GEOTHERMAL DISTRIBUTION RULE OF SHUNHEXI OREFIELD IN YONGCHENG CITY, HENAN PROVINCE
-
摘要:
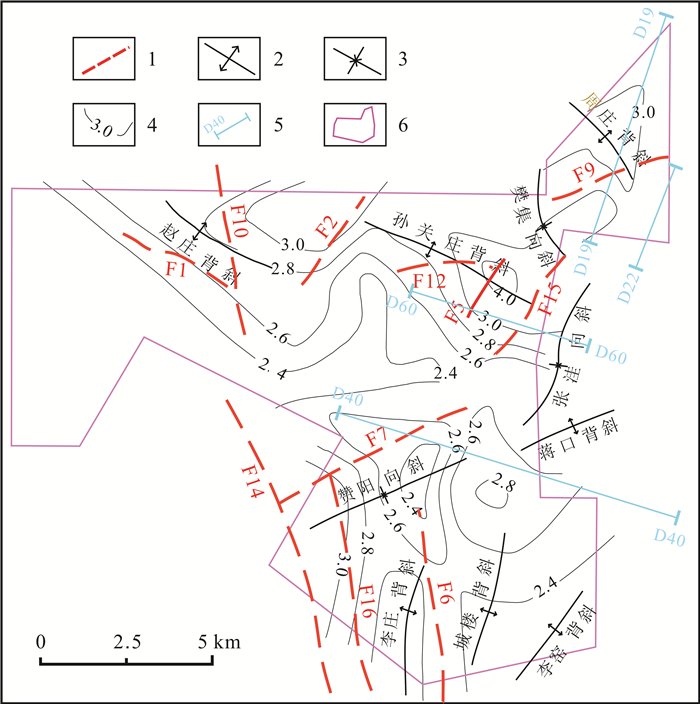
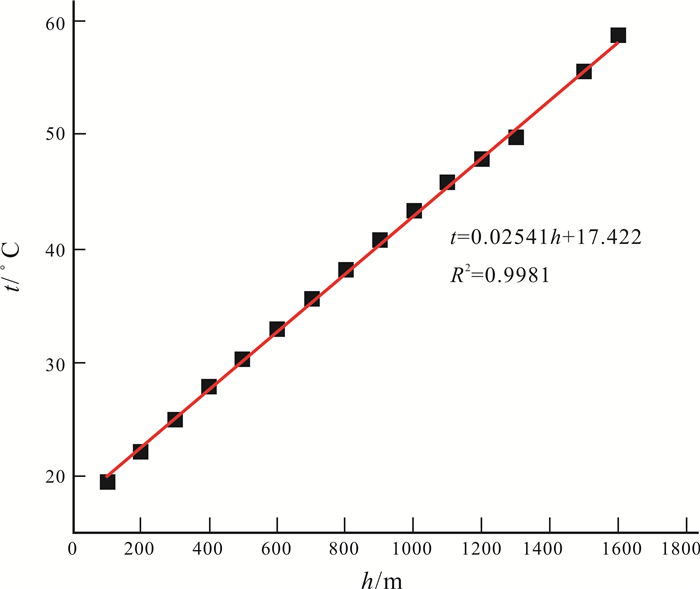
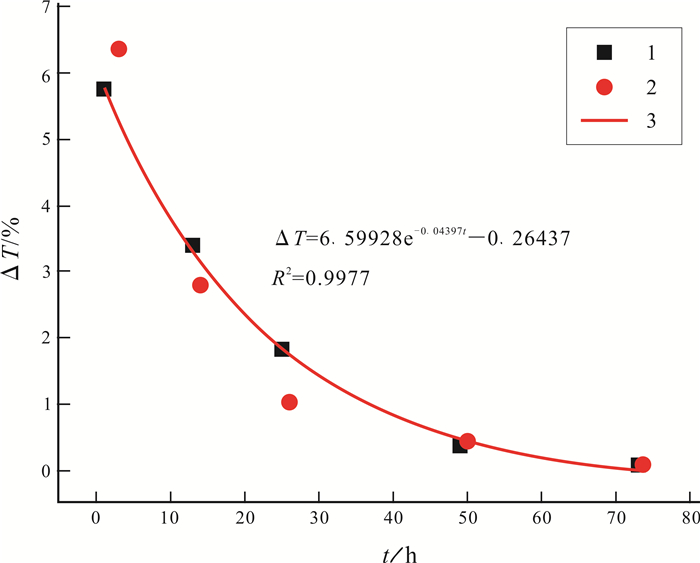
对永城市顺河西矿区内2个近似稳态测温和44个简易测温数据进行分析,并结合矿区地质资料,通过数据拟合,建立数据模型,反映了矿区内似稳态测温钻孔孔底温度增量ΔT与钻机静井时间t的关系.根据数据模型校正了简易测温钻孔的孔底温度,通过数据拟合发现矿区埋深与温度之间的线性关系.在此基础上,从横向上和纵向上分析了顺河西矿区的地温分布规律,为下一步矿山开发提供参考依据.
Abstract:The paper analyzes the data for approximate steady state temperature measurements of 2 boreholes and simple temperature measurements of 44 boreholes in Shunhexi orefield of Yongcheng City, and establishes data model through data fitting combined with the geological information of orefield to reflect the relationship between temperature increment at the bottom of approximate steady state boreholes and static well time. The bottom temperature of simple temperature measurement borehole is corrected according to the data model, and the linear relationship between buried depth and temperature is found through data fitting. On this basis, the horizontal and vertical distribution law of geothermal temperature in the study area is analyzed for reference of further mining development.
-
Key words:
- geothermal field /
- geothermal gradient /
- numerical simulation /
- Yongcheng City /
- Henan Province
-

-
表 1 近似稳态测温孔ΔT-t关系统计表
Table 1. Relationship between temperature recovery increment and time of approximate steady state boreholes
Z0103孔 Z0708孔 t/h ΔT/% t/h ΔT/% 2 5.75 3 6.36 14 3.38 15 2.79 26 1.82 27 1.02 50 0.36 51 0.43 74 0.07 75 0.08 表 2 简易测温钻孔校正后的孔底温度
Table 2. Corrected bottom temperature of simple temperature measurement borehole
孔号 Tj/℃ t/h ΔT/% To/℃ Z0102 44.52 7.9 0.0439 46.56 Z0303 42.85 7.5 0.0449 44.86 Z0304 37.95 7.7 0.0443 39.71 Z0305 46.59 7.0 0.0459 48.83 Z0402 41.01 6.4 0.0471 43.04 Z0405 39.43 6.7 0.0465 41.35 Z0410 50.20 7.2 0.0454 52.59 Z0502 44.77 7.3 0.0453 46.89 Z0503 42.51 6.9 0.0462 44.57 Z0504 38.30 6.4 0.0471 40.19 Z0506 31.74 7.5 0.0448 33.23 Z0509 46.60 7.6 0.0447 48.78 Z0510 36.33 7.4 0.0450 38.04 Z0701 37.18 6.5 0.0470 39.02 Z0702 36.91 6.1 0.0479 38.77 Z0703 42.93 6.1 0.0478 45.09 Z0901 36.49 6.3 0.0474 38.31 Z0902 36.38 7.1 0.0457 38.12 Z0903 46.05 7.9 0.0439 48.16 Z0904 44.42 7.4 0.0450 46.51 Z1002 39.42 7.4 0.0451 41.28 Z1003 45.37 6.8 0.0463 47.57 Z1201 45.66 6.1 0.0478 47.95 Z1202 44.34 6.0 0.0480 46.57 Z1402 45.41 6.7 0.0464 47.62 Z1601 48.75 6.1 0.0478 51.2 Z1901 35.13 7.2 0.0455 36.8 Z1902 43.08 6.3 0.0474 45.22 Z1904 41.71 7.6 0.0445 43.65 Z2401 38.20 6.4 0.0471 40.09 Z0101 46.97 7.0 0.0459 49.23 Z0201 33.30 7.3 0.0452 34.88 Z0205 40.97 7.4 0.0450 42.9 Z0207 44.62 6.2 0.0475 46.85 Z0306 53.14 7.0 0.0458 55.69 Z0403 40.38 6.7 0.0465 42.35 Z0407 42.83 7.9 0.0440 44.8 Z0408 40.56 7.9 0.0440 42.43 Z0409 41.89 7.6 0.0447 43.85 Z0507 38.59 6.6 0.0467 40.48 Z0508 41.70 6.9 0.0461 43.72 Z0606 43.38 6.0 0.0480 45.57 Z0607 44.86 7.2 0.0454 46.99 Z1903 36.28 7.0 0.0459 38.02 -
[1] 冯斌, 李文前, 刘建方. 河南永夏煤田地质[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2017: 125-130.
Feng B, Li W Q, Liu J F. Geology of Yongxia coalfield, Henan Province[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2017: 125-130. (in Chinese)
[2] 张连强. 顺和西煤矿区地温特征及其影响因素分析[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2012, 24(7): 29-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2012.07.07
Zhang L Q. Geotemperature characteristics and impacts from geological factors in Shunhexi Mine area[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2012, 24(7): 29-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2012.07.07
[3] 何莉. 河南省东部新生界深度图及其地质意义[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2015, 12(5): 692-699. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7940.2015.05.021
He L. The map of Cenozoic depth in eastern Henan and its geological significance[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2015, 12(5): 692-699. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7940.2015.05.021
[4] 彭松民, 李振国, 王令全, 等. 河南省侵入岩构造单元的划分及其特征[J]. 矿产与地质, 2014, 28(3): 264-271, 283. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2014.03.002
Peng S M, Li Z G, Wang L Q, et al. Division and characteristics of tectonic units of intrusive rocks in Henan Province[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2014, 28(3): 264-271, 283. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2014.03.002
[5] 易家伟. 宿东矿区地温分布规律及影响因素分析[D]. 淮南: 安徽理工大学, 2017.
Yi J W. Analysis of geothermal distribution and influencing factors in the Sudong mining area[D]. Huainan: Anhui University of Science & Technology, 2017.
[6] 中华人民共和国国土资源部. DZ/T 0080-2010煤炭地球物理测井规范[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2010.
Ministry of Land and Resources of the People's Republic of China. DZ/T 0080-2010 Specifications for geophysical logging of coal[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2010.
[7] 苏媛媛. 豫东下古生界地热资源潜力评价[J]. 山东煤炭科技, 2017(6): 185-187. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2801.2017.06.078
Su Y Y. Lower Paleozoic geothermal resource potential evaluation[J]. Shandong Coal Science and Technology, 2017(6): 185-187. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2801.2017.06.078
[8] 王海军. 简易测温曲线的近似稳态校正方法——以LYL井田为例[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2016, 44(1): 90-93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2016.01.017
Wang H J. Approximate steady state correction of simple well temperature curve: With LYL mine field as an example[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2016, 44(1): 90-93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2016.01.017
[9] 任自强. 潘集矿区深部地温地质特征及地热资源评价[D]. 淮南: 安徽理工大学, 2016.
Ren Z Q. Geothermal characteristics and assessment of geothermal resources in the depth of Panji mining area[D]. Huainan: Anhui University of Science & Technology, 2016.
[10] 谭静强, 琚宜文, 侯泉林, 等. 淮北煤田宿临矿区现今地温场分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 地球物理学报, 2009, 52(3): 732-739. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200903018.htm
Tan J Q, Ju Y W, Hou Q L, et al. Distribution characteristics and influence factors of present geo-temperature field in Su-Lin mine area, Huaibei coalfield[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2009, 52(3): 732-739. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200903018.htm
[11] 彭涛, 吴基文, 任自强, 等. 淮北煤田现今地温场特征及大地热流分布[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2015, 40(6): 1083-1092. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201506013.htm
Pen T, Wu J W, Ren Z Q, et al. Distribution characteristics of current geothermal field and terrestrial heat flow in Huaibei Coalfield[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2015, 40(6): 1083-1092. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201506013.htm
[12] 李腾超, 王书宏, 寇正卫. 河南省地温场分布规律及成因机制分析[J]. 城市地质, 2020, 15(2): 194-200. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1903.2020.02.012
Li T C, Wang S H, Kou Z W. Analysis of the distribution and formation mechanism of the geothermal field in Henan Province[J]. Urban Geology, 2020, 15(2): 194-200. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1903.2020.02.012
[13] 王康, 姚多喜, 鲁海峰. 淮南潘三矿区地温分布规律及其影响因素分析[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2014, 26(5): 38-40, 48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2014.05.09
Wang K, Yao D X, Lu H F. Geotherm distribution pattern and impacting factor analysis in Panji No. 3 coalmine, Huainan[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2014, 26(5): 38-40, 48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2014.05.09
[14] 郭艳, 吴基文, 冯松宝. 宿县矿区地温特征及控制因素分析[J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 38(5): 694-699. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HEFE201505024.htm
Guo Y, Wu J W, Feng S B. Geotemperature features in Suxian mining area and control factors[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science), 2015, 38(5): 694-699. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HEFE201505024.htm
[15] 张庆松, 高阳, 李术才, 等. 含水构造附近围岩温度场响应特征与影响因素研究[J]. 山东大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(3): 72-77. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDGY201103015.htm
Zhang Q S, Gao Y, Li S C, et al. Research on the temperature response feature of a rock mass around a water-bearing structure and affecting factors[J]. Journal of Shandong University (Engineering Science), 2011, 41(3): 72-77. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDGY201103015.htm
[16] 黄光寿, 郭丽丽, 黄凯. 河南省沉积盆地区五大构造单元地热地质特征[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(2): 172-179. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2020.02.009 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10189.shtml
Huang G S, Guo L L, Huang K. Geothermal geological characteristics of five tectonic units in the sedimentary basins of Henan Province[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(2): 172-179. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2020.02.009 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10189.shtml
[17] 郭飒飒, 朱传庆, 邱楠生, 等. 雄安新区深部地热资源形成条件与有利区预测[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(7): 2026-2035. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.07.011
Guo S S, Zhu C Q, Qiu N S, et al. Formation conditions and favorable areas for the deep geothermal resources in Xiong'an New Area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(7): 2026-2035. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.07.011
[18] 路畅, 李营, 陈志, 等. 华北断陷盆地中北部地热水地球化学特征及成因初探[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2018, 37(4): 663-673. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201804011.htm
Lu C, Li Y, Chen Z, et al. A primary study on geochemical characteristics and genesis of geothermal water in the north-central part of the North China Downfaulted Basin[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2018, 37(4): 663-673. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201804011.htm
[19] 张连强. 永夏煤田水文地质特征及开采技术条件评价[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2012, 24(8): 48-52, 84. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMT201208013.htm
Zhang L Q. Evaluation of Yongxia Coalfield hydrogeological characteristics and mining technical conditions[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2012, 24(8): 48-52, 84. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMT201208013.htm
[20] 张连强, 李建涛, 杨义栋, 等. 对豫东地区地下水资源的理性分析[J]. 地下水, 2011, 33(6): 222-224. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXSU201106087.htm
Zhang L Q, Li J T, Yang Y D, et al. Rational analysis of groundwater resources in eastern Henan Province[J]. Ground Water, 2011, 33(6): 222-224. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXSU201106087.htm
-



 下载:
下载: