STUDY ON THE FAULT SYSTEM OF HEBAOSHAN-CHANGXING VEIN GOLD DEPOSITS IN TAINING COUNTY, FUJIAN PROVINCE
-
摘要:
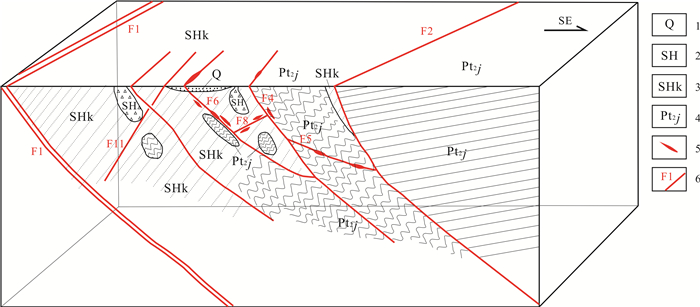
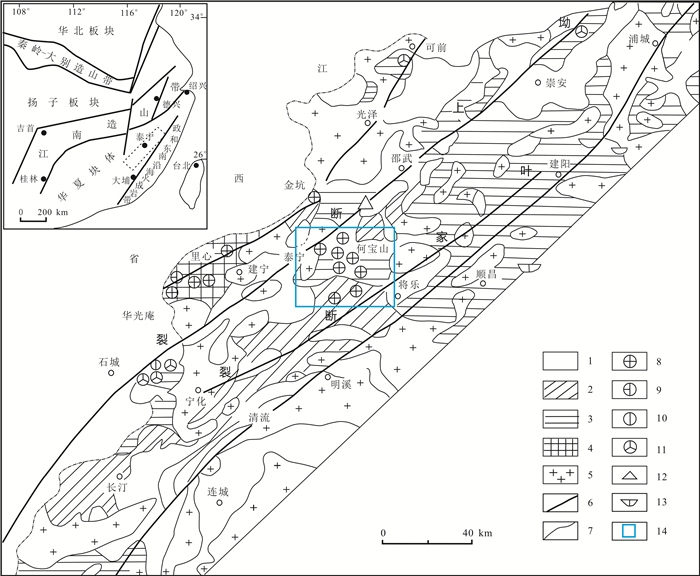
以何宝山和长兴脉状金矿床为研究对象,意在找到多级断裂构造与成矿关联,解决制约本区深部及外围找矿难题.基于矿田构造调研和室内多元信息研究分析,总结了控矿构造框架中多级断裂对不同规模成矿单元的控矿特征,建立了构造格架.主要成果如下:1)坳上-南溪及叶家断裂,为矿分布区控岩控矿构造,控制矿田的空间展布;2)朱溪、大马圩断裂,为何宝山矿田控岩控矿构造,控制矿床的空间分布;3)北东向、北西向断裂,为主要的控矿(导矿)断裂,属成矿期构造,控制矿带产出位置;4)北东东、北西向断裂,属成矿期赋矿断裂,控制矿体产出;5)朱溪、大马圩断裂为脉状金矿床边界断裂,外围成矿规模及品位锐减;6)矿体受加里东期侵入岩接触带和北东东、北西向构造控制明显,在断裂构造复合部位、不同岩性接触部位和产状变化明显处,均可能是成矿有利部位可做为找矿构造标志.
Abstract:Taking Hebaoshan-Changxing vein gold deposits as the study object, the paper aims to find the relation between multi-order fault structures and mineralization and solve the problems restricting the deep and periphery prospecting in the area. The ore-controlling characteristics of multi-order faults on different scales of metallogenic units are summarized and the tectonic framework is established on the basis of orefield structure survey and indoor multivariate information analysis. The main results are as follows: Aoshang-Nanxi and Yejia faults, as the rock- and ore-controlling structures in the orefield distribution area, control the spatial distribution of orefield. Zhuxi and Damaxu faults are the rock- and ore-controlling structures in Hebaoshan orefield to control the spatial distribution of deposit. The NE- and NW-trending faults are the major ore-controlling/conducting faults, belonging to metallogenic structure and controlling the location of ore belt. The NEE- and NW-trending ore-host faults of the metallogenic period control the orebody occurrence. Zhuxi and Damaxu faults are the boundary faults of the vein gold deposit, beyond which the metallogenic scale and grade drop down sharply. The orebody is obviously controlled by the contact zone of Caledonian intrusive rocks, NEE- and NW-trending structures. The composite of faults, lithological contact and position with obvious occurrence change are all potential mineralization sites and structural indicators for prospecting.
-
Key words:
- vein gold deposit /
- tectonic framework /
- ore-controlling structure /
- multiple phase /
- Fujian Province
-

-
[1] 余心起, 吴淦国, 张达, 等. 北武夷地区逆冲推覆构造的特征及其控矿作用[J]. 地质通报, 2008, 27(10): 1667-1677. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200810010.htm
Yu X Q, Wu G G, Zhang D, et al. Thrust Nappe structure and its ore-controlling effects in the North Wuyi area, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2008, 27(10): 1667-1677. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200810010.htm
[2] 黄春鹏. 福建省金矿成矿特征和成矿预测研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2003.
Huang C P. Research on the metallogenic characteristics and forecast of gold deposits in Fujian Province, China[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2003.
[3] 陈国建. 福建泰宁何宝山金矿田成矿规律与找矿预测[J]. 福建地质, 2016, 35(1): 46-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJDZ201601005.htm
Chen G J. The metallogensis and prospecting prediction of Hebaoshan gold ore field, Taining county, Fujian Province[J]. Geology of Fujian, 2016, 35(1): 46-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJDZ201601005.htm
[4] 舒良树. 华南构造演化的基本特征[J]. 地质通报, 2012, 31(7): 1035-1053. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201207004.htm
Shu L S. An analysis of principal features of tectonic evolution in South China Block[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2012, 31(7): 1035-1053. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201207004.htm
[5] 姜耀辉, 陈鹤年, 陈三元. 闽西北三种新的金矿成因类型及地质特征[J]. 矿产与地质, 2000, 14(4): 209-214. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD200004000.htm
Jiang Y H, Chen H N, Chen S Y. Geological characteristics and three new genesises of gold ore deposit in north-west Fujian province[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2000, 14(4): 209-214. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD200004000.htm
[6] Wang Y J, Fan W M, Sun M, et al. Geochronological, geochemical and geothermal constraints on petrogenesis of the Indosinian peraluminous granites in the South China Block: A case study in the Hunan Province[J]. Lithos, 2007, 96(3/4): 475-502. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493706003033
[7] 于津海, 魏震洋, 王丽娟, 等. 华夏地块: 一个由古老物质组成的年轻陆块[J]. 高校地质学报, 2006, 12(4): 440-447. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2006.04.004
Yu J H, Wei Z Y, Wang L J, et al. Cathaysia block: A young continent composed of ancient materials[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2006, 12(4): 440-447. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2006.04.004
[8] 刘锐, 张利, 周汉文, 等. 闽西北加里东期混合岩及花岗岩的成因: 同变形地壳深熔作用[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(6): 1205-1222. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200806006.htm
Liu R, Zhang L, Zhou H W, et al. Petrogenesis of the Caledonian migmatites and related granites in northwestern Fujian province, south China: syn-deformational crustal anatexis[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2008, 24(6): 1205-1222. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200806006.htm
[9] 陈国建, 张伟波, 刘江涛. 福建省泰宁县何宝山金矿床长兴岩体锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 2015, 42(2): 547-555. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201502014.htm
Chen G J, Zhang W B, Liu J T. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating and geological features of Changxing intrusion in the Hebaoshan gold deposit, Taining County, Fujian Province[J]. Geology in China, 2015, 42(2): 547-555. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201502014.htm
[10] 张芳荣, 舒良树, 王德滋, 等. 华南东段加里东期花岗岩类形成构造背景探讨[J]. 地学前缘, 2009, 16(1): 248-260. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200901034.htm
Zhang F R, Shu L S, Wang D Z, et al. Discussions on the tectonic setting of Caledonian granitoids in the eastern segment of South China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2009, 16(1): 248-260. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200901034.htm
[11] 刘锐. 华夏地块前海西期地壳深熔作用——以浙闽地区为例[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2009.
Liu R. Pre-hercynian crustal anatexis in the Cathaysia block: A case study from Zhejiang and Fujian provinces[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2009.
[12] 梅勇文. 武夷地区成矿地质条件与主要矿产分布规律[J]. 江西地质科技, 1996, 23(4): 151-160. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXZK199604000.htm
Mei Y W. Metallogenic geological conditions and distribution of main mineral resources in Wuyi area[J]. Geological Science and Technology of Jiangxi, 1996, 23(4): 151-160. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXZK199604000.htm
[13] 宋美佳. 华南早古生代与早中生代陆内构造演化[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2017.
Song M J. Early Paleozoic and early Mesozoic intracontinental tectonic evolution in South China[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2017.
[14] 舒良树, 卢华复, 贾东, 等. 华南武夷山早古生代构造事件的40Ar/39Ar同位素年龄研究[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学), 1999, 35(6): 26-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJDZ199906002.htm
Shu L S, Lu H F, Jia D, et al. Study of the 40Ar/39Ar isotopic age for the Early Paleozoic tectonothermal event in the Wuyishan region, South China[J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Sciences), 1999, 35(6): 26-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJDZ199906002.htm
[15] Yao W H, Li Z X, Li W X, et al. Corrigendum to "Post-kinematic lithospheric delamination of the Wuyi-Yunkai orogen in South China: evidence from ca. 435Ma high-Mg basalts"[J]. Lithos, 2012, 154: 115-129. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.06.033
[16] Xia Y, Xu X S, Zou H B, et al. Early Paleozoic crust-mantle interaction and lithosphere delamination in South China Block: evidence from geochronology, geochemistry, and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopes of granites[J]. Lithos, 2014, 184-187: 416-435. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2013.11.014
[17] Tong J N, Yin H F. The lower Triassic of South China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2002, 20(7): 803-815. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(01)00058-X
[18] 舒良树, 周新民, 邓平, 等. 南岭构造带的基本地质特征[J]. 地质论评, 2006, 52(2): 251-265. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200602017.htm
Shu L S, Zhou X M, Deng P, et al. Principal geological features of Nanling tectonic belt, South China[J]. Geological Review, 2006, 52(2): 251-265. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200602017.htm
[19] Sun T, Zhou X M, Chen P R, et al. Strongly peraluminous granites of Mesozoic in eastern Nanling Range, southern China: Petrogenesis and implications for tectonics[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2005, 48(2): 165-174. doi: 10.1360/03YD0042
[20] 徐先兵, 张岳桥, 贾东, 等. 华南早中生代大地构造过程[J]. 中国地质, 2009, 36(3): 573-593. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200903009.htm
Xu X B, Zhang Y Q, Jia D, et al. Early Mesozoic geotectonic processes in South China[J]. Geology In China, 2009, 36(3): 573-593. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200903009.htm
[21] 郭春丽, 郑佳浩, 楼法生, 等. 华南印支期花岗岩类的岩石特征、成因类型及其构造动力学背景探讨[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2012, 36(3): 457-472. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201203022.htm
Guo C L, Zheng J H, Lou F S, et al. Petrography, genetic types and geological dynamical settings of the Indosinian Granitoids in South China[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2012, 36(3): 457-472. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201203022.htm
[22] Wang Y J, Fan W M, Cawood P A, et al. Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic constraints on multiple mantle domains for Mesozoic mafic rocks beneath the South China Block hinterland[J]. Lithos, 2008, 106(3/4): 297-308.
[23] Wang Y J, Zhang Y H, Fan W M, et al. Structural signatures and 40Ar/39Ar geochronology of the Indosinian Xuefengshan tectonic belt, South China Block[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2005, 27(6): 985-998. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0191814105000714
[24] 陈润生, 林东燕, 江剑丽. 福建早侏罗世火山作用的动力学机制及大地构造学意义探讨[J]. 福建地质, 2008, 27(2): 156-165. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJDZ200802009.htm
Chen R S, Lin D Y, Jiang J L. Dynamical mechanism and tectonics significance of early Jurassic volcanism in Fujian Province[J]. Geology of Fujian, 2008, 27(2): 156-165. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJDZ200802009.htm
[25] 李建华. 华南中生代大地构造过程[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2013.
Li J H. Mesozoic tectonic processes in South China[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2013.
[26] 李晔. 华南东南部早白垩世演化及其地质意义: 来自长乐-南澳地区变质和岩浆作用的启示[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2015.
Li Y. The early Cretaceous evolution of SE China and its tectonic implications: insights from magmatism and metamorphism in Changle-Nan'ao Metamorphic Belt[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2015.
-



 下载:
下载: