岩和粉砂岩现场直剪试验研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 45(10): 3544−3550
ZHOU Han, CAO Ping, ZHANG Ke. In-situ direct shear test on Xigeda Formation clay stone and siltstone[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2014, 45(10): 3544-3550.
[35] 周平, 王志杰, 侯伟名, 等. 昔格达地层隧道局部浸湿失稳特征及突变预测研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2020, 42(03): 503-512 doi: 10.11779/CJGE202003012
ZHOU Ping, WANG Zhijie, HOU Weiming et al. Local slaking instability characteristics and catastrophic prediction of deep tunnels in Xigeda strata[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2020, 42(3): 503-512. doi: 10.11779/CJGE202003012
[36] 左永振, 张伟, 张晓川, 等. 昔格达组粉砂岩作为筑坝土料的工程特性研究[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2016, 33(3): 84-88 doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20140937
ZUO Yongzhen, ZHANG Wei, ZHANG Xiaochuan, et al. Engineering properties of Xigeda strata siltstone as the filling material of earth-rock dam[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2016, 33(3): 84-88. doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20140937
[37] Deng Bin, David Chew, Chris Mark, et al. Late Cenozoic drainage reorganization of the paleo-Yangtze river constrained by multi-proxy provenance analysis of the Paleo-lake Xigeda[J]. Bulletin of the Geological Society of America, 2020, 133(1-2): 199-211.
[38] Ding Wenfu, Zhang Guangzhe, Song Zhang. Research on the engineering geological characteristics and engineering countermeasures of Xigeda Strata of Chengdu-Kunming Railway[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2017, 34(4): 1-5.
[39] Du Yuxiang, Sheng Qian, Wang Shuai, et al. Study of microstructure and mechanical properties of semi-diagenetic rock of Xigeda Formation[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2020, 41(4): 1247-1269.
[40] Fu Xiaodong, Du Yuxiang, Sheng Qian, et al. Influences of water on the microstructure and mechanical behavior of the Xigeda Formation[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2022, 81(01): 72. doi: 10.1007/s10064-022-02567-5
[41] Kong Ping, Granger Darryl E, Wu Fuyuan, et al. Cosmogenic nuclide burial ages and provenance of the Xigeda paleo-lake: Implications for evolution of the Middle Yangtze River[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2009, 278: 131-141. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2008.12.003
[42] Wu Lizhou, Deng Hui, Huang Runqiu, et al. Evolution of lakes created by landslide dams and the role of dam erosion: A case study of the Jiajun landslide on the Dadu River, China[J]. Quaternary International, 2019, 503: 41-50. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2018.08.001
[43] Xue Xinhua, Fan Xu, Jiang Chusheng, et al. Research on the deformation properties of Xigeda Layer high fill embankment[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2018, 35(2): 41-45.
[44] Yang Zheng, Guo Ning, Zhang Heng. Study on microstructure characteristics of clay rock of Xigeda Formation in Xichang City based on softening test and image recognition[J]. Hydraulic and Civil Engineering Technology VI, 2021, 19: 73-78.
[45] Zhou Ping, Zhou Feicong, Lin Jiayong, et al. Decoupling analysis of interaction between tunnel surrounding rock and support in Xigeda formation strata[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2021, 25(2): 1-16.
-



 下载:
下载: