Climate change since Holocene recorded in Mishan black soil profile of Heilongjiang Province
-
摘要:
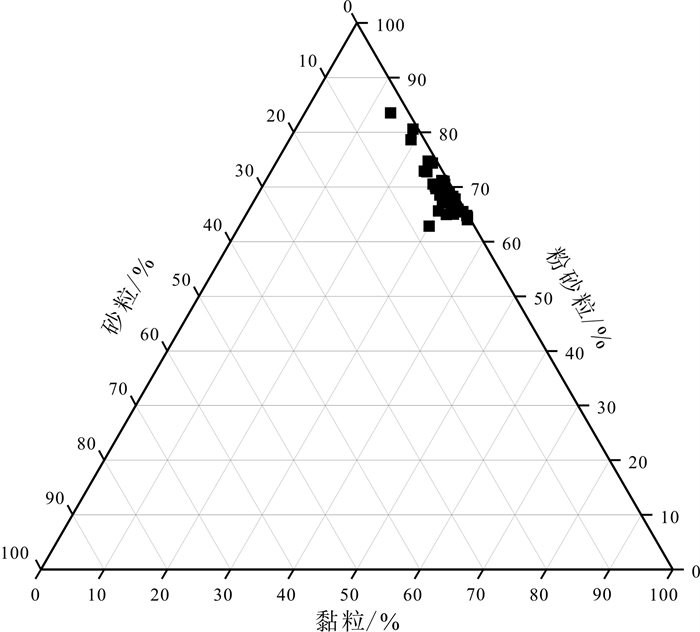
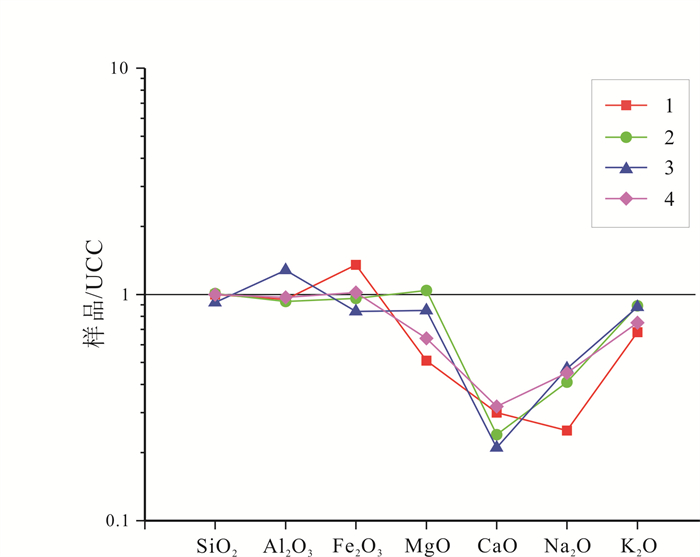
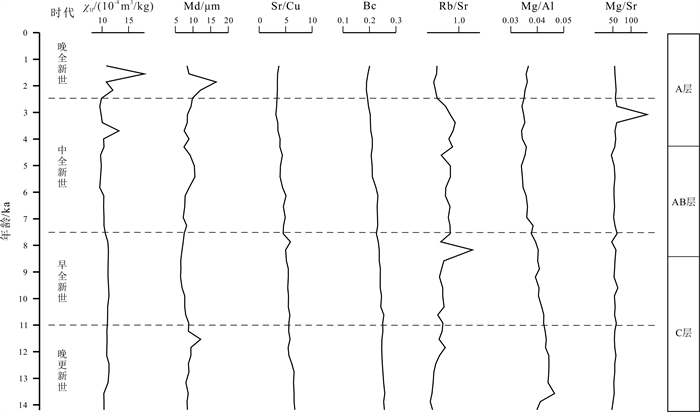
对密山黑土剖面(0~1.42 m)开展年代学、磁化率、粒度和元素地球化学研究, 结果表明, 密山市黑土剖面沉积物以粉砂为主, 占比约70%;年龄曲线显示密山市黑土的沉积速率为9.62 cm/ka.元素地球化学数据显示, 密山黑土剖面的主要常量元素组合特征与其他典型风成堆积物相似, 上部陆壳(UCC)标准化曲线的变化趋势基本一致, 表明密山黑土成土母质可能为风成成因.多指标综合分析表明, 密山黑土剖面自全新世以来的气候变化经历了3个阶段: 早全新世的升温变暖、中全新世的温暖湿润和晚全新世降温变凉.
Abstract:The paper studies the geochronology, magnetic susceptibility, particle size and element geochemistry of black soil profile(0-1.42 m) in Mishan City. The results show that the sediments of black soil profile are mainly silt, accounting for about 70%, and the deposition rate of black soil is 9.62 cm/ka according to the age curve. The element geochemical data reveals that the major element combination characteristics of Mishan black soil profile are similar to those of other typical eolian deposits, and the change trend of UCC-normalized curves is basically the same, indicating the parent material of Mishan black soil may be of aeolian origin. The multi-index comprehensive analysis shows that the climate change of Mishan black soil profile since Holocene has experienced three stages, i.e. temperature rising in the Early Holocene, warm and humid in the Middle Holocene and cooling down in the Late Holocene.
-

-
表 1 密山黑土土壤剖面描述
Table 1. Description of Mishan black soil profile
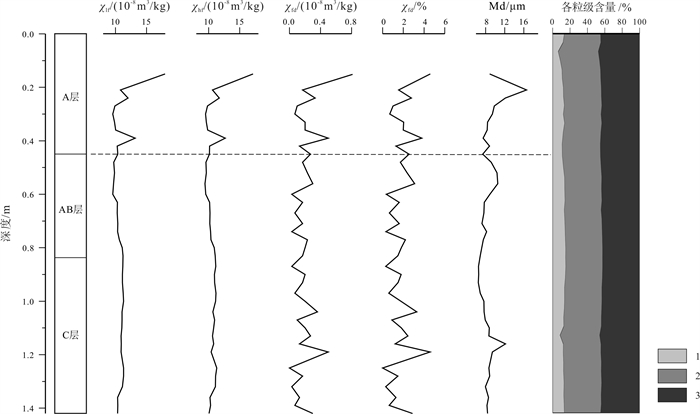
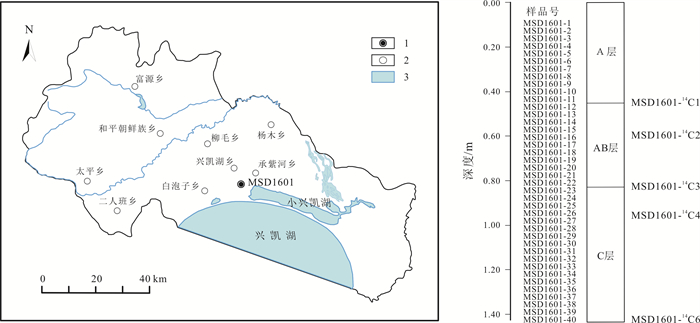
距表层深度/cm 分层情况 详细描述 0~45 A(黑土层) 黑色黏土,团粒结构,略为湿润,紧实,可见大量根系 45~83 AB 灰黑色-灰褐色黏土,团粒结构,略为湿润,略为紧实,未见根系 83~142 C 黄褐色黏土,团块结构,湿润,紧实,未见根系 表 2 密山黑土土壤剖面14C测年数据
Table 2. 14C dating data of Mishan black soil profile
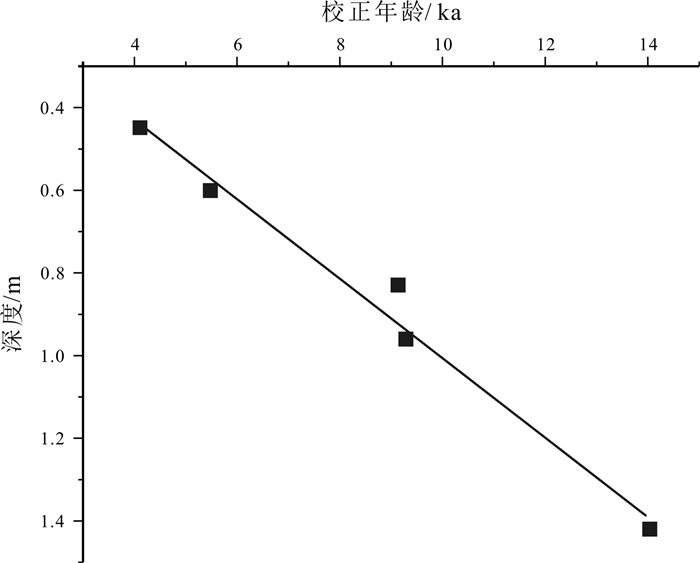
样品编号 实验室编号 深度/m 测年材料 年龄*/a 校正年龄#/cal.a MSD1601-14C1 22110213OCSP 0.45 有机碳 3780±30 4127±118 MSD1601-14C2 22110214OCSP 0.60 有机碳 4675±30 5447±126 MSD1601-14C3 22110215OCSP 0.83 有机碳 8150±50 9139±147 MSD1601-14C4 22110216OCSP 0.96 有机碳 8305±50 9290±154 MSD1601-14C5 22110218OCSP 1.42 有机碳 12130±80 13969±214 测试单位: 中国地质科学院水文地质环境地质研究所. *运用样品相对于现代(1950年)大气14C活度的分数(FM)和半衰期5 568 a计算的传统14C年龄; #树轮校正的14C年龄. 表 3 密山黑土剖面样品和其他典型风成堆积物的常量元素含量
Table 3. Contents of major elements in Mishan black soil profile and other typical aeolian deposits
剖面名称 SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 K2O Na2O MgO CaO 密山黑土剖面 66.20 14.42 6.77 2.30 0.98 1.12 1.24 洛川黄土 66.40 14.20 4.81 3.01 1.61 2.29 1.02 荒山黄土 60.85 19.47 4.22 3.00 1.84 1.88 0.87 海伦黑土 66.05 14.67 5.10 2.56 1.75 1.40 1.33 UCC 66.00 15.20 5.00 3.40 3.90 2.20 4.20 含量单位: %. 表 4 密山黑土剖面部分元素分析结果
Table 4. Element analysis results of Mishan black soil profile
样品号 深度/cm 主量元素含量/% 微量元素含量/10-6 Al2O3 MgO Na2O K2O Cu Rb Sr MSPM1601-H1 0-15 15.1 1.10 0.91 2.11 32.9 97.0 122 MSPM1601-H2 15-18 14.8 1.06 0.85 2.03 33.1 90.9 115 MSPM1601-H3 18-21 14.9 1.08 0.83 2.00 33.3 87.2 114 MSPM1601-H4 21-24 15.1 1.07 0.81 2.03 31.5 84.9 109 MSPM1601-H5 24-27 15.0 1.05 0.83 2.06 32.9 88.5 111 MSPM1601-H6 27-30 15.1 1.04 0.83 2.15 31.1 89.8 103 MSPM1601-H7 30-33 15.1 1.06 0.84 2.23 14.0 40.6 44.2 MSPM1601-H8 33-36 15.0 1.06 0.84 2.23 30.0 102 105 MSPM1601-H9 36-39 14.9 1.02 0.85 2.21 31.3 105 111 MSPM1601-H10 39-42 15.0 1.03 0.88 2.28 27.1 97.3 107 MSPM1601-H11 42-45 14.9 1.07 0.88 2.27 29.8 110 117 MSPM1601-H12 45-48 15.1 1.07 0.87 2.25 32.1 117 141 MSPM1601-H13 48-52 15.0 1.02 0.87 2.28 28.5 106 115 MSPM1601-H14 52-56 15.0 1.03 0.87 2.28 28.4 103 112 MSPM1601-H15 56-60 14.7 1.02 0.96 2.35 26.2 101 116 MSPM1601-H16 60-63 14.7 1.05 0.96 2.44 23.5 104 119 MSPM1601-H17 63-67 14.7 1.07 0.96 2.41 25.7 108 118 MSPM1601-H18 67-71 14.5 1.04 0.98 2.37 24.6 109 121 MSPM1601-H19 71-74 14.4 1.11 0.95 2.38 26.1 110 120 MSPM1601-H20 74-77 14.6 1.10 0.94 2.38 24.0 99.9 109 MSPM1601-H21 77-80 14.5 1.14 0.98 2.39 24.9 122 147 MSPM1601-H22 80-83 14.2 1.15 0.97 2.39 23.8 134 119 MSPM1601-H23 83-87 14.2 1.14 1.00 2.39 24.1 106 124 MSPM1601-H24 87-90 14.1 1.16 1.03 2.38 23.3 107 128 MSPM1601-H25 90-93 14.2 1.12 1.02 2.41 23.0 103 126 MSPM1601-H26 93-97 14.1 1.15 1.02 2.39 20.2 92.2 109 MSPM1601-H27 97-100 14.1 1.14 1.04 2.42 22.8 107 126 MSPM1601-H28 100-104 14.2 1.18 1.02 2.41 23.1 109 127 MSPM1601-H29 104-107 14.0 1.19 1.15 2.41 22.6 105 130 MSPM1601-H30 107-110 14.0 1.19 1.09 2.41 21.5 103 121 MSPM1601-H31 110-113 13.9 1.20 1.08 2.41 23.5 111 131 MSPM1601-H32 113-116 13.9 1.21 1.07 2.36 23.0 109 134 MSPM1601-H33 116-119 14.1 1.21 1.07 2.40 24.1 115 132 MSPM1601-H34 119-122 13.9 1.23 1.08 2.36 22.7 104 128 MSPM1601-H35 122-125 13.5 1.20 1.09 2.28 21.2 103 131 MSPM1601-H36 125-128 13.6 1.21 1.12 2.30 20.1 101 132 MSPM1601-H37 128-132 13.6 1.20 1.12 2.33 21.3 105 138 MSPM1601-H38 132-136 13.3 1.24 1.19 2.24 21.0 104 139 MSPM1601-H39 136-139 13.7 1.13 1.16 2.31 20.4 98.2 134 MSPM1601-H40 139-142 14.0 1.12 1.18 2.41 21.3 108 143 -
[1] 程峰. 中国南方更新世红土沉积物的特征及其物源研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2018.
Cheng F. Study on characteristics and source provenance of the Pleistocene red earth sediments in southern China[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2018.
[2] An Z S, Liu T, Lu Y C, et al. The long-term paleomonsoon variation recorded by the loess-paleosol sequence in central China[J]. Quaternary International, 1990, 7/8: 91-95.
[3] Ding Z L, Xiong S F, Sun J M, et al. Pedostratigraphy and paleomagnetism of a ~7.0 Ma eolian loess-red clay sequence at Lingtai, Loess Plateau, north-central China and the implications for paleomonsoon evolution[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1999, 152(1/2): 49-66.
[4] Sun J M. Provenance of loess material and formation of loess deposits on the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 203(3/4): 845-859.
[5] Powlson D S, Gregory P J, Whalley W R, et al. Soil management in relation to sustainable agriculture and ecosystem services[J]. Food Policy, 2011, 36(S1): S72-S87.
[6] 杜贯新. 松嫩黑土区西北部多流域黑土地球化学及重金属累积特征[D]. 大庆: 东北石油大学, 2023.
Du G X. The geochemical and heavy metal accumulation characteristics of black soil in the northwest of Songnen black soil region were studied [D]. Daqing: Northeast Petroleum University, 2023.
[7] 宋运红, 刘凯, 戴慧敏, 等. 松嫩平原东部典型黑土剖面孢粉组合、时代及其对古气候的指示[J]. 地质通报, 2022, 41(9): 1528- 1538.
Song Y H, Liu K, Dai H M, et al. Palynological assemblages of typical black soil profile in the eastern Songliao Plain and their age and its implication for paleoclimatic[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2022, 41(9): 1528-1538.
[8] Guan H C, Zhu C, Zhu T X, et al. Grain size, magnetic susceptibility and geochemical characteristics of the loess in the Chaohu Lake Basin: Implications for the origin, palaeoclimatic change and provenance[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016, 117: 170- 183.
[9] 肖春晖, 王永红, 林间. 近1 Ma以来帕里西维拉海盆沉积物物源和古气候: 粒度和黏土矿物特征的指示[J]. 沉积学报, 2022, 40(2): 508-524.
Xiao C H, Wang Y H, Lin J. Provenance and Paleoclimate ofsediments in the Parece Vela Basin in past 1 Ma: Inferences from grain-size and clay mineral distribution[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2022, 40(2): 508-524.
[10] 王兆夺, 黄春长, 庞奖励, 等. 甘肃庄浪全新世黄土土壤物源分析及古气候恢复重建[J]. 沉积学报, 2020, 38(4): 781-789.
Wang Z D, Huang C C, Pang J L, et al. Provenance analysis and reconstruction of the climate change for the Holocene loess profile in the Zhuanglang County of Gansu Province, China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2020, 38(4): 781-789.
[11] 梁爱民, 屈建军, 董治宝, 等. 库姆塔格沙漠沉积物粒度端元特征及其物源启示[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(2): 33-42.
Liang A M, Qu J J, Dong Z B, et al. The characteristic of grain size end members in Kumtagh Desert and its implication for sediment source[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(2): 33-42.
[12] 胡凯程, 贾佳, 胡忠行, 等. 湿润气候条件下温度对土壤磁化率影响的再认识[J]. 第四纪研究, 2022, 42(2): 461-471.
Hu K C, Jia J, Hu Z X, et al. New insight into the temperature dependence of pedogenic magnetic susceptibility in humid climate region[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2022, 42(2): 461-471.
[13] 刘硕, 迟云平, 郝冬梅, 等. 中更新世以来松嫩平原夏季风演化: 来自哈尔滨黄土的磁化率、地球化学和总有机碳记录[J]. 地质科学, 2021, 56(4): 1279-1298.
Liu S, Chi Y P, Hao D M, et al. Evolution of summer monsoon in Songnen Plain since Middle Pleistocene: Magnetic susceptibility, geochemistry and total organic carbon records from Harbin loess[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2021, 56(4): 1279-1298.
[14] 邱世藩, 欧阳婷萍, 朱照宇, 等. 中国东部表层土壤磁化率特征及其指示意义[J]. 地球科学--中国地质大学学报, 2014, 39(10): 1554-1564.
Qiu S F, Ouyang T P, Zhu Z Y, et al. Magnetic susceptibility characteristics of weathering-Pedogenic topsoil along east part of China and its significance[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2014, 39(10): 1554-1564.
[15] 刘凯, 戴慧敏, 刘国栋, 等. 基于主成分聚类法的典型黑土区土壤地球化学分类[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(5): 1132-1140.
Liu K, Dai H M, Liu G D, et al. Geochemical classification of the soil in a typical black soil area using the principal component analysis combined with K-means clustering algorithm[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(5): 1132-1140.
[16] 戴慧敏, 刘凯, 宋运红, 等. 东北地区黑土退化地球化学指示与退化强度[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(6): 510-517. doi: 10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2025.01.002
Dai H M, Liu K, Song Y H, et al. Black soil degradation and intensity in Northeast China: Geochemical indication[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(6): 510-517. doi: 10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2025.01.002
[17] 韩晓萌, 戴慧敏, 梁帅, 等. 黑龙江省拜泉地区典型黑土剖面元素地球化学特征及其环境指示意义[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(6): 556-563. doi: 10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2025.01.002
Han X M, Dai H M, Liang S, et al. Element geochemistry of the typical black soil sections in Baiquan area, Heilongjiang Province: Environmental implication[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29 (6): 556-563. doi: 10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2025.01.002
[18] 王攀, 张培新, 杨振京, 等. 靖边黄土剖面记录的末次冰期以来的气候变化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019, 39(3): 162-170.
Wang P, Zhang P X, Yang Z J, et al. Climate change since the last glacial stage recorded in Jingbian loess section[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2019, 39(3): 162-170.
[19] 吴鹏, 谢远云, 康春国, 等. 哈尔滨荒山黄土的成因--粒度、地球化学、磁化率、沉积和地貌特征的整合记录[J]. 地球学报, 2020, 41(3): 420-430.
Wu P, Xie Y Y, Kang C G, et al. The genesis of Huangshan loess in Harbin: Integrated evidence from grain size, geochemistry, magnetization, sedimentation and landform[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2020, 41 (3): 420-430.
[20] 陈骏, 季峻峰, 仇纲, 等. 陕西洛川黄土化学风化程度的地球化学研究[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 1997, 27(6): 531-536.
Chen J, Ji J F, Qiu G, et al. Geochemical studies on the intensity of chemical weathering in Luochuan loess-paleosol sequence, China[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 1998, 41(3): 235-241.
[21] 宋运红, 杨凤超, 刘凯, 等. 黑龙江省海伦地区黑土剖面常量元素地球化学特征及其对物源的指示意义[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46 (5): 1105-1113.
Song Y H, Yang F C, Liu K, et al. Geochemical characteristics of major elements in the black soil profiles of the Hailun area, Heilongjiang Province and their implications for provenance[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(5): 1105-1113.
[22] 刘青松, 邓成龙. 磁化率及其环境意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 2009, 52(4): 1041-1048.
Liu Q S, Deng C L. Magnetic susceptibility and its environmental significances[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2009, 52(4): 1041-1048.
[23] Wang X Y, Yi S W, Lu H Y, et al. Aeolian process and climatic changes in loess records from the northeastern Tibetan Plateau: Response to global temperature forcing since 30 ka[J]. Paleoceanography, 2015, 30(6): 612-620.
[24] Lu H Y, Wang X Y, Ma H Z, et al. The Plateau monsoon variation during the past 130 kyr revealed by loess deposit at northeast Qinghai-Tibet (China)[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2004, 41 (3/4): 207-214.
[25] 陶慧, 王建华, 陈慧娴, 等. 伶仃洋ZK19孔全新统有机物δ13C和C/N值特征及东亚季风演变记录[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 58(3): 1-12.
Tao H, Wang J H, Chen H X, et al. Characteristics of δ13C and C/N in the Holocene organic material of borehole ZK19 in Lingdingyang Bay and the records of east Asian monsoon variation[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2019, 58(3): 1-12.
[26] 李拓宇, 莫多闻, 朱高儒, 等. 晋南全新世黄土剖面常量元素地球化学特征及其古环境意义[J]. 地理研究, 2013, 32(8): 1411- 1420.
Li T Y, Mo D W, Zhu G R, et al. Geochemical characteristics of major elements and its paleoenvironmental significance of Holocene loess profile in southern Shanxi, China[J]. Geographical Research, 2013, 32(8): 1411-1420.
[27] 王丰年, 李保生, 蒋树萍, 等. 查格勒布鲁剖面记录的OIS3a巴丹吉林沙漠季风气候变化[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2017, 31(6): 97-102.
Wang F N, Li B S, Jiang S P, et al. Monsoonal climate changes from the Chagelebulu section of the Badain Jaran Desert in China during the OIS3a[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2017, 31(6): 97-102.
[28] 李福春, 谢昌仁, 潘根兴. 南京老虎山黄土剖面的磁化率及Rb和Rb/Sr对古气候的指示意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2002, 22 (4): 47-52.
Li F C, Xie C R, Pan G X. Paleoclimatic implication of distribution of Rb, Rb/Sr and magnetic susceptibility in loess and paleosols from Laohushan profile, Nanjing[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2002, 22(4): 47-52.
[29] 刘阳, 邵铁全, 刘云焕, 等. 陕南西乡寒武纪梅树村期微古生物群产出层位的地球化学特征及古环境和古气候条件研究[J]. 地质论评, 2022, 68(1): 309-322.
Liu Y, Shao T Q, Liu Y H, et al. Geochemical characteristics and palaeo-environment and palaeoclimate conditions of Early Cambrian Meishucun micropalaeontological strata in Xixiang, southern Shaanxi [J]. Geological Review, 2022, 68(1): 309-322.
[30] 张培新, 杨振京, 王攀, 等. 陕西靖边三道沟黄土剖面特征及古气候意义[C]//中国古生物学会孢粉学分会十届一次学术年会论文摘要集. 赤峰: 中国古生物学会孢粉学分会, 2017: 42.
Zhang P X, Yang Z J, Wang P, et al. Profile characteristics and paleoclimatic significance of Sandaogou loess in Jingbian, Shaanxi [C]//Abstracts of the 10th Annual Conference of Palynology Branch of Paleontological Society of China. Chifeng: Palynology Branch of Paleontological Society of China, 2017: 42. (in Chinese)
[31] 周家兴, 吴利杰, 于娟, 等. 铜川地区11.4~1.5 ka B.P. 期间黄土地球化学风化特征及其古气候意义[J]. 地球与环境, 2019, 47(1): 64-73.
Zhou J X, Wu L J, Yu J, et al. Characteristics of geochemical weathering of loess in the Tongchuan area during 11.4-1.5 ka B.P. and its Paleoclimatic implications[J]. Earth and Environment, 2019, 47(1): 64-73.
[32] Yuan D X, Cheng H, Edwards R L, et al. Timing, duration, and transitions of the last interglacial Asian monsoon[J]. Science, 2004, 304(5670): 575-578.
[33] Wang Y J, Cheng H, Edwards R L, et al. The Holocene Asian monsoon: Links to solar changes and North Atlantic climate[J]. Science, 2005, 308(5723): 854-857.
[34] 赵超, 李小强, 周新郢, 等. 北大兴安岭地区全新世植被演替及气候响应[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2016, 46(6): 870-880.
Zhao C, Li X Q, Zhou X Y, et al. Holocene vegetation succession and responses to climate change in the northern sector of Northeast China[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2016, 59(7): 1390-1400.
[35] 祁福利, 张孟才, 鲁守刚, 等. 三江平原地区第四纪地质[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2015: 22-23.
Qi F L, Zhang M C, Lu S G, et al. Quaternary geology in Sanjiang Plain[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2015: 22-23. (in Chinese)
[36] Wang H, Stumpf A J, Kumar P. Radiocarbon and stable carbon isotopes of labile and inert organic carbon in the critical zone observatory in Illinois, USA[J]. Radiocarbon, 2018, 60(3): 989- 999.
[37] 崔静怡, 郭利成, 陈雨露, 等. 松嫩平原全新世黑土14C年龄-深度关系空间格局[J]. 第四纪研究, 2021, 41(5): 1332-1341.
Cui J Y, Guo L C, Chen Y L, et al. Spatial distribution of 14C age and depth of mollisol sections in the Songnen Plain during the Holocene[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2021, 41(5): 1332-1341.
-



 下载:
下载: