PRIMARY HALO ZONING AND DEEP PREDICTION OF THE MAIN ORE BELT IN HUACHANGGOU GOLD DEPOSIT, WESTERN QINLING MOUNTAINS
-
摘要:
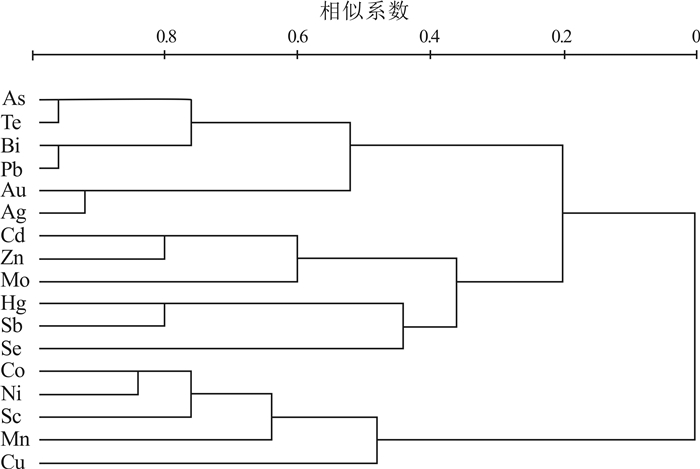
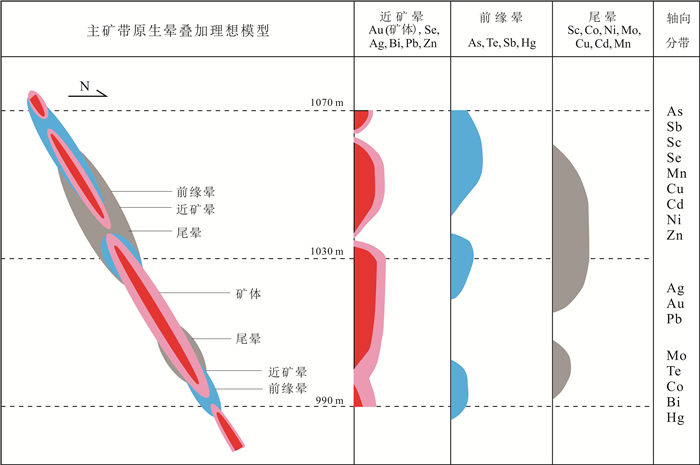
为了解铧厂沟金矿原生晕分布规律、提高找矿勘查效率,对铧厂沟金矿的原生晕进行了元素相关性分析、R型聚类分析以及因子分析等,并结合了野外工作及前人研究成果,得到铧厂沟金矿床理想的分带组合:前缘晕为As-Te-Sb-Hg,近矿晕为Ag-Au-Bi-Pb-Zn-Se,尾晕为Sc-Co-Ni-Mo-Cu-Cd-Mn.铧厂沟金矿的主矿带分带顺序为:Sc-Se-Mn-Cu-Cd-Ni-Zn-Ag-Au-Pb-Sb-Mo-Te-Co-Bi-Hg.结合原生晕理想的叠加模型,得到矿体从1150中段至990中段呈现不连续现象,表现为在1070中段以及下部矿体延伸至1030中段附近出现尖灭.新矿体从1030中段再次出现往下部延伸至990中段附近,并且存在往深部延伸的趋势.
Abstract:To know about the distribution rule of primary halo in Huachanggou gold deposit and improve the efficiency of prospecting and exploration, the paper makes the element correlation analysis, R-mode cluster analysis and factor analysis of the primary halo, combined with the field survey and previous research results, and obtains the ideal zoning combination of Huachanggou gold deposit as follows: As-Te-Sb-Hg for the front halo, Ag-Au-Bi-Pb-Zn-Se for the near-ore halo and Sc-Co-Ni-Mo-Cu-Cd-Mn for the rear halo, with Sc-Se-Mn-Cu-Cd-Ni-Zn-Ag-Au-Pb-Sb-Mo-Te-Co-Bi-Hg as the zoning sequence of main ore belt. Combined with the ideal model of primary superimposed halo, it is concluded that the orebody is discontinuous from Level 1150 m to Level 990 m, that is, the orebody extending from Level 1070 m downward and pinching out near Level 1030 m, then appearing again from Level 1030 m to Level 990 m, showing a tendency of deep extension.
-
Key words:
- primary halo /
- geo-mathematical analysis /
- axial zonation /
- gold deposit /
- Shaanxi Province
-

-
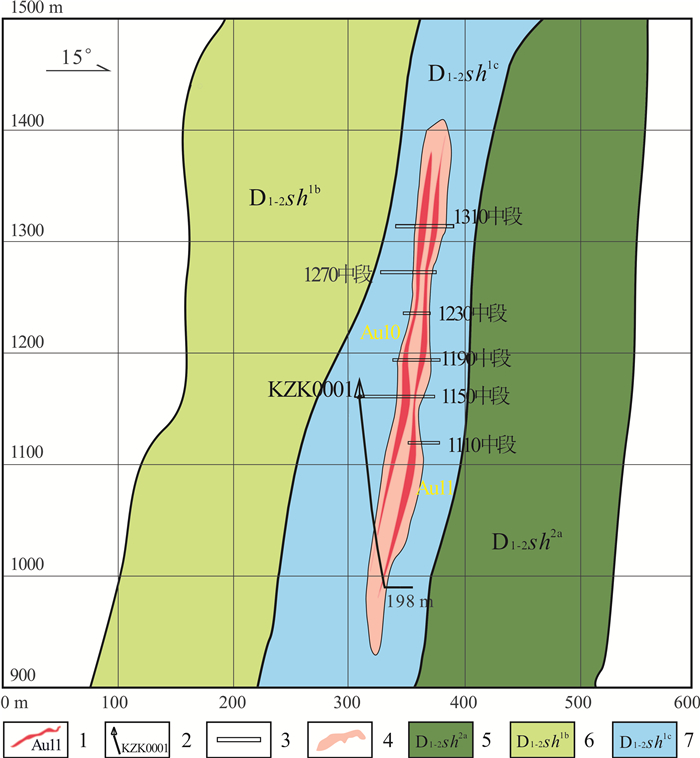
图 1 铧厂沟金矿地质简图(据文献[23])
Figure 1.
表 1 主矿带元素相关系数
Table 1. Correlation coefficients of elements in the main ore belt
元素 Au Ag As Bi Cd Co Cu Hg Mn Mo Ni Pb Sb Sc Se Te Zn Au 1 0.805 0.403 0.275 -0.027 0.069 -0.005 0.417 -0.140 0.021 -0.098 0.247 0.062 -0.268 -0.307 0.406 0.151 Ag 0.805 1 0.386 0.243 -0.077 0.085 0.025 0.484 -0.156 0.005 -0.058 0.211 0.080 -0.198 -0.232 0.425 0.080 As 0.403 0.386 1 0.581 0.166 0.128 -0.009 0.432 -0.251 0.000 -0.220 0.695 0.186 -0.431 0.046 0.901 0.176 Bi 0.275 0.243 0.581 1 -0.104 0.174 -0.061 0.406 -0.191 0.039 -0.045 0.849 0.115 -0.511 0.017 0.760 0.097 Cd -0.027 -0.077 0.166 -0.104 1 0.255 -0.003 0.112 0.449 0.345 0.219 0.064 0.192 0.143 0.178 -0.021 0.575 Co 0.069 0.085 0.128 0.174 0.255 1 0.207 0.096 0.401 -0.088 0.702 -0.029 0.279 0.590 0.161 0.097 0.451 Cu -0.005 0.025 -0.009 -0.061 -0.003 0.207 1 0.004 0.234 -0.171 0.118 -0.036 0.127 0.317 -0.023 0.048 0.061 Hg 0.417 0.484 0.432 0.406 0.112 0.096 0.004 1 -0.153 -0.049 -0.150 0.371 0.631 -0.333 0.056 0.426 0.195 Mn -0.140 -0.156 -0.251 -0.191 0.449 0.401 0.234 -0.153 1 0.205 0.425 -0.261 0.029 0.512 0.070 -0.268 0.265 Mo 0.021 0.005 0.000 0.039 0.345 -0.088 -0.171 -0.049 0.205 1 -0.214 0.029 -0.066 -0.169 0.136 0.043 0.376 Ni -0.098 -0.058 -0.220 -0.045 0.219 0.702 0.118 -0.150 0.425 -0.214 1 -0.275 0.032 0.557 0.047 -0.200 0.173 Pb 0.247 0.211 0.695 0.849 0.064 -0.029 -0.036 0.371 -0.261 0.029 -0.275 1 0.031 -0.632 -0.046 0.781 0.157 Sb 0.062 0.080 0.186 0.115 0.192 0.279 0.127 0.631 0.029 -0.066 0.032 0.031 1 0.108 0.479 0.119 0.212 Sc -0.268 -0.198 -0.431 -0.511 0.143 0.590 0.317 -0.333 0.512 -0.169 0.557 -0.632 0.108 1 0.219 -0.526 0.119 Se -0.307 -0.232 0.046 0.017 0.178 0.161 -0.023 0.056 0.070 0.136 0.047 -0.046 0.479 0.219 1 -0.001 0.001 Te 0.406 0.425 0.901 0.760 -0.021 0.097 0.048 0.426 -0.268 0.043 -0.200 0.781 0.119 -0.526 -0.001 1 0.120 Zn 0.151 0.080 0.176 0.097 0.575 0.451 0.061 0.195 0.265 0.376 0.173 0.157 0.212 0.119 0.001 0.120 1 表 2 主矿带因子载荷矩阵
Table 2. Factor loading matrix of the main ore belt
元素 F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 Te 0.89 0.16 0.00 -0.05 -0.27 Pb 0.83 0.05 0.20 -0.02 -0.39 As 0.82 0.23 0.05 -0.05 -0.16 Bi 0.78 0.15 0.06 -0.11 -0.42 Sc -0.73 0.48 -0.27 -0.11 -0.01 Hg 0.62 0.32 -0.08 -0.26 0.47 Au 0.57 0.14 -0.48 0.37 0.36 Ag 0.56 0.15 -0.52 0.28 0.39 Co -0.10 0.83 -0.27 -0.06 -0.26 Zn 0.11 0.67 0.27 0.40 0.08 Cd -0.09 0.64 0.45 0.28 0.09 Ni -0.39 0.58 -0.34 0.01 -0.33 Mn -0.45 0.56 0.06 0.25 -0.10 Mo 0.04 0.14 0.63 0.50 0.20 Cu -0.11 0.28 -0.34 -0.17 -0.13 Sb 0.17 0.50 0.10 -0.61 0.47 Se -0.09 0.30 0.49 -0.59 0.13 表 3 主矿带方差极大正交旋转矩阵
Table 3. Varimax orthogonal rotation matrix of the main ore belt
元素 F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 Pb 0.93 -0.15 0.04 0.05 -0.01 Te 0.90 -0.04 0.25 -0.01 0.08 Bi 0.90 0.02 0.06 -0.03 0.04 As 0.81 -0.04 0.25 0.08 0.17 Co 0.14 0.86 0.06 0.26 0.15 Ni -0.11 0.82 -0.07 0.11 -0.10 Sc -0.56 0.71 -0.15 0.09 0.09 Cu -0.01 0.48 0.05 -0.14 0.07 Ag 0.19 0.01 0.89 -0.02 0.03 Au 0.22 -0.02 0.89 0.04 -0.04 Cd 0.01 0.17 -0.07 0.80 0.18 Zn 0.14 0.21 0.17 0.77 0.08 Mo -0.01 -0.38 -0.04 0.75 -0.06 Mn -0.25 0.50 -0.13 0.50 -0.07 Sb 0.05 0.15 0.11 0.06 0.92 Se 0.02 0.01 -0.44 0.13 0.70 Hg 0.34 -0.07 0.52 0.03 0.62 表 4 主矿带因子贡献百分比
Table 4. Factor contribution percentage of the main ore belt
因子 载荷矩阵 方差极大正交旋转矩阵 特征值 累积特征值 特征值 累积特征值 F1 27.91 27.91 22.16 22.16 F2 18.28 46.19 15.60 37.76 F3 10.85 57.04 13.45 51.21 F4 9.50 66.54 12.88 64.09 F5 8.45 74.99 10.90 74.99 表 5 主矿带地球化学元素分带指数
Table 5. Geochemical element zoning index of the main ore belt
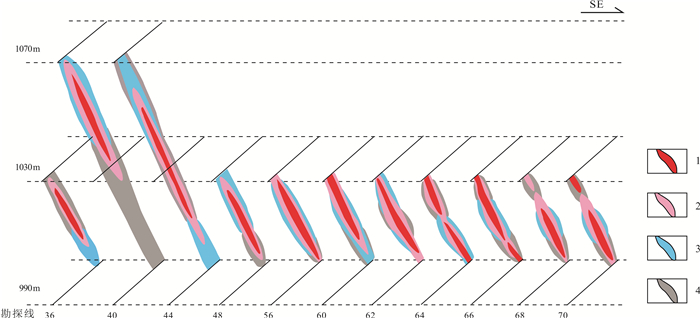
采样位置 990中段 1030中段 1070中段 1110中段 1150中段 Au 0.0184 0.0117 0.0093 0.0084 0.0112 Ag 0.1025 0.0502 0.0224 0.0257 0.0600 As 0.0709 0.0673 0.0185 0.0216 0.0223 Bi 0.1270 0.1024 0.0263 0.0414 0.0422 Cd 0.0133 0.0213 0.0210 0.0235 0.0176 Co 0.0591 0.0592 0.0915 0.0638 0.0831 Cu 0.0980 0.0908 0.1189 0.1266 0.1152 Hg 0.0440 0.1356 0.0204 0.0271 0.0323 Mn 0.0224 0.0226 0.0328 0.0336 0.0340 Mo 0.1028 0.0314 0.1166 0.1613 0.0914 Ni 0.0586 0.0310 0.1750 0.0913 0.1533 Pb 0.0342 0.0452 0.0131 0.0196 0.0121 Sb 0.0222 0.0554 0.0320 0.0217 0.0519 Sc 0.0280 0.0097 0.0722 0.0659 0.0717 Se 0.0378 0.0490 0.0307 0.0915 0.0585 Te 0.0220 0.0203 0.0050 0.0095 0.0068 Zn 0.1386 0.1969 0.1943 0.1675 0.1365 表 6 主矿带勘探线原生晕轴线分带序列
Table 6. Primary halo axis zoning sequence of exploratory lines in the main ore belt
勘探线 轴向分带序列 36线 Hg-Bi-Pb-Ag-Te-Mo-Zn, Cu-Sc-Co-Cd-Mn-Sb-Ni-Se-Au-As 40线 Au-Sc-Te-Se-Ag, Sb-Mo-Mn-Bi-Hg-Pb-Cd, Co-As-Ni-Cu-Zn 44线 Cd-Ag-As, Hg-Pb-Mo-Se, Au-Cu-Sc-Co-Ni-Mn-Zn-Bi-Te-Sb 48线 Sb-Hg-As-Bi-Mo-Se-Cd-Ag, Au-Co-Mn-Cu-Sc-Ni-Pb-Zn-Te 56线 Hg-Sb-Zn-Au-Ag-Sc, Se-Pb-Bi-Mo-Te-As-Cd-Mn-Ni-Co-Cu 60线 Se-Cu-Pb-Zn-Te-Cd-Au-Co-As-Bi-Ni-Sc, Mo-Mn-Ag-Hg-Sb 62线 Cu-Te-As-Bi-Se-Ag-Ni, Mn-Mo-Hg-Sb-Zn-Au-Co-Cd-Sc-Pb 64线 Sc-Mo-Ni-Mn-Se-Zn-Cd-Co-Cu, Ag-As-Te-Bi-Au-Hg-Pb-Sb 66线 Cd-Mn-Sc-Zn-Hg-Ni-Cu-Sb, Bi-Te-Mo-Co-Ag-As-Au-Se-Pb 68线 Sc-Se-Cd-Mo-Mn, Ag-Cu-Au-Sb-Te-Bi-As-Hg-Pb-Co-Ni-Zn 70线 Sc-Ni-Mn-Cu-Co-Cd-Se-Zn, Bi-Au-Te-As-Ag-Pb-Hg-Sb-Mo -
[1] 邵跃. 矿床元素原生分带的研究及其在地球化学找矿中的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 1984, 2(2): 47-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT198402009.htm
Shao Y. The study of the primary zoning of mineral deposits and its application in geochemical prospecting[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 1984, 2(2): 47-55. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT198402009.htm
[2] 黄薰德, 吴郁彦. 地球化学找矿[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1986: 1-180.
Huang X D, Wu Y Y. Geochemical prospecting[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1986: 1-180. (in Chinese)
[3] Beus A A, Grigorian S V. Geochemical exploration methods for mineral deposits[M]. Wilmette, USA: Applied Publishing Ltd, 1977: 1-287.
[4] Goldberg I S, Abramson G Y, Los V L. Depletion and enrichment of primary haloes: Their importance in the genesis of and exploration for mineral deposits[J]. Geochemistry: Exploration, Environment, Analysis, 2003, 3(3): 281-293. doi: 10.1144/1467-7873/03-011
[5] 邵跃. 金矿化探异常评价的几个问题[J]. 中国地质, 1988, 2(5): 22-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI198805008.htm
Shao Y. Several issues on the evaluation of geochemical abnormality of gold deposit[J]. Geology in China, 1988, 2(5): 22-23. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI198805008.htm
[6] 邵跃. 热液矿床岩石测量(原生晕法)找矿[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1997: 1-62.
Shao Y. Measurements (primary halo method) in the hydrochermal deposit prospecting[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1997: 1-62. (in Chinese)
[7] 李惠, 张文华, 刘宝林, 等. 中国主要类型金矿床的原生晕轴向分带序列研究及其应用准则[J]. 地质与勘探, 1999, 35(1): 32-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT901.008.htm
Li H, Zhang W H, Liu B L, et al. The study on axial zonality sequence of primary halo and some criteria for the application of this sequence for major types of gold deposits in China[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 1999, 35(1): 32-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT901.008.htm
[8] 李惠, 张文华, 常凤池. 大型、特大型金矿盲矿预测的原生叠加晕理想模型[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 1999, 9(3): 25-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK199903003.htm
Li H, Zhang W H, Chang F C. Ideal models of overprint of primary halo for large, mega-size blind au ore deposits[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 1999, 9(3): 25-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK199903003.htm
[9] 张国伟, 张本仁, 袁学诚, 等. 秦岭造山带与大陆动力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001: 1-855.
Zhang G W, Zhang B R, Yuan X C, et al. Qinling orogenic beit and continental dynamics[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2001: 1-855.
[10] 张国伟, 孟庆任, 于在平, 等. 秦岭造山带的造山过程及其动力学特征[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 1996, 26(3): 193-200. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK199603000.htm
Zhang G W, Meng Q R, Yu Z P, et al. Orogenesis and dynamics of the Qinling Orogen[J]. Science in China Series D-Earth Sciences, 1996, 39(3): 225-234. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK199603000.htm
[11] 朱赖民, 张国伟, 李犇, 等. 秦岭造山带重大地质事件、矿床类型和成矿大陆动力学背景[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2008, 27(4): 384-390. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200804012.htm
Zhu L M, Zhang G W, Li B, et al. Main geological events, genetic types of metallic deposits and their geodynamical setting in the Qinling Orogenic belt[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2008, 27(4): 384-390. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200804012.htm
[12] 陈衍景. 秦岭印支期构造背景、岩浆活动及成矿作用[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(4): 854-865. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201004005.htm
Chen Y J. Indosinian tectonic setting, magmatism and metallogenesis in Qinling Orogen, central China[J]. Geology in China, 2010, 37(4): 854-865. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201004005.htm
[13] 刘家军, 郑明华, 刘建明, 等. 西秦岭大地构造演化与金成矿带的分布[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 1997, 21(4): 307-314. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK199704003.htm
Liu J J, Zheng M H, Liu J M, et al. Geotectonic evolution and mineralization zone of gold deposits in western Qinling[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 1997, 21(4): 307-314. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK199704003.htm
[14] 成志雁, 刘开君, 余平辉, 等. 西秦岭金矿床成矿年代和成矿期次划分[J]. 黄金, 2015, 36(10): 13-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJZZ201510007.htm
Cheng Z Y, Liu K J, Yu P H, et al. Classification of metallogenic epochs and metallogenic periods of the gold deposits in Western Qinling Mountains[J]. Gold, 2015, 36(10): 13-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJZZ201510007.htm
[15] 陈衍景, 张静, 张复新, 等. 西秦岭地区卡林-类卡林型金矿床及其成矿时间、构造背景和模式[J]. 地质论评, 2004, 50(2): 134-152. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200402004.htm
Chen Y J, Zhang J, Zhang F X, et al. Carlin and Carlin-like gold deposits in western Qinling mountains and their metallogenic time, tectonic setting and model[J]. Geological Review, 2004, 50(2): 134-152. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200402004.htm
[16] 陈衍景, 翟明国, 蒋少涌. 华北大陆边缘造山过程与成矿研究的重要进展和问题[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(11): 2695-2726. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200911003.htm
Chen Y J, Zhai M G, Jiang S Y. Significant achievements and open issues in study of orogenesis and metallogenesis surrounding the North China continent[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2009, 25(11): 2695-2726. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200911003.htm
[17] 闫全人, 王宗起, 闫臻, 等. 碧口群火山岩的时代-SHRIMP锆石U-Pb测年结果[J]. 地质通报, 2003, 22(6): 456-458. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200306011.htm
Yan Q R, Wang Z Q, Yan Z, et al. Geochronology of the Bikou Group volcanic rocks: Newest results from SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2003, 22(6): 456-458. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200306011.htm
[18] 周振菊, 秦艳, 刘振林, 等. 西秦岭铧厂沟金矿床流体包裹体特征研究及矿床成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(5): 1311-1326. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201105008.htm
Zhou Z J, Qin Y, Liu Z L, et al. Study of fluid inclusion characteristic and genetic type of the Huachanggou gold deposit, West Qinling Orogen[J] Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2011, 27(5): 1311-1326. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201105008.htm
[19] 许寻会, 王海岗. 西秦岭铧厂沟地区金矿床成矿规律研究[J]. 西安科技大学学报, 2014, 34(3): 331-336. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XKXB201403015.htm
Xu X H, Wang H G. Research on metallogenic regularity in Huachanggou gold deposits of West Qinling Mountains[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Science and Technology, 2014, 34(3): 331-336. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XKXB201403015.htm
[20] 白忠. 陕西铧厂沟金矿床成矿地质特征[J]. 西南工学院学报, 1995, 10(2): 30-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNGX502.005.htm
Bai Z. Ore-forming geological character of Huachanggou gold deposit in Shanxi[J]. Journal of Southwest Institute of Technology, 1995, 10(2): 30-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNGX502.005.htm
[21] 杨隆勃, 刘家军, 王建平, 等. 陕西铧厂沟金矿床成矿特征及物质来源研究[J]. 中国地质, 2013, 40(4): 1218-1230. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201304021.htm
Yang L B, Liu J J, Wang J P, et al. Metallogenic characteristics and ore-forming material sources of the Huachanggou gold deposit in Shaanxi Province[J]. Geology in China, 2013, 40(4): 1218-1230. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201304021.htm
[22] 李宏安, 邰瑜辉. 铧厂沟金矿地质特征及成因分析[J]. 有色金属(矿山部分), 2007, 59(3): 23-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKU200703007.htm
Li H A, Tai Y H. Geological characteristics and genesis of gold deposits in Huachanggou mine[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Mining Section), 2007, 59(3): 23-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKU200703007.htm
[23] 吴杰, 刘家军, 王建平, 等. 陕西铧厂沟金矿床中细碧岩的岩石学和元素地球化学特征研究[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2014, 33(4): 411-420. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201404001.htm
Wu J, Liu J J, Wang J P, et al. Petrological and geochemical characteristics of the spilite in the Huachanggou gold deposit in the Shaanxi Province[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2014, 33(4): 411-420. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201404001.htm
[24] 魏钢锋, 姜修道, 刘永华, 等. 铧厂沟金矿床地质特征及控矿因素分析[J]. 矿床地质, 2000, 19(2): 138-146. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200002004.htm
Wei G F, Jiang X D, Liu Y H, et al. Geological characteristics and ore-controlling factors of the Huachanggou gold deposit[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2000, 19(2): 138-146. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200002004.htm
[25] 刘冲昊, 刘家军, 王建平, 等. 陕西省略阳县铧厂沟金矿北矿带地球化学原生晕特征及其地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 2012, 39(5): 1397-1405. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201205025.htm
Liu C H, Liu J J, Wang J P, et al. Primary halo characteristics of the north ore zone in the Huachanggou gold deposit, Lueyang County, Shaanxi Province[J]. Geology in China, 2012, 39(5): 1397-1405. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201205025.htm
[26] 杨隆勃, 刘家军, 王建平, 等. 陕西略阳铧厂沟金矿床金的赋存状态研究[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(2): 303-313. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201302008.htm
Yang L B, Liu J J, Wang J P, et al. Study of occurrence of native gold in the Huachanggou gold deposit, Shaanxi Province, China[J]. Geoscience, 2013, 27(2): 303-313. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201302008.htm
[27] 王立新, 贾磊, 吴杰, 等. 陕西铧厂沟金矿床地质特征及成矿规律[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2013, 21(6): 11-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ201306010.htm
Wang L X, Jia L, Wu J, et al. Geological characteristics and metallogenic regularity of Huachanggou gold deposit, Shaanxi Province[J]. Gold Science and Technology, 2013, 21(6): 11-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ201306010.htm
[28] 宗静婷. 陕西略阳铧厂沟金矿床地质与矿床类型[J]. 西北地质, 2004, 37(1): 97-101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI200401016.htm
Zong J T. Features of Huachanggou gold deposit and its type in Lueyang County, Shaanxi[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2004, 37(1): 97-101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI200401016.htm
[29] 陈新跃. 铧厂沟金矿床构造特征及其对金矿的控制作用[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2003: 1-66.
Chen X Y. Tectonic characteristics of Huachanggou gold deposit and its control of gold deposit[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2003: 1-66.
[30] 张彦艳, 王建新, 赵志, 等. R型聚类分析在成矿阶段划分中的应用: 以桦甸大庙子-菜抢子金矿区为例[J]. 世界地质, 2006, 25(1): 29-33, 38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJDZ200601005.htm
Zhang Y Y, Wang J X, Zhao Z, et al. Application of R-type clustering analyses in subdivision of mineral stages: An example from gold ore area in Damiaozi-Caiqiangzi of Huadian[J]. Global Geology, 2006, 25(1): 29-33, 38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJDZ200601005.htm
[31] 董庆吉, 陈建平, 唐宇. R型因子分析在矿床成矿预测中的应用——以山东黄埠岭金矿为例[J]. 地质与勘探, 2008, 44(4): 64-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT200804011.htm
Dong Q J, Chen J P, Tang Y. Application of R type factor analyses in mineralization prognosis: By an example of Huangbuling gold deposit, Shandong Province[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2008, 44(4): 64-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT200804011.htm
[32] 刘晓玲, 陈建平. R型因子分析在青海省治多杂多地区成矿预测中的应用[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2010, 32(3): 332-336. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTHT201003022.htm
Liu X L, Chen J P. A case study of R-factor analysis for metallogenic prognosis applied to Zhiduo-Zaduo area of Qinghai Province[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2010, 32(3): 332-336. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTHT201003022.htm
[33] 邢利琦, 刘炳璋. 矿床原生地球化学晕分带性研究[J]. 四川地质学报, 2011, 31(4): 489-492, 495. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCDB201104030.htm
Xing L Q, Liu B Z. Study of zonation of primary halo of hydrothermal deposits[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 2011, 31(4): 489-492, 495. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCDB201104030.htm
[34] 陈永清, 韩学林, 赵红娟, 等. 内蒙花敖包特Pb-Zn-Ag多金属矿床原生晕分带特征与深部矿体预测模型[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2010, 36(2): 236-246. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201102009.htm
Chen Y Q, Han X L, Zhao H J, et al. Characteristics of primary halo zonation and prediction pattern of deep orebody of the Huaaobaote Pb-Zn-Ag polymetallic deposit, inner Mongolia[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2010, 36(2): 236-246. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201102009.htm
-




 下载:
下载: