CHARACTERISTICS AND APPLICABILITY OF GROUNDWATER QUALITY IN OROQEN QI, INNER MONGOLIA
-
摘要:
在调查、取样、钻井基础上,充分利用前人成果资料,应用SPSS分析软件、地下水污染分析软件,得到鄂伦春地区区域地质条件、地下水质量、生活饮用水质量、农田灌溉用水质量特征.认为鄂伦春自治旗地下水铁、锰含量受东北地区铁、锰土壤高背景值控制,含量普遍较高,引起地下水色度和浑浊度升高.地下水中As、SO42-、NH4+、NO2-在不同区域质量浓度值相差较大,受人类活动的影响较大.以农业和工业用水质量要求以及一定水平的人体健康风险为依据,铁、锰、色度、浑浊度、pH值、硫酸根、氟离子含量高,造成部分井位地下水达到Ⅳ类水标准,基本适用于农业和部分工业用水,适当处理后可作生活饮用水使用.在充分认识这一区域地下水质变化规律的基础上,应尽量减少人为因素对地下水造成的污染.
Abstract:Based on the investigation, sampling and drilling, combined with previous data, the SPSS and groundwater pollution analysis softwares are used to analyze the regional geological conditions, groundwater quality, drinking water quality and farmland irrigation water quality characteristics in Oroqen Qi. It is considered that the groundwater iron and manganese contents in Oroqen Qi is controlled by the high background values of soil iron and manganese in Northeast China, and the generally high contents result in the increase of groundwater chroma and turbidity. Influenced by human activities, the mass concentrations of As, SO42-, NH4+ and NO2- in groundwater of different areas vary greatly. According to the agricultural and industrial water quality requirements and certain level of human health risk, high iron, manganese, chroma, turbidity, pH value, sulfate radical and fluoride ion content result in the groundwater in part of well locations reaching the Class Ⅳ water standard, basically suitable for agriculture and some industrial water, and used for drinking water after proper treatment. By fully understanding the variation rule of groundwater quality in the region, it is suggested that the pollution of groundwater caused by human factors be reduced as far as possible.
-
Key words:
- groundwater /
- water quality /
- soil /
- water pollution /
- applicability /
- Inner Mongolia
-

-
表 1 地下水质量评价指标及限值
Table 1. Evaluation indexes and limits of groundwater quality
类别 Ⅰ类 Ⅱ类 Ⅲ类 Ⅳ类 Ⅴ类 pH 6.5~8.5 5.5~6.5, < 5.5,>9 8.5~9 总硬度(以CaCO3计) ≤150 ≤300 ≤450 ≤650 >650 混浊度 ≤3 ≤3 ≤3 ≤10 >10 溶解性总固体(TDS) ≤ 300 ≤ 500 ≤ 1000 ≤ 2000 > 2000 硫酸盐 ≤ 50 ≤ 150 ≤ 250 ≤ 350 > 350 氯化物 ≤ 50 ≤ 150 ≤ 250 ≤ 350 > 350 铁(Fe) ≤ 0.1 ≤ 0.2 ≤ 0.3 ≤ 2.0 > 2.0 锰(Mn) ≤ 0.05 ≤ 0.05 ≤ 0.1 ≤ 1.5 > 1.5 铜(Cu) ≤ 0.01 ≤ 0.05 ≤ 1.0 ≤ 1.5 > 1.5 硝酸盐(以N计) ≤ 2.0 ≤ 5.0 ≤ 20 ≤ 30 > 30 亚硝酸盐(以N计) ≤ 0.01 ≤ 0.1 ≤ 1.00 ≤ 4.80 > 4.80 氨氮(以N计) ≤ 0.02 ≤ 0.10 ≤ 0.50 ≤ 1.5 > 1.5 汞(Hg) ≤ 0.0001 ≤ 0.0001 ≤ 0.001 ≤ 0.002 > 0.002 砷(As) ≤ 0.001 ≤ 0.001 ≤ 0.01 ≤ 0.05 > 0.05 铅(Pb) ≤ 0.005 ≤ 0.005 ≤ 0.01 ≤ 0.1 > 0.1 氟化物 ≤ 1.0 ≤ 1.0 ≤ 1.0 ≤ 2.0 > 2.0 耗氧量(COD) ≤ 1.0 ≤ 2.0 ≤ 3.0 ≤ 10.0 > 10.0 色度 ≤ 5 ≤ 5 ≤ 15 ≤ 25 > 25 嗅和味 无 无 无 无 无 肉眼可见物 无 无 无 无 无 含量单位: mg/L. 表 2 地下水单项组分质量评价分级表
Table 2. Quality evaluation grading of single component of groundwater
类别 Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ Ⅳ Ⅴ Pi 0 1 3 6 10 表 3 地下水质量综合评价分级表
Table 3. Comprehensive evaluation grading of groundwater quality
代号 Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ Ⅳ Ⅴ 级别 优良 良好 较好 较差 极差 污染程度 未污染 轻微污染 中等污染 较重污染 重污染 P综 < 0.80 0.80~2.50 2.50~4.25 4.25~7.20 > 7.20 表 4 地下水检出率、超标率测试评价结果
Table 4. Evaluation results of groundwater detection and excessive rates
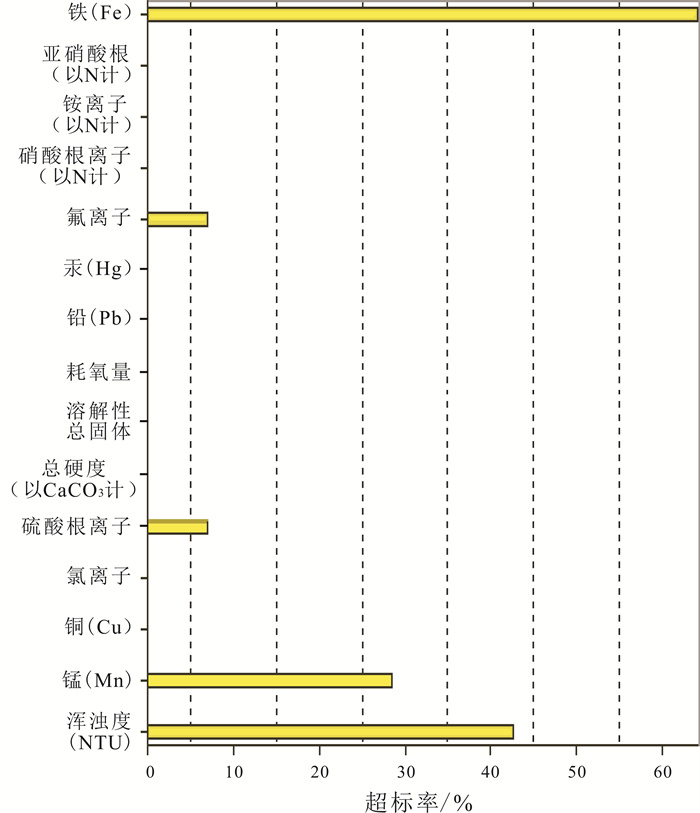
编号 测试指标 样品基数 检出井数 检出率/% 超标井数 超标率/% 检出样品指标平均值/(mg/L) 超标样品指标平均值/(mg/L) 1 锰(Mn) 14 11 78.57 4 28.57 0.18 0.39 2 铜(Cu) 14 3 21.43 0 0 0.004 3 氯离子 14 0 0 0 0 4 硫酸根离子 14 0 0 1 7.14 263.42 5 总硬度(以CaCO3计) 14 0 0 0 0 6 溶解性总固体 14 0 0 0 0 7 耗氧量 14 0 0 0 0 8 铅(Pb) 14 1 7.14 0 0 0.002 9 汞(Hg) 14 0 0 0 0 10 氟离子 14 0 0 1 7.14 1.83 11 硝酸根离子(以N计) 14 2 14.28 2 14.28 41.89 41.89 12 铵离子(以N计) 14 0 0 0 0 13 亚硝酸根(以N计) 14 0 0 0 0 14 铁(Fe) 14 13 92.86 9 64.29 0.93 1.27 15 砷(As) 14 0 0 0 0 表 5 地下水水质单指标评价统计表
Table 5. Evaluation statistics of single index of groundwater quality
编号 项目 测试总井数 Ⅰ类井数 Ⅰ类水占比/% Ⅱ类井数 Ⅱ类水占比/% Ⅲ类井数 Ⅲ类水占比/% Ⅳ类井数 Ⅳ类水占比/% Ⅴ类井数 Ⅴ类水类水占比/% 1 色 14 2 14.29 3 21.43 2 14.29 7 50 2 嗅和味 14 14 100 3 浑浊度 14 8 57.14 6 42.86 4 肉眼可见物 14 14 100 5 pH值 14 12 85.71 1 7.14 1 7.14 6 Fe 14 2 14.29 1 7.14 2 14.29 6 42.86 3 21.43 7 Mn 14 6 42.86 4 28.57 4 28.57 8 Cu 14 14 100 9 Cl- 14 13 92.86 1 7.14 10 SO42- 14 13 92.86 1 7.14 11 总硬度(CaCO3) 14 12 85.71 1 7.14 1 7.14 12 溶解性总固体 14 13 92.86 1 7.14 13 耗氧量 14 9 64.29 5 35.71 14 As 14 14 100 15 Pb 14 14 100 16 Hg 14 14 100 17 F- 14 5 35.71 7 50 1 7.14 1 7.14 18 NO3- 14 10 71.43 2 14.29 2 14.29 19 NH4+ 14 11 78.57 3 21.43 20 NO2- 14 3 21.43 9 64.29 2 14.29 表 6 地下水水质综合评价统计表
Table 6. Comprehensive evaluation of groundwater quality
序号 样品编号 评价分值 地下水质量分级 影响因子 1 Esj11 4.25 较差(Ⅳ类) pH值 2 Esj10 7.12 较差(Ⅳ类) 浑浊度、Fe、Mn 3 Esj07 7.12 较差(Ⅳ类) 浑浊度、Fe、Mn 4 Esj08 4.3 较差(Ⅳ类) 浑浊度、Fe、Mn 5 Esj06 4.26 较差(Ⅳ类) Fe 6 Esj09 4.32 较差(Ⅳ类) 浑浊度、Fe、SO42- 7 Esj05 4.3 较差(Ⅳ类) 浑浊度、Fe 8 Esj01 7.08 较差(Ⅳ类) pH值 9 Esj03 2.14 良好(Ⅱ类) 10 Esj04 2.13 良好(Ⅱ类) 11 Esj02 2.14 良好(Ⅱ类) 12 Esj12 4.26 较差(Ⅳ类) Fe 13 Esj14 4.27 较差(Ⅳ类) Fe 14 Esj13 7.17 较差(Ⅳ类) 浑浊度、Fe、Mn、F- 表 7 毒理指标分析结果
Table 7. Analysis results of toxicological indexes
指标 As F- NO3- 饮用水标准值 0.05 1.2 20 Esj01 0.0001 0.31 0.84 Esj02 0.0001 0.045 60.53 Esj03 0.0001 0.11 23.24 Esj04 0.0001 0.37 12.85 Esj05 0.0000 0.19 15.25 Esj06 0.0000 0.48 0.06 Esj07 0.0000 0.15 0.06 Esj08 0.0000 0.27 1.20 Esj09 0.0000 0.40 0.35 Esj10 0.0000 0.22 0.06 Esj11 0.0000 0.31 0.11 Esj12 0.0000 0.17 5.74 Esj13 0.0008 1.83 0.01 Esj14 0.0000 0.63 0.00 含量单位: mg/L. 表 8 感官性状和一般化学指标分析结果
Table 8. Analysis results of sensory properties and general chemical indexes
指标 pH 色度 浑浊度 TDS 总硬度 COD Mn TFe Cl- SO42- 饮用水标准值 6.5~9.5 20 3 1500 550 5 0.3 0.5 300 300 Esj01 9.30 30 1.99 96.4 11.1 0.72 0.0052 0.14 2.15 1.51 Esj02 6.66 10 0.13 107 339 0.96 0.0031 0.020 52.9 33.4 Esj03 6.96 10 0.47 72.6 128 0.61 0.011 0.25 15.8 8.29 Esj04 7.24 20 1.11 70.2 71.3 0.46 0.0069 0.22 5.01 4.05 Esj05 6.90 70 8.27 232 111 1.02 0.090 1.55 12.5 10.5 Esj06 7.64 40 0.68 206 154 0.67 0.095 0.31 7.86 7.28 Esj07 6.79 100 7.27 192 97.5 0.91 0.57 3.05 1.26 10.4 Esj08 7.40 30 3.02 219 71.3 0.64 0.20 0.41 19.3 17.7 Esj09 7.31 40 4.94 478 60.3 0.41 0.048 0.52 2.10 263 Esj10 6.69 10 3.46 209 133 0.56 0.55 2.68 20.0 33.7 Esj11 6.34 0 0.46 208 147 1.63 0.019 0.068 2.26 5.18 Esj12 6.80 0 0.60 193 143 1.35 0.083 0.42 10.0 16.0 Esj13 7.32 30 6.93 194 120 1.10 0.22 2.01 0.53 7.29 Esj14 7.34 20 2.16 212 144 1.46 0.077 0.45 1.02 5.09 含量单位: mg/L. 表 9 农田灌溉指标分析结果
Table 9. Analysis results of irrigation indexes of farmland
指标 Pb Cu F- As COD pH 灌溉水标准值(水作) 0.2 0.5 2 0.05 150 5.5~8.5 灌溉水标准值(旱作) 0.2 1 2 0.1 200 5.5~8.5 灌溉水标准值(蔬菜) 0.2 1 2 0.1 60 5.5~8.5 Esj01 0.0007 0.0007 0.31 0.0001 0.72 9.3 Esj02 0.0003 0.0008 0.045 0.0001 0.96 6.66 Esj03 0.0002 0.0005 0.11 0.0001 0.61 6.96 Esj04 0.0003 0.0005 0.37 0.0001 0.46 7.24 Esj05 0 0.004 0.19 0 1.02 6.9 Esj06 0 0.0016 0.48 0 0.67 7.64 Esj07 0 0.0031 0.15 0 0.91 6.79 Esj08 0.0003 0.0015 0.27 0 0.64 7.4 Esj09 0.0004 0.0053 0.4 0 0.41 7.31 Esj10 0.0004 0.0015 0.22 0 0.56 6.69 Esj11 0 0 0.31 0 1.63 6.34 Esj12 0 0 0.17 0 1.35 6.8 Esj13 0 0 1.83 0.0008 1.1 7.32 Esj14 0 0 0.63 0 1.46 7.34 含量单位: mg/L. 表 10 地下水水化学参数相关性系数矩阵
Table 10. Correlation coefficient matrix of groundwater hydrochemical parameters
TDS Mn TFe F- NO3- 氨氮 pH 色度 浑浊度 TDS 1 Mn 0.132 1 TFe 0.161 0.912** 1 F- 0.12 0.04 0.218 1 NO3- -0.407 -0.347 -0.303 -0.339 1 氨氮 0.780** -0.107 -0.028 0.324 -0.25 1 pH -0.13 -0.255 -0.257 0.175 -0.274 0.075 1 色度 0.246 0.457 0.580* -0.007 -0.214 0.045 0.105 1 浑浊度 0.426 0.519 0.757** 0.35 -0.306 0.257 -0.035 0.773** 1 ** 为在0.01水平(双侧)上显著相关;* 为在0.05水平(双侧)上显著相关. 表 11 地下水化学组分统计特征值
Table 11. Statistical eigenvalues of groundwater chemical compositions
组分 Mn TFe Pb Cu F- Cl- SO42- NO3- As TDS CaCO3 COD NO2- NH4+ 极小值 0.0031 0.02 0 0 0.045 0.53 1.51 0 0 70.2 11.1 0.41 0.0021 0 极大值 0.57 3.05 0.0007 0.0053 1.83 52.9 263 60.53 0.0008 478 339 1.63 0.14 0.51 均值 0.1413 0.86414 0.000186 0.001393 0.39179 10.9064 30.2421 8.5929 0.000086 192.086 123.607 0.8929 0.017129 0.06879 变异系数 1.34 1.18 1.19 1.18 1.13 1.28 2.24 1.94 2.45 0.52 0.60 0.43 2.14 2.17 含量单位: mg/L. -
[1] 钱会, 马致远. 水文地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2005.
Qian H, Ma Z Y. Hydro-geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2005. (in Chinese)
[2] 沈照理, 朱宛华, 钟佐辛. 水文地球化学基础[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1993.
Shen Z L, Zhu W H, Zhong Z X. Basic hydro-geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1993. (in Chinese)
[3] 章光新, 邓伟, 何岩, 等. 中国东北松嫩平原地下水水化学特征与演变规律[J]. 水科学进展, 2006, 17(1): 20-28. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.2006.01.004
Zhang G X, Deng W, He Y, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution laws of groundwater in Songnen Plain, Northeast China[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2006, 17(1): 20-28. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.2006.01.004
[4] 谢振华, 刘凯, 李志萍, 等. 基于沉积物物质来源的地下水化学特征分析: 以北京市平原区为例[J]. 地学前缘, 2010, 17(6): 81-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201006010.htm
Xie Z H, Liu K, Li Z P, et al. Analysis of groundwater chemical characteristics based on sediment provenance analysis: A case study of Beijing Plain[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2010, 17(6): 81-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201006010.htm
[5] 李旭光, 何海洋, 田辉, 等. 通辽科尔沁地区地下水水化学特征分析[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2019, 38(6): 92-98. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GGPS201906015.htm
Li X G, He H Y, Tian H, et al. Geochemistry of groundwater in Tongliao Horqin area[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2019, 38(6): 92-98. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GGPS201906015.htm
[6] 安乐生, 赵全升, 叶思源, 等. 黄河三角洲浅层地下水化学特征及形成作用[J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(2): 370-378.
An L S, Zhao Q S, Ye S Y, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of shallow groundwater in the Yellow River delta[J]. Environmental Science, 2012, 33(2): 370-378.
[7] 张涛, 何锦, 李敬杰, 等. 蛤蟆通河流域地下水化学特征及控制因素[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(11): 4981-4990.
Zhang T, He J, Li J J, et al. Major ionic features and possible controls in the groundwater in the Hamatong River basin[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(11): 4981-4990.
[8] 孙立梅, 刘晓洁. 吉林省松辽平原东部高平原白垩系地下水水化学特征[J]. 吉林地质, 2005, 24(3): 22-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2427.2005.03.005
Sun L M, Liu X J. The hydrochemical characteristics of the Cretaceous ground water in the high east plain, Songliao Plain, Jilin Province[J]. Jilin Geology, 2005, 24(3): 22-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2427.2005.03.005
[9] 王水献, 王云智, 董新光. 焉耆盆地浅层地下水埋深与TDS时空变异及水化学的演化特征[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2007, 26(5): 90-93. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GGPS200705024.htm
Wang S X, Wang Y Z, Dong X G. The spatio-temporal variation of shallow groundwater TDS, depth and it's evolvement characteristic of water chemistry in Yanqi Basin[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2007, 26(5): 90-93. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GGPS200705024.htm
[10] 邢立亭, 张凤娟, 李常锁, 等. 鲁北平原浅层地下水水化学特征[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2015, 34(6): 90-94.
Xing L T, Zhang F J, Li C S, et al. Hydro-chemical characteristics of shallow groundwater in the North Shandong plain[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2015, 34(6): 90-94.
[11] 陈倩, 钟金先, 李长顺. 数理统计方法在区域浅层地下水水文地球化学研究中的应用[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(3): 607-613. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2012.03.023
Chen Q, Zhong J X, Li C S. Application of mathematical statistics methods on the study of hydrogeochemistry for the shallow groundwater[J]. Geoscience, 2012, 26(3): 607-613. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2012.03.023
[12] 孙斌, 邢立亭. 济南市区附近地下水化学特征研究[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2010(11): 33-37, 40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNSD201011008.htm
Sun B, Xing L T. Research on groundwater chemical characteristics in urban areas in Jinan[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2010(11): 33-37, 40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNSD201011008.htm
[13] 张伟敬, 孙晓明, 柳富田, 等. 曹妃甸地区地下水水化学特征及影响因素的R型因子分析[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2010, 17(1): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1556.2010.01.001
Zhang W J, Sun X M, Liu F T, et al. Application of R-mode analysis on chemical characters and influential factors of quaternary groundwater in Caofeidian Area[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2010, 17(1): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1556.2010.01.001
[14] 袁建飞, 邓国仕, 徐芬, 等. 毕节市北部岩溶地下水水化学特征及影响因素的多元统计分析[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(4): 1446- 1456. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201604029.htm
Yuan J F, Deng G S, Xu F, et al. The multivariate statistical analysis of chemical characteristics and influencing factors of karst groundwater in the northern part of Bijie City, Guizhou Province[J]. Geology in China, 2016, 43(4): 1446-1456. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201604029.htm
[15] 孙岐发, 田辉, 郭晓东, 等. 吉林长春地区地下水中发现偏硅酸和锶富集区[J]. 中国地质, 2017, 44(5): 1031-1032. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201705017.htm
Sun Q F, Tian H, Guo X D, et al. The discovery of silicic acid and strontium enrichment areas in groundwater of Changchun area, Jilin Province[J]. Geology in China, 2017, 44(5): 1031-1032. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201705017.htm
[16] 孙岐发, 田辉, 郭晓东, 等. 长春莲花山发现锶富集区[J]. 中国地质, 2019, 46(2): 430-431.
Sun Q F, Tian H, Guo X D, et al. Strontium-enriched areas discovered in Lianhuashan, Changchun[J]. Geology in China, 2019, 46(2): 430-431.
[17] 冯亿年, 张建涛, 王路, 等. 永城市芒山矿泉水特征及成因研究[J]. 水文地质, 2015, 40(5/6): 24-25, 28.
Feng Y N, Zhang J T, Wang L, et al. Genesis and Characteristics Research on Mineral Water in Mangshan Mountain of Yongcheng City[J]. Hydrogeology, 2015, 40(5): 24-25, 28.
[18] 杨炳超, 李小等, 张戈, 等. 诺木洪河流域地下水水化学特征及演化规律研究[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 44(10): 214-220. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBNY201610030.htm
Yang B C, Li X D, Zhang G, et al. Hydrochemistry characteristics and evolution of groundwater in Nomhon River Basin in Qinghai[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(10): 214-220. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBNY201610030.htm
[19] 姜凌. 干旱区绿洲地下水水化学成分形成及演化机制研究——以阿拉善腰坝绿洲为例[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2009.
Jiang L. Study on hydrochemical composition formation and evolution mechanisms of the groundwater in oasis of arid areas: A case of Yaoba Oasis in Alashan[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2009.
[20] 钱程, 武雄. 盐池内流区地下水水化学特征及其形成作用[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2016, 30(3): 169-175.
Qian C, Wu X. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of groundwater in the inner flow area in Yanchi[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2016, 30(3): 169-175.
[21] 孙岐发, 田辉, 张扩. 下辽河平原地区历史地面沉降情况研究[J]. 地质与资源, 2014, 23(5): 450-452. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2014.05.007 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract8881.shtml
Sun Q F, Tian H, Zhang K. Study on the history of land subsidence in lower Liaohe River plain[J]. Geology and Resources, 2014, 23(5): 450-452. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2014.05.007 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract8881.shtml
[22] 孔庆轩, 刘彩虹, 吴庭雯. 黑龙江省黑河市地下水脆弱性评价及地下水资源保护区划[J]. 地质与资源, 2013, 22(4): 279-283. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2013.04.004 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract8962.shtml
Kong Q X, Liu C H, Wu T W. Assessment of groundwater vulnerability and regionalization for water resources in Heihe City, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geology and Resources, 2013, 22(4): 279-283. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2013.04.004 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract8962.shtml
[23] 苑丽华. 松嫩平原地下水化学特征[J]. 地质与资源, 2006, 15(2): 122-124, 132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2006.02.008 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract9487.shtml
Yuan L H. Hydrochemistry of the groundwater in Songnen Plain[J]. Geology and Resources, 2006, 15(2): 122-124, 132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2006.02.008 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract9487.shtml
[24] 田辉, 金洪涛, 孙岐发, 等. 基于层次分析法的盘锦湿地生态评价[J]. 地质与资源, 2018, 27(3): 268-271, 287. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2018.03.009 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/article/searchArticle.do
Tian H, Jin H T, Sun Q F, et al. Ecological evaluation on Panjin Wetland based on analytic hierarchy process[J]. Geology and Resources, 2018, 27(3): 268-271, 287. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2018.03.009 http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/article/searchArticle.do
[25] 孔庆轩, 董宏志, 王燕, 等. 哈尔滨地区浅层地下水质量与污染评价[J]. 地质与资源, 2015, 24(1): 70-74. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract8706.shtml
Kong Q X, Dong H Z, Wang Y, et al. Assessment for the quality and pollution of shallow groundwater in Harbin, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geology and Resources, 2015, 24(1): 70-74. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract8706.shtml
-



 下载:
下载: