CHARACTERISTICS OF SOIL HEAVY METAL POLLUTION AND ECOLOGICAL RISK ASSESSMENT OF JINZHOU CITY
-
摘要:
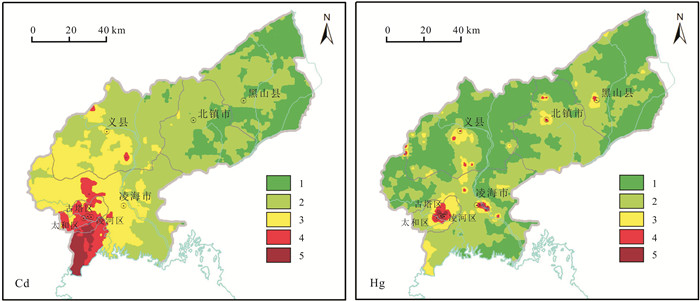
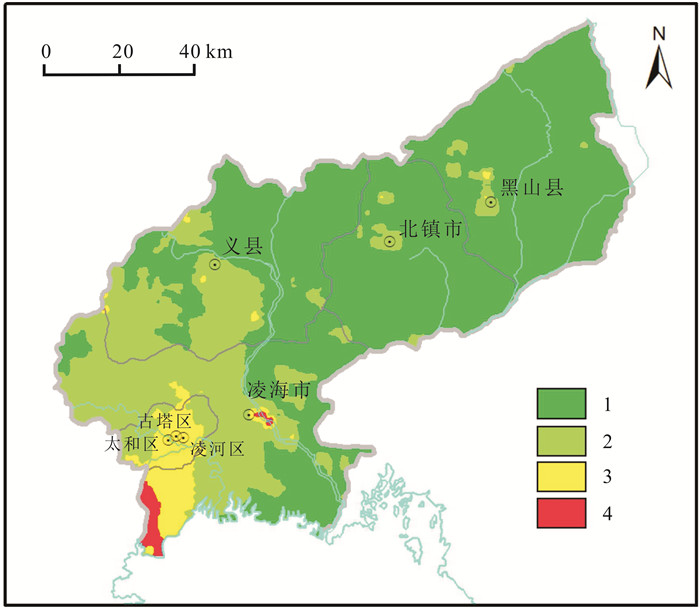
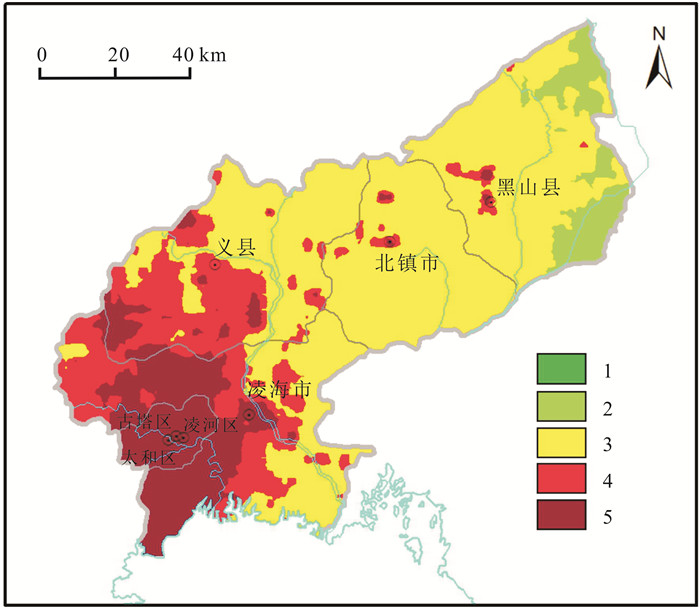
以锦州市为研究区,分析8种土壤重金属As、Cd、Hg、Cr、Cu、Pb、Zn、Ni的污染特征,采用单因子污染指数法、地累积指数法、内梅罗综合指数法和Hakanson潜在生态风险指数法确定锦州市土壤重金属污染程度,评价土壤重金属潜在生态风险.结果表明,锦州市土壤重金属Cd和Cr含量高于全国土壤及辽宁省土壤背景值,Cu、Hg、Ni和Pb含量高于辽宁省土壤背景值.采用单因子污染指数评价,Cd为中度污染,Hg、Pb、Cr、Ni和Cu为轻度污染.经地累积指数法评价,Cd为轻中度污染,其他重金属为无污染.内梅罗综合污染指数平均值为2.25,为中度污染等级.研究区综合潜在风险指数平均值为157.34,处于中等生态风险,造成局部地区土壤潜在生态风险较高的重金属为Cd和Hg.
Abstract:Taking Jinzhou City as the study area, the paper analyzes the pollution characteristics of 8 soil heavy metals including As, Cd, Hg, Cr, Cu, Pb, Zn and Ni, and uses the methods of single factor pollution index, geoaccumulation index, Nemerow comprehensive index and Hakanson potential ecological risk index to determine the degree of soil heavy metal pollution and evaluate the potential ecological risk. The results show that the contents of Cd and Cr in soil are higher than the soil background values of China and Liaoning Province, and the contents of Cu, Hg, Ni and Pb also higher than the soil background values of the province. The single factor index evaluation results reveal Cd is at moderate pollution level, while Hg, Pb, Cr, Ni and Cu mild pollution. The geoaccumulation index evaluation results reflect Cd is at light-moderate pollution level and other heavy metals pollution-free. The average Nemerow comprehensive pollution index is 2.25, indicating a moderate pollution grade. The average comprehensive potential risk index is 157.34, suggesting the study area is at moderate ecological risk. Cd and Hg contribute to high potential ecological risk in parts of the area.
-

-
表 1 单项污染指数分级标准
Table 1. Grading standard of single factor pollution index
污染指数 Pi≤1 1 < Pi≤2 2 < Pi≤3 Pi > 3 污染分级 无污染 轻度污染 中度污染 重度污染 表 2 内梅罗综合指数分级标准
Table 2. Grading standard of Nemerow comprehensive index
综合指数 P综≤0.7 0.7<P综≤1 1<P综≤2 2<P综≤3 P综 > 3 污染分级 清洁(安全) 尚清洁(警戒) 轻度污染 中度污染 重度污染 表 3 地累积指数分级标准
Table 3. Grading standard of geoaccumulation index
地累积指数 Igeo≤0 0<Igeo≤1 1<Igeo≤2 2<Igeo≤3 3<Igeo≤4 4<Igeo≤5 Igeo>5 污染程度 无污染 轻中度污染 中度污染 中强度污染 强度污染 极强度污染 极严重污染 表 4 潜在生态风险评价法分级标准
Table 4. Grading standard of potential ecological risk index
Ei Ei < 40 40≤Ei < 80 80≤Ei < 160 160≤Ei < 320 Ei≥320 RI RI < 150 150≤RI < 300 300≤RI < 600 RI≥600 - 潜在生态风险等级 轻微 中等 强 很强 极强 表 5 锦州市土壤重金属含量统计
Table 5. Contents of soil heavy metals in Jinzhou City
元素 平均值 最大值 最小值 标准差 变异系数 背景值 辽宁省 全国 As 6.90 122.00 2.09 3.12 0.45 8.8 11 Cd 0.30 2.98 0.05 0.30 1.02 0.108 0.097 Cr 65.78 562.00 21.70 27.30 0.41 57.9 61 Cu 20.23 137.00 1.10 6.97 0.34 19.8 23 Hg 0.04 0.94 0.01 0.05 1.11 0.037 0.065 Ni 26.81 152.00 8.50 14.58 0.54 25.6 27 Pb 24.71 176.00 9.60 6.75 0.27 21.1 26 Zn 61.69 298.00 13.20 23.22 0.38 63.5 74 注:辽宁省背景值据文献[10],全国背景值据文献[11]. 含量单位:10-6. 表 6 锦州市土壤重金属单因子评价结果
Table 6. Evaluation results of single factor index method for soil heavy metal pollution in Jinzhou City
元素 最大值(Pmax) 最小值(Pmin) 平均值(Pave) 各级样点所占比例/% 超标率/% 无污染 轻度污染 中度污染 重度污染 As 13.86 0.24 0.78 87.63 11.93 0.32 0.12 12.37 Cd 27.59 0.44 2.73 7.51 44.90 22.17 25.42 92.49 Cr 9.71 0.37 1.14 42.21 52.13 4.66 1.00 57.79 Cu 6.92 0.06 1.02 53.61 45.02 1.20 0.16 46.39 Hg 25.41 0.16 1.20 57.47 34.78 4.42 3.33 42.53 Ni 5.94 0.33 1.05 63.61 30.32 4.18 1.89 36.39 Pb 8.34 0.45 1.17 23.53 75.06 1.20 0.20 76.47 Zn 4.69 0.21 0.97 59.76 38.71 1.20 0.32 40.24 表 7 锦州市土壤重金属地累积指数评价结果
Table 7. Evaluation results of geoaccumulation index for soil heavy metal pollution in Jinzhou City
元素 平均值Igeo 各级样点所占比例/% 无污染 轻中度污染 中度污染 中强度污染 强度污染 极强度污染 极严重污染 As -1.00 98.80 1.08 0.08 0 0.04 0 0 Cd 0.50 34.02 40.56 19.00 4.06 2.25 0.12 0 Cr -0.48 88.80 10.20 0.96 0.04 0 0 0 Cu -0.62 93.73 6.10 0.12 0.04 0 0 0 Hg -0.60 84.26 12.41 2.21 0.80 0.24 0.08 0 Ni -0.65 90.04 8.07 1.89 0 0 0 0 Pb -0.39 91.73 8.07 0.16 0.04 0 0 0 Zn -0.71 94.66 5.02 0.32 0 0 0 0 样点污染程度比例计算方式同表 6. 表 8 锦州市土壤重金属Hakanson潜在生态风险评价结果
Table 8. Evaluation results of Hakanson potential ecological risk index for soil heavy metals in Jinzhou City
元素 最大值(Emax) 最小值(Emin) 平均值(Eave) 各级样点所占比例/% 轻微 中等 强 很强 极强 As 138.64 2.38 7.84 99.96 0.00 0.04 0.00 0.00 Cd 827.78 13.06 82.01 24.62 44.18 23.09 5.26 2.85 Cr 19.41 0.75 2.27 100.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 Cu 34.60 0.28 5.11 100.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 Hg 1016.22 6.49 48.04 54.78 37.15 6.02 1.37 0.68 Ni 29.69 1.66 5.24 100.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 Pb 41.71 2.27 5.86 99.96 0.04 0.00 0.00 0.00 Zn 4.69 0.21 0.97 100.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 -
[1] 李春辉, 孔祥科, 韩占涛, 等. 皖南山区土壤重金属污染及潜在生态风险评价——以池州市为例[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2018, 46(34): 105-110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2018.34.035
Li C H, Kong X K, Han Z T, et al. Pollution and potential ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metals in the south mountain area of Anhui-taking Chizhou city as an example[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 46(34): 105-110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2018.34.035
[2] Wong C S C, Wu S C, Duzgoren-Aydin N S, et al. Trace metal contamination of sediments in an e-waste processing village in China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2006, 145(2): 434-442. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16824655
[3] 方晓波, 史坚, 廖欣峰, 等. 临安市雷竹林土壤重金属污染特征及生态风险评价[J]. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26(6): 1883-1891. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYSB201506039.htm
Fang X B, Shi J, Liao X F, et al. Heavy metal pollution characteristics and ecological risk analysis for soil in Phyllostachys praecox stands of Lin'an[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2015, 26(6): 1883-1891. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYSB201506039.htm
[4] 刘品祯, 贾亚琪, 程志飞, 等. 不同方法评价喀斯特煤矿区农田土壤重金属生态风险比较[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(3): 371-378. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201803007.htm
Liu P Z, Jia Y Q, Cheng Z F, et al. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soils around karst coal mining areas: A comparison of various methods[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(3): 371-378. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201803007.htm
[5] 王斐, 黄益宗, 王小玲, 等. 江西钨矿周边土壤重金属生态风险评价: 不同评价方法的比较[J]. 环境化学, 2015, 34(2): 225-233. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201502004.htm
Wang F, Huang Y Z, Wang X L, et al. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surrounding soils of tungsten ores: Comparison of different evaluation methods[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 34(2): 225-233. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201502004.htm
[6] Hakanson L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sedimentological approach[J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
[7] 谢小进, 康建成, 李卫江, 等. 上海宝山区农用土壤重金属分布与来源分析[J]. 环境科学, 2010, 31(3): 768-774. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201003042.htm
Xie X J, Kang J C, Li W J, et al. Analysis on heavy metal concentrations in agricultural soils of Baoshan, Shanghai[J]. Environmental Science, 2010, 31(3): 768-774. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201003042.htm
[8] 钟晓兰, 周生路, 李江涛, 等. 长江三角洲地区土壤重金属污染的空间变异特征——以江苏省太仓市为例[J]. 土壤学报, 2007, 44(1): 33-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB200701005.htm
Zhong X L, Zhou S L, Li J T, et al. Spatial variability of soil heavy metals contamination in the Yangtze river delta: A case study of Taicangcity in Jiangsu province[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2007, 44(1): 33-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB200701005.htm
[9] 高姝. 锦州市土壤质量现状及对策建议[J]. 绿色科技, 2017(6): 73, 75. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LVKJ201706027.htm
Gao S. Current situation and suggestions of soil quality in Jinzhou[J]. Journal of Green Science and Technology, 2017(6): 73, 75. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LVKJ201706027.htm
[10] 迟清华, 鄢明才. 应用地球化学元素丰度数据手册[M] 北京: 地质出版社, 2007: 82-83.
Chi Q H, Yan M C. Handbook of elemental abundance for applied geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2007: 82-83.
[11] 鲍士海. 锦州市基本农田土壤环境质量现状及分析[J]. 绿色科技, 2013(12): 184-185. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9944.2013.12.074
Bao S H. Survey of environmental quality of basic farmland in Jinzhou, Liaoning province[J]. Journal of Green Science and Technology, 2013(12): 184-185. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9944.2013.12.074
[12] 李瑞, 席北斗, 姜玉, 等. 北方主要农产地土壤污染风险评估与综合防治战略[J]. 中国工程科学, 2018, 20(5): 45-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCKX201805008.htm
Li R, Xi B D, Jiang Y, et al. Soil pollution risk assessment and comprehensive prevention strategy for major agricultural producing areas in North China[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2018, 20(5): 45-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCKX201805008.htm
[13] 张思洋, 于大涛, 张戈. 锦州湾三河入海口重金属分布特征及污染评价[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2020, 36(6): 20-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT202006003.htm
Zhang S Y, Yu D T, Zhang G. Distribution of heavy metals at the junction of Lianshan, Wuli and Cishan estuaries, Jinzhou bay and their contamination evaluation[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2020, 36(6): 20-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT202006003.htm
[14] 于锐, 王洋, 王晨旭, 等. 榆树市玉米种植区黑土重金属污染状况及来源浅析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2017, 26(10): 1788-1794. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ201710020.htm
Yu R, Wang Y, Wang C X, et al. Survey of heavy metal pollution and source identification of black soil in Zea mays L. cultivated region of Yushu city, China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2017, 26(9): 1788-1794. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYJ201710020.htm
[15] 余涛, 程新彬, 杨忠芳, 等. 辽宁省典型地区大气颗粒物重金属元素分布特征及对土地质量影响研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2008, 15(5): 146-154. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200805015.htm
Yu T, Cheng X B, Yang Z F, et al. Distributional characteristics of heavy metal elements in atmospheric particulate matter and their impact on land quality in Liaoning province[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2008, 15(5): 146-154. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200805015.htm
[16] Kluge B, Werkenthin M, Wessolek G. Metal leaching in a highway embankment on field and laboratory scale[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 493: 495-504. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969714008122
[17] 王寅. 锦州市典型畜禽养殖场周边土壤污染状况调查分析[J]. 黑龙江环境通报, 2014, 38(4): 88-90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HLJO201404028.htm
Wang Y. Investigation and analysis of soil pollution of typical livestock and poultry breeding farms in Jinzhou City[J]. Heilongjiang Environmental Journal, 2014, 38(4): 88-90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HLJO201404028.htm
[18] 王寅. 锦州市典型电镀企业周边土壤污染状况调查分析及防治措施[J]. 农业与技术, 2015, 35(5): 47-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NYYS201505023.htm
Wang Y. Investigation and analysis of soil pollution around typical electroplating enterprises in Jinzhou city and its prevention and control measures[J]. Agriculture & Technology, 2015, 35(5): 47-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NYYS201505023.htm
[19] 范小杉, 罗宏. 工业废水重金属排放区域及行业分布格局[J]. 中国环境科学, 2013, 33(4): 655-662. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ201304014.htm
Fan X B, Luo H. Spatial and industrial distribution pattern of heavy metals emission in industrial waste water[J]. China Environmental Science, 2013, 33(4): 655-662. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ201304014.htm
[20] 李艺红, 王宏, 刘瑞志, 等. 锦州湾表层沉积物重金属潜在生态风险评价[J]. 沈阳理工大学学报, 2013, 32(5): 17-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SGXY201305005.htm
Li Y H, Wang H, Liu R Z, et al. Potential ecological risk evaluation of heavy metals in the surface sediments of Jinzhou Bay[J]. Transactions of Shenyang Ligong University, 2013, 32(5): 17-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SGXY201305005.htm
[21] 李珊珊, 单保庆, 张洪. 滏阳河河系表层沉积物重金属污染特征及其风险评价[J]. 环境科学学报, 2013, 33(8): 2277-2284. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201308028.htm
Li S S, Shan B Q, Zhang H. Characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface sediments of Fuyang River[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2013, 33(8): 2277-2284. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201308028.htm
-



 下载:
下载: