CALCITE Sm-Nd ISOCHRON AGE OF THE ERGADIJI LEAD-ZINC DEPOSIT IN WESTERN SICHUAN PROVINCE: Geological Implication
-
摘要:
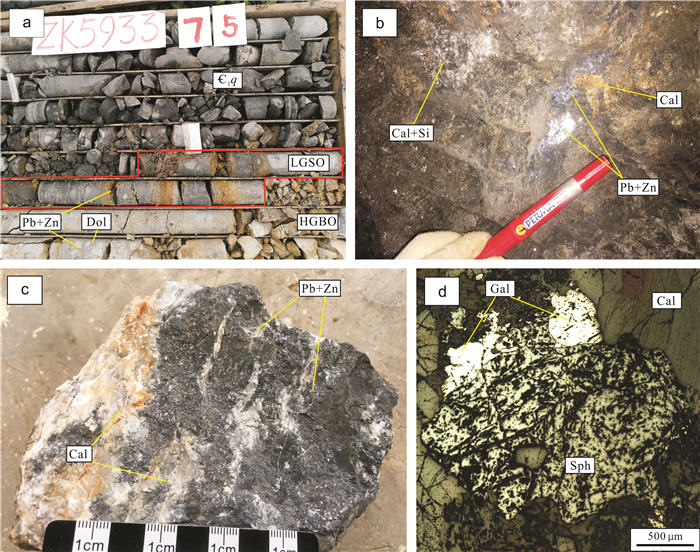
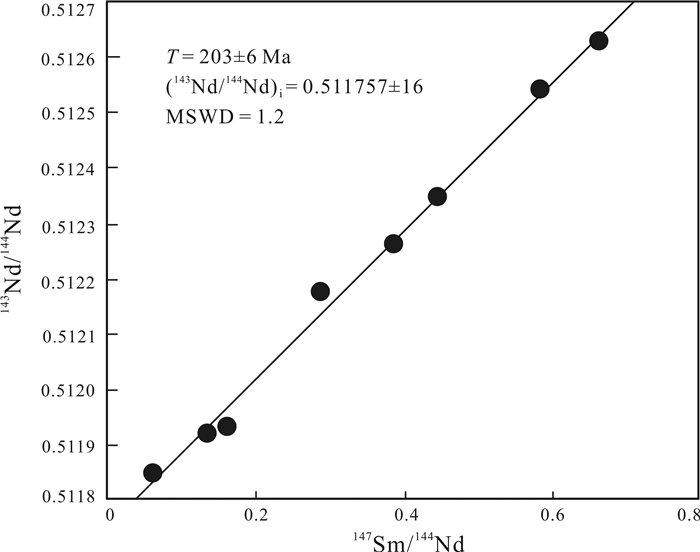
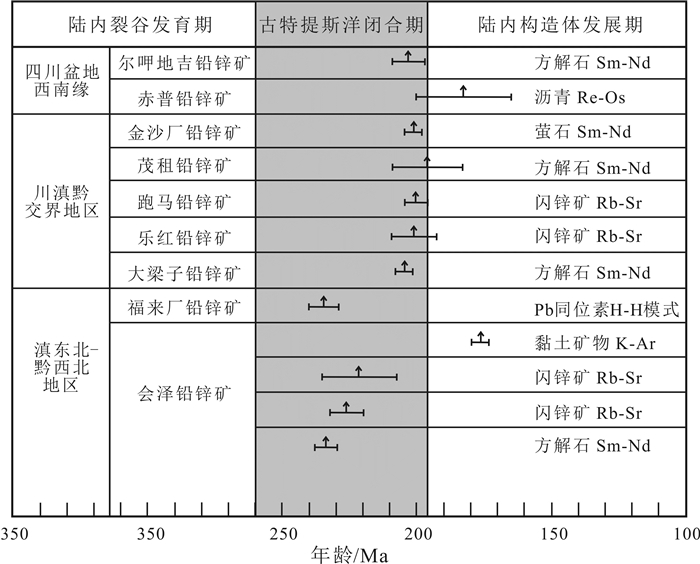
尔呷地吉中型铅锌矿床位于扬子地块西南缘川滇黔交界地带.矿体主要呈似层状、透镜状赋存于震旦系灯影组白云岩中,顶板为下寒武统筇竹寺组含炭质砂页岩.主要金属矿物为闪锌矿和方铅矿,Zn平均品位5.30%,Pb平均品位3.25%;主要非金属矿物为方解石和石英.矿石结构主要有自形晶结构、交代-侵蚀结构和固溶体分离结构,矿石构造主要有细脉-浸染状、块状和角砾状.矿床中铅锌矿化与硅化、沥青化和方解石化密切相关.对尔呷地吉Pb-Zn矿床成矿期8件与铅锌矿共生的方解石样品进行了Sm-Nd同位素体系研究,结果表明方解石的147Nd/144Nd值变化于0.058489~0.663246,143Nd/144Nd值变化于0.511852~0.512626,获得Sm-Nd等时线年龄为203±6 Ma(MSWD=1.2),该年龄代表了尔呷地吉MVT Pb-Zn矿床的成矿年龄.尔呷地吉Pb-Zn矿床是典型的MVT Pb-Zn矿床,其矿床成矿作用与峨眉山玄武岩岩浆活动无关,与古特提斯洋闭合背景下的造山运动密切相关.
-
关键词:
- MVT Pb-Zn矿床 /
- 方解石 /
- Sm-Nd等时线年龄 /
- 尔呷地吉 /
- 四川省
Abstract:The Ergadiji medium-sized lead-zinc deposit is located on the junction of Sichuan, Yunnan, and Guizhou provinces, southwestern margin of Yangtze block. The orebody is mainly occurred in stratoid and lenticular forms in the dolomite of Sinian Dengying Formation, with the carbonaceous sand shale of Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation as the roof. The main metallic minerals are sphalerite and galena with the Zn grade of 5.30% and Pb grade of 3.25% averagely. The nonmetallic minerals are mainly calcite and quartz. The ores are in idiomorphic crystal, metasomatism-erosion and solid solution separation textures and veinlet-disseminated, massive and brecciated structures. The Pb-Zn mineralization of the deposit is closely related to silicification, bituminization and calcilization. Through the study on the Sm-Nd isotope system of 8 calcite samples associated with Pb-Zn ores in the metallogenic period, the results show 147Nd/144Nd is 0.058489-0.663246, 143Nd/144Nd 0.511852-0.512626, and the Sm-Nd isochron age of 203±6 Ma (MSWD=1.2), also representing the ore-forming age of the deposit. The Ergadiji Pb-Zn deposit is of typical Mississippi Valley type (MVT), with its mineralization closely related to the orogeny after the closure of Paleo-Tethys Ocean, rather than the magma activity of Mount Emei basalt.
-
Key words:
- MVT Pb-Zn deposit /
- calcite /
- Sm-Nd isochron age /
- Ergadiji area /
- Sichuan Province
-

-
表 1 尔呷地吉Pb-Zn矿床方解石Sm-Nd同位素组成
Table 1. Sm-Nd isotopic composition of the calcite samples from Ergadiji Pb-Zn deposit
样品编号 采样位置 产状 Sm/10-6 Nd/10-6 147Sm/144Nd 143Nd/144Nd(2σ) εNd(t) Erga-01 Ⅰ号矿体 网脉状 0.636 6.550 0.058489 0.511852(16) -11.76 Erga-02 Ⅰ号矿体 网脉状 0.175 0.788 0.133527 0.511922(14) -12.33 Erga-03 Ⅱ号矿体 脉状 0.588 1.231 0.287692 0.512174(12) -11.41 Erga-04 Ⅱ号矿体 脉状 0.584 2.201 0.159745 0.511935(16) -12.76 Erga-05 Ⅲ号矿体 透镜状 0.457 0.414 0.663246 0.512626(18) -12.33 Erga-06 Ⅲ号矿体 透镜状 0.419 0.568 0.443768 0.512348(20) -12.06 Erga-07 Ⅳ号矿体 浸染状 0.715 1.121 0.384873 0.512263(21) -12.19 Erga-08 Ⅳ号矿体 浸染状 0.876 0.904 0.583884 0.512542(18) -11.92 -
[1] 柳贺昌, 林文达. 滇东北铅锌银矿床规律研究[M]. 昆明: 云南大学出版社, 1999: 1-300.
Liu H C, Lin W D. Study on the regularity of Pb-Zn-Ag deposits in the northeast Yunnan Province[M]. Kunming: Yunnan University Press, 1999: 1-300. (in Chinese)
[2] Nakai S, Halliday A N, Kesler S E, et al. Rb-Sr dating of sphalerites from Tennessee and the genesis of Mississippi Valley type ore deposits[J]. Nature, 1990, 346(6282): 354-357. doi: 10.1038/346354a0
[3] Sangster D F. Mississippi Valley-type lead-zinc[M]//Eckstrand O R, Sinclair W D, Thorpe R I. Geology of Canadian Mineral Deposit Types. Ottawa: Geological Society of America, 1995: 253-261.
[4] 魏菊英, 王关玉. 同位素地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1988: 1-166.
Wei J Y, Wang G Y. Isotope geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1988: 1-166.
[5] 赵振华. 微量元素地球化学原理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1997: 1-93.
Zhao Z H. Principles of trace elements geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1997: 1-93. (in Chinese)
[6] 王中刚, 于学元, 赵振华, 等. 稀土元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989: 1-535.
Wang Z G, Yu X Y, Zhao Z H, et al. Rare earth element geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1989: 1-535.
[7] 李文博, 黄智龙, 王银喜, 等. 会泽超大型铅锌矿田方解石Sm-Nd等时线年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地质论评, 2004, 50(2): 189-195. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2004.02.011
Li W B, Huang Z L, Wang Y X, et al. Age of the giant Huize Zn-Pb deposits determined by Sm-Nd dating of hydrothermal calcite[J]. Geological Review, 2004, 50(2): 189-195. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2004.02.011
[8] Zhou J X, Huang Z L, Yan Z F. The origin of the Maozu carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn deposit, Southwest China: Constrained by C-O-S-Pb isotopic compositions and Sm-Nd isotopic age[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 73: 39-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.04.031
[9] 吴越. 川滇黔地区MVT铅锌矿床大规模成矿作用的时代与机制[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学, 2013.
Wu Y. The age and ore-forming process of MVT deposits in the boundary area of Sichuan-Yunnan-Guizhou provinces, Southwest China[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2013.
[10] 曾令刚. 四川甘洛则板沟铅锌矿床成因及找矿方向探讨[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2006.
Zeng L G. Discussion on genesis and prospecting direction of Zebangou Pb-Zn deposit in Ganluo County, Sichuan[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2006. (in Chinese)
[11] 张长青. 中国川滇黔交界地区密西西比型(MVT)铅锌矿床成矿模型[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2008.
Zhang C Q. The genetic model of Mississippi Valley-type deposits in the boundary area of Sichuan, Yunnan and Guizhou provinces, China[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2008.
[12] 韩润生, 胡煜昭, 王学琨, 等. 滇东北富锗银铅锌多金属矿集区矿床模型[J]. 地质学报, 2012, 86(2): 280-294. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201202008.htm
Han R S, Hu Y Z, Wang X K, et al. Mineralization model of rich Ge-Ag-bearing Zn-Pb polymetallic deposit concentrated district in northeastern Yunnan, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2012, 86(2): 280-294. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201202008.htm
[13] 王登红. 地幔柱的概念、分类、演化与大规模成矿——对中国西南部的探讨[J]. 地学前缘, 2001, 8(3): 67-72. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2001.03.008
Wang D H. Basic concept, classification, evolution of mantle plume and large scale mineralization-Probe into southwestern China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2001, 8(3): 67-72. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2001.03.008
[14] 骆耀南, 傅德明, 何虹. 峨眉地幔柱活动的成矿作用及其成矿系列[C]//峨眉地幔柱与资源环境效应学术研讨会论文集. 成都: 中国地质学会, 2003: 99-100.
Luo Y N, Fu D M, He H. Metallogenesis and metallogenic series of Emeishan mantle plume activity[C]//Proceedings of the Symposium on Emeishan Mantle Plume and Resource Effects. Chengdu: Geological Society of China, 2003: 99-100. (in Chinese)
[15] 黄智龙, 陈进, 刘丛强, 等. 峨眉山玄武岩与铅锌矿床成矿关系初探-以云南会泽铅锌矿床为例[J]. 矿物学报, 2001, 21(4): 681-688. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2001.04.019
Huang Z L, Chen J, Liu C Q, et al. A preliminary discussion on the genetic relationship between Emeishan basalts and Pb-Zn deposits as exemplified by the Huize Pb-Zn deposit, Yunnan Province[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2001, 21(4): 681-688. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2001.04.019
[16] 刘丛强, 黄智龙, 李和平, 等. 地幔流体及其成矿作用[J]. 地学前缘, 2001, 8(4): 231-243. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2001.04.001
Liu C Q, Huang Z L, Li H P, et al. The geofluid in the mantle and its role in ore-forming processes[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2001, 8(4): 231-243. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2001.04.001
[17] 王奖臻, 李朝阳, 李泽琴, 等. 川滇地区密西西比河谷型铅锌矿床成矿地质背景及成因探讨[J]. 地质地球化学, 2001, 29(2): 41-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9250.2001.02.007
Wang J Z, Li C Y, Li Z Q, et al. The geological setting, characters and origin of Mississippi Valley-type Pb-Zn deposits in Sichuan and Yunnan provinces[J]. Geology-Geochemistry, 2001, 29(2): 41-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9250.2001.02.007
[18] 顾尚义. 黔西北铅锌矿稀土元素组成特征——兼论黔西北地区铅锌矿成矿与峨眉山玄武岩的关系[J]. 贵州地质, 2006, 23(4): 274-277. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2006.04.006
Gu S Y. Characteristics of rare-earth elements composition within lead-zinc deposits in northwestern Guizhou: In addition to a discussion of relationship between lead-zinc deposits and Emeishan basalts in northwestern Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Geology, 2006, 23(4): 274-277. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2006.04.006
[19] 张招崇, 王福生. 峨眉山玄武岩Sr、Nd、Pb同位素特征及其物源探讨[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2003, 28(4): 431-439. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200304012.htm
Zhang Z C, Wang F S. Sr, Nd and Pb isotopic characteristics of Emeishan basalt province and discussion on their source region[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2003, 28(4): 431-439. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200304012.htm
[20] 谭俊, 魏俊浩, 谭文娟, 等. 同源岩浆成因金矿成岩成矿时差的统计研究[J]. 地质论评, 2006, 52(1): 54-62. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2006.01.008
Tan J, Wei J H, Tan W J, et al. Statistic study of diagenesis-mineralization time gap for comagmatic gold deposits[J]. Geological Review, 2006, 52(1): 54-62. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2006.01.008
[21] Leach D L, Sangster D F, Kelley K D, et al. Sediment-hosted lead-zinc deposits: a global perspective[MJ]//Hedenquist J W, Thompson J F H, Goldfarb R J, et al. One Hundredth Anniversary Volume. America: Society of Economic Geologists, 2005: 561-607.
[22] Yin M D, Li W B, Sun X W. Rb-Sr isotopic dating of sphalerite from the giant Huize Zn-Pb ore field, Yunnan Province, Southwestern China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 2009, 28(1): 70-75. doi: 10.1007/s11631-009-0070-5
[23] 张长青, 毛景文, 刘峰, 等. 云南会泽铅锌矿床粘土矿物K-Ar测年及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2005, 24(3): 317-324. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2005.03.011
Zhang C Q, Mao J W, Liu F, et al. K-Ar dating of altered clay minerals from Huize Pb-Zn deposit in Yunnan province and its geological significance[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2005, 24(3): 317-324. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2005.03.011
[24] 汤世凯, 马筱, 李学刚, 等. 黔西北福来厂铅锌矿床Pb同位素研究及地质意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2012, 36(4): 549-558. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2012.04.009
Tang S K, Ma X, Li X G, et al. Pb isotope composition of the Fulaichang lead-zinc ore deposit in northwest Guizhou and its geological implications[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2012, 36(4): 549-558. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2012.04.009
[25] 张云新, 吴越, 田广, 等. 云南乐红铅锌矿床成矿时代与成矿物质来源: Rb-Sr和S同位素制约[J]. 矿物学报, 2014, 34(3): 305-311. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201403002.htm
Zhang Y X, Wu Y, Tian G, et al. Mineralization age and the source of ore-forming material at Lehong Pb-Zn deposit, Yunnan province: Constraints from Rb-Sr and S isotopes system[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2014, 34(3): 305-311. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201403002.htm
[26] 蔺志永, 王登红, 张长青. 四川宁南跑马铅锌矿床的成矿时代及其地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(2): 488-494. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.02.023
Lin Z Y, Wang D H, Zhang C Q. Rb-Sr isotopic age of sphalerite from the Paoma lead-zinc deposit in Sichuan province and its implications[J]. Geology in China, 2010, 37(2): 488-494. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.02.023
[27] 张宗清, 张国伟, 唐索寒, 等. 秦岭勉略带中安子山麻粒岩的年龄[J]. 科学通报, 2002, 47(22): 1751-1755. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200222017.htm
Zhang Z Q, Zhang G W, Tang S H, et al. Age of Anzishan granulites in the Mianxian-Lueyang suture zone of Qingling orogen: With a discussion of the timing of final assembly of Yangtze and North China craton blocks[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2002, 47(22): 1925-1930. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200222017.htm
[28] 李龚健, 王庆飞, 禹丽, 等. 哀牢山古特提斯洋缝合时限: 晚二叠世花岗岩类锆石U-Pb年代学与地球化学制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(11): 3883-3990. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201311020.htm
Li G J, Wang Q F, Yu L, et al. Closure time of the Ailaoshan Paleo-Tethys Ocean: Constraints from the zircon U-Pb dating and geochemistry of the Late Permian granitoids[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013, 29(11): 3883-3990. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201311020.htm
[29] 李文渊. 古亚洲洋与古特提斯洋关系初探[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(8): 2201-2210. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201808001.htm
Li W Y. The primary discussion on the relationship between Paleo-Asian Ocean and Paleo-Tethys Ocean[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2018, 34(8): 2201-2210. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201808001.htm
[30] Selby D, Creaser R A. Direct radiometric dating of hydrocarbon deposits using rhenium-osmium isotopes[J]. Science, 2005, 308(5726): 1293-1295. doi: 10.1126/science.1111081
[31] Muhling J R, Fletcher I R, Rasmussen B. Dating fluid flow and Mississippi Valley Type base-metal mineralization in the Paleoproterozoic Earaheedy Basin, Western Australia[J]. Precambrian Research, 2012, 212-213: 75-90. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035434236510_bbd0.html
[32] 李厚民, 张长青. 四川盆地富硫天然气与盆地周缘铅锌铜矿的成因联系[J]. 地质论评, 2012, 58(3): 495-510. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0371-5736.2012.03.010
Li H M, Zhang C Q. The genetic relationship between the H2S-bearing gas in Sichuan basin and lead-zinc-copper deposits around the basin[J]. Geological Review, 2012, 58(3): 495-510. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0371-5736.2012.03.010
[33] 龚银杰, 张遵遵, 陈立波, 等. 川东南褶皱带洞岩铅锌矿床闪锌矿Rb-Sr同位素测年及其构造变形时代[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(2): 485-496. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202002016.htm
Gong Y J, Zhang Z Z, Chen L B, et al. Sphalerite Rb-Sr isotopic dating of the Dongyan Pb-Zn deposit in southeastern Sichuan fold belt and its constraint on the timing of tectonic deformation[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(2): 485-496. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202002016.htm
[34] 许志琴, 侯立玮, 王宗秀, 等. 中国松潘-甘孜造山带的造山过程[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1992: 1-192.
Xu Z Q, Hou L W, Wang Z X, et al. Orogenic processes of the Songpan-Ganze orogenic belt of China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1992: 1-192.
[35] 刘树根, 罗志立, 戴苏兰, 等. 龙门山冲断带的隆升和川西前陆盆地的沉降[J]. 地质学报, 1995, 69(3): 204-214. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE199503001.htm
Liu S G, Luo Z L, Dai S L, et al. The uplift of the Longmenshan thrust belt and subsidence of the western Sichuan foreland basin[J]. Acta Geological Sinica, 1995, 69(3): 204-214. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE199503001.htm
[36] 杜远生, 黄虎, 杨江梅, 等. 晚古生代-中三叠世右江盆地的格局和转换[J]. 地质论评, 2013, 59(1): 1-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0371-5736.2013.01.001
Du Y S, Huang H, Yang J M, et al. The basin translation from Late Paleozoic to Triassic of the Youjiang Basin and its tectonic signification[J]. Geological Review, 2013, 59(1): 1-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0371-5736.2013.01.001
-



 下载:
下载: