Genesis of Wushan Fluorite Deposit in Jinyun County, Zhejiang Province: Constraints from Fluorite Rare Earth Elements, Fluid Inclusions and Infrared Spectroscopy
-
摘要:
吾山萤石矿床位于华夏板块北东端,浙江萤石矿集区中部。矿床产于下白垩统馆头组与燕山晚期花岗岩接触带中,矿体受NW向断裂控制,发育条带状萤石。在野外地质调查的基础上,对不同颜色萤石的稀土元素、流体包裹体及红外光谱开展研究。研究结果表明,不同颜色萤石的稀土元素含量、成矿温度呈现规律性的变化。从绿色萤石到紫色萤石再到黄色萤石,具有δEu值增大,∑REE值减小,LREE/HREE值增大,成矿温度逐渐降低的特征。结合矿床地质特征,认为3种颜色萤石结晶成矿过程为温度变化范围较大的还原环境,萤石形成顺序为绿色萤石先结晶,紫色萤石次之,黄色萤石最后形成。Tb/Ca-Tb/La、La/Ho-Y/Ho图解和包裹体测温显示,区内不同颜色萤石为同一流体来源在同一成矿期次不同阶段成矿。条带状萤石的形成是成矿热液周期性脉动上涌的结果。研究区萤石矿床的成矿流体属于中–低温、低盐度、低密度含F热液,吾山萤石矿床属于中–低温热液裂隙填充型萤石矿床。
Abstract:The Wushan fluorite deposit is located at the northeast end of the Cathaysia Block, in the central part of the fluorite mining area in Zhejiang Province. The deposit is located in the contact zone between the Guantou Formation of the Cretaceous and the Yanshan granite. The distribution of the ore body is controlled by northwest trending faults, and banded fluorite is developed. Based on geological surveys, research was conducted on rare earth elements, fluid inclusions, and infrared spectra of fluorite with different colors. The research results indicate that the rare earth element content and mineralization temperature of fluorite with different colors shows regular changes. From green fluorite to purple fluorite and then to yellow fluorite, δEu increases, the ∑REE decreases, the LREE/HREE ratio increases and mineralization temperature decrease. Based on the geological characteristics of the deposit, this study suggests that the crystallization and mineralization process of the three colors of fluorite is a reducing environment with a large temperature range. The formation sequence of fluorite is that green fluorite is formed first, followed by purple fluorite, and yellow fluorite is formed latest. The Tb/Ca-Tb/La and La/Ho-Y/Ho diagrams and inclusion temperature measurements show that different colored fluorites in the area are formed from the same fluid source at different stages of the same mineralization period. The formation of banded fluorite is the result of periodic pulsation and upwelling of ore-forming hydrothermal fluids. Overall, the ore-forming fluid of the fluorite deposit in the study area belongs to medium low temperature, low salinity, and low-density F-containing hydrothermal fluids. In summary, the Wushan fluorite deposit belongs to the medium to low temperature hydrothermal fissure filling type fluorite deposit
-

-
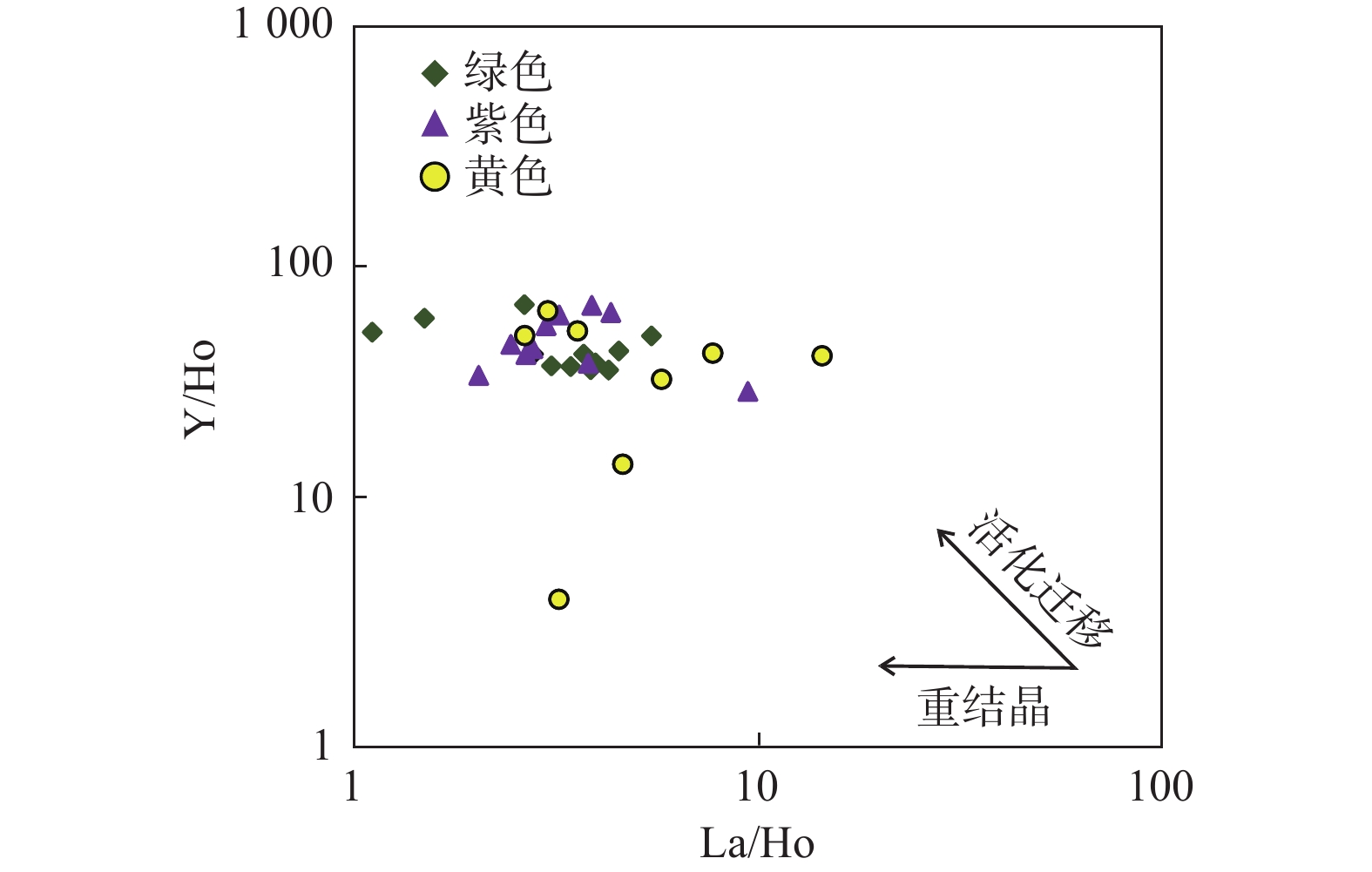
图 7 吾山萤石矿床3种颜色萤石La/Ho-Y/Ho关系图(底图据Bau et al., 1995)
Figure 7.
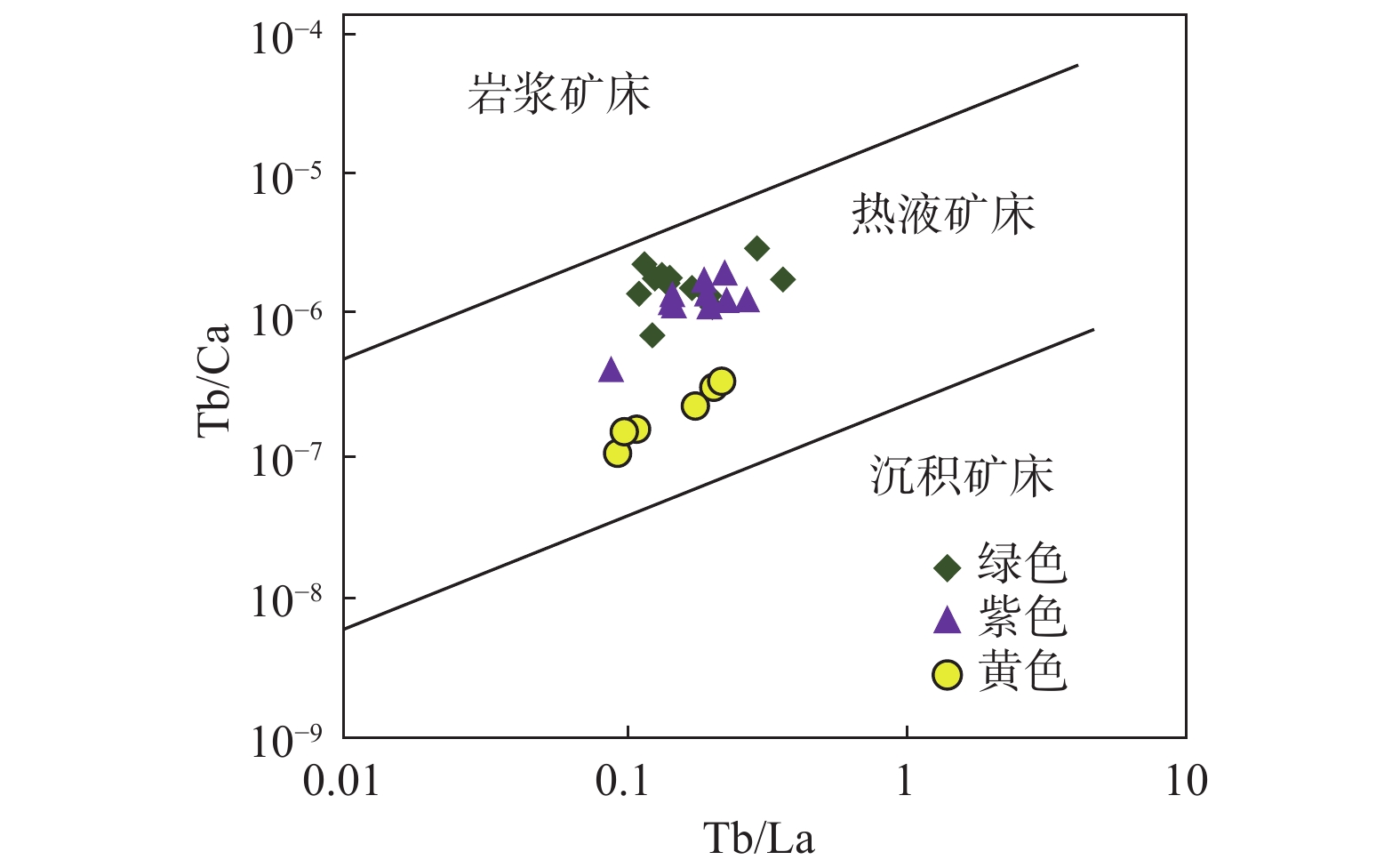
图 8 吾山萤石矿床3种颜色萤石Tb/Ca-Tb/La关系图(底图据Möller et al., 1976)
Figure 8.
图 9 吾山萤石矿床成矿模式图(据Fang et al., 2020修改)
Figure 9.
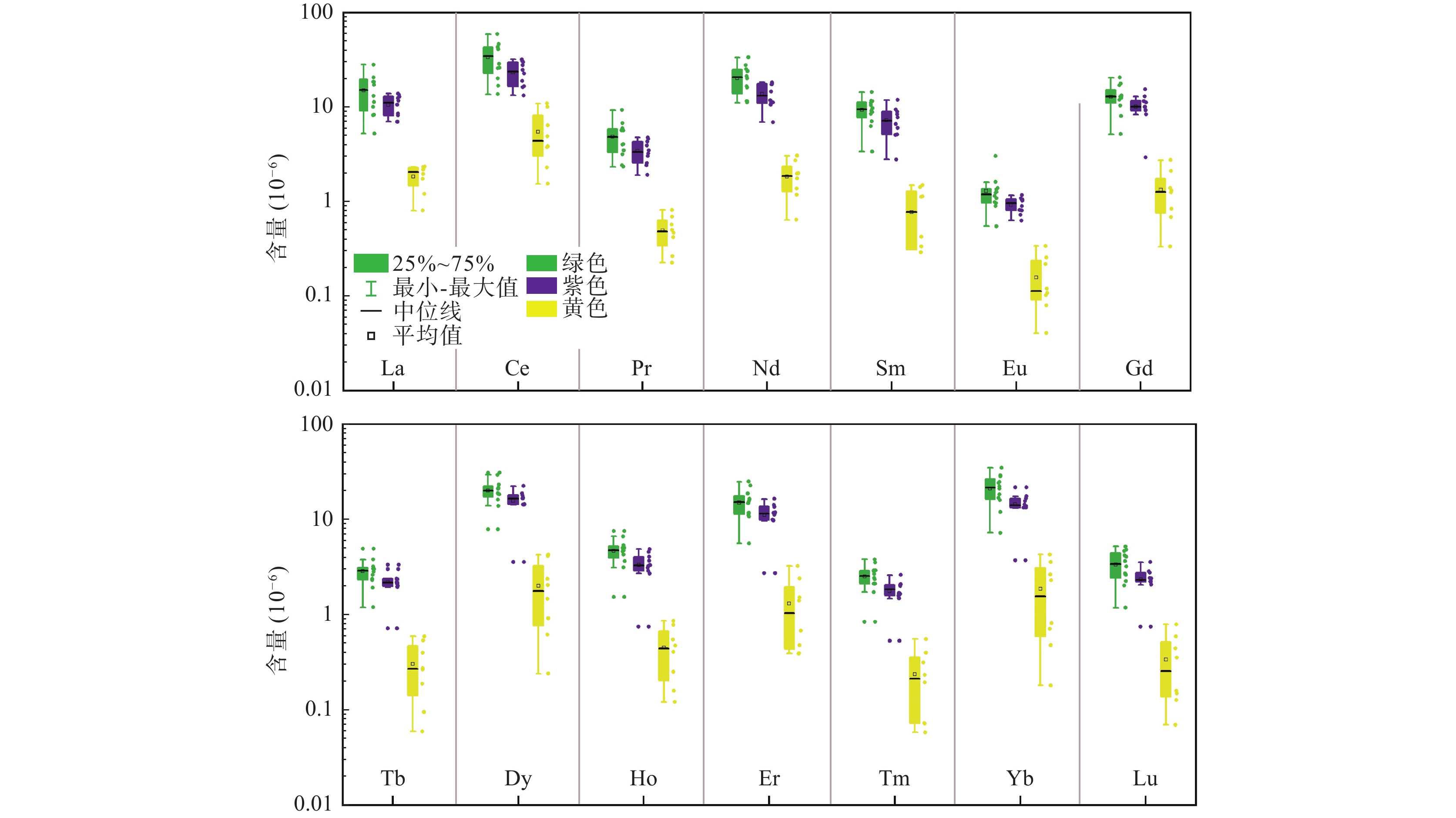
表 1 吾山萤石矿床3种颜色萤石微量元素(10−6)分析结果
Table 1. Analysis results of REE (10−6) of the three colours of fluorite in Wushan deposit
样品编号 萤石颜色 Rb Ba Th U Nb Sr Zr Ti La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu WS1-G-01 绿色萤石 0.038 0.042 0.051 0.12 0.13 227 11.8 1083 8.53 16.6 2.43 11.1 5.15 0.73 9.37 1.96 14.4 3.10 9.70 1.64 14.3 2.21 WS1-G-02 绿色萤石 0.088 0.45 0.013 0.082 0.0003 223 0.74 1054 7.02 16.3 2.57 10.7 5.09 0.81 9.20 2.19 14.3 2.89 9.88 1.59 13.8 2.24 WS1-G-03 绿色萤石 0.24 0.17 0.065 0.10 0.096 235 4.80 1074 8.20 18.8 3.02 11.2 7.79 1.03 10.1 2.17 18.0 4.05 11.8 2.09 17.5 2.75 WS1-G-04 绿色萤石 0.036 0.22 0.35 0.19 0.41 579 58.0 1154 13.1 28.7 4.02 16.6 8.89 1.61 12.5 2.61 18.3 4.28 11.1 2.12 18.3 2.61 WS2-G-05 绿色萤石 0.49 3.76 0.083 0.20 0.076 195 135 1098 20.6 46.2 6.76 27.9 11.0 1.09 13.2 3.20 23.3 5.37 18.8 2.91 28.3 4.81 WS2-G-06 绿色萤石 0.060 0.027 − 0.024 0.066 215 − 1184 28.2 59.1 9.30 33.6 14.5 1.40 17.7 3.80 29.4 6.65 22.6 3.81 34.9 5.20 WS2-G-07 绿色萤石 0.17 − − 0.0091 0.0099 194 1.75 1082 17.3 41.5 5.63 23.9 9.74 0.90 13.4 2.81 21.4 5.05 16.1 2.92 24.7 4.07 WS2-G-08 绿色萤石 1.17 0.23 0.0050 0.026 0.051 165 − 1145 18.5 42.6 5.99 24.2 10.5 1.15 11.9 2.38 19.0 4.70 16.5 2.87 24.2 4.68 WS2-G-09 绿色萤石 0.41 − 0.048 0.15 0.27 133 − 1284 8.22 16.8 3.17 11.6 7.07 0.99 8.06 1.93 13.9 3.13 10.7 2.35 16.8 2.26 WS2-G-10 绿色萤石 0.0068 0.13 0.078 0.012 0.070 130 − 1111 11.3 26.1 4.06 21.3 11.6 1.36 20.6 4.92 30.8 7.58 24.9 3.54 29.0 4.18 WS2-G-11 绿色萤石 0.61 0.23 0.67 0.62 0.13 473 7.93 1113 5.26 13.7 2.42 11.6 8.49 1.26 17.0 3.00 21.0 4.76 11.7 2.12 11.9 2.02 WS2-G-12 绿色萤石 10.1 25.8 3.50 16.1 6.32 0.96 10.4 2.31 16.1 3.66 11.6 1.73 15.9 2.71 0.025 0.16 0.030 0.21 0.039 219 0.040 1131 WS1-P-01 紫色萤石 0.084 0.15 0.34 0.012 − 181 − 1062 8.31 20.1 2.35 11.2 3.39 0.55 5.18 1.20 7.86 1.54 5.62 0.84 7.23 1.18 WS1-P-02 紫色萤石 0.065 0.95 0.37 0.15 0.031 247 4.29 1287 18.4 40.8 5.63 25.2 9.18 3.05 13.1 3.06 21.0 5.01 14.9 2.68 21.1 3.20 WS1-P-03 紫色萤石 1.07 0.20 0.24 0.056 0.097 311 6.23 1281 20.6 43.5 5.72 20.1 11.7 1.24 12.8 3.03 18.8 4.59 15.6 2.43 22.2 3.63 WS1-P-04 紫色萤石 − 0.13 0.67 0.25 0.33 156 2.88 1147 8.53 16.6 2.43 11.1 5.15 0.73 9.37 1.96 14.4 3.10 9.70 1.64 14.3 2.21 WS1-P-05 紫色萤石 − 0.29 0.021 0.0021 − 130 1.06 1087 7.02 16.3 2.57 10.7 5.09 0.81 9.20 2.19 14.3 2.89 9.88 1.59 13.8 2.24 WS1-P-06 紫色萤石 0.010 − 0.20 0.15 0.20 201 − 1257 8.20 18.8 3.02 11.2 7.79 1.03 10.1 2.17 18.0 4.05 11.8 2.09 17.5 2.75 WS3-P-07 紫色萤石 0.96 1.01 0.080 0.043 0.099 178 − 1184 13.1 28.7 4.02 16.6 8.89 1.61 12.5 2.61 18.3 4.28 11.1 2.12 18.3 2.61 WS3-P-08 紫色萤石 − − 0.048 0.049 − 157 0.42 1119 20.6 46.2 6.76 27.9 11.0 1.09 13.2 3.20 23.3 5.37 18.8 2.91 28.3 4.81 WS3-P-09 紫色萤石 0.12 0.25 0.012 0.035 0.16 190 − 1167 28.2 59.1 9.30 33.6 14.5 1.40 17.7 3.80 29.4 6.65 22.6 3.81 34.9 5.20 WS3-P-10 紫色萤石 − 0.36 0.13 0.015 0.026 167 1.07 1152 17.3 41.5 5.63 23.9 9.74 0.90 13.4 2.81 21.4 5.05 16.1 2.92 24.7 4.07 WS1-Y-01 黄色萤石 − 0.31 0.069 2.42 0.041 256 264 1162 0.80 1.54 0.23 0.64 0.29 0.041 0.34 0.060 0.24 0.25 0.39 0.073 0.18 0.070 WS1-Y-02 黄色萤石 − − 0.085 0.23 0.19 244 7.94 1254 2.18 11.0 0.47 2.01 0.43 0.22 0.84 0.27 1.48 0.47 0.68 0.23 0.71 0.15 WS1-Y-03 黄色萤石 − 0.078 0.024 0.16 0.037 237 − 1210 1.74 3.86 0.42 1.76 − 0.11 1.26 0.19 0.92 0.12 0.48 0.058 0.81 0.13 WS1-Y-04 黄色萤石 − 0.39 − 0.22 − 205 0.59 1093 2.33 4.93 0.50 1.19 1.12 0.12 1.30 0.27 2.05 0.41 1.40 0.19 2.31 0.35 WS4-Y-05 黄色萤石 0.031 0.100 0.054 0.049 0.079 163 − 1212 2.27 6.42 0.70 2.74 1.49 0.34 2.12 0.54 4.26 0.86 3.25 0.56 4.29 0.79 WS4-Y-06 黄色萤石 − 0.18 0.012 0.089 0.054 155 0.95 1102 1.96 3.78 0.57 1.98 1.43 0.10 1.39 0.40 2.38 0.55 1.51 0.32 2.63 0.44 WS4-Y-07 黄色萤石 − 0.28 0.37 0.033 0.068 173 0.041 1098 2.35 10.0 0.82 3.06 1.13 0.26 2.76 0.59 4.15 0.78 2.40 0.40 3.58 0.59 WS4-Y-08 黄色萤石 − − − 0.023 − 154 − 1244 1.22 2.30 0.27 1.37 0.34 0.081 0.69 0.095 0.62 0.16 0.40 0.072 0.48 0.16 注:“−”为低于检测限。 -
[1] 曹华文, 张寿庭, 高永璋, 等. 内蒙古林西萤石矿床稀土元素地球化学特征及其指示意义[J]. 地球化学, 2014, 43(2): 131−140.
CAO Huawen, ZHANG Shouting, GAO Yongzhang, et al. REE geochemistry of fluorite from Linxi fluorite deposit and its geological implications, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region[J]. Geochimica,2014,43(2):131−140.
[2] 曹俊臣. 中国与花岗岩有关的萤石矿床地质特征及成矿作用[J]. 地质与勘探, 1994, 30(5): 1−6.
CAO Junchen. Geological feature and mineralization of fluorite deposit related to granite in China[J]. Geology and Prospecting,1994,30(5):1−6.
[3] 曹俊臣. 华南低温热液脉状萤石矿床稀土元素地球化学特征[J]. 地球化学, 1995(3): 225−234. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1995.03.003
CAO Junchen. REE geochemical characteristics of epithermal vein fluorite deposits in south China[J]. Geochimica,1995(3):225−234. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1995.03.003
[4] 范天一, 秦亚, 冯佐海, 等. 桂北地区龙胜韧性剪切带的应变特征及构造意义[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 50(5): 613−628.
FAN Tianyi,QIN Ya,FENG Zuohai,et al. The strain characteristics and tectonic significance of the Longsheng ductile shear zone in Northern Guangxi, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2023,50(5):613−628.
[5] 方乙, 钟祥, 白甜甜. 浙江缙云骨洞坑萤石矿床成矿流体特征[J]. 2017, 39(3): 13-22.
FANG Yi, ZHONG Xiang, BAi Tiantian. Ore-forming Fluids Characteristics of Fluorite Deposits in Gudongkeng. Jinyun County, Zhejiang Province[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 39(3): 13-22.
[6] 付乐兵, 魏俊浩, 张道涵, 等. 单个流体包裹体成分LA-ICP-MS分析与矿床学应用进展[J]. 中南大学学报, 2015, 46(10): 3833−3840.
FU Lebing, WEl Junhao, ZHANG Daohan, et al. A review of LA-ICPMS analysis for individual fluid inclusions and its applications in ore deposits[J]. Journal of Central South University,2015,46(10):3833−3840.
[7] 韩文斌, 马承安. 萤石矿床地质及地球化学特征-以浙江武义矿田为例[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1991.
HAN Wenbin, MA Chenan. Geology and Geochemical Characteristics of Fluorite Deposits With Wuyi Oreflield in Zhejiang Province as Example[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1991.
[8] 冯李强, 顾雪祥, 章永梅, 等. 山东蓬莱石家金矿床含金黄铁矿微量元素地球化学特征及其对成矿流体的约束[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(5): 262−277.
FENG Liqiang, GU Xuexiang, ZHANG Yongmei, et al. Trace Element Geochemical Characteristics of Gold-Bearing Pyrite from the Shijia Gold Deposit in Penglai, Shandong Province and Its Constraints on Ore-Forming Fluids[J]. Northwestern Geology,2023,56(5):262−277.
[9] 李欣宇, 邹灏, 张强, 等. 浙江缙云盆地吾山萤石矿床流体包裹体研究[J]. 资源环境与地学空间信息技术新进展学术讨论会, 2016, 25(6): 569−571.
LI Xinyu, ZOU Hao, ZHANG Qiang, et al. Research on fluid inclusions in Wushan fluorite deposit in Jinyun Basin, Zhejiang Province[J]. Academic Symposium on New Advances in Resource Environment and Geospatial Information Technology,2016,25(6):569−571.
[10] 李长江, 蒋叙良. 浙江武义-东阳地区萤石矿床的锶同位素地球化学研究[J]. 矿床地质, 1989, 8(3): 10.
LI Changjiang, JIANG Xuliang. Strontium Isotopic Geochemistry of Fluorite Deposits in Dongyang-Wuyi Area, Zhejiang Province[J]. Mineral Deposits,1989,8(3):10.
[11] 栗克坤, 王春连, 陈新立, 等. 福建邵武地区萤石矿微量、稀土元素特征及对成矿物质指示[J]. 中国地质, 2023, 50(03): 806-817.
LI Kekun, WANG Chunlian, CHEN Xinli, et al. Characteristics of trace and rare earth elements and direction for ore-forming materials in Shaowu area, Fujian Province[J]. Geology in China, 2021, 50(03): 806-817.
[12] 刘宁. 河南嵩县竹园沟萤石矿的宝石矿物学特征研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2021.
LIU Ning. The Study on Gemological and Mineralogical Characteristics of Fluorite in Zhuyuangou Deposit, Song County, Henan[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2021.
[13] 卢焕章, 范宏瑞, 倪培. 流体包裹体[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004.
LU Huangzhang, FANG Hongrui, NI Pei. Fluid inclusions[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2004.
[14] 王吉平, 商朋强, 熊先孝, 等. 中国萤石矿床成矿规律[J]. 中国地质, 2015, 42(1): 18−32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2015.01.003
WANG Jiping, SHANG Pengqiang, XIONG Xianxiao, et al. Metallogenic regularities of fluorite deposits in China[J]. Geology in China,2015,42(1):18−32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2015.01.003
[15] 苏静, 顾雪祥, 彭义伟, 等. 新疆西天山阿尔恰勒Pb–Zn–Cu矿床成因来自流体包裹体和同位素的证据[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(1): 81−98.
SU Jing, GU Xuexiang, PENG Yiwei, et al. Genesis of the Arqiale Pb-Zn-Cu Deposit in the Western Tianshan, Xinjiang: Evidence from Fluid Inclusions and Isotopes[J]. Northwestern Geology,2023,56(1):81−98.
[16] 徐旃章, 吴志俊. 浙江省萤石成矿规律与成矿预测[M]. 成都: 四川科学技术出版社, 1991.
XU Zhangzhang, WU Zhijun. Metallogenic Law and Prediction of Fluorite in Zhejiang Province[M]. Chengdu: Sichuan Science and Technology Press, 1991.
[17] 徐旃章, 张寿庭. 浙江省萤石矿时空演化序列与典型萤石矿田的剖析及评价[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2014.
XU Zhangzhang, ZHANG Shouting. Analysis and evaluation of the spatiotemporal evolution sequence of fluorite deposits and typical fluorite fields in Zhejiang Province[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2014.
[18] 叶锡芳. 浙江萤石矿床成矿规律与成矿模式[J]. 西北地质, 2014, 47(1): 208−220. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2014.01.019
YE Xifang. Mineralization and Metallogenic Model of Fluorite Deposits in the Zhejiang Area[J]. Northwestern Geology,2014,47(1):208−220. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2014.01.019
[19] 俞国华. 浙江省岩石地层[M]. 北京: 中国地质大学出版社, 1986.
YU Guanghua. Rock Stratigraphy in Zhejiang Province[M]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences Press, 1986.
[20] 曾湘怡. 浙江武义萤石的宝石矿物学特征研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2019.
ZENG Xianyi. A Study on the Gemological Mineralogical Characteristics of Fluorite in Wuyi, Zhejiang Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2019.
[21] 张理刚. 稳定同位素在地质科学中的应用: 金属活化热液成矿作用及找矿[M]. 西安: 陕西科学技术出版社, 1985.
ZHANG Ligang. The Application of Stable Isotopes in Geological Sciences: Metal-activated Hydrothermal Mineralization and Prospecting[M]. Xi’an: Shaanxi Science and Technology Press, 1985.
[22] 张建芳, 陈浩然, 伍江涵, 等. 萤石矿床成因研究方法及发展趋势[J]. 西北地质, 2024, 57(4): 98−113.
ZHANG Jianfang, CHEN Haoran, WU Jianghan, et al. Review on the Progress of Genetic Research Methods of Fluorite Deposits[J]. Northwestern Geology,2024,57(4):98−113.
[23] 张苏坤, 王辉, 冯绍平, 等. 河南省栾川县杨山萤石矿成矿作用: 来自氢氧同位素和元素地球化学的约束[J]. 西北地质, 2022, 55(2): 209−216.
ZHANG Sukun, WANG hui, FENG Shaoping, et al. Mineralization of Yangshan Fluorite Deposit in Luanchuan County, Henan Province: Constraints from H-O Isotopes and Element Geochemistry[J]. Northwestern Geology,2022,55(2):209−216.
[24] 赵钰, 董树义, 陈珲, 等. 广东乳源地区棋梓桥组-天子岭组碳酸盐岩地球化学特征及其古环境意义[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 50(1): 65−78.
ZHAO Yu, DONG Shuyi, CHEN Hui, et al. Geochemical characteristics and paleoenvironmental significance of Qiziqiao-Tianziling Formation carbonate rocks in Ruyuan area, Guangdong, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2023,50(1):65−78.
[25] 赵辛敏, 高永宝, 燕洲泉, 等. 阿尔金卡尔恰尔超大型萤石矿带成因: 来自年代学、稀土元素和Sr–Nd同位素的约束[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(1): 31−47.
ZHAO Xinmin, GAO Yongbao, YAN Zhouquan, et al. Genesis of Kalqiaer Super–large Fluorite Zone in Altyn Tagh Area: Chronology, Rare Earth Elements and Sr–Nd Isotopes Constraints[J]. Northwestern Geology,2023,56(1):31−47.
[26] 周慧, 郗爱华, 熊益学, 等. 流体包裹体的研究进展[J]. 矿物学报, 2013, 33(5): 92−100.
ZHOU Hui, XI Aihua, XIONG Yixue, et al. Progress in the Research on Fluid lnclusions[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica,2013,33(5):92−100.
[27] 邹灏, 方乙, 陈合毛, 等. 浙江天台盆地下陈萤石矿稀土元素地球化学特征及成因[J]. 中国地质, 2014, 41(4): 1375−1386. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.04.027
ZOU Hao, FANG Yi, CHEN Hemao, et al. REE geochemistry and genesis of the Xiachen fluorite deposit in Tiantai basin, Zhejiang Province[J]. Geology in China,2014,41(4):1375−1386. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.04.027
[28] Bau M, Dulski P. Comparative study of yttrium and rare-earth element behaviours in fluorine-rich hydrothermal fluids[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,1995,199:213−223.
[29] Bau M, Moeller P. Rare-earth element fractionation in metamorphogenic hydrothermal calcite, magnesite and siderite[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology,1992,4:231−246.
[30] Bau M. Controls on the fractionation of isovalent trace elements in magamatic and aqueous systems: Evidence from Y/Ho, Zr/Hf, and lanthanide tetrad effect[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,1996,123:323−333. doi: 10.1007/s004100050159
[31] Chen J, Liu Y, Yan L, et al. Research on development trend of strategic nonmetallic minerals such as graphite and fluorite[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2021,42(2):287−296.
[32] Constantopoulos J. Fluid inclusions and rare earth element geochemistry of fluorite from south-central Idaho[J]. Economic Geology,1988,83(3):626−636. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.83.3.626
[33] Deng X H, Chen Y J, Yao J M, et al. Fluorite REE-Y (REY) geochemistry of the CA. 850Ma Tumen molybdenite-fluorite deposit, eastern Qinling, China: Constraints on ore genesis[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2014,63(2):532−543.
[34] Fang Y, Zou H, Leon B, et al. Fluorite deposits in the Zhejiang Province, southeast China: The possible role of extension during the late stages in the subduction of the Paleo-Pacific oceanic plate, as indicated by the Gudongkeng fluorite deposit[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2020,117:103276. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103276
[35] Ge X, Guo Q, Wang Q, et al. Mineralogical Characteristics and Luminescent Properties of Natural Fluorite with Three Different Colors[J]. Materials,2022,15(6):1983−1983. doi: 10.3390/ma15061983
[36] Geological Survey, U. S. Mineral commodity summaries 2019[M]. U. S. Geology. Survey, 2019: 60−61.
[37] Golpira E A, Iain M S, Joel E G. The trace element chemistry and cathodoluminescence characteristics of fluorite in the Mount Pleasant Sn-W-Mo deposits: Insights into fluid character and implications for exploration[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration,2017,172:1−19. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.09.010
[38] Hammerli J, Kemp A I S, Spandler C. Neodymium isotope equilibration during crustal metamorphism revealed by in situ microanalysis of REE-rich accessory minerals[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2014,392:133−142. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2014.02.018
[39] He Z Y, Xu X S. Petrogenesis of the Late Yanshanian mantle-derived intrusions in southeastern China: response to the geodynamics of paleo-Pacific plate subduction[J]. Chemical Geology,2012,328:208−221.
[40] Li Z X, Li X H. Formation of the 1300-km-wide intracontinental orogen and postorogenic magmatic province in Mesozoic South China: a flat-slab subduction model[J]. Geology,2017,35:179−182.
[41] Mao M, Simandl G J, Spence J, et al. Fluorite trace-element chemistry and its potential as an indicator mineral: Evaluation of LA-ICP-MS method[J]. Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland Bulletin, 2015: 251−264.
[42] Mielczarski E, Mielczarski J A, Cases J M, et al. Influence of solution conditions and mineral surface structure on the formation of oleate adsorption layers on fluorite[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2002,205(1/2):73−73.
[43] Migdisov A A, Williams-jones A E, Wagner T. An experimental study of the solubility andspeciation of the Rare Earth Elements (III) in fluoride- and chloride-bearing aqueous solutionsat temperatures up to 300 C[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2013,73(23):7087−7109.
[44] Moller P, Bau M, Dulski P. REE and Y fractionation in fluorite and their bearing on fluorite formation[J]. Proceedings of the 9th Quadrennial IAGOD Symp, Schweizerbart, Stuttgart, 1998: 575−592.
[45] Möller P, Parekh P P, Schneider H J. The application of Tb/Ca-Tb/La abundance ratios to problems of fluorspar genesis[J]. Mineralium Deposita,1976,11(1):111−116. doi: 10.1007/BF00203098
[46] Paterson M S. The determination of hydroxyl by infrared absorption in quartz, silicate glasses and similar materials[J]. Bull Mineral,1982,105(1):20−29.
[47] Singh R K. FTIR spectroscpy of natural fluorite from Ambadongar, Gujarat[J]. Journal of the Geological Society of India,2013,81(2):215−218. doi: 10.1007/s12594-013-0024-8
[48] Sun S, Mcdonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications,1989,42(1):313−345.
[49] Taylor R P. Rare earth element geochemistry as an aid to interpreting hydrothermal ore deposits[J]. Metallization associated with acid magmatism, 1982: 357−365.
[50] Veksler I V, Dorfman A M, Kamenetsky M. Partitioning of lanthanides and Y between immiscible silicate and fluoride melts, fluorite and cryolite and the origin of the lanthanide tetrad effect in igneous rocks[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2005,69(11):2847−2860. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2004.08.007
[51] Yang S W, Feng C Y, Lou F S. Origin of the Tongda fluorite deposit related to the Palaeo‐Pacific Plate subduction in southern Jiangxi Province, China: New evidence from geochronology, geochemistry, fluid inclusion, and H-O isotope compositions[J]. Geological Journal,2022,57(1):238−253. doi: 10.1002/gj.4295
[52] Yu L M, Zou H, Santosh M, et al. The link between Paleo-Tethys subduction and regional metallogeny in the SW Yangtze Block: New evidence from the Zubu carbonate-hosted F-Pb-Zn deposit[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2022,144:104809. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2022.104809
[53] Zou H, Li M, M. Santosh M, et al. Fault-controlled carbonate-hosted barite-fluorite mineral systems: The Shuanghe deposit, Yangtze Block, South China[J]. Gondwana Research,2022,101:26−43. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2021.07.020
-




 下载:
下载: