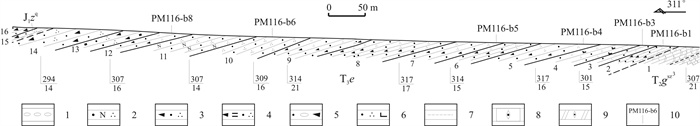
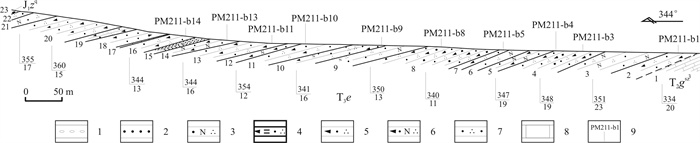
SANDSTONE GRAIN SIZE ANALYSIS OF UPPER TRIASSIC ERQIAO FORMATION IN ZHONGPING AREA, GUIZHOU PROVINCE: Implication of Sedimentary Environment
-
摘要:
通过对贵州中坪地区上三叠统二桥组16件砂岩样品进行粒度分析,结合二桥组砂岩地层所在的区域地质背景,研究砂岩形成时的沉积环境及水动力情况.对砂岩的粒度概率累计曲线、C-M图、粒度特征参数、结构参数散点图解等的分析显示,二桥组砂岩粒度概率累积曲线图具有较好的正态分布特征,频率直方图多呈单峰式;正态概率累计曲线主要为多跳一悬式、一跳一悬式、一跳一悬夹过渡式,主要由悬浮组分和跳跃组分组成,缺少滚动组分.中坪地区上三叠统二桥组从下部到上部处于一个由三角洲平原及前缘相向浅湖相过渡的沉积环境.
Abstract:Through the grain size analysis of 16 sandstone samples from the Upper Triassic Erqiao Formation in Zhongping area of Guizhou Province, combined with the regional geological setting, the paper studies the sedimentary environment and hydrodynamic conditions during the formation of the sandstone. The analysis on the probability cumulative grain size curves, C-M diagram, grain size characteristic parameters and scatter diagram of structure parameters of the sandstone indicates that the probability cumulative grain size curves of the sandstone from Erqiao Formation show good normal distribution, and the frequency histograms mostly show single-peak curves. The normal probability cumulative curves are mainly multi-bouncing population-one suspension population, one bouncing population-one suspension population, and one bouncing population-one suspension population-transitional zone patterns, mainly composed of suspended and jumping components, but lack of rolling components. The Upper Triassic Erqiao Formation in Zhongping area from the lower to the upper part is in a sedimentary environment transitioning from delta plain and delta front facies to shallow lake facies.
-
Key words:
- Upper Triassic /
- Erqiao Formation /
- grain size analysis /
- sedimentary environment /
- Guizhou Province
-

-
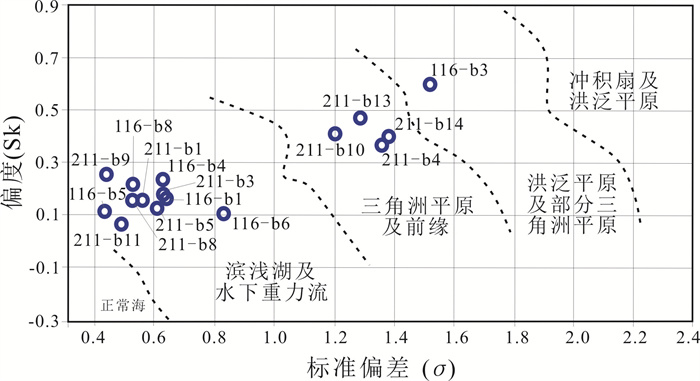
图 7 贵州中坪地区上三叠统二桥组砂岩偏度标准偏差离散图(据文献[27])
Figure 7.
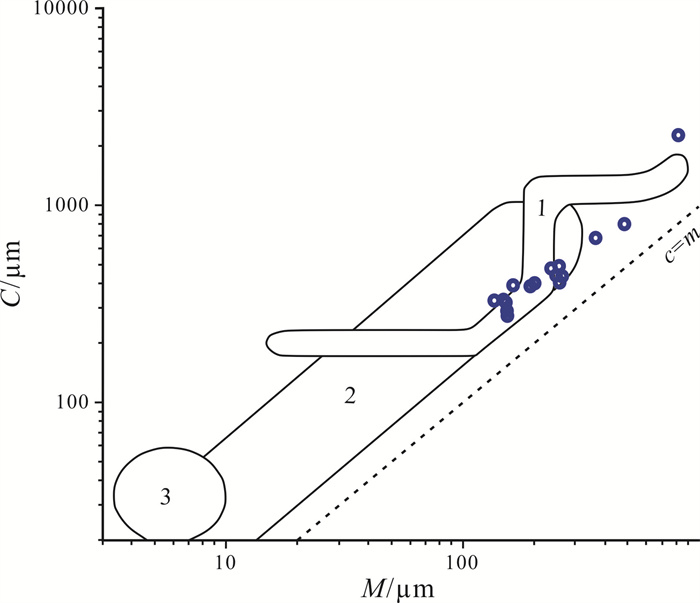
图 8 贵州中坪地区上三叠统二桥组砂岩C-M图(据文献[27])
Figure 8.
表 1 贵州中坪地区上三叠统二桥组砂岩矿物成分统计表
Table 1. Mineral compositions in the sandstone from Upper Triassic Erqiao Formation in Zhongping area, Guizhou Province
序号 样品号 岩性 Qm Qp Q F Lv Ls L Lt 1 PM116-b1 细中粒岩屑石英砂岩 64 8 72 4 - 6 6 8 2 PM116-b3 中粒石英砂岩 85 3 88 3 - - - 3 3 PM116-b4 细中粒岩屑石英砂岩 70 8 78 3 7 7 15 4 PM116-b5 硅质胶结中粒石英砂岩 76 13 89 - 1 - 1 14 5 PM116-b6 硅质胶结含砾不等粒石英砂岩 52 38 90 - - - - 38 6 PM116-b8 硅质胶结中细粒岩屑石英砂岩 77 8 85 - - 5 5 13 7 PM211-b1 硅质胶结中粒岩屑石英砂岩 76 6 82 2 - 5 5 11 8 PM211-b3 细粒岩屑石英砂岩 75 5 80 3 - 7 7 12 9 PM211-b4 细粒岩屑石英砂岩 75 3 78 4 - 8 8 11 10 PM211-b5 硅质胶结细粒岩屑石英砂岩 68 15 83 1 - 5 5 20 11 PM211-b8 中细粒岩屑石英砂岩 70 3 73 5 - 12 12 15 12 PM211-b9 细粒岩屑砂岩 54 7 61 6 - 23 23 30 13 PM211-b10 细粒岩屑石英砂岩 66 4 70 4 - 15 15 19 14 PM211-b11 细粒岩屑石英砂岩 70 3 73 4 1 10 10 13 15 PM211-b13 细中粒长石岩屑砂岩 65 3 68 7 - 13 13 16 16 PM211-b14 中细粒岩屑砂岩 62 3 65 4 - 18 18 21 注:Q—总石英质颗粒;Qm—单晶石英颗粒;Qp—多晶石英质岩屑(燧石等);F—总长石颗粒;L—总非稳定隐晶岩屑;Lv—火山、半深成、变质火山岩屑;Ls—沉积和变质沉积岩屑;Lt—多晶质岩屑颗粒(L+Qp). 表 2 贵州中坪地区上三叠统二桥组砂岩粒度分析统计表
Table 2. Sandstone grain size analysis of the Upper Triassic Erqiao Formation in Zhongping area, Guizhou Province
序号 样品号 岩性 砾石 巨砂 粗砂 中砂 细砂 极细砂 粗粉砂 细粉砂 黏土 Φ≤-1 -1<Φ≤0 0<Φ≤1 1<Φ≤2 2<Φ≤3 3<Φ≤4 4<Φ≤5 5<Φ≤8 Φ > 8 1 PM116-b1 细中粒岩屑石英砂岩 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 46.94% 43.60% 6.31% 0.14% 0.01% 3.00% 2 PM116-b3 中粒石英砂岩 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 56.45% 29.91% 2.60% 0.04% 0.00% 11.00% 3 PM116-b4 细中粒岩屑石英砂岩 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 54.41% 39.09% 1.51% 0.00% 0.00% 5.00% 4 PM116-b5 硅质胶结中粒石英砂岩 0.00% 0.00% 44.04% 52.66% 1.28% 0.02% 0.00% 0.00% 2.00% 5 PM116-b6 硅质胶结含砾不等粒石英砂岩 4.95% 24.60% 53.66% 12.04% 1.72% 0.04% 0.00% 0.00% 3.00% 6 PM116-b8 硅质胶结中细粒岩屑石英砂岩 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 17.59% 68.52% 11.50% 0.39% 0.00% 2.00% 7 PM211-b1 硅质胶结中粒岩屑石英砂岩 0.00% 0.00% 18.12% 64.25% 15.78% 0.84% 0.01% 0.00% 1.00% 8 PM211-b3 细粒岩屑石英砂岩 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 27.59% 55.95% 13.13% 0.32% 0.01% 3.00% 9 PM211-b4 细粒岩屑石英砂岩 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 15.90% 59.01% 17.70% 0.38% 0.01% 7.00% 10 PM211-b5 硅质胶结细粒岩屑石英砂岩 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 9.04% 62.25% 23.94% 0.76% 0.01% 4.00% 11 PM211-b8 中细粒岩屑石英砂岩 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 2.54% 69.68% 23.38% 0.40% 0.00% 4.00% 12 PM211-b9 细粒岩屑砂岩 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 54.15% 40.85% 0.97% 0.03% 0.00% 4.00% 13 PM211-b10 细粒岩屑石英砂岩 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 6.37% 60.25% 27.45% 0.93% 0.00% 5.00% 14 PM211-b11 细粒岩屑石英砂岩 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 4.46% 69.51% 22.86% 0.17% 0.01% 3.00% 15 PM211-b13 细中粒长石岩屑砂岩 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 49.72% 42.73% 2.53% 0.01% 0.00% 5.00% 16 PM211-b14 中细粒岩屑砂岩 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 6.45% 49.39% 34.27% 2.86% 0.03% 7.00% 表 3 贵州中坪地区上三叠统二桥组砂岩粒度参数表
Table 3. Sandstone grain size parameters of the Upper Triassic Erqiao Formation in Zhongping area, Guizhou Province
序号 样品号 岩性 Mz σ Sk Kg Y1 Y2 Y3 1 PM116-b1 细中粒岩屑石英砂岩 2.07 0.63 0.17 1.07 -3.64547616 8.1412173 80.06498679 2 PM116-b3 中粒石英砂岩 2.07 1.51 0.60 3.67 -22.0201246 24.0381537 211.5944169 3 PM116-b4 细中粒岩屑石英砂岩 1.97 0.62 0.24 1.62 -3.88118016 11.4563438 78.94578004 4 PM116-b5 硅质胶结中粒石英砂岩 1.08 0.43 0.12 1.07 -1.83740736 7.1757583 49.73243659 5 PM116-b6 硅质胶结含砾不等粒石英砂岩 0.30 0.82 0.11 1.30 -6.24421536 7.5665248 69.37489984 6 PM116-b8 硅质胶结中细粒岩屑石英砂岩 2.43 0.52 0.16 1.10 -2.39106656 8.5433958 77.20693864 7 PM211-b1 硅质胶结中粒岩屑石英砂岩 1.49 0.55 0.16 1.02 -2.942486 7.4288335 64.60200475 8 PM211-b3 细粒岩屑石英砂岩 2.37 0.62 0.18 1.00 -3.50339216 8.0595378 84.12071404 9 PM211-b4 细粒岩屑石英砂岩 2.61 1.35 0.37 3.78 -16.75133 23.6459675 185.8141358 10 PM211-b5 硅质胶结细粒岩屑石英砂岩 2.71 0.60 0.13 1.15 -2.942098 8.771976 86.934213 11 PM211-b8 中细粒岩屑石英砂岩 2.74 0.52 0.22 1.11 -2.59576456 9.2239198 83.14591864 12 PM211-b9 细粒岩屑砂岩 2.00 0.43 0.26 1.28 -2.24994936 9.8935133 66.66855859 13 PM211-b10 细粒岩屑石英砂岩 2.78 1.20 0.41 3.37 -13.588138 22.022051 164.065767 14 PM211-b11 细粒岩屑石英砂岩 2.72 0.48 0.07 1.07 -1.52116056 8.0040718 77.48842164 15 PM211-b13 细中粒长石岩屑砂岩 2.05 1.28 0.47 3.70 -15.8013698 23.5659238 166.7618964 16 PM211-b14 中细粒岩屑砂岩 2.91 1.37 0.40 2.83 -17.3319842 19.0143953 194.6279438 -
[1] 刘宝珺, 张锦泉. 沉积成岩作用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1992: 65-92.
Liu B J, Zhang J Q. Sedimentary diagenesis[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1992: 65-92. (in Chinese)
[2] 赵澄林. 沉积学原理[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2001: 1-214.
Zhao C L. Principles of sedimentology[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2001: 1-214.
[3] 姜在兴. 沉积学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2003: 136-152.
Jiang Z X. Sedimentology[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2003: 136-152. (in Chinese)
[4] 成都地质学院陕北队. 沉积岩(物)粒度分析及其应用[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1978: 1-133.
Shanbei Team of Chengdu College of Geology. Grain size analysis and application for sediments[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1978: 1-133. (in Chinese)
[5] 张帅军. 西藏岗玛日地区下三叠统康鲁组砂岩粒度分析及环境意义[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学, 2013.
Zhang S J. Sandstone grain size analysis and environmental significance of Lower Triassic Kanglu Formation, Gangmari region, Xizang[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2013.
[6] 丁旭林. 粒度分析与重矿物组合的地质应用[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2012, 12(14): 3439-3442. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2012.14.033
Ding X L. Geologic application of grain size analysis and heavy mineral assemblage[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2012, 12(14): 3439-3442. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2012.14.033
[7] Weiss E L, Frock H N. Rapid analysis of particle size distributions by laser light scattering[J]. Powder Technology, 1976, 14(2): 287-293. doi: 10.1016/0032-5910(76)80077-0
[8] 肖晨曦. 粒度分析及其在沉积学中应用研究[J]. 新疆师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 25(3): 118-123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSZ200603034.htm
Xiao C X. The research summary of grain size analysis and its application in the sedimentation[J]. Journal of Xinjiang Normal University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2006, 25(3): 118-123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSZ200603034.htm
[9] 贵州省地质矿产局. 贵州省区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1987: 76-135.
Guizhou Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources. Regional geology of Guizhou Province[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1987: 76-135. (in Chinese)
[10] 贵州省地质矿产局. 贵州省岩石地层[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1997: 136-201.
Guizhou Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources. Stratigraphy (lithostratic) of Guizhou Province[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1997: 136-201.
[11] 孙平原, 何碧, 赵飞, 等. 贵州乌蒙山黔西地区二叠系玄武岩地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2019, 19(12): 41-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201912006.htm
Sun P Y, He B, Zhao F, et al. Geochemical characteristics and their geological significance of Permian basalt rocks in Qianxi area, Wumengshan of Guizhou Province[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2019, 19(12): 41-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201912006.htm
[12] 何碧, 张向文, 赵飞, 等. 贵州黔西官坝地区二叠系-三叠系地质界面黏土岩的火山岩特征、LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(5): 1028-1042. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ202005015.htm
He B, Zhang X W, Zhao F, et al. Volcanic characteristics, LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb ages of claystone at the Permian-Triassic boundary, Guanba area in Guizhou Province, South China and the geological implications[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(5): 1028-1042. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ202005015.htm
[13] 王宁祖, 张向文, 何碧, 等. 贵州省黔西县大寨地区中三叠统关岭组绿豆岩锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 矿物岩石, 2019, 39(1): 82-91. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS201901010.htm
Wang N Z, Zhang X W, He B, et al. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry of the mung bean rocks of the Middle Triassic Guanling Formation in Dazhai area of Qianxi County, Guizhou Province[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 2019, 39(1): 82-91. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS201901010.htm
[14] 乔卫涛, 陈仁, 胡歆睿, 等. 贵州开阳地区澄江组第二段砂岩粒度分析与沉积环境[J]. 贵州地质, 2020, 37(1): 59-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZDZ202001009.htm
Qiao W T, Chen R, Hu X R, et al. Grain-size analysis and depositional environment of the second member of Chengjiang Formation at Kaiyang area of Guizhou Province[J]. Guizhou Geology, 2020, 37(1): 59-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZDZ202001009.htm
[15] 陈逵. 元坝地区须家河组储层岩石学特征和图像法粒度分析研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2014.
Chen K. Reservoir petrology characteristics study and image method grain-size analysis of Xujiahe Formation in Yuanba area[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2014.
[16] Folk R L, Ward W C. Brazos River bar: A study in the significance of grain size parameters[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 1957, 27(1): 3-26. doi: 10.1306/74D70646-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D
[17] Visher G S. Grain size distributions and depositional processes[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 1969, 39(3): 1074-1106.
[18] 王立亭. 试论黔西北及邻区非海相三叠系/侏罗系界线[J]. 贵州地质, 2002, 19(3): 175-178, 162. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZDZ200203005.htm
Wang L T. Initial discussion on the boundary of the Triassic-Jurassic of the non-marine facies in Northwest Guizhou and its adjacent areas[J]. Guizhou Geology, 2002, 19(3): 175-178, 162. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZDZ200203005.htm
[19] 周冰洋, 赵兵, 孙剑, 等. 贵州大方地区二桥组地层特征及沉积相分析[J]. 地质学刊, 2017, 41(1): 46-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSDZ201701005.htm
Zhou B Y, Zhao B, Sun J, et al. Stratigraphic features and sedimentary facies analysis of the Erqiao Formation in the Dafang area of Guizhou Province[J]. Journal of Geology, 2017, 41(1): 46-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSDZ201701005.htm
[20] 周冰洋. 贵州大方地区中-晚三叠世地层划分对比及沉积相分析[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2017.
Zhou B Y. Stratigraphic division and comparison and sedimentary facies analysis of Middle-Late Triassic in Dafang County of Guizhou Province[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2017.
[21] 胡阳, 龚晓波, 廖阮颖子. 重庆长寿地区上三叠统地层特征研究[J]. 四川有色金属, 2020, 29(4): 29-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ACJS202004010.htm
Hu Y, Gong X B, Liao R Y Z. Stratigraphic characteristics of upper Triassic in Changshou area of Chongqing[J]. Sichuan Nonferrous Metals, 2020, 29(4): 29-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ACJS202004010.htm
[22] 孙建勋, 吴亮, 肖长源, 等. 黔北普宜地区晚三叠世二桥组砂岩碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄、重矿物分析及地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2022, 96(3): 824-839. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202203006.htm
Sun J X, Wu L, Xiao C Y, et al. Implications of detrital zircon U-Pb ages and analysis of heavy minerals from sandstone of the Late Triassic Erqiao Formation in Puyi area, North Guizhou[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2022, 96(3): 824-839. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202203006.htm
[23] 王云飞. 抚仙湖现代湖泊沉积物中海绿石的发现及成因的初步研究[J]. 科学通报, 1983(22): 1388-1392. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB198322011.htm
Wang Y F. the Discovery and Preliminary study on genesis of glauconite in modern lake sediments of Fuxian Lake[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1983(22): 1388-1392. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB198322011.htm
[24] 朱政源, 董凌峰, 于航, 等. 海绿石的成因与应用[J]. 科技创新与应用, 2015(33): 16-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CXYY201533008.htm
Zhu Z Y, Dong L F, Yu H, et al. Genesis and application of glauconite[J]. Technology Innovation and Application, 2015(33): 16-18. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CXYY201533008.htm
[25] 吴龙, 宗维, 杜小峰, 等. 鄂西恩施白垩纪盆地跑马岗组砂砾岩粒度分析[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2019, 33(2): 164-169. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK201902004.htm
Wu L, Zong W, Du X F, et al. Grain size analysis of sand-conglomerate of Paomagang Formation in Enshi Cretaceous basin, western Hubei Province[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2019, 33(2): 164-169. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK201902004.htm
[26] Friedman G M. Dynamic processes and statistical parameters compared for size frequency distribution of beach and river sands[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 1967, 37(2): 327-354.
[27] Passega R. Grain size representation by CM patterns as a geologic tool[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 1964, 34(4): 830-847.
-



 下载:
下载: