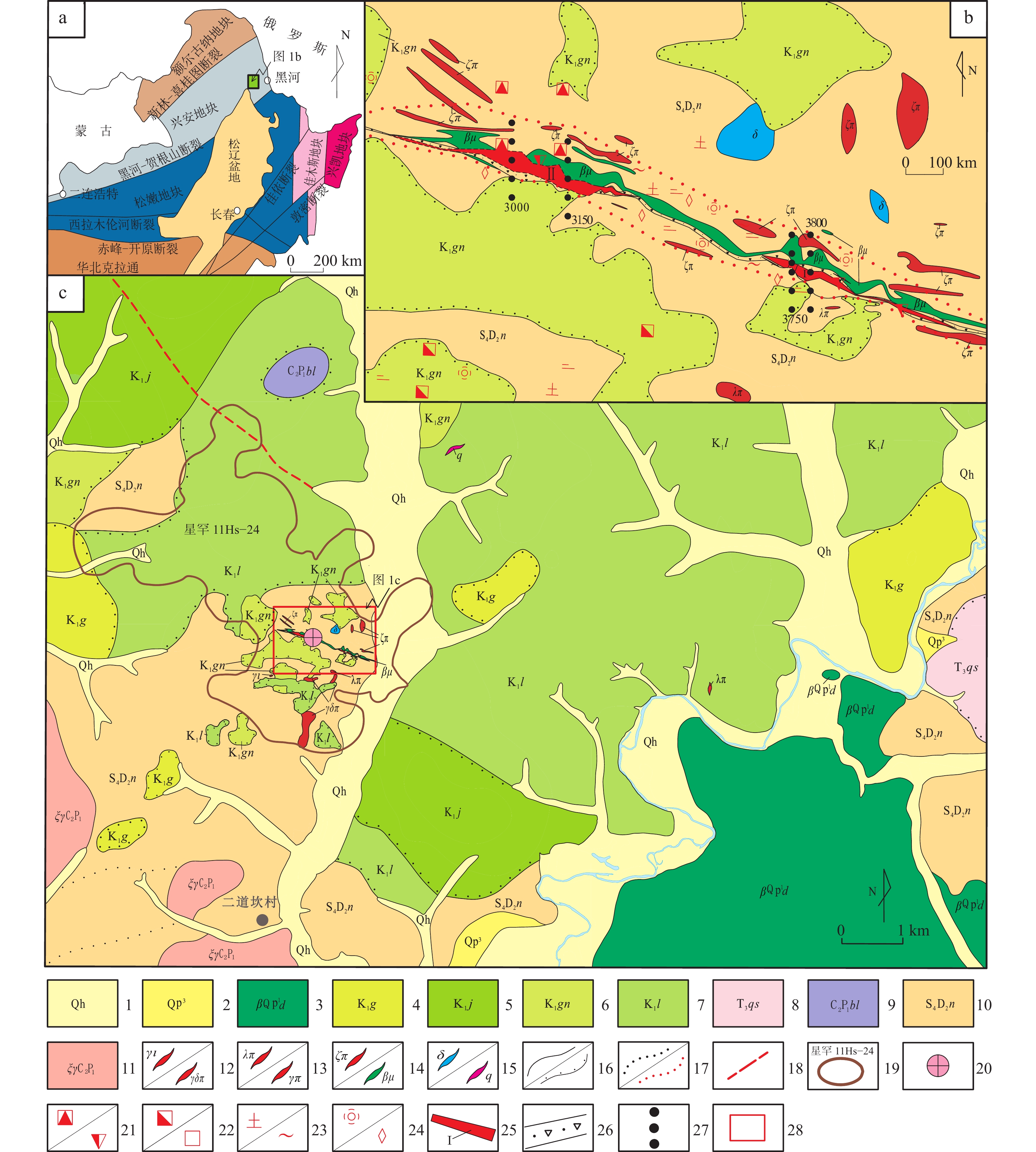
Study on Geochemical Prospecting Methods in Forest Swamp Area of Northeast Daxing’an Mountains: Example from Erdaokan Silver Polymetallic Mine Area in Heilongjiang Province
-
摘要:
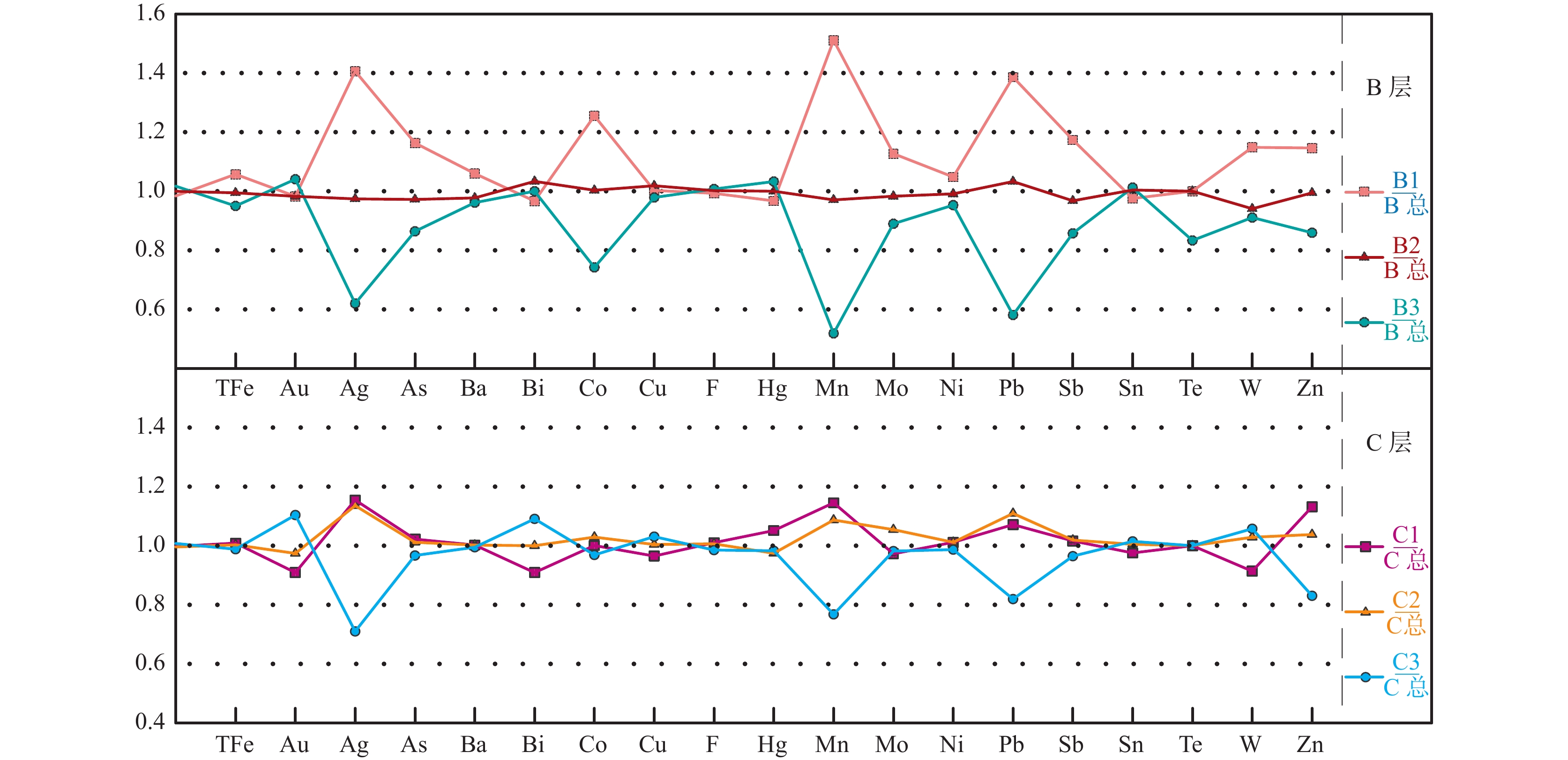
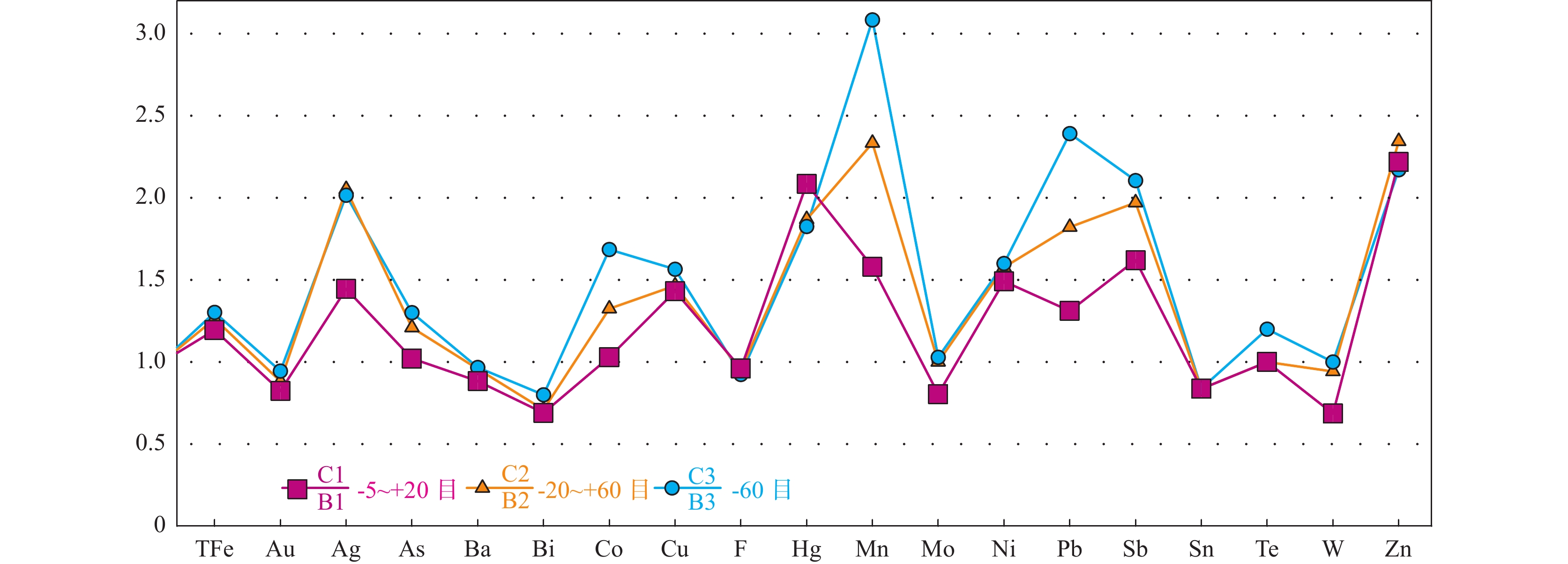
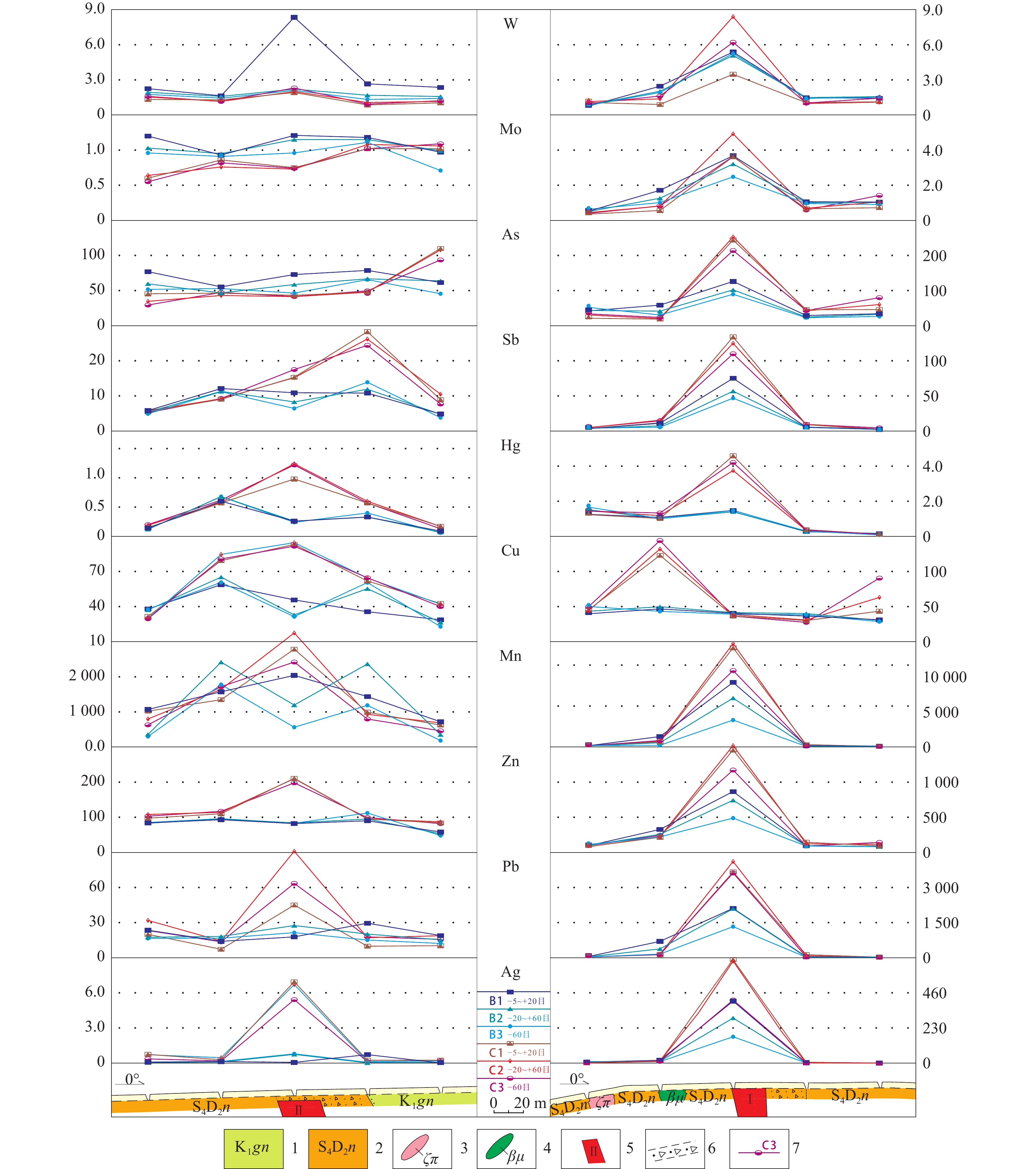
在黑龙江省二道坎森林–沼泽浅覆盖区,采用B、C层不同样品粒级对照分析方法,开展了土壤、岩屑测量采样方法技术剖面试验研究,选择采取的−5~+20目、−20~+60目和−60目3种粒级试验样品,并对比不同粒级样品中各元素在地球化学特征、元素组合以及异常圈定等方面存在的差异。结果表明,不同粒级样品所圈定的成矿元素地球化学异常都具备Ag-Pb-Zn-Mn多元素异常组合的特征,且异常分布范围与深部矿体较为一致,元素浓集中心与深部矿体空间位置吻合较好。具体表现为岩屑、土壤测量皆可以有效地指示银铅锌矿体,可作为该区寻找银铅锌矿的有效手段。而C层−20~+60目粒级岩屑测量效果更好,表现在元素含量更高,异常强度更强,元素组合指示意义更明显,定位矿体更精准,可以强化土壤微弱异常,有利于发现和识别弱的矿化信息。因此,在研究区内开展地球化学测量适宜采用−20~+60目粒级岩屑采样方法,其可为森林–沼泽覆盖区如二道坎地区以及多宝山矿集区开展1∶1万化探详查和找矿预测提供了技术依据。
Abstract:In the shallow forest-swamp overlying area of Erdaokan, Heilongjiang Province, the experimental study on the technical profile of soil and rock debris measurement and sampling methods was carried out by using the method of comparative analysis of different sample sizes in B and C layers. The samples of −5~+20 mesh, −20~+60 mesh and −60 mesh were selected. The differences in geochemical characteristics, element combination and anomaly delineation of each element in different sample sizes were also compared. The results show that the geochemical anomalies of ore-forming elements delineated by different sized samples have the characteristics of Ag-Pb-Zn-Mn multi-element anomaly combination, and the distribution range of anomalies is consistent with the deep ore body, and the element concentration center is in good agreement with the spatial location of the deep ore body, indicating that the ore-body can be effectively indicated by rock debris and soil survey. It can be used as an effective means to find silver-lead-zinc deposits in this area. Through the study, the measurement results of C−20~+60 mesh rock cuttings collected in the mining area are higher and better, which are manifested in higher element content, stronger anomaly intensity, more obvious indication of element combination, and more accurate ore body positioning, which can strengthen the weak soil anomaly, and is conducive to the discovery and identification of weak mineralization information. Therefore, the sampling method of −20~+60 mesh cuttings is suitable for geochemical survey in the study area, which provides a technical basis for the detailed survey of 1∶10 000 geochemical exploration in forest-swamp overlying region including the Erdaokanzi and Duobaoshan ore concentration areas.
-

-
表 1 各项指标的分析方法及检出限表
Table 1. The analysis method and detection limit of target elements
分析指标 实测检出限 规范要求 分析指标 实测检出限 规范要求 Al2O3 0.044 0.05 Cu 0.859 1 CaO 0.045 0.05 F 50 100 K2O 0.05 0.05 Hg 0.0005 0.003 MgO 0.05 0.05 Mn 5.48 10 Na2O 0.1 0.1 Mo 0.044 0.3 SiO2 0.095 0.1 Ni 0.00006 2 TFe 0.048 0.05 Pb 1.86 2 Au 0.1 0.3 Sb 0.05 0.05 Ag 0.02 0.02 Sn 0.5 1 As 1 1 Te 0.016 0.02 Ba 8.5 10 W 0.015 0.4 Bi 0.01 0.05 Zn 1.78 4 Co 0.221 1 注: 化合物含量为%,Au含量为10−9,其余元素含量均为10−6。 表 2 研究区不同粒级样品分析元素(化合物)地球化学参数统计表
Table 2. Geochemical parameters for analysis of elements (compounds) at different gain levels in the samples of this study area
特征 化学场 背景场 中国
土壤K D 均值 标准差 各粒级平均值 Xsum Ssum Cvsum Xo So Cvo B总 C总 B总 C总 B1 B2 B3 C1 C2 C3 Al2O3 15.35 1.58 0.10 15.35 1.10 0.07 12.5 1.23 1.44 15.44 15.27 1.27 1.85 15.4 15.5 15.5 15.2 15.3 15.4 CaO 0.70 0.87 1.24 0.55 1.39 2.53 2.2 0.32 0.80 0.56 0.84 0.15 1.22 0.53 0.57 0.6 0.85 0.82 0.86 K2O 2.11 0.47 0.22 2.05 1.28 0.62 2.3 0.92 0.38 2.24 1.98 0.26 0.59 2.24 2.25 2.24 1.97 1.98 2 MgO 1.24 0.43 0.35 1.17 1.42 1.21 1.3 0.96 0.32 1.16 1.32 0.25 0.55 1.14 1.17 1.17 1.33 1.32 1.32 Na2O 1.19 0.34 0.28 1.16 1.32 1.14 1.5 0.79 0.26 1.23 1.15 0.22 0.42 1.21 1.21 1.26 1.14 1.13 1.17 SiO2 61.33 5.74 0.09 61.56 1.09 0.02 65 0.94 5.26 63.32 59.35 4.58 6.13 62.3 63.3 64.4 59.2 59.1 59.8 TFe 6.08 1.85 0.30 58.4 13.23 0.23 4.2 1.45 0.01 5.40 6.76 1.32 2.06 5.71 5.37 5.13 6.82 6.78 6.68 Au 1.63 0.57 0.35 1.54 1.41 0.92 1.4 1.17 0.43 1.73 1.54 0.55 0.57 1.7 1.7 1.8 1.4 1.5 1.7 Ag 25.45 101.84 4.00 0.94 11.27 11.99 0.08 318.09 244.7 18.44 32.45 65.90 128.32 25.93 17.96 11.43 37.47 36.85 23.04 As 52.05 37.98 0.73 41.94 1.67 0.04 1 52.05 28.29 48.14 55.95 21.68 49.07 56 46.8 41.6 57.2 56.6 54.1 Ba 422.52 105.52 0.25 409.6 1.29 0.003 500 0.85 84.70 436.9 408.11 85.01 121.65 463 427 420 409 409 406 Bi 0.26 0.08 0.31 0.25 1.46 5.86 0.3 0.87 0.06 0.30 0.22 0.05 0.09 0.29 0.31 0.3 0.2 0.22 0.24 Co 25.00 11.79 0.47 22.6 1.60 0.07 1.3 19.23 8.13 21.83 28.18 10.68 12.06 27.4 21.9 16.2 28.2 29 27.3 Cu 46.98 21.89 0.47 42.7 1.48 0.03 24 1.96 16.31 37.80 56.17 11.52 25.72 37.9 38.5 37 54.2 56.4 57.9 F 532.8 76.8 0.14 527.4 1.15 0.002 480 1.11 67.34 547.94 517.67 70.4 80.5 544 549 552 523 521 510 Hg 0.89 1.21 1.35 0.43 3.32 7.73 40 0.02 0.75 0.61 1.17 0.82 1.45 0.59 0.61 0.63 1.23 1.14 1.15 Mn 7 814.2 20 496.0 2.62 1 654.0 3.37 0.002 600 13.02 28 758 5 068 10 559.9 13 124 25 678 7 658 4 919 2 629 12 094 11 479 8 107 Mo 1.14 0.67 0.59 0.97 1.42 1.47 0.8 1.43 0.56 1.18 1.10 0.55 0.78 1.33 1.16 1.05 1.07 1.16 1.08 Ni 66.76 46.40 0.69 54.60 1.85 0.03 26 2.57 30.66 52.47 81.06 30.28 54.85 55 52 50 82 82 80 Pb 320.8 779.8 2.43 55.7 4.97 0.09 23 13.95 903.9 238.0 403.59 531.2 964.3 329.9 245.8 138.3 432.4 447.7 330.7 Sb 13.71 21.48 1.57 7.80 2.13 0.27 0.8 17.14 17.69 9.55 17.87 12.17 27.32 11.21 9.24 8.19 18.16 18.21 17.24 Sn 2.24 0.60 0.27 2.15 1.27 0.59 2.5 0.89 0.49 2.44 2.04 0.50 0.62 2.38 2.45 2.47 1.99 2.05 2.07 Te 0.06 0.02 0.34 0.06 1.45 26.40 40 0.00 0.01 0.06 0.06 0.01 0.02 0.06 0.06 0.05 0.06 0.06 0.06 W 1.88 1.33 0.71 1.57 1.54 0.98 1.8 1.05 1.03 2.02 1.74 1.23 1.41 2.32 1.9 1.84 1.59 1.79 1.84 Zn 260.8 449.8 1.72 136.1 2.27 0.02 68 3.84 379.6 160.7 360.97 169.1 599.1 184.2 159.8 138.1 408.5 374.6 299.8 注:化合物含量为%,Au含量为10−9,其余元素含量均为10−6;富集系数K=X/中国土壤,D=(X×S)/(Xo×So)。 表 3 研究区土壤样品元素含量因子分析正交旋转因子载荷矩阵表
Table 3. Orthometric rotating factor loading matrix of factor analysis of elemental content of soil samples in study area
元素 F1 F2 F3 Pb 0.965 0.08 0.048 Mn 0.955 0.088 −0.178 Sb 0.954 0.06 −0.126 Mo 0.905 0.314 −0.012 As 0.87 0.228 0.042 Ag 0.845 0.225 −0.367 Zn 0.816 −0.182 0.292 W 0.805 0.147 0.109 Hg 0.788 −0.241 0.205 TFe 0.758 −0.534 −0.072 Sn 0.642 0.58 −0.001 Co 0.077 −0.843 −0.244 Cu 0.138 −0.83 0.105 Ni −0.065 −0.817 −0.322 Bi 0.022 0.667 0.59 Au 0.298 0.54 0.011 F 0.117 0.452 0.048 Te −0.205 0.102 0.814 Ba 0.207 0.21 0.608 累计方差% 43.07 64.21 74.14 注:主成分已提取了 3 个成分; 旋转法具有 Kaiser 标准化的正交旋转法,旋转在 5 次迭代后收敛。 表 4 研究区土壤样品粒级与风化指数关系表
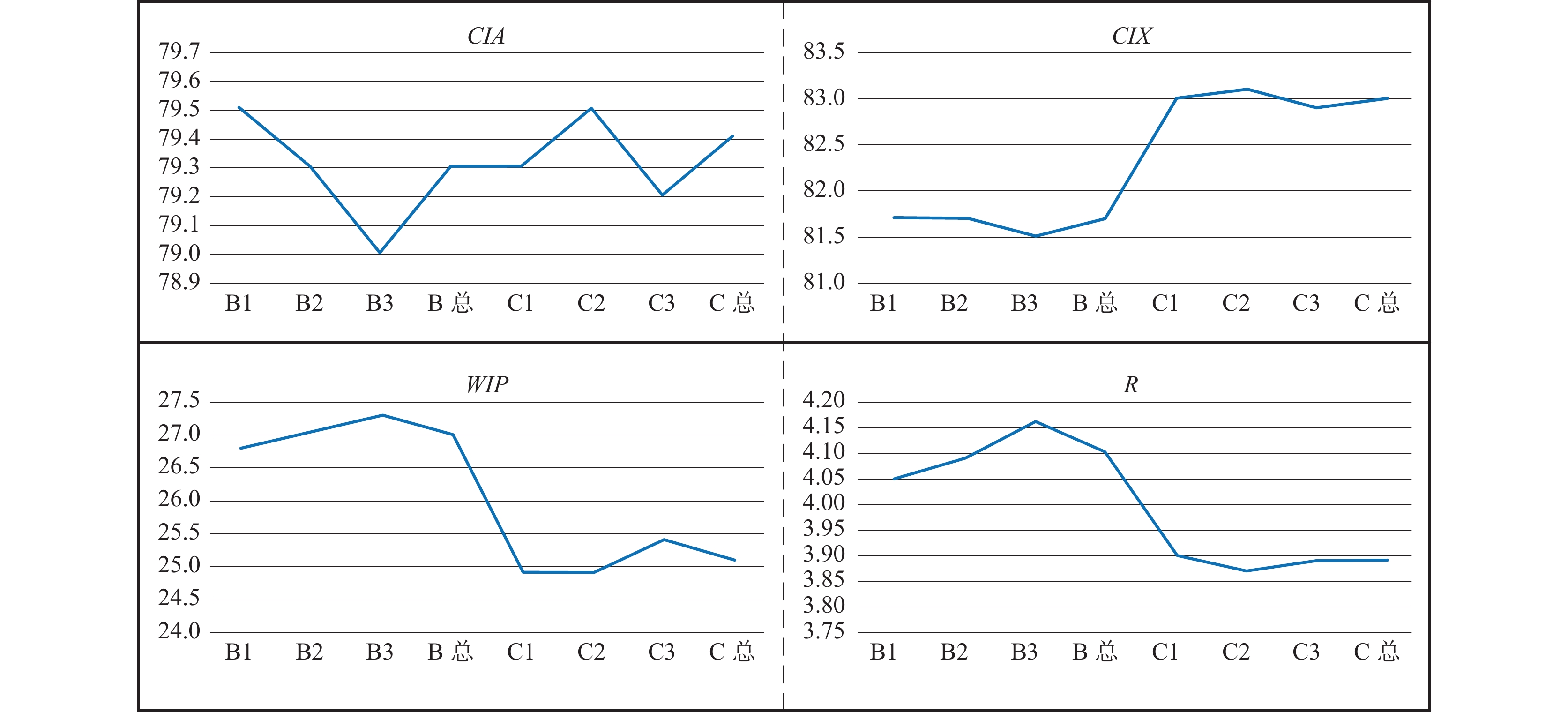
Table 4. Relationship between granularities and weathering indexes
指标 计算公式 B层(n=63) C层(n=63) B1 B2 B3 B总 C1 C2 C3 C总 CIA [Al2O3/(Al2O3+CaO+Na2O+K2O)]×100 79.5 79.3 79.0 79.3 79.3 79.5 79.2 79.4 CIX [Al2O3/(Al2O3+Na2O+K2O)]×100 81.7 81.7 81.5 81.7 83.0 83.1 82.9 83.0 WIP [2Na2O/0.35+2K2O/0.25+MgO/0.9+CaO/0.7]×100 26.8 27.0 27.3 27.0 24.9 24.9 25.4 25.1 R Al2O3/SiO2 4.05 4.09 4.16 4.10 3.90 3.87 3.89 3.89 -
[1] 鲍希波, 尹国良, 于献章 . 黑龙江省嫩江县二道坎村银多金属矿床地质特征及找矿标志[J]. 黄金,2019 ,40 (7 ):20 −23 .BAO Xibo, YIN Guoliang, YU Xianzhang . Geological Charact -eristics of Erdaokancun Silver Polymetallic Deposit, Nenjiang County, Heilongjiang Province and Its Prospecting Indicators[J]. Gold,2019 ,40 (7 ):20 −23 .[2] 陈虹, 杨晓, 田世攀, 等. 覆盖区智能地质填图的探索与实践——以森林沼泽区为例[J]. 地质通报, 2022, 41(2−3): 218−241.
CHEN Hong, YANG Xiao, TIAN Shipan, et al. Technical innovation and practice of intelligent geological mapping in the coverage area: a case study in the forest-swamp area[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2022, 41(2−3): 218−241.
[3] 邓昌州, 张立东, 孙梓耀, 等 . 黑龙江翠峦石英脉型银矿的发现及意义[J]. 物探与化探,2015 ,39 (2 ):240 −244 .DENG Changzhou, ZHANG Lidong, SUN Ziyao, et al . The discovery of the Cuiluan quartz type silver deposit in Heilongjlang Province and its significance[J]. Ceophysicaland Geochemical Exploration,2015 ,39 (2 ):240 −244 .[4] 董娟, 袁茂文, 李成禄 . 黑龙江多宝山矿集区二道坎银铅锌矿床热液 菱锰矿地球化学特征及其指示意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2022 ,52 (3 ):855 −865 .DONG Juan, YUAN Maowen, LI Chenglu . Geochemical Characteristics of Hydrothermal Rhodochrosite in Erdaokan Ag-Pb-Zn Deposit Duobaoshan Metallogenic Belt, Heilongjiang Province and Its Indications[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2022 ,52 (3 ):855 −865 .[5] 段星星, 黑欢, 梁楠, 等 . 新疆东天山玉海铜矿外围浅覆盖区1∶5万化探方法技术及应用[J]. 西北地质,2019 ,52 (3 ):143 −150 .DUAN Xingxing, HEI Huan, LIANG Nan, et al . 1∶50, 000 Geochemical Prospecting Techniques and their Applications in Shallow Covered Area outside the Yuhai Copper Deposit in East Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang[J]. Northwestern Geology,2019 ,52 (3 ):143 −150 .[6] 丁兆举, 常昊, 张年生, 等 . 热带雨林景观土壤测量采样深度与样品粒级试验研究—以加纳国雅卡锰金矿为例[J]. 地质与勘探,2021 ,57 (3 ):554 −562 .DING Zhaoju, CHANG Hao, ZHANG Niansheng, et al . Experimental study on sampling depth and sample granularity of soil survey in tropical rainforest landscape: Taken the Yakau Mn-Au deposit in Ghana as an example[J]. Geology and Exploration,2021 ,57 (3 ):554 −562 .[7] 范红科 . 岩屑地球化学测量方法在找矿中的应用—以内蒙古白音查干银(金)多金属矿为例[J]. 黄金科学技术,2010 ,18 (1 ):32 −35 .FAN Hongke . Application of Debris Geochemical Survey Method in Ore Prospecting: A Case Study of Baiyinchagan Silver (gold) Polymetallic Deposit in Inner Mongolia[J]. Cold Science and Technology,2010 ,18 (1 ):32 −35 .[8] 耿卫华, 杨乃峰, 马晓阳 . 黑龙江森林沼泽区地球化学亚景观类型划分[J]. 物探与化探,2006 ,30 (4 ):18 −20 .GENG Weihua, YANG Naifeng, MA Xiaoyang . The Preliminary Classification of Geochemical Sublandscape Types in The Forest-swamp Area of Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration,2006 ,30 (4 ):18 −20 .[9] 蒋艳明. 黑龙江省三道湾子金矿土壤和岩石地球化学异常特征及其意义[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2009: 1−67. JIANG Yanming. Soil and Rock Geochemical Anomalies of Sandaowanzi Gold Deposit and Their Significance, Heilongjiang Province [D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2009: 1−67. [10] 刘国卿. 黑龙江省二道坎银多金属矿床矿石特征及银的赋存状态研究[D].长春: 吉林大学, 2020, 1−66. LIU Guoqing. Ore Characteristics and Occurrence of Silver of the Erdaokan Silver Polymetallic Deposit in HeilongJiang Province[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2020, 1−66. [11] 刘汉粮, 张必敏, 王学求, 等 . 土壤微细粒测量地球化学模式的再现性与可对比性[J]. 物探与化探,2018 ,42 (3 ):506 −512 .LIU Hanliang, ZHANG Bimin, WANG Xueqiu, et al . The Reproducibility and Comparability of The Fine Particle Soil Survey Geochemical Pattexns[J]. Geophysical and Ceochemical Exploration,2018 ,42 (3 ):506 −512 .[12] 李文明, 刘拓, 孙吉明, 等 . 新疆北山白山地区地球化学特征及找矿远景预测[J]. 西北地质,2021 ,54 (4 ):42 −48 .LI Wenming, LIU Tuo, SUN Jiming, et al . Geochemical Characteristics and Prospecting Prognosis in Baishan Area of Xinjiang Beishan[J]. Northwestern Geology,2021 ,54 (4 ):42 −48 .[13] 李重阳, 刘宗彦, 王辉, 等 . 豫西黄土覆盖区土壤地球化学测量粒度试验研究[J]. 矿产勘查,2020 ,11 (7 ):1553 −1561 .LI Chongyang, LIU Zongyan, WANG Hui, et al . Experimental study of soil size of the loess coverage area in geochemical survey, west Henan Province[J]. Mineral Exploration,2020 ,11 (7 ):1553 −1561 .[14] 林俞亨, 王立立, 欧阳永棚, 等. 基于浓度–面积分形模型和模糊证据权的铜矿资源潜力评价: 以江西九瑞地区为例[J]. 西北地质, 2024, 57(1): 165−178
LIN Yuheng, WANG Lili, OUYANG Yongpeng, et al. Evaluation of Copper Mineral Resource Potential Using Concentration–Area Fractal Model and Fuzzy Evidence Weighting: A Case Study of the Jiurui Region in Jiangxi[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2024, 57(1): 165−178
[15] 雷自强, 陈杰, 陈世明, 等 . 岩屑地球化学测量在甘肃北山干旱戈壁荒漠区的找矿效果—以三白墩地区金砷矿的发现为例[J]. 物探与化探,2022 ,46 (3 ):585 −596 .LEI Ziqiang, CHEN Jie, CHEN Shiming, et al . Application of Geochemical Survey of Lithic Fragments in Ore Prospecting in Arid Gobi Desert of The Beishan Area, Gansu Province:A Case Study of The Discovery of The Gold-arsenic Deposit in Sanbaidun Area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration,2022 ,46 (3 ):585 −596 .[16] 鲁涛, 孙刚, 袁茂文 . 大兴安岭东北部多宝山矿集区二道坎银铅锌矿床有机质特征及对成矿作用的影响[J]. 世界地质,2021 ,40 (2 ):1 −9 .LU Tao, SUN Gang, YUAN Maowen . Organic Matter Characteristics and Influence on Mineralization of Erdaokan Ag-Pb-Zn Deposit in Duobaoshan Ore Concentrated Area, Northeast Great Xing'an Range[J]. Global Geology,2021 ,40 (2 ):1 −9 .[17] 史冬岩, 张坤, 张玉鹏, 等 . 黑龙江省浅覆盖区地物化特征与找矿标志-以黑河市340高地金矿化区为例[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2021 ,51 (4 ):1042 −1053 .SHI Dongyan, ZHANG Kun, ZHANG Yupeng, et al . Geophysical and Geochemical Characteristics and Prospecting Criteria of Shallow Overburden Area in Heilongjiang Province:A Case study of 340 Highland Gold Mineralization Area in Heihe City[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition),2021 ,51 (4 ):1042 −1053 .[18] 史冬岩, 张坤, 张玉鹏, 等 . 因子分析在土壤地球化学测量中的应用: 以大兴安岭北段呼中地区为例[J]. 世界地质,2021 ,40 (1 ):1 −11 .SHI Dongyan, ZHANG Kun, ZHANG Yupeng, et al . Application of Principal Component Analysis in Soil Geochemical Survey: A Case Study of Huzhong Area in North of Great Xing'an Range[J]. Global Geology,2021 ,40 (1 ):1 −11 .[19] 谈艳, 张鑫利, 王泰山, 等 . 青海三岔河北金多金属矿地球化学异常特征及找矿潜力分析[J]. 西北地质,2019 ,52 (4 ):170 −181 .TAN Yan, ZHANG Xinli, WANG Taishan, et al . Geochemical Anomaly Characteristics and Prospecting Potential of Gold Polymetallic Deposits in Sanchahebei Area, Qinghai Province[J]. Northwestern Geology,2019 ,52 (4 ):170 −181 .[20] 吴蓓娟, 彭渤, 张坤, 等 . 黑色页岩化学风化程度指标研究[J]. 地球学报,2016 ,90 (4 ):818 −832 .WU Beijuan, PENG Bo, ZHANG Kun, et al . A New Chemical Index of identifying the Weathering Degree of Black Shales[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2016 ,90 (4 ):818 −832 .[21] 王乔林, 孔牧, 韩伟, 等 . 土壤地球化学测量在甘肃北山白头山铷矿找矿中的应用[J]. 地质与勘探,2021 ,57 (1 ):110 −121 .WANG Qiaolin, KONG Mu, HAN Wei, et al . Application of Soil Geochemical Survey in The Baitoushan Rubidium Deposit, Beishan Area, Gansu Province[J]. Geology and Exploration,2021 ,57 (1 ):110 −121 .[22] 王亚磊, 李文渊, 林艳海, 等 . 金川超大型铜镍矿床钴的赋存状态与富集过程研究[J]. 西北地质,2023 ,56 (2 ):133 −150 .WANG Yalei, LI Wenyuan, LIN Yanhai, et al . Study on the Occurrence State and Enrichment Process of Cobalt in Jinchuan Giant Magmatic Ni−Cu Sulfide Deposit[J]. Northwestern Geology,2023 ,56 (2 ):133 −150 .[23] 徐文喜, 李成禄, 鲍希波, 等 . 大兴安岭东北部首个三叠纪银矿床地质特征及矿床成因分析[J]. 矿产与地质,2019 ,33 (3 ):434 −441 .XU Wenxi, LI Chenglu, BAO Xibo, et al . Geological characteristics and genesis analysis of the first Triassic silver deposit discovered in Northeast of Da Hinggan Mountains[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology,2019 ,33 (3 ):434 −441 .[24] 袁茂文.天然沥青与非层控金属成矿关系研究: 以二道坎银铅锌矿床为例[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2020: 1−123. YUAN Maowen. The Contribution of the Bitumen to the Mineralization of the Non-stratabound Metal Deposit: A Case Study from the Erdaokan Ag-Pb-Zn Deposit [D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2020: 1−123. [25] 张津瑞, 陈华, 任军平, 等. 矿产资源潜力评价方法对比及其发展趋势探讨[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(2): 292−305.
ZHANG Jinrui, CHEN Hua, REN Junping, et al. Mineral Resource Assessment Methods Comparison and Its Development Trend Discussion[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(2): 292−305.
[26] 张玉鹏, 史冬岩, 吕明奇, 等 . 岩屑地球化学测量在黑龙江省三道湾子浅覆盖区的找矿应用效果[J]. 黄金科学技术,2022 ,30 (5 ):651 −663 .ZHANG Yupeng, SHI Dongyan, LV Mingqi, et al . Application Effect of Rock Debris Geochemical Survey in Prospecting in Sandaowanzi Shallow Overburden Area, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Gold Science and Technology,2022 ,30 (5 ):651 −663 .[27] 张沁瑞, 李欢, 邓宇飞, 等 . 北京东南郊土壤重金属元素分布及其在表层土壤中的富集特征[J]. 物探与化探,2022 ,46 (2 ):490 −501 .ZHANG Qinrui, LI Huan, DENG Yufei, et al . Distribution of Heavy Metal Elements in Soil of the Southeastern Suburbs of Beijing and their Enrichment Characteristics in Surface Soil[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration,2022 ,46 (2 ):490 −501 .[28] An Y L, Yin X L, Gong Q J, et al . Classification and Provenance on Geochemical Lithogenes: A Case Study on Rock-Soil-Sediment System in Wanquan Area of Zhangjiakou, North China[J]. Applied Sciences,2023 ,13 (2 ):1 −12 .[29] Bhat N A, Ghosh P, Ahmed W, et al . Comparative Evaluation of Weathering Indices of Rock-Soil Sequences in parts of Peninsular Gneissic Complex, Western Dharwar Craton, Karnataka, India[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences,2022 ,15 (11 ):1087 .[30] Cai W Y, Wang K Y, Li J, et al . Geology, geochronology and geochemistry of large Duobaoshan Cu-Mo-Au orefield in NE China: Magma genesis and regional tectonic implications[J]. Geoscience Frontiers,2020 ,12 (1 ):265 −292 .[31] Chai H, Ma Y F, M . Santosh, et al. Late Carboniferous to Early Permian oceanic subduction in central Inner Mongolia and its correlation with the tectonic evolution of the southeastern Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Gondwana Research,2020 ,84 :245 −259 .[32] Chen J C, Wang K Y, Cai W Y, et al . Fluid evolution and genesis of the Sankuanggou Fe-Cu skarn deposit, Duobaoshan ore field, Northeast China: Evidence from fluid inclusions and H-O-S-Pb isotopes[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration,2023 ,252 .[33] Deng C Z, Li C L, Rong Y M, et al . Different Metal Sources in the Evolution of an Epithermal Ore System: Evidence from Mercury Isotopes Associated with the Erdaokan Epithermal Ag-Pb-Zn Deposit, NE China[J]. Gondwana Research,2021 ,95 :1 −9 .[34] Dinis Pedro A., Sá Pereira José, Ivo Alves Eduardo, et al . Compositional variability of regoliths on equatorial highlands (East Timor). Source-rock control and competing effects of weathering and denudation[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2021 ,207 :104658 .[35] Hao Y J, Ren Y S, Duan M X, et al . Metallogenic events and tectonic setting of the Duobaoshan ore field in Heilongjiang Province, NE China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2015 ,97 :442 −458 .[36] Li Y Q, Zhang D H, Dai L, et al . Characteristics of structurally superimposed geochemical haloes at the polymetallic Xiasai silver-lead-zinc ore deposit in Sichuan Province, SW China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration,2016 ,169 :100 −122 .[37] Li L, Sun F Y, Li B L, et al . Identification of Hydrothermal Alteration and Mineralization in The Sancha Magmatic Cu-Ni-Au Sulfide Deposit, NW China: Implications for Timing and Genesis of Mineralization[J]. Geology Reviews,2022 ,143 :104770 .[38] Liu J, Li Y, Zhou Z H, OuYang, et al . The Ordovician igneous rocks with high Sr/Y at the Tongshan porphyry copper deposit, satellite of the Duobaoshan deposit, and their metallogenic role[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2017 ,86 :600 −614 .[39] Meng F W, Liu Y H, Han J T, et al . Paleozoic suture and Mesozoic tectonic evolution of the lithosphere between the northern section of the Xing'an Block and the Songnen Block: Evidence from three-dimensional magnetotelluric detection[J]. Tectonophysics,2022 ,823 :229210 .[40] Kelley K D, Spry P G, Virginia V T, et al. Alkalic-type epithermal gold deposit model[R]. Reston: U.S.Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report, 2020: 1−74. [41] Primus A T, Jean P T, Emile T, et al . Characteristics, Source Area-weathering, Sedimentary Processes, Tectonic Setting and Taxonomy of Vertisols Developed on Alluvial Sediments in the Benue Trough of North Cameroon[J]. Journal of Geosciences and Geomatics,2022 ,10 (1 ):1 −17 .[42] Sorokina O A . Reconstruction of Sources in River Sediments in the Lower Part of the Bureya River Based on Geochemical Indices[J]. Russian Journal of Pacific Geology,2019 ,13 (2 ):176 −185 .[43] Sun Q F, Wang K Y, Wang Y C, et al . Superimposing mineralization in the Zhengguang Au-Zn deposit, NE China: Evidence from pyrite Re-Os geochronology, fluid inclusion, and H-O-S-Pb isotopes[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2021 ,137 :104307 .[44] Tang Z Y, Sun D Y, Mao A Q, et al . Timing and evolution of Mesozoic volcanism in the central Great Xing'an Range, northeastern China[J]. Geological Journal,2019 ,54 (6 ):3737 −3754 .[45] Wang L, Qin K Z, Song G X, et al . Geology and genesis of the Early Paleozoic Zhengguang intermediate-sulfidation epithermal Au-Zn deposit, northeast China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2020 ,124 :103602 .[46] Wu Z J, Yang X Y, Ma Y S, et al . A Synthesis of Geochemistry of Mesozoic Igneous Rocks in NE China and Tectonic Superposition and Transformation of the Easternmost Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2021 ,227 :105032 .[47] Yuan M W, Li L, Li S R, et al . Mineralogy, Fluid Inclusions and S-Pb-H-O Isotopes of the Erdaokan Ag-Pb-Zn Deposit, Duobaoshan Metallogenic belt, NE China: Implications for Ore Genesis[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2019 ,113 :103074 .[48] Yuan M W, Li L, Li S R, et al . Bitumen Sm-Nd, Pyrite Rb-Sr and Zircon U-Pb Isotopes Constrain Timing of Ore Formation and Hydrocarbon Deposition in the Erdaokan Ag-Pb-Zn Deposit, NE China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2021 ,134 :104161 .[49] Yuan M W, Li L, Li C L, et al . The Genesis of Bitumen and its Relationship with Mineralization in the Erdaokan Ag-Pb-Zn Deposit from the Great Xing'an Range, Northeastern China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2021 ,139 :104464 .[50] Zhang Z Q, Wu Q B, Hou M T, et al . Permafrost change in Northeast China in the1950s-2010s[J]. Advances in Climate Change Research,2021 ,12 (1 ):18 −28 .[51] Zhou X J, Li A C, JIang F Q, et al . Effects of grain size distribution on mineralogical and chemical compositions: a case study from size-fractional sediments of the Huanghe (Yellow River) and Changjiang (Yangtze River)[J]. Geological Journal,2015 ,50 (4 ):414 −433 . -



 下载:
下载: