GEOLOGY AND GENESIS OF NANZHUANG LEND-ZINC DEPOSIT IN NANZHAO COUNTY, HENAN PROVINCE
-
摘要:
南庄铅锌矿床的矿体大多呈隐伏型,产于下古生界二郎坪群火神庙组石英角斑凝灰岩中.通过对矿床地质特征、矿石稀土元素和微量元素特征、同位素地球化学特征的综合分析研究,发现矿床具热水沉积特征和海水硫与幔源硫混合特性,成矿物质主要来源于上地幔,并混有造山带和上地壳的特征.基本确定该矿床属于弱变质作用改造的海底火山喷流型块状硫化物型矿床,建立了地层-岩性-蚀变-物探找矿标志.
Abstract:The orebodies in Nanzhuang lead-zinc deposit, mostly concealed, are occurred in the quartz-keratophyre tuff of Huoshenmiao Formation, Erlangping Group, Lower Paleozoic. Through comprehensive analysis on the geological features of deposit, characteristics of trace and rare earth elements in ores, and isotopic geochemistry, it is found that the deposit is characterized by hydrothermal deposition and mixing of seawater sulfur and mantle-derived sulfur, with the ore-forming materials mainly derived from the upper mantle, mixed with the characteristics of orogenic belt and upper crust. It is basically determined that the deposit belongs to submarine volcanic exhalation massive sulfide type reformed by weak metamorphism, and the strata-lithology-alteration-geophysical prospecting indicators are established based on the above.
-

-
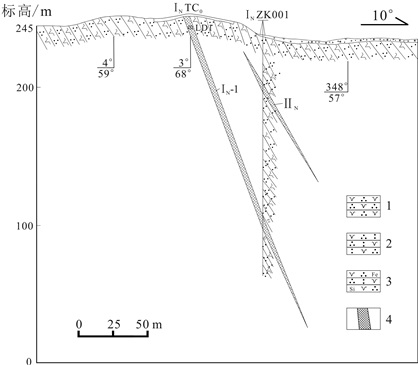
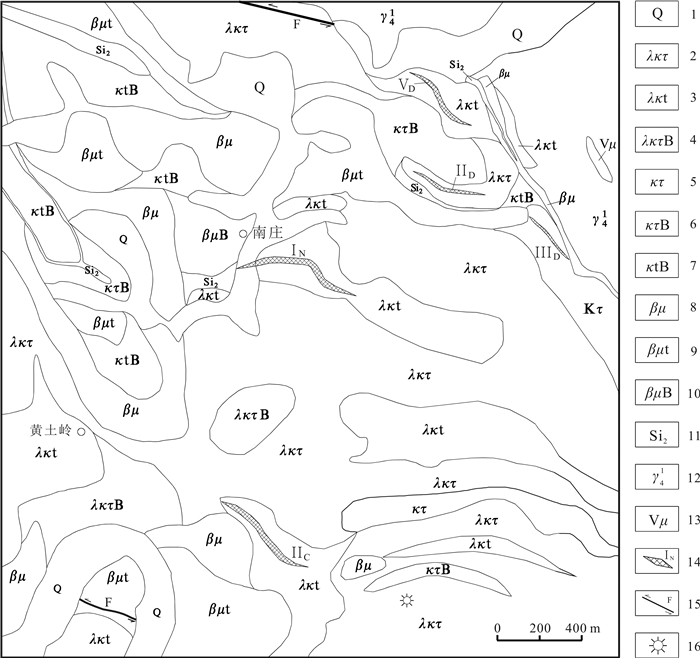
图 1 图 1南庄铅锌矿区地质简图
Figure 1.
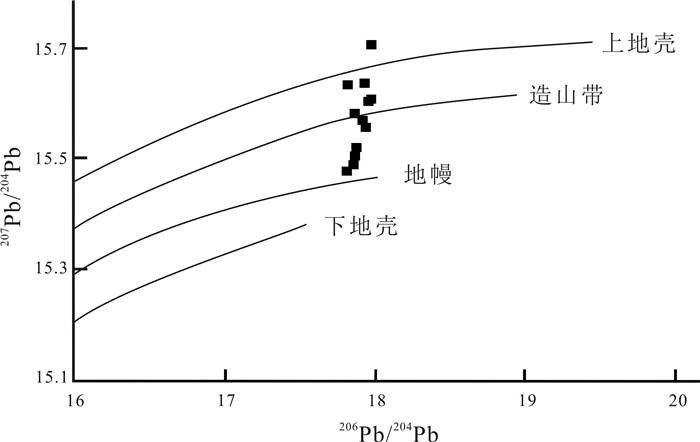
图 4 铅同位素构造模式图(据文献[20])
Figure 4.
表 1 南庄铅锌矿区矿体特征表
Table 1. Characteristics of orebodies in Nanzhuang Pb-Zn deposit
矿体编号 形态 标高/m 埋深/m 延深/m 长度/m 厚度/m 倾向/(°) 倾角/(°) Zn品位/% Pb品位/% IN-1 层状 32~252 0~203 165 260 2.65 3 66 0.71~1.52 0.53~2.43 IN-2 层状、似层状 113~244 48~170 128 240 2.83 12 69 0.81~2.26 0.33~0.47 IIN 似层状 132~222 23~102 68 160 1.50 3 60 0.76~3.56 0.62~1.27 表 2 南庄铅锌矿床矿石微量元素含量分析数据表
Table 2. Trace element contents in ores from Nanzhuang Pb-Zn deposit
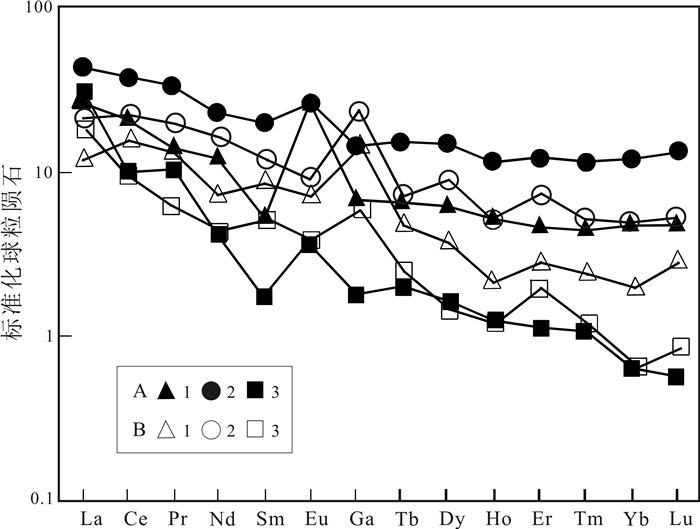
元素 La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu Y ∑REE LREE/HREE 浸染状矿石 10.3 23.0 3.24 10.8 3.02 1.52 2.92 0.56 3.79 0.68 2.04 0.30 2.02 0.34 16.0 64.5 4.41 块状矿石 6.43 13.1 1.32 5.62 0.77 1.56 1.38 0.24 1.55 0.29 0.74 0.11 0.80 0.12 6.66 34.0 5.51 角砾状矿石 3.19 4.04 0.48 0.60 0.18 0.19 0.33 0.17 0.41 0.11 0.20 0.03 0.40 0.02 0.90 10.4 5.20 元素 Cu Pb Zn Au Ag As Sb Ba W Mo Co Cd Sr S δCe δEu (La/Yb)N 浸染状矿石 0.09 0.51 1.12 0.19 36.4 3.46 7.64 32.1 1.47 14.2 17.4 177 353 5.71 0.97 1.56 3.66 块状矿石 0.12 0.68 1.94 0.23 54.3 3.33 8.92 46.8 2.57 62.5 22.0 1000 202 17.3 0.71 4.63 5.77 角砾状矿石 0.05 0.39 0.82 0.13 21.6 2.70 16.9 21.7 1.14 51.1 20.6 83.0 649 5.9 0.76 1.63 5.83 测试单位: 南京大学地科系中心实验室.含量单位: 比值及δ值为1;Cu、Pb、Zn、Ba、S为%; 其余为10-6. 表 3 硫同位素统计表
Table 3. Statistics of sulfur isotope data
矿石类型 测定对象 δ34SCDT/‰ 块状矿石 闪锌矿 9.5 块状矿石 黄铜矿 10.1 块状矿石 黄铁矿 5.2 矿脉 闪锌矿 8.1 矿脉 黄铜矿 8.8 矿脉 黄铁矿 6.7 石英角斑凝灰岩 闪锌矿 6.5 石英角斑凝灰岩 黄铜矿 6.1 石英角斑凝灰岩 黄铁矿 3.8 石英角斑凝灰岩 黄铁矿 5.4 重晶石岩 闪锌矿 6.5 含火山角砾石英角斑岩 黄铁矿 6.7 数据来源: 据文献[20]. -
[1] 张国伟, 张本仁, 袁学诚, 等. 秦岭造山带与大陆动力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001: 706-714.
Zhang G W, Zhang B R, Yuan X C, et al. Qinling orogenic belt and continental dynamics[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2001: 706-714.
[2] 张国伟, 张本仁, 袁学诚. 秦岭造山带造山过程和岩石圈三维结构图丛[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1996: 11-67.
Zhang G W, Zhang B R, Yuan X C. Book of orogenic process and lithosphere three dimension framework in Qinling orogenic belt[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1996: 11-67. (in Chinese)
[3] 冯胜斌, 周洪瑞, 燕长海, 等. 东秦岭(河南段)二郎坪群铜多金属成矿环境及成矿效应[J]. 矿产与地质, 2006, 20(6): 598-607. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2006.06.005
Feng S B, Zhou H R, Yan C H, et al. Metallogenic environment of copper polymetallic deposit in Erlangping Group of East Qinling and its metallogeny[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2006, 20(6): 598-607. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2006.06.005
[4] 宋峰, 刘铁, 王铭生, 等. 东秦岭二郎坪群蛇绿岩中的火山成因硫化物矿床[J]. 中国区域地质, 1999, 18(1): 80-85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.1999.01.013
Song F, Liu T, Wang M S, et al. Volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits in the ophiolite of the Erlangping Group in the eastern Qinling[J]. Regional Geology of China, 1999, 18(1): 80-85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.1999.01.013
[5] 陈建立. 二郎坪群海相火山岩中块状硫化物矿床地质特征及其找矿方向[J]. 地质与勘探, 2004, 40(6): 38-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.2004.06.009
Chen J L. The characteristics and ore exploration of massive sulfide deposits in Erlangping Group marine volcanic rocks[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2004, 40(6): 38-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.2004.06.009
[6] 金守文. 二郎坪群两点商议[J]. 河南地质, 1994, 12(1): 36-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNDD401.005.htm
Jin S W. Discussions on Erlangping Group[J]. Henan Geology, 1994, 12(1): 36-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNDD401.005.htm
[7] 江少卿, 徐毅, 孙尚信, 等. 全球铅锌矿资源分布[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(3): 224-232. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2020.03.003 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10196.shtml
Jiang S Q, Xu Y, Sun S X, et al. Global distribution of lead-zinc resources[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(3): 224-232. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2020.03.003 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10196.shtml
[8] Finlow-Bates T. The chemical and physical controls on the genesis of submarine exhalative orebodies and their implications for formulating exploration concepts: A review[J]. Geologisches Jahrbuch, 1980, 40: 131-168.
[9] 侯增谦, 韩法, 夏林圻, 等. 现代与古代海底热水成矿作用——以若干火山成因块状硫化物矿床为例[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2003: 35-180.
Hou Z Q, Han F, Xia L Q, et al. Hydrothermal systems and metallogeny on the modern and ancient sea-floor[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2003: 35-180.
[10] Mills R A, Elderfield H. Rare earth element geochemistry of hydrothermal deposits from the active TAG Mound, 26°N Mid-Atlantic Ridge[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(17): 3511-3524. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00224-N
[11] Michard A, Albarède F. The REE content of some hydrothermal fluids[J]. Chemical Geology, 1986, 55(1/2): 51-60.
[12] 丁振举, 刘丛强, 姚书振, 等. 海底热液沉积物稀土元素组成及其意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2000, 19(1): 27-30, 34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200001006.htm
Ding Z J, Liu C Q, Yao S Z, et al. REE composition and implication of hydrothermal sedimentation of sea-floor[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2000, 19(1): 27-30, 34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200001006.htm
[13] Michard A. Rare earth element systematics in hydrothermal fluids[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1989, 53(3): 745-750.
[14] 吴朝东, 杨承运, 陈其英. 新晃贡溪-天柱大河边重晶石矿床热水沉积成因探讨[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 1999, 35(6): 774-785. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0479-8023.1999.06.008
Wu C D, Yang C Y, Chen Q Y. The hydrothermal sedimentary genesis of barite deposits in West Hunan and East Guizhou[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 1999, 35(6): 774-785. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0479-8023.1999.06.008
[15] Ohmoto H. Formation of volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits: The Kuroko perspective[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 1996, 10(3): 135-177. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.989.7965&rep=rep1&type=pdf
[16] 魏菊英, 王关玉. 同位素地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1988.
Wei J Y, Wang G Y. Isotope geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1988. (in Chinese)
[17] 张革利, 田涛, 王瑞廷, 等. 凤太矿集区东塘子铅锌矿床S、Pb同位素组成对成矿物质来源的示踪[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(2): 472-484. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202002015.htm
Zhang G L, Tian T, Wang R T, et al. S, Pb isotopic composition of the Dongtangzi Pb-Zn deposit in the Fengtai ore concentration area of Shaanxi Province for tracing sources of ore-forming materials[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(2): 472-484. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202002015.htm
[18] 杨荣勇, 徐兆文, 任启江, 等. 河南南召水洞岭锌铜矿床的类型及成矿条件[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 1996, 35(4): 95-100. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSDZ604.018.htm
Yang R Y, Xu Z W, Ren Q J, et al. The type and metallogenic conditions of Shuidongling zinc copper deposit in Nanzhao, Henan Province[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 1996, 35(4): 95-100. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSDZ604.018.htm
[19] Ohmoto H. Systematics of sulfur and carbon isotopes in hydrothermal ore deposits[J]. Economic Geology, 1972, 67(5): 551-578.
[20] 葛军. 水洞岭铜锌矿床硫、铅同位素地球化学特征及成矿机理探讨[J]. 化工矿产地质, 2003, 25(4): 213-218. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGKC200304003.htm
Ge J. Sulfur and lead isotopic geochemistry of Shuidongling copper-zinc deposit and ore-forming mechanism[J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals, 2003, 25(4): 213-218. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGKC200304003.htm
[21] 吴开兴, 胡瑞忠, 毕献武, 等. 矿石铅同位素示踪成矿物质来源综述[J]. 地质地球化学, 2002, 30(3): 73-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ200203012.htm
Wu K X, Hu R Z, Bi X W, et al. Ore lead isotopes as a tracer for ore-forming material sources: A review[J]. Geology-Geochemistry, 2002, 30(3): 73-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ200203012.htm
[22] Zartman R E, Doe B R. Plate tectonics: The model[J]. Tectonophysics, 198l, 75(1/2): 135-162.
-



 下载:
下载: