The Characteristics of Ore-forming Fluids and Metallogenic Mechanism of the Kumutashi Fluorite Deposit in West Altyn Tagh, China
-
摘要:
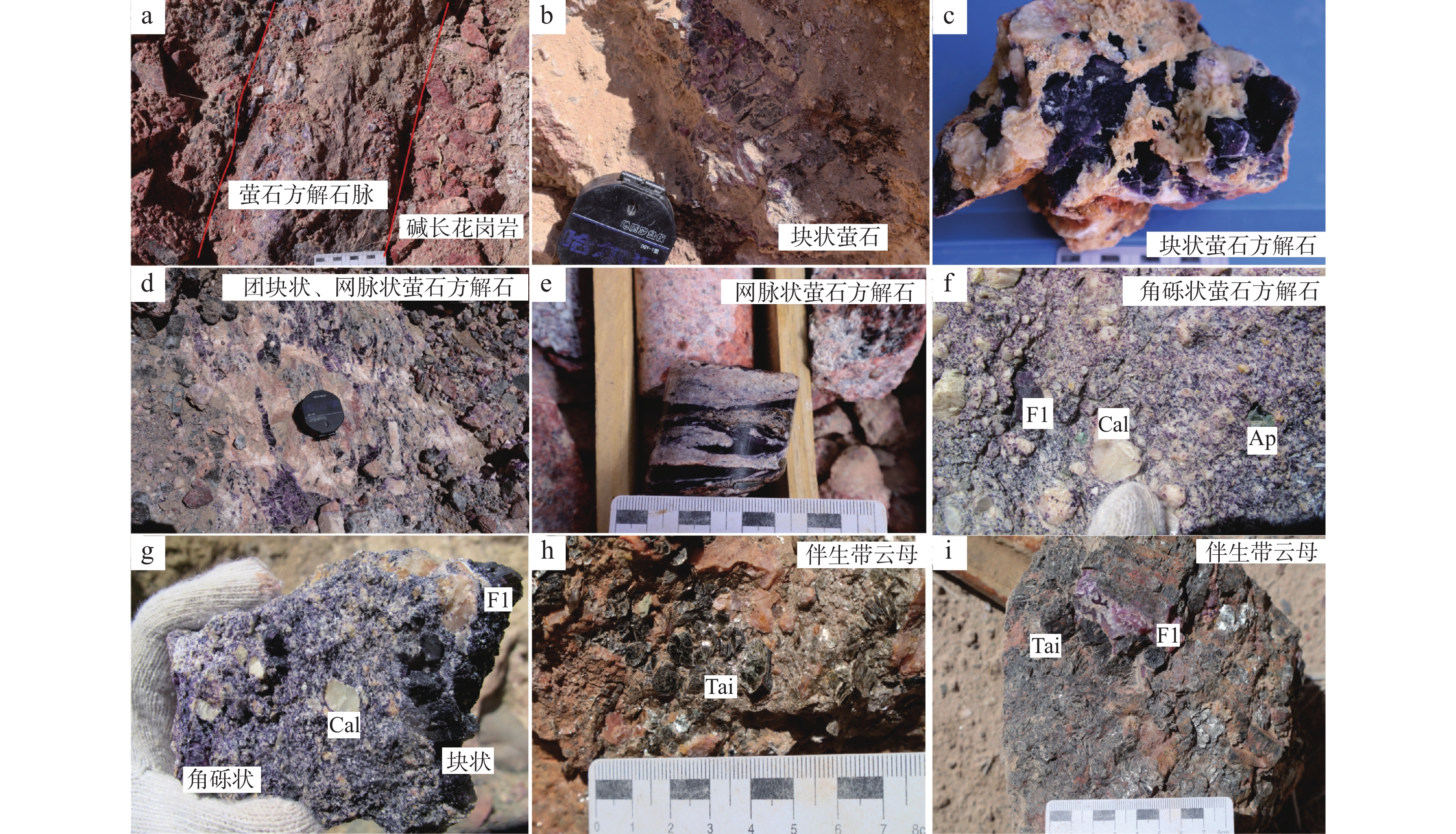
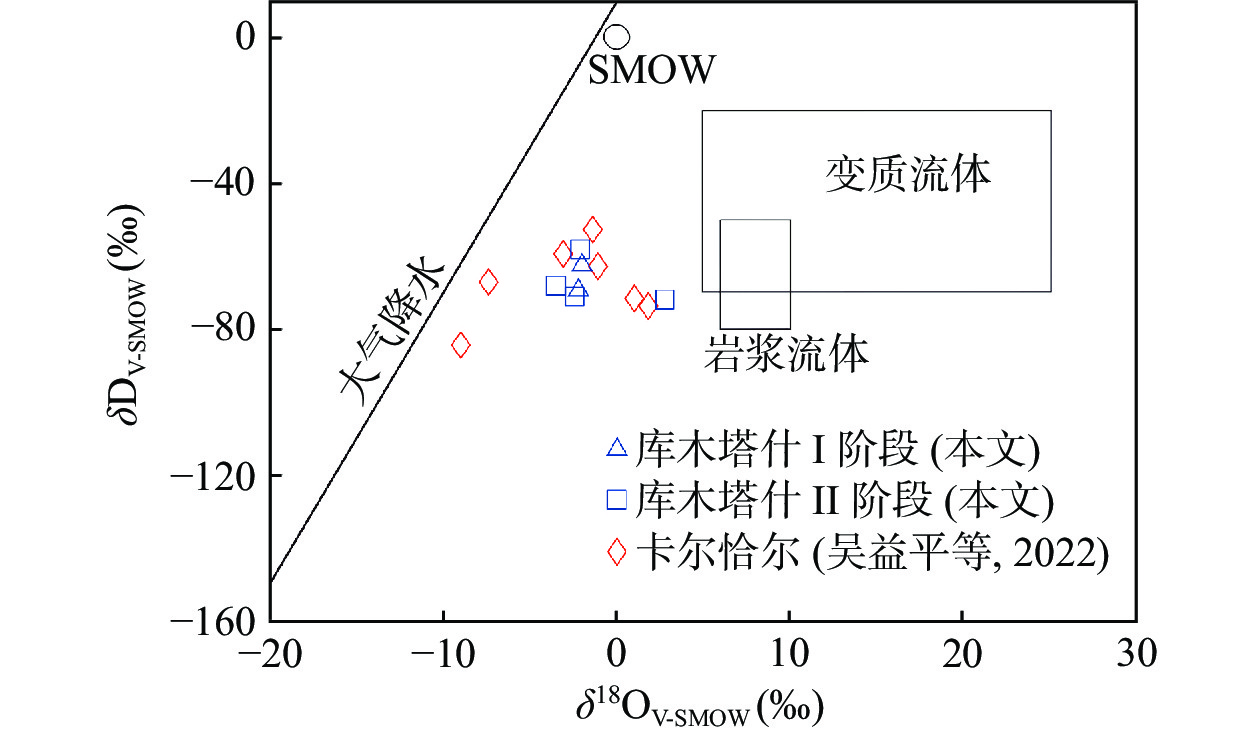
库木塔什萤石矿床位于阿尔金西段卡尔恰尔超大型萤石矿带内,是近年来新发现的一处大型萤石矿床,矿体以萤石–方解石脉型为主,伴生含锂带云母,产于古元古界阿尔金岩群的NE向与近EW向断裂中。目前,关于矿床成矿流体特征与成矿机制的研究较为薄弱。本研究以不同成矿阶段萤石和方解石的流体包裹体为研究对象,开展流体包裹体岩相学、显微测温、激光拉曼光谱和H、O同位素研究。成矿过程可划分早阶段(Ⅰ)、晚阶段(Ⅱ)两个阶段。早阶段形成块状矿石,主要发育富气两相水溶液包裹体和CO2三相包裹体,均一温度为225.1~410.8 ℃,盐度为5.20~9.63 wt%NaCleqv,密度为0.25~0.76 g/cm3;晚阶段形成角砾状、网脉状矿石,主要发育富液两相和富气两相水溶液包裹体,均一温度为117.2~347.8 ℃,盐度为0.53~12.73 wt%NaCleqv,密度为0.40~0.91 g/cm3。包裹体的液相成分以H2O为主,含有少量CO2,气相成分以CO2为主,含少量的CH4、N2、H2及H2S等。成矿早期流体为中高温、中低盐度、低密度的NaCl-H2O-CO2热液体系,成矿晚期流体为中低温、低盐度、低密度的NaCl-H2O-CO2热液体系。H、O同位素研究结果表明,成矿流体来源于岩浆热液和大气降水的混合。成矿早期萤石的沉淀机制主要为岩浆热液和大气降水混合以及水–岩反应,晚期进一步发生流体混合作用,致使温度降低,形成角砾状及网脉状矿石。库木塔什萤石矿床属岩浆热液充填型脉状萤石矿床。
Abstract:Kumutashi fluorite deposit is located in the Kaerqiaer super-large fluorite ore belt in the western Altyn Tagh, which is a newly discovered large fluorite deposit in recent years. The ore body is dominated by fluorite-calcite vein type, associated with lithium-bearing mica, and occurs in the NE and nearly EW faults of the Paleoproterozoic Altyn Tagh rock group. At present, the research on the characteristics of ore-forming fluid and ore-forming mechanism is relatively weak. Fluid inclusions in fluorite and calcite from different mineralization stages were studied by petrography, microthermometry, laser Raman spectroscopy, and hydrogen and oxygen isotopes. The ore-forming process can be divided into two stages: the early stage (Ⅰ) and the late stage (Ⅱ). The massive ores formed in the early stage are mainly gas-rich two-phase aqueous inclusions and CO2 three-phase inclusions with homogenization temperature ranging from 225.1 to 410.8 ℃, salinity from 5.20 to 9.63 wt%NaCleqv and density from 0.25 to 0.76 g/cm3; In the late stage, brecciated and stockwork ores were formed, and liquid-rich two-phase and gas-rich two-phase aqueous inclusions were mainly developed, with homogenization temperature ranging from 117.2 to 347.8 ℃, salinity from 0.53 to 12.73 wt%NaCleqv, and density from 0.40 to 0.91 g/cm3. The liquid phase of the inclusion is mainly composed of H2O with a small amount of CO2, and the gas phase is mainly composed of CO2 with a small amount of CH4, N2, H2 and H2S. In the early stage of mineralization, the fluid was a NaCl-H2O-CO2 hydrothermal system with medium-high temperature, medium-low salinity and low density, while in the late stage of mineralization, the fluid was a NaCl-H2O-CO2 hydrothermal system with medium-low temperature, low salinity and low density. The results of hydrogen and oxygen isotope studies indicate that the ore-forming fluids were derived from a mixture of magmatic hydrothermal and meteoric water. Fluorite precipitation in the early stage of mineralization was mainly due to the mixing of magmatic hydrothermal solution and meteoric water, as well as water-rock reaction. In the late stage, fluid mixing further occurred, resulting in the decrease of temperature and the formation of brecciated and stockwork ores. Kumutashi fluorite deposit belongs to magmatic hydrothermal filling type vein fluorite deposit.
-
Key words:
- fluid inclusion /
- H-O isotopes /
- metallogenic mechanism /
- Kumutashi /
- west Altyn Tagh
-

-
图 1 研究区所属位置(a)、区域构造格架图(b)、卡尔恰尔超大型萤石矿带地质矿产图(c)(据高永宝等,2023修改)
Figure 1.
图 2 库木塔什萤石矿区地质图(据高永宝等,2023)
Figure 2.
图 8 库木塔什萤石矿床成矿流体H、O同位素图解(底图据Taylor, 1974)
Figure 8.
表 1 库木塔什萤石矿床流体包裹体特征参数
Table 1. Characteristics parameters of fluid inclusions in the Kumutashi fluorite deposit
阶段 矿物 均一温度(℃)
均值冰点温度(℃)
均值盐度(wt%NaCleqv)
均值密度(g/cm3)
均值压力(MPa)
均值深度(km)
均值Ⅰ 萤石 225.1~390.2
315.7 (n=13)−5.8~−3.2
−4.2 (n=13)5.20~8.91
6.720.63~0.88
0.7561.0~108.7
85.82.03~3.62
2.86粗晶方解石 321.2~410.8
368.4 (n=27)−7.4~−3.82
−5.2 (n=27)6.12~11.00
8.140.58~0.76
0.6887.9~112.7
100.92.93~3.76
3.36Ⅱ 萤石 117.2~214.8
156.4 (n=16)−8.9~−0.3
−4.4 (n=16)0.53~12.73
6.860.89~1.02
0.9632.3~58.9
40.11.08~1.96
1.36细晶方解石 206.4~291.2
241.5 (n=24)−6.8~−3.2
−4.9 (n=24)5.20~10.24
7.670.78~0.93
0.8755.8~78.5
65.91.86~2.62
2.20表 2 库木塔什萤石矿床流体包裹体气、液相成分激光拉曼探针分析结果
Table 2. Results of laser Raman probe analysis of gas and liquid components of fluid inclusions in the Kumutashi fluorite deposit
成矿阶段 样品号 寄主
矿物包裹体类型 x(气相)(%) x(液相)(%) CO2 H2S CH4 N2 H2 总和 CO2 H2S CH4 SO2 H2O 总和 Ⅰ阶段 KM1-1-3 萤石 富气两相 100 100 100 100 KM1-1-5 萤石 富气两相 90.4 9.59 100 10.5 89.5 100 KM1-1-4 萤石 富液两相 100 100 19.8 80.2 100 KM1-2-2 萤石 富液两相 61.6 38.4 100 100 100 KM1-2-3 萤石 富液两相 38.8 61.2 100 100 100 KM1-1-2 粗晶方解石 富气两相 93.1 6.92 100 100 100 KM1-2-4 粗晶方解石 富气两相 100 100 0.05 99.9 100 KM1-3-3 粗晶方解石 富气两相 88.6 11.4 100 100 100 KM1-4-1 粗晶方解石 富气两相 100 100 0.07 99.9 100 KM1-5-1 粗晶方解石 富气两相 71.7 3.5 24.8 100 0.07 99.9 100 Ⅱ阶段 KM3-1-1 细晶方解石 富液两相 100 100 100 100 KM3-2-1 细晶方解石 富液两相 100 100 100 100 KM3-2-2 细晶方解石 富液两相 60.0 16.9 100 100 100 KM3-4-1 细晶方解石 富液两相 83.4 16.6 100 100 100 KM3-3-2、3 细晶方解石 富液两相 100 100 100 100 KM3-3-4 细晶方解石 富液两相 100 100 0.02 99.9 100 注:x(气相)(%)为摩尔数的相对百分含量;x(液相)(%)为摩尔数的相对百分含量。 表 3 库木塔什萤石矿床流体H、O同位素组成
Table 3. Hydrogen and oxygen isotopic composition of fluid in the Kumutashi fluorite deposit
成矿阶段 样品号 样品名称 δDV-SMOW(‰) δ18OV-SMOW(‰) I阶段 KM23-2 萤石 −61.6 −2.0 KM23-3 萤石 −68.6 −2.2 Ⅱ阶段 KM23-1 萤石 −58.1 −2.1 KM23-5 萤石 −70.3 −2.4 KM23-6 萤石 −71.9 2.8 KM03-d1 萤石 −68.1 −3.5 -
[1] 曹俊臣 . 中国与花岗岩有关的萤石矿床地质特征及成矿作用[J]. 地质与勘探,1994 ,30 (5 ):1 −13 .CAO Junchen . Geological Feature and Mineraliztion of Fluorite Deposit Related to Granite in China[J]. Geology and Exploration,1994 ,30 (5 ):1 −13 .[2] 曹玉亭, 刘良, 王超, 等 . 阿尔金南缘塔特勒克布拉克花岗岩的地球化学特征、锆石U-Pb定年及Hf同位素组成[J]. 岩石学报,2010 ,26 (11 ):3259 −3271 .CAO Yuting, LIU Liang, WANG Chao, et al . Geochemical, Zircon U-Pb Dating and Hf Isotope Compositions Studies for Tatelekebulake Granite in South Altyn Tagh[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2010 ,26 (11 ):3259 −3271 .[3] 池国祥, 赖健清 . 流体包裹体在矿床研究中的作用[J]. 矿床地质,2009 ,28 (6 ):850 −855 .CHI Guoxiang, LAI Jianqing . Roles of fluid inclusions in study of mineral deposits[J]. Mineral Deposits,2009 ,28 (6 ):850 −855 .[4] 崔军文 . 南阿尔金断裂的韧性剪切作用时代及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报,2011 ,27 (11 ):3422 −3434 .CUI Junwen . Ductile shearing age of the south Altun fault and its tectonic implications[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2011 ,27 (11 ):3422 −3434 .[5] 陈衍景, 倪培, 范宏瑞, 等 . 不同类型热液金矿系统的流体包裹体特征[J]. 岩石学报,2007 ,23 (9 ):2085 −2108 .CHEN Yanjing, NI Pei, FAN Hongrui, et al . Diagnstic fluid inclusion of different types hydrothermal gold deposits[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2007 ,23 (9 ):2085 −2108 .[6] 陈军元, 刘艳飞, 颜玲亚, 等 . 石墨、萤石等战略非金属矿产发展趋势研究[J]. 地球学报,2021 ,42 (2 ):287 −296 .CHEN Junyuan, LIU Yanfei, YAN Lingya, et al . Research on Development Trend of Strategic Nonmetallic Minerals such as Graphite and Fluorite[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2021 ,42 (2 ):287 −296 .[7] 代德荣, 何小虎, 金少荣, 等 . 黔西南萤石矿床流体包裹体地球化学特征[J]. 矿物学报,2018 ,38 (6 ):693 −700 .DAI Derong, HE Xiaohu, JIN Shaorong, et al . Geochemical characteristics of fluid inclusions in fluorite deposits, Southwest Guizhou, China[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica,2018 ,38 (6 ):693 −700 .[8] 高永宝, 赵辛敏, 王博, 等 . 阿尔金西段卡尔恰尔—库木塔什超大型萤石矿带矿床地质、控矿花岗岩特征及找矿远景[J]. 中国地质,2023 ,50 (3 ):704 −729 .GAO Yongbao, ZHAO Xinmin, WANG Bo, et al . Ore deposit geology, Geochemical characteristics of ore controlling granite and Prospecting Potential of Superlarge Fluorite Ore Belt in the Kaerqiaer-KumutashiArea, West Altyn-Tagh[J]. Geology in China,2023 ,50 (3 ):704 −729 .[9] 冯李强, 顾雪祥, 章永梅, 等 . 山东蓬莱石家金矿床含金黄铁矿微量元素地球化学特征及其对成矿流体的约束[J]. 西北地质,2023 ,56 (5 ):262 −277 .FENG Liqiang, GU Xuexiang, ZHANG Yongmei, et al . Trace Element Geochemical Characteristics of Gold−Bearing Pyrite from the Shijia Gold Deposit in Penglai, Shandong Province and Its Constraints on Ore−Forming Fluids[J]. Northwestern Geology,2023 ,56 (5 ):262 −277 .[10] 高永宝, 陈康, 王亮, 等 . 阿尔金西段库木塔什萤石矿床成因: 磷灰石U-Pb年龄、原位Sr-Nd同位素、地球化学约束[J]. 西北地质,2024 ,57 (4 ):1 −20 .GAO Yongbao, CHEN Kang, WANG Liang, et al . Genesis of Kumutashi Fluorite Deposit in the West Altyn-Tagh Orogen, NW China: Constraints from Apatite in situ U-Pb Dating, Sr-Nd Isotope and Chemistry[J]. Northwestern Geology,2024 ,57 (4 ):1 −20 .[11] 康磊, 校培喜, 高晓峰, 等 . 阿尔金南缘早古生代岩浆作用及碰撞造山过程[J]. 地质学报,2016 ,90 (10 ):2527 −2550 .KANG Lei, XIAO Peixi, GAO Xiaofeng, et al . Early Paleozoic Magmatism and Collision Orogenic Process of the South Altyn[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2016 ,90 (10 ):2527 −2550 .[12] 李秉伦 . 研究矿物中气液包裹体的问题[J]. 地质科学,1981 ,16 (2 ):159 −163 .LI Binglun . Some Problems in the Study of Gas-Liquid Inclusion in Minerals[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology,1981 ,16 (2 ):159 −163 .[13] 李敏, 邹灏, 陈海锋, 等 . 黔东北双河重晶石-萤石矿床流体包裹体组合研究及成因[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报,2021 ,40 (4 ):858 −870 .LI Min, ZOU Hao, CHEN Haifeng, et al . Study on Fluid Inclusion Assemblages(FIA)and Origin of the Shuanghe Barite-fluorite Deposit in the Northeastern Guizhou[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry,2021 ,40 (4 ):858 −870 .[14] 卢焕章, 范宏瑞, 倪培, 等. 流体包裹体[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004, 1−444. [15] 刘斌, 段光贤 . NaCl−H2O溶液包裹体的密度式和等容式及其应用[J]. 矿物学报,1987 ,7 (4 ):345 −352 .LIU Bin, DUAN Guangxian . Density and isovolumetric formulae of NaCl−H2O inclusions and their applications[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica,1987 ,7 (4 ):345 −352 .[16] 刘良, 张安达, 陈丹玲, 等 . 阿尔金江尕勒萨依榴辉岩和围岩锆石LA-ICP-MS微区原位定年及其地质意义[J]. 地学前缘,2007 ,14 (1 ):98 −107 .LIU Liang, ZHANG Anda, CHEN Danling, et al . Implication based on LA-ICP-MS ages of eclogite and its country rock from Jianggalesayi area, Altyn Tagh[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2007 ,14 (1 ):98 −107 .[17] 龙腾, 王国芝, 李娜, 等 . 四川盆地米仓山南缘新立萤石矿床成矿流体研究[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报,2016 ,35 (3 ):552 −558 .LONG Teng, WANG Guozhi, LI Na, et al . Study on the Metallogenic Fluids of the Xinli Fluorite Deposit in the South Margin of the Micang Mountains, Sichuan Basin[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry,2016 ,35 (3 ):552 −558 .[18] 马中平, 李向民, 徐学义, 等 . 南阿尔金山清水泉镁铁-超镁铁质侵入体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb同位素定年及其意义[J]. 中国地质,2011 ,38 (4 ):1071 −1078 .MA Zhongping, LI Xiangmin, XU Xueyi, et al . Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb isotopic dating for Qingshuiquan layered mafic-ulmafic intrusion southern Altun orogen, in northwestern China and its implication[J]. Geology in China,2011 ,38 (4 ):1071 −1078 .[19] 马承安 . 武义萤石矿床矿物包裹体研究[J]. 华东地质,1990 ,11 (3 ):13 −24 .Ma Cheng’an . Study on mineral inclusions of fluorite deposit in Wuyi, Zhejiang Province[J]. East China Geology,1990 ,11 (3 ):13 −24 .[20] 倪培, 范宏瑞, 丁俊英 . 流体包裹体研究进展[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报,2014 ,33 (1 ):1 −5 .NI Pei, FAN Hongrui, DING Junying . Progress in Fluid Inclusions[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry,2014 ,33 (1 ):1 −5 .[21] 邵洁涟, 梅建明 . 浙江火山岩区金矿床的矿物包裹体标型特征研究及其成因与找矿意义[J]. 矿物岩石,1986 ,6 (3 ):103 −111 .SHAO Jielian, MEI Jianming . Study on the Characterization of Mineral Inclusions in Gold Deposits in Volcanic Rocks of Zhejiang Province and Its Genesis and Prospecting Significance[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology,1986 ,6 (3 ):103 −111 .[22] 王吉平, 商朋强, 熊先孝, 等 . 中国萤石矿床成矿规律[J]. 中国地质,2015 ,42 (1 ):18 −32 .WANG Jiping, SHANG Pengqiang, XIONG Xianxiao, et al . Metallogenic regularities of fluorite deposits in China[J]. Geology in China,2015 ,42 (1 ):18 −32 .[23] 孙非非, 张爱奎, 刘智刚, 等 . 东昆仑西段阿其音金矿成矿流体特征及其成因机制[J]. 西北地质,2023 ,56 (6 ):82 −94 .SUN Feifei, ZHANG Aikui, LIU Zhigang, et al . Analysis of the Genesis and H−O−S−Pb Isotopic Characteristics of Aqiyin Gold Deposit in the Western Section of the East Kunlun[J]. Northwestern Geology,2023 ,56 (6 ):82 −94 .[24] 王亮, 裴秋明, 曹华文, 等 . 内蒙古林西地区小北沟萤石矿床成矿流体特征及矿床成因探讨[J]. 桂林理工大学学报,2018 ,38 (2 ):189 −198 .WANG Liang, PEI Qiuming, CAO Huawen, et al . Characteristics of ore-forming fluids and genesis of Xiaobeigou fluorite deposit in Linxi area, Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology,2018 ,38 (2 ):189 −198 .[25] 吴锁平, 王梅英, 戚开静 . A型花岗岩研究现状及其述评[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志,2007 (1 ):57 −66 .WU Suoping, WANG Meiying, QI Kaijing . Present situation of researches on A-type granites: a review[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica,2007 (1 ):57 −66 .[26] 吴益平, 张连昌, 袁波, 等 . 新疆阿尔金地区卡尔恰尔超大型萤石矿床地质特征及成因[J]. 地球科学与环境学报,2021 ,43 (6 ):962 −977 .WU Yiping, ZHANG Lianchang, YUAN Bo, et al . Geological Characteristics and Genesis of the Super-large Kalqiar Fluorite Deposit in Altyn Tagh Area of Xinjiang, China[J]. Journal of Earch Sciences and Environment,2021 ,43 (6 ):962 −977 .[27] 吴益平, 张连昌, 周月斌, 等 . 阿尔金卡尔恰尔超大型萤石矿床成矿流体特征及形成机制探讨[J]. 地质科学,2022 ,57 (2 ):495 −509 .WU Yiping, ZHANG Lianchang, ZHOU Yuebin, et al . Study on fluid characteristics and metallogenic mechanism of the super-large Kalqiar fluorite deposit in Altyn Tagh area[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology,2022 ,57 (2 ):495 −509 .[28] 伍光锋, 魏龙飞, 王博, 等 . 阿尔金山库木塔什萨依萤石矿成矿地质特征及控矿因素[J]. 化工矿产地质,2022 ,44 (2 ):137 −145 .WU Guangfeng, WEI Longfei, WANG Bo, et al . Metallogenic geological characteristics and ore-controlling factors of kumutashisayi fluorite deposit in Altun Mountains[J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals,2022 ,44 (2 ):137 −145 .[29] 许志琴, 杨经绥, 张建新, 等 . 阿尔金断裂两侧构造单元的对比及岩石圈剪切机制[J]. 地质学报,1999 ,73 (3 ):193 −205 .XU Zhiqin, YANG Jingsui, ZHANG Jianxin, et al . A Comparison between the Tectonic Units on the Two Sides of the Altun Sinistral Strike-slip Fault and the Mechanism of Lithospheric Shearing[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,1999 ,73 (3 ):193 −205 .[30] 许东青, 聂凤军, 钱明平, 等 . 苏莫查干敖包超大型萤石矿床的稀土元素地球化学特征及其成因意义[J]. 矿床地质,2009 ,28 (1 ):29 −41 .XU Dongqing, NIE Fengjun, QIAN Mingping, et al . REE geochemistry and genesis of Sumochagan Obo superlarge fluorite deposit[J]. Mineral Deposits,2009 ,28 (1 ):29 −41 .[31] 许东青. 内蒙古苏莫查干敖包超大型萤石矿化区形成环境、地质特征及成矿机理研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2009. XU Dongqing. Geological Setting, features and Origin of the Sumochagan Obo Super-large Fluorite Mineralized District[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2009. [32] 校培喜, 高晓峰, 胡云绪. 西昆仑—阿尔金成矿带基础地质综合研究[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2014. XIAO Peixi, GAO Xiaofeng, HU Yunxu. Comprehensive Research of Basic Geology for Western Kunlun-Altgn Tagh Metallogenic Zone[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2014. [33] 杨子荣, 吴晓娲, 程琳, 等. 辽宁义县地区萤石矿床流体包裹体研究[A]. 全国成矿理论与深部找矿新方法及勘查开发关键技术交流研讨会论文集[C]. 辽宁工程技术大学, 2010: 5. [34] 杨文强, 刘良, 丁海波, 等 . 南阿尔金迪木那里克花岗岩地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学与Hf同位素特征及其构造地质意义[J]. 岩石学报,2012 ,28 (12 ):4139 −4150 .YANG Wenqiang, LIU Liang, DING Haibo, et al . Geochemistry, geochronology and zircon Hf isotopes of the Dimunalike granite in South Altyn Tagn and its geological significance[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2012 ,28 (12 ):4139 −4150 .[35] 杨世文. 赣南兴国-宁都成矿带萤石矿床成因[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2019. YANG Shiwen. Genesis of fluorite deposits in Xingguo-Ningdu metallogenic belt, southern Jiangxi[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2019. [36] 张安达, 刘良, 孙勇, 等 . 阿尔金超高压花岗质片麻岩中锆石SHRIMP U-Pb 定年及其地质意义[J]. 科学通报,2004 (22 ):2335 −2341 .ZHANG Anda, LIU Liang, SUN Yong, et al . SHRIMP U-Pb dating of zircons and its geological significance from UHP granitoid gneiss in Altyn Tagh[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2004 (22 ):2335 −2341 .[37] 张寿庭, 曹华文, 郑硌等 . 内蒙古林西水头萤石矿床成矿流体特征及成矿过程[J]. 地学前缘,2014 ,21 (5 ):31 −40 .ZHANG Shouting, CAO Huawen, ZHENG Ge, et al . Characteristics of ore forming fluids and mineralization processes of the Shuitou fluorite deposit in Linxi, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2014 ,21 (5 ):31 −40 .[38] 张建芳, 陈浩然, 伍江涵, 等 . 萤石矿床成因研究方法及发展趋势[J]. 西北地质,2024 ,57 (4 ):98 −113 .ZHANG Jianfang, CHEN Haoran, WU Jianghan, et al . Review on the Progress of Genetic Research Methods of Fluorite Deposits[J]. Northwestern Geology,2024 ,57 (4 ):98 −113 .[39] 张苏坤, 王辉, 冯绍平, 等 . 河南省栾川县杨山萤石矿成矿作用: 来自氢氧同位素和元素地球化学的约束[J]. 西北地质,2022 ,55 (2 ):209 −216 .ZHANG Sukun, WANG Hui, FENG Shaoping, et al . Mineralization of Yangshan Fluorite Deposit in Luanchuan County, Henan Province: Constraints from H-O Isotopes and Element Geochemistry[J]. Northwestern Geology,2022 ,55 (2 ):209 −216 .[40] 曾昭法, 曹华文, 高峰, 等 . 内蒙古林西地区萤石矿床流体包裹体研究[J]. 地球化学,2013 ,42 (1 ):73 −81 .ZENG Zhaofa, CAO Huawen, GAO Feng, et al . Fluid inclusion study of fluorite deposits in Linxi region, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geochimica,2013 ,42 (1 ):73 −81 .[41] 赵辛敏, 高永宝, 燕洲泉, 等 . 阿尔金卡尔恰尔超大型萤石矿带成因: 来自年代学、稀土元素和Sr–Nd同位素的约束[J]. 西北地质,2023 ,56 (1 ):31 −47 .ZHAO Xinmin, GAO Yongbao, YAN Zhouquan, et al . Genesis of Kalqiaer Super–large Fluorite Zone in Altyn Tagh Area: Chronology, Rare Earth Elements and Sr–Nd Isotopes Constraints[J]. [J]. Northwestern Geology,2023 ,56 (1 ):31 −47 .[42] 邹灏, 张寿庭, 方乙, 等 . 中国萤石矿的研究现状及展望[J]. 国土资源科技管理,2012 ,29 (5 ):35 −42 .ZOU Hao, ZHANG Shouting, FANG Yi, et al . Current Situation and Prospect of Fluorite Deposit Researches in China[J]. Scientific and Technological Management of Land and Resources,2012 ,29 (5 ):35 −42 .[43] 邹灏. 川东南地区重晶石-萤石矿成矿规律与找矿方向[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2013. ZOU Hao. Metallogenic Regularity and Prospecting Direction of Barite-Fluorite Deposit In Southeast Sichuan[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2013. [44] 邹灏, 淡永, 张寿庭, 等 . 重庆东南部彭水地区重晶石-萤石矿床的成矿物质来源探讨: 地球化学证据[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,2016 ,40 (1 ):71 −85 .ZOU Hao, DAN Yong, ZHANG Shouting, et al . Geochemical Evidence for Sources of Ore-forming Material of Barite-Fluorite Deposits in Pengshui Area, Southeast Chongqing[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia,2016 ,40 (1 ):71 −85 .[45] 朱敬宾, 王吉平, 商朋强, 等 . 中国萤石矿床锶同位素、氢氧同位素地球化学特征[J]. 化工矿产地质,2021 ,43 (1 ):7 −16 .ZHU Jingbin, WANG Jiping, SHANG Pengqiang, et al . Geochemical characteristics of strontium and hydrogen and oxygen isotopes in fluorite deposits in China[J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals,2021 ,43 (1 ):7 −16 .[46] Bischoff J L . Densities of liquids and vapors in boiling NaCl-H2O solutions - a PVTX summary from 300° to 500 ℃[J]. American Journal of Science,1991 ,291 (4 ):309 −338 .[47] Bau M, Dulski P . Compartive study of yttrium and rare-earth element behaviors in fluorite-rich hydrothermal fluids[J]. Contributions Mineralogy Petrology,1995 ,119 :213 −223 .[48] Becker S P, Fall A, Bodnar R . Synthetic fluid inclusions. XVII. 1 PVTX properties of high salinity H2O−NaCl solutions (>30 wt% NaCl): Application to fluid inclusions that homogenize by halite disappearance from porphyry copper and other hydrothermal ore deposits[J]. Economic Geology,2008 ,103 (3 ):539 −554 .[49] Catherine K, Richardson, Darrell M, et al . The chemical and thermal evolution of the fluids in the Cave-in-Rock fluorspar district, Illinois; mineralogy, paragenesis, and fluid inclusions[J]. Economic Geology,1984 ,79 (8 ):1833 −1856 .[50] Constantopoulos J . Fluid inclusions and rare earth element geochemistry of fluorite from south-central Idaho[J]. Economic Geology,1988 ,83 (3 ):626 −636 .[51] Goldstein R H, Reynolds T J . Systematics of fluid inclusions in diagenetic minerals: SEPM Short Course 31[J]. Society for Sedimentary Geology,1994 ,31 :1 −199 .[52] Hall D L, Stemer S M, Bodnar R J . Freezing point depression of NaCl-KCl-H2O solutions[J]. Economic Geology,1988 ,83 (1 ):197 −202 .[53] Hedenquist J W, Lowenstern J B . The role of magmas in the formation of hydrothermal ore deposits[J]. Nature,1994 ,370 (6490 ):519 −527 .[54] Korges M, Weis P, Lüders V, et al . Depressurization and boiling of a single magmatic fluid as a mechanism for tin-tungsten deposit formation[J]. Geology,2018 ,46 (1 ):75 −78 .[55] Ni P, Wang G G, Yu W, et al . Evidence of fluid inclusions for two stages of fluid boiling in the formation of the giant Shapinggou porphyry Mo deposit, Dabie Orogen, Central China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2015 ,65 :1078 −1094 .[56] Richardson C K, Holland H D . The Solubility of fluorite in hydrothermal solutions an experimental study[J]. Geochemica et Cosmochimica Acta,1979 ,43 (8 ):1315 −1325 .[57] Zhang J X, Yu S Y, Mattinson C G . Early Paleozoic polyphase metamorphism in northern Xizang, China[J]. Gondwana Research,2017 ,41 :267 −289 .[58] Taylor H P . The application of oxygen and hydrogen isotope studies to problems of hydrothermal alteration and ore deposition[J]. Economic Geology,1974 ,69 (6 ):843 −883 .[59] Zhang D H, Audétat A . A Plea for More Skepticism Toward Fluid Inclusions: Part I. Postentrapment Changes in Fluid Density and Fluid Salinity Are Very Common[J]. Economic Geology,2023 ,118 (1 ):15 −41 . -




 下载:
下载: