SPATIOTEMPORAL VARIATION OF BLACK SOIL LAYER THICKNESS IN BLACK SOIL REGION OF NORTHEAST CHINA
-
摘要:
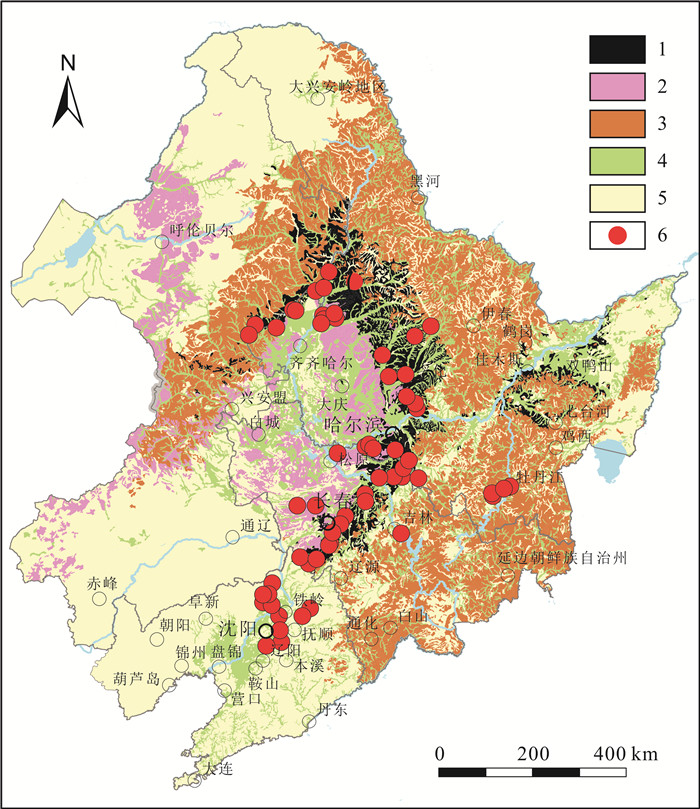
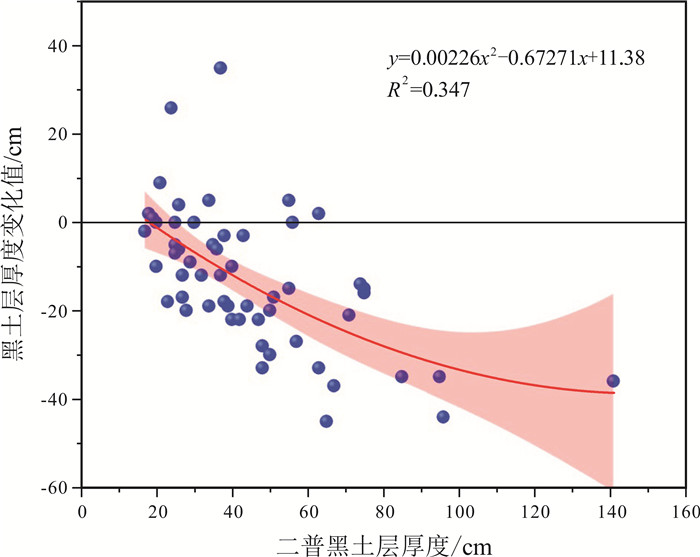
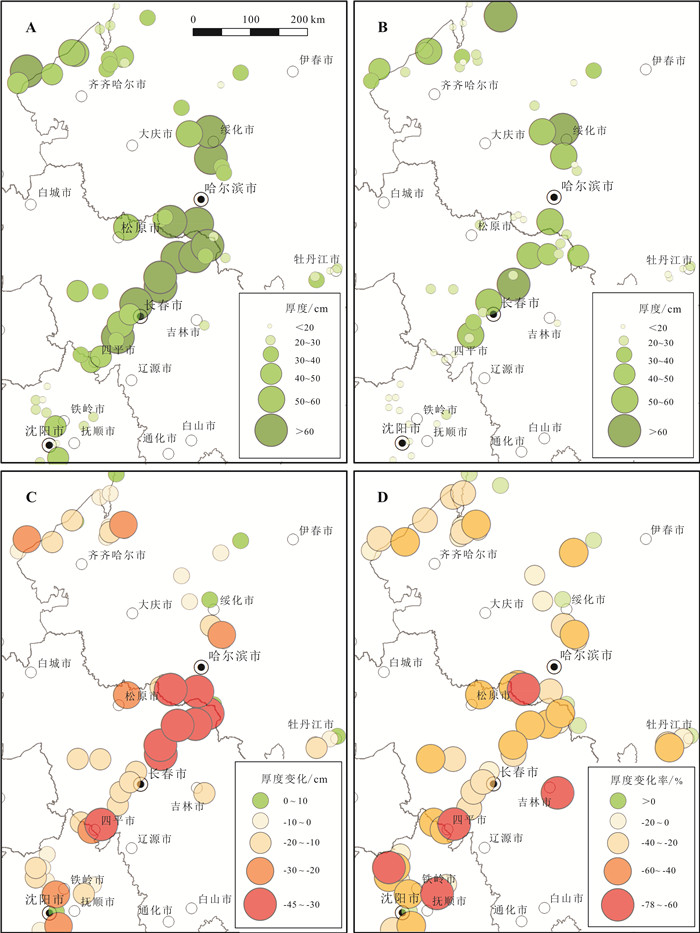
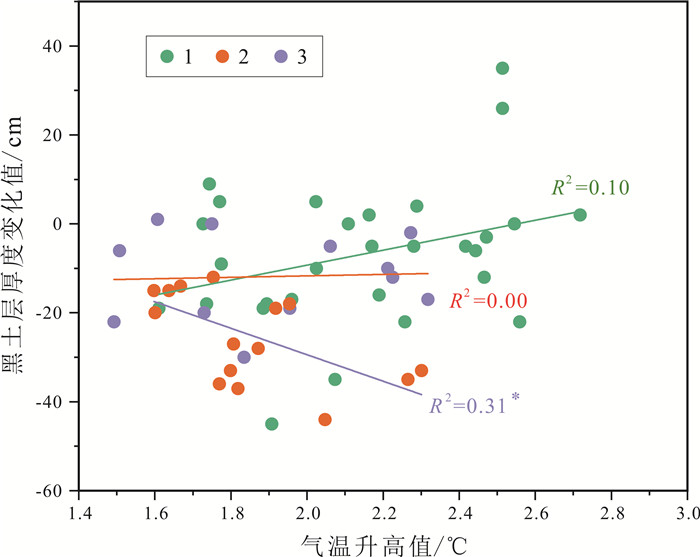
黑土层厚度是评价东北黑土区土壤质量的重要参数,但其厚度的空间分布及多年变化情况仍然不够明确.针对东北黑土区第二次土壤普查的61处典型土壤剖面进行了现状实地调查,并对黑土层厚度变化进行了对比分析.结果表明: 近40年来,东北黑土区黑土层厚度平均减少了12 cm,平均减薄速度为0.32 cm/a.四省(区)黑土层减薄厚度具有显著差异,表现为吉林(23.65 cm)>辽宁(11.83 cm)>内蒙古(10.33 cm)>黑龙江(6.83 cm).吉林省黑土层减薄厚度和比例最大,生态风险最为严峻.吉林省黑土层厚度变化值与气温升高值呈显著的负相关关系,表明随着气候变暖,土壤有机质下降明显,黑土层的厚度也呈减薄趋势.研究表明,水蚀作用也是黑土层厚度减薄的重要影响因素.未来应加强黑土层厚度判定和黑土层厚度空间制图等方面研究,对指导黑土地保护利用具有重要意义.
Abstract:The thickness of black soil layer is an important parameter to evaluate the soil quality in Northeast China. To find out its spatial distribution and secular variation, the paper conducts field investigation on the present condition of 61 typical soil profiles from the Second National Soil Survey in the black soil region of Northeast China and analyzes the variation of black soil layer thickness. The results show that the thickness of black soil layer has decreased by 12 cm on average, with the mean thinning rate of 0.32 cm/a in the past 40 years. The thinning thickness of black soil layer in four provinces/regions are significantly different, with the largest thickness and proportion of black soil layer thinning and the most severe ecological risk in Jilin(23.65 cm), followed by Liaoning(11.83 cm), Inner Mongolia(10.33 cm) and Heilongjiang(6.83 cm). There is a remarkable negative correlation between the black soil layer thickness variation and rising temperature in Jilin Province, indicating that with the climate warming, soil organic matter decreases obviously, and also the thickness of black soil layer. In addition, water erosion is also an important factor affecting the thickness thinning of black soil layer. It is suggested the study on black soil thickness determination and spatial mapping be strengthened in the future, which is of great significance to guide the protection and utilization of black land.
-

-
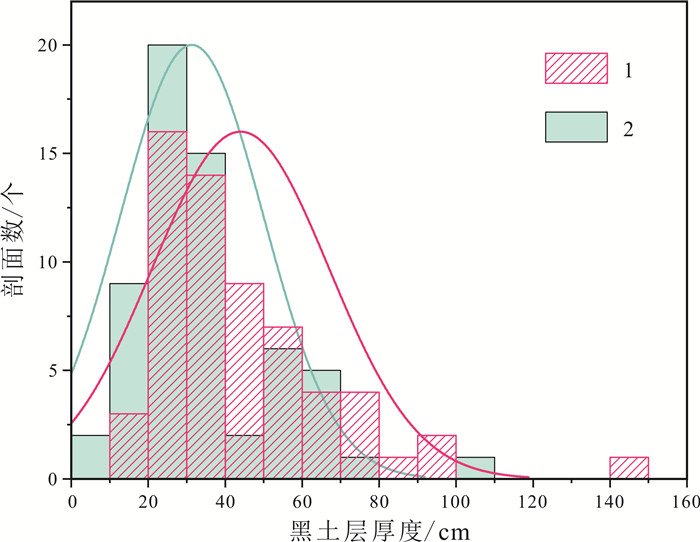
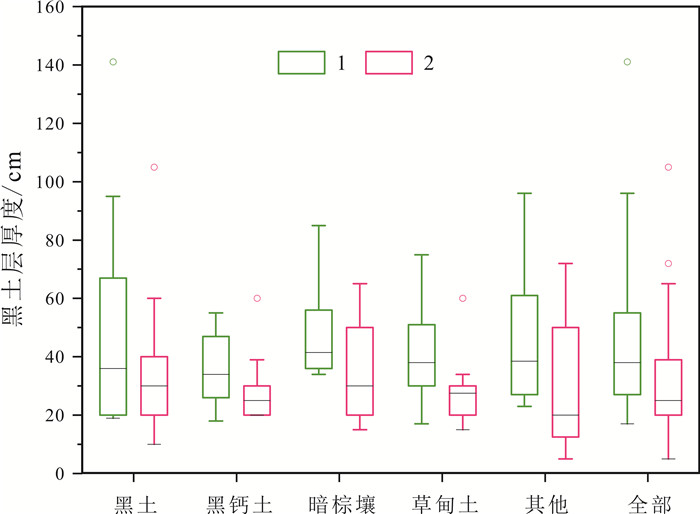
表 1 黑土层厚度统计表
Table 1. Statistics of black soil layer thickness
黑土层厚度 均值 中位数 变幅 标准离差 二普/cm 44 38 17~141 22.99 实测/cm 31.32 25 8~105 19.39 变化值/cm -12.67 -12 -45~+35 15.06 变化率/% -25 -29.58 -78~+108 34.40 表 2 四省(区)黑土层实测厚度及变化量统计表
Table 2. Statistics of surveyed thickness and variations of black soil layer in four provinces/regions
厚度 地区 样品数 平均值 标准差 最小值 中位数 最大值 实测值 黑龙江 29 33.38 16.89 10 30 72 吉林 17 37.47 22.99 5 30 105 辽宁 12 16.50 5.20 8 17.5 25 内蒙古 3 36.00 16.37 18 40 50 变化值 黑龙江 29 -6.83 16.13 -45 -5 35 吉林 17 -23.65 11.24 -44 -20 -6 辽宁 12 -11.83 9.83 -30 -11 1 内蒙古 3 -10.33 9.45 -21 -7 -3 单位: cm. -
[1] Sorokin A, Owens P, Láng V, et al. "Black soils" in the Russian soil classification system, the US soil taxonomy and the WRB: Quantitative correlation and implications for pedodiversity assessment[J]. Catena, 2021, 196: 104824. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2020.104824
[2] 张新荣, 焦洁钰. 黑土形成与演化研究现状[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2020, 50(2): 553-568. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202002020.htm
Zhang X R, Jiao J Y. Formation and evolution of black soil[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2020, 50(2): 553-568. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202002020.htm
[3] Liu K, Dai HM, Liu GD, et al. Spatial analysis of land use change effect on soil organic carbon stocks in Sanjiang Plain of China between 1980 and 2016[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 2019, 93(S1): 130-131. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1674987116300573
[4] 宋运红, 刘凯, 戴慧敏, 等. 35年来东北松辽平原耕地土壤全氮时空变化[J]. 中国地质, 2021, 48(1): 332-333. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202101024.htm
Song Y H, Liu K, Dai HM, et al. Spatio-temporal variation of total N content in farmland soil of Songliao Plain in Northeast China during the past 35 years[J]. Geology in China, 2021, 48(1): 332-333. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202101024.htm
[5] 刘国栋, 李禄军, 戴慧敏, 等. 松辽平原土壤碳库变化及其原因分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(5): 1109-1120. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH202105002.htm
Liu G D, Li L J, Dai H M, et al. Change in soil carbon pool in Songliao Plain and its cause analysis[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(5): 1109-1120. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH202105002.htm
[6] 宋运红, 张哲寰, 杨凤超, 等. 黑龙江海伦地区垦殖前后典型黑土剖面主要养分元素垂直分布特征[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(6): 543-549. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10243.shtml
Song Y H, Zhang Z H, Yang F C, et al. Vertical distribution of major nutrient elements in typical black soil sections in Hailun, Heilongjiang Province: Before and after reclamation[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(6): 543-549. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10243.shtml
[7] 戴慧敏, 刘凯, 宋运红, 等. 东北地区黑土退化地球化学指示与退化强度[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(6): 510-517. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10239.shtml
Dai H M, Liu K, Song Y H, et al. Black soil degradation and intensity in Northeast China: Geochemical indication[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(6): 510-517. http://manu25.magtech.com.cn/Jweb_dzyzy/CN/abstract/abstract10239.shtml
[8] 卜崇峰, 吴淑芳, 张兴昌, 等. 东北黑土结皮发育过程[J]. 应用生态学报, 2008, 19(2): 357-362. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYSB200802021.htm
Bu C F, Wu S F, Zhang X C, et al. Development process of crust in black soil of Northeast China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2008, 19(2): 357-362. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYSB200802021.htm
[9] 魏丹, 匡恩俊, 迟凤琴, 等. 东北黑土资源现状与保护策略[J]. 黑龙江农业科学, 2016(1): 158-161.
Wei D, Kuang E J, Chi F Q, et al. Status and protection strategy of black soil resources in northeast of China[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2016(1): 158-161.
[10] 韩晓增, 李娜. 中国东北黑土地研究进展与展望[J]. 地理科学, 2018, 38(7): 1032-1041. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX201807004.htm
Han X Z, Li N. Research progress of black soil in Northeast China[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2018, 38(7): 1032-1041. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX201807004.htm
[11] 李骜, 段兴武. 利用黑土层厚度评价东北黑土区土壤生产力——以鹤北小流域为例[J]. 水土保持通报, 2014, 34(1): 154-159. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STTB201401031.htm
Li A, Duan X W. Productivity assessment for black soil region in Northeastern China using black soil thickness: A case study of Hebei watershed[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2014, 34(1): 154-159. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STTB201401031.htm
[12] Gu Z J, Xie Y, Gao Y, et al. Quantitative assessment of soil productivity and predicted impacts of water erosion in the black soil region of northeastern China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 637- 638: 706-716. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.061
[13] Duan X W, Xie Y, Ou T H, et al. Effects of soil erosion on long- term soil productivity in the black soil region of northeastern China [J]. Catena, 2011, 87(2): 268-275. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2011.06.012
[14] 沈波, 范建荣, 潘庆宾, 等. 东北黑土区水土流失综合防治试点工程项目概况[J]. 中国水土保持, 2003(11): 7-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0941.2003.11.004
Shen B, Fan J R, Pan Q B, et al. General situation of pilot project of comprehensive prevention and control of soil and water loss of chernozem region in northeast of China[J]. Soil and Water Conservation in China, 2003(11): 7-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0941.2003.11.004
[15] 刘丙友. 典型黑土区土壤退化及可持续利用问题探讨[J]. 中国水土保持, 2003(12): 28-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0941.2003.12.014
Liu B Y. Approach to issues of soil deterioration and sustainable utilization of typical chernozem region[J]. Soil and Water Conservation in China, 2003(12): 28-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0941.2003.12.014
[16] 于磊, 张柏. 基于GIS的黑土区土壤相对环境容量空间分异特征研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2004, 41(4): 511-516. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2004.04.003
Yu L, Zhang B. Spatial characteristics of environmental capacity in black soil area based on GIS[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2004, 41 (4): 511-516. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2004.04.003
[17] 解运杰, 王岩松, 王玉玺. 东北黑土区地域界定及其水土保持区划探析[J]. 水土保持通报, 2005, 25(1): 48-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-288X.2005.01.013
Xie Y J, Wang Y S, Wang Y X. Defining of chernozem area and zoning of soil and water conservation in northeastern China[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2005, 25(1): 48-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-288X.2005.01.013
[18] 张之一. 黑土开垦后黑土层厚度的变化[J]. 黑龙江八一农垦大学学报, 2010, 22(5): 1-3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2090.2010.05.001
Zhang Z Y. The thickness changes of Ah horizon after the phaeozems cultivated[J]. Journal of Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, 2010, 22(5): 1-3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2090.2010.05.001
[19] 刘慧, 魏永霞. 黑土区土壤侵蚀厚度对土地生产力的影响及其评价[J]. 农业工程学报, 2014, 30(20): 288-296. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2014.20.035
Liu H, Wei Y X. Influence of soil erosion thickness on soil productivity of black soil and its evaluation[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2014, 30(20): 288-296. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2014.20.035
[20] Soil Survey Staff. Keys to soil taxonomy[M]. 12th ed. United States Department of Agriculture, 2014: 1-360.
[21] 中国科学院南京土壤研究所土壤系统分类课题组, 中国土壤系统分类课题研究协作组. 中国土壤系统分类检索[M]. 3版. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社, 2001.
Soil System Classification Group, Nanjing Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China Soil Systematic Classification Research Cooperation Group. Soil systematic classification search in China[M]. 3rd ed. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China Press, 2001.
[22] Fisher J P, Estop-Aragonés C, Thierry A, et al. The influence of vegetation and soil characteristics on active-layer thickness of permafrost soils in boreal forest[J]. Global Change Biology, 2016, 22(9): 3127-3140. doi: 10.1111/gcb.13248
[23] Shi Z, Allison S D, He Y J, et al. The age distribution of global soil carbon inferred from radiocarbon measurements[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2020, 13(8): 555-559. doi: 10.1038/s41561-020-0596-z
[24] Doetterl S, Stevens A, Six J, et al. Soil carbon storage controlled by interactions between geochemistry and climate[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2015, 8(10): 780-783. doi: 10.1038/ngeo2516
[25] Liu X M, Li Q, Liang W J, et al. Distribution of soil enzyme activities and microbial biomass along a latitudinal gradient in farmlands of Songliao Plain, Northeast China[J]. Pedosphere, 2008, 18(4): 431-440. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0160(08)60034-X
[26] Liu X Y, Zhao Y C, Shi X Z, et al. Uncertainty in CENTURY- modelled changes in soil organic carbon stock in the uplands of Northeast China, 1980-2050[J]. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 2019, 113(1): 77-93. doi: 10.1007/s10705-018-9963-1
[27] IPCC. Summary for policymakers[C]//IPCC. Climate change 2021: The physical science basis: Working Group I contribution to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2021.
[28] 任国玉, 初子莹, 周雅清, 等. 中国气温变化研究最新进展[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2005, 10(4): 701-716. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHYH200504001.htm
Ren G Y, Chu Z Y, Zhou Y Q, et al. Recent progresses in studies of regional temperature changes in China[J]. Climatic and Environmental Research, 2005, 10(4): 701-716. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHYH200504001.htm
[29] 《东北区域气候变化评估报告: 2020》编写委员会. 东北区域气候变化评估报告: 2020[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2021.
Editorial Committee for Regional Climate Change Assessment Report of Northeast China: 2020. Regional climate change assessment report of Northeast China: 2020[M]. Beijing: Meteorological Press, 2021. (in Chinese)
[30] Davidson E A, Janssens I A. Temperature sensitivity of soil carbon decomposition and feedbacks to climate change[J]. Nature, 2006, 440 (7081): 165-173. doi: 10.1038/nature04514
[31] Zhou Y, Hartemink A E, Shi Z, et al. Land use and climate change effects on soil organic carbon in north and northeast China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 647: 1230-1238. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.016
[32] 范昊明, 蔡强国, 王红闪. 中国东北黑土区土壤侵蚀环境[J]. 水土保持学报, 2004, 18(2): 66-70. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2004.02.017
Fan H M, Cai Q G, Wang H S. Condition of soil erosion in phaeozem region of Northeast China[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2004, 18(2): 66-70. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-2242.2004.02.017
[33] Liu J T, Han X L, Chen X, et al. Prediction of soil thicknesses in a headwater hillslope with constrained sampling data[J]. Catena, 2019, 177: 101-113. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2019.02.009
[34] Huang D H, Pei M Z, Zhou L L, et al. Identification of sediment sources and exploration of scale effects in the black soil region of Northeast China[J]. Catena, 2020, 195: 104848. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2020.104848
[35] Wang H, Yang S L, Wang Y D, et al. Rates and causes of black soil erosion in Northeast China[J]. Catena, 2022, 214: 106250. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2022.106250
[36] 吴才武, 杨越, 夏建新. 基于RGB的黑土有机质快速测定方法研究[J]. 土壤通报, 2016, 47(4): 853-859. https://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10052-1015625967.htm
Wu C W, Yang Y, Xia J X. Rapid method for estimating organic matter of black soil based on RGB[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2016, 47(4): 853-859. https://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10052-1015625967.htm
[37] 诸莉燕, 毕利东, 柳开楼. 基于图像处理的土壤颜色判别方法研究[J]. 广东农业科学, 2018, 45(12): 125-130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDNY201812022.htm
Zhu L Y, Bi L D, Liu K L. Soil color discrimination method based on image processing[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 45 (12): 125-130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDNY201812022.htm
[38] 陈剑科, 袁大刚, 晏昭敏, 等. 测色仪与中国标准土壤色卡测定土壤颜色比较——以川中丘陵区为例[J]. 土壤学报, 2019, 56(1): 78-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB201901008.htm
Chen J K, Yuan D G, Yan Z M, et al. Comparison between colorimeter and new standard soil colour chart of China in determining Munsell color of soils: A case study of central Sichuan hilly region[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2019, 56(1): 78-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRXB201901008.htm
[39] Wang W, Zhao Y, Zhang T L, et al. Regional soil thickness mapping based on stratified sampling of optimally selected covariates[J]. Geoderma, 2021, 400: 115092. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2021.115092
[40] Zhang S, Liu G, Chen S L, et al. Assessing soil thickness in a black soil watershed in northeast China using random forest and field observations[J]. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 2021, 9(1): 49-57. doi: 10.1016/j.iswcr.2020.09.004
[41] Scarpone C, Schmidt M G, Bulmer C E, et al. Modelling soil thickness in the critical zone for Southern British Columbia[J]. Geoderma, 2016, 282: 59-69. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.07.012
-




 下载:
下载: