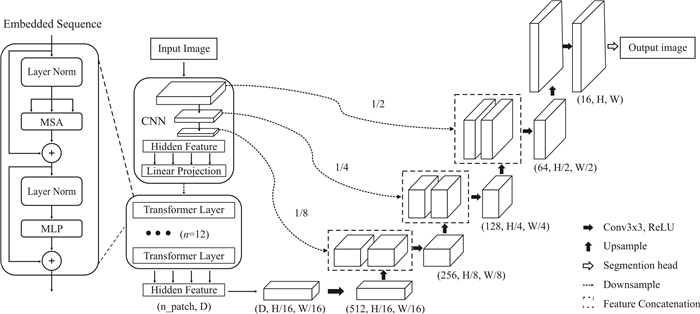
Intelligent characterization of particles and pores in thin slice images of tight reservoirs based on deep learning algorithm
-
摘要:
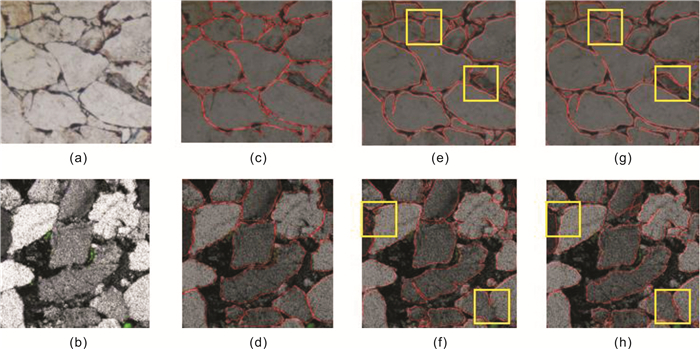
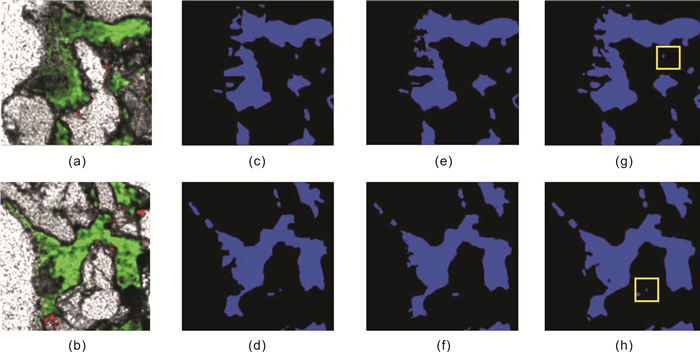
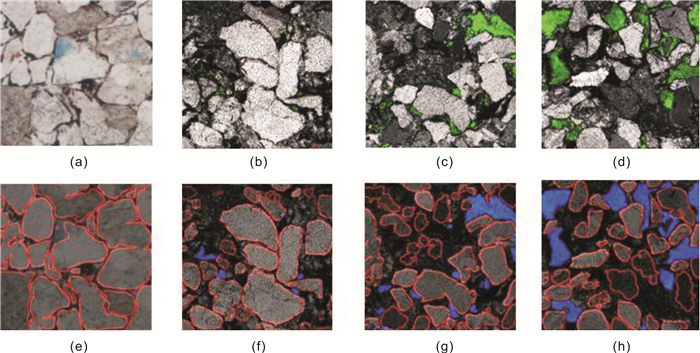
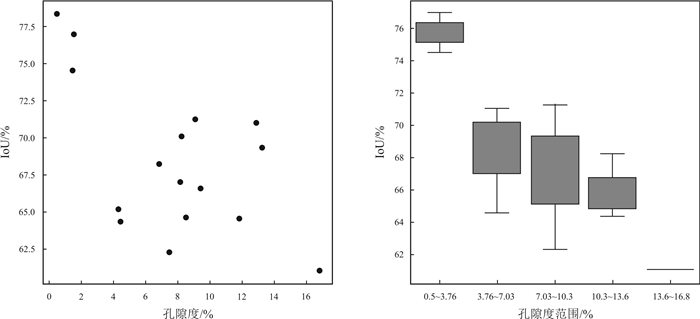
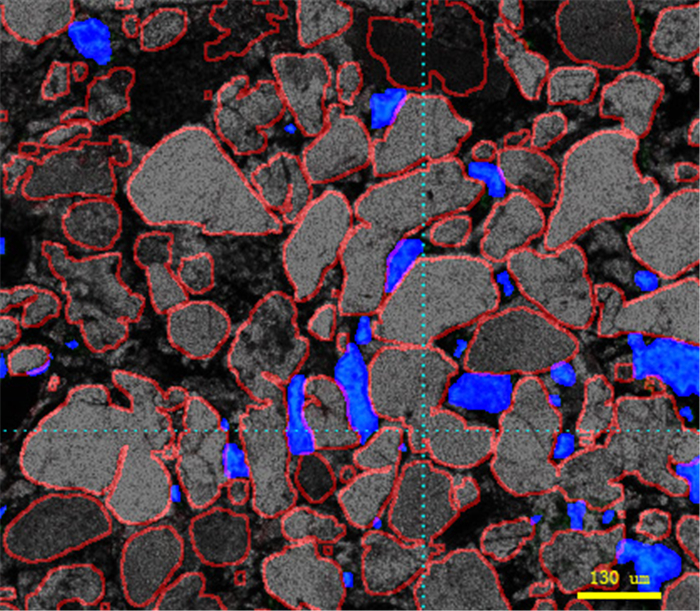
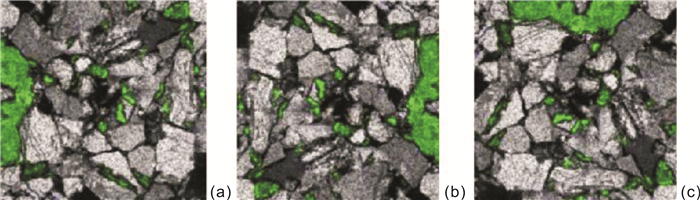
在致密砂岩储层薄片图像分析中, 针对传统方法的准确率不足和任务繁重等问题, 采用结合了Transformer和卷积神经网络的TransUnet及Unet神经网络, 用于颗粒、孔隙特征的高效表征.Unet、TransUnet在颗粒特征表征方面表现优异, 实验数据显示Unet的交并比达到79.6%, 召回率为87.3%, 精确率为89.7%, TransUnet的交并比达到71.3%, 召回率为86.1%, 精确率为82.5%.实验图像显示, 在局部像素差异较大的情况, TransUnet优于传统方法, 证明其在紧密复杂颗粒分割的有效性.Unet在孔隙特征方面也表现出高效表征效果, 其交并比、召回率和精确率分别为82.4%、84.3%和95.3%.实验还表明, 虽然面孔率影响交并比, 但模型整体仍保持高效率和准确性.这些结果充分说明深度学习方法, 在复杂致密储层薄片图像的精确分割中效果显著, 为非常规致密储层研究提供新思路, 展现了其在地质学领域应用的巨大潜力.
Abstract:In the thin-section image analysis of tight sandstone reservoir, to solve the problems such as low accuracy and heavy work of traditional methods, TransUnet and Unet neural networks by combining Transformer with convolutional neural network(CNN) are used for efficient characterization of particles and pores. The TransUnet has excellent performance in particle characterization. The experiment shows that the intersection over union(IoU) reaches 0.86, with the recall rate of 0.824 and precision of 0.839, which is superior to traditional methods, proving its effectiveness in tight particle segmentation. The Unet shows efficient characterization of pores as well, with the IoU of 0.824, recall rate of 0.843 and precision of 0.953. Besides, experiment indicates that although porosity affects IoU, the model still maintains high efficiency and accuracy generally. These results fully demonstrate that deep learning method, especially TransUnet, is significantly effective in accurate segmentation of thin section images of complex tight reservoir, providing new ideas for the study of unconventional tight reservoir and showing its great potential in the field of geology.
-
Key words:
- deep learning /
- thin section analysis /
- tight reservoir /
- particle size analysis /
- TransUnet
-

-
表 1 实验环境参数表
Table 1. Experimental environment parameters
操作系统 Ubuntu 22.04 内存 10核32 GB 显存 1卡* 24 GB 硬盘 50 GB 表 2 颗粒、孔隙识别模型指标结果
Table 2. Model index results of particle and pore identification
指标 颗粒识别 孔隙识别 Unet TransUnet Dice_Loss_Unet CE_Loss_Unet MIoU 79.6% 71.3% 77.4% 82.4% Recall 87.3% 86.1% 77.3% 84.3% Precision 89.7% 82.5% 95.7% 95.3% F1-score 88.4% 84.0% 85.2% 89.3% 注:Dice_Loss_Unet是以Dice为损失函数的Unet;CE_Loss_Unet是以交叉熵为损失函数的Unet. 表 3 模型识别与人工识别粒度分析参数结果
Table 3. Particle size parameter results by model recognition and manual recognition analysis
识别方式 平均粒径(Mz)/φ 标准偏差(Sd)/φ 偏度(Sk) 峰度(Kg) 模型识别分析 2.70 1.26 3.539 21.7 人工识别分析 2.61 1.08 1.642 10.2 -
[1] 苏程, 朱孔阳. 岩石薄片图像智能分析研究进展[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2023, 42(1): 13-25.
Su C, Zhu K Y. Research progress of intelligent image analysis for petrographic thin section images[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2023, 42(1): 13-25.
[2] 陈宇豪. 简述薄片鉴定在岩石特征分析中的应用[J]. 新疆有色金属, 2022, 45(4): 23-24.
Chen Y H. The application of thin section identification in rock characteristic analysis[J]. Xinjiang Nonferrous Metals, 2022, 45(4): 23-24. (in Chinese)
[3] Tang D G, Milliken K L, Spikes K T. Machine learning for point counting and segmentation of arenite in thin section[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 120: 104518. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104518
[4] Das R, Mondal A, Chakraborty T, et al. Deep neural networks for automatic grain-matrix segmentation in plane and cross-polarized sandstone photomicrographs[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2022, 52(3): 2332-2345. doi: 10.1007/s10489-021-02530-z
[5] 姜枫, 顾庆, 郝慧珍, 等. 基于语义特征提取的砂岩薄片图像颗粒分割方法[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2020, 50(1): 109-127.
Jiang F, Gu Q, Hao H Z, et al. Grain segmentation of sandstone thin section images based on semantic feature extraction[J]. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2020, 50(1): 109-127.
[6] 张利军, 鲁文豪, 张建东, 等. 基于深度学习的镜下岩石、矿物薄片识别[J]. 地学前缘, 2024, 31(3): 498-510.
Zhang L J, Lu W H, Zhang J D, et al. Rock and mineral thin section identification based on deep learning[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2024, 31(3): 498-510.
[7] Saxena N, Day-Stirrat R J, Hows A, et al. Application of deep learning for semantic segmentation of sandstone thin sections[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2021, 152: 104778.
[8] 徐圣嘉, 苏程, 朱孔阳, 等. 基于深度学习的岩石薄片矿物自动识别方法[J]. 浙江大学学报(理学版), 2022, 49(6): 743-752.
Xu S J, Su C, Zhu K Y, et al. Automatic identification of mineral in petrographic thin sections based on images using a deep learning method[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Science Edition), 2022, 49(6): 743-752.
[9] Koh E J Y, Amini E, McLachlan G J, et al. Utilising convolutional neural networks to perform fast automated modal mineralogy analysis for thin-section optical microscopy[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2021, 173: 107230.
[10] 陈宗铭, 唐玄, 梁国栋, 等. 基于深度学习的页岩扫描电镜图像有机质孔隙识别与比较[J]. 地学前缘, 2023, 30(3): 208-220.
Chen Z M, Tang X, Liang G D, et al. Identification and comparison of organic matter-hosted pores in shale by SEM image analysis: A deep learning-based approach[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2023, 30(3): 208-220.
[11] Liu H, Ren Y L, Li X, et al. Rock thin-section analysis and identification based on artificial intelligent technique[J]. Petroleum Science, 2022, 19(4): 1605-1621.
[12] Zou C N, Zhu R K, Liu K Y, et al. Tight gas sandstone reservoirs in China: Characteristics and recognition criteria[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2012, 88-89: 82-91.
[13] 林森虎, 邹才能, 袁选俊, 等. 美国致密油开发现状及启示[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2011, 23(4): 25-30, 64.
Lin S H, Zou C N, Yuan X J, et al. Status quo of tight oil exploitation in the United States and its implication[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2011, 23(4): 25-30, 64.
[14] 贾承造, 邹才能, 李建忠, 等. 中国致密油评价标准、主要类型、基本特征及资源前景[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(3): 343-350.
Jia C Z, Zou C N, Li J Z, et al. Assessment criteria, main types, basic features and resource prospects of the tight oil in China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(3): 343-350.
[15] Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C] //Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer- Assisted Intervention. Munich: Springer, 2015: 234-241.
[16] 王媛媛, 董芳, 尚丽娜, 等. 基于改进TransUnet网络的血管内超声图像边界提取方法研究[J]. 中国生物医学工程学报, 2023, 42(1): 41-50.
Wang Y Y, Dong F, Shang L N, et al. Research on the IVUS border detection method based on improved TransUnet[J]. Chinese Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2023, 42(1): 41-50.
[17] Shorten C, Khoshgoftaar T M. A survey on image data augmentation for deep learning[J]. Journal of Big Data, 2019, 6(1): 60.
[18] Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, et al. Attention is all you need [C] //Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach: Curran Associates Inc. 2017: 6000-6010.
[19] 王金祥, 付立军, 尹鹏滨, 等. 基于CNN与Transformer的医学图像分割[J]. 计算机系统应用, 2023, 32(4): 141-148.
Wang J X, Fu L J, Yin P B, et al. Medical image segmentation based on CNN and transformer[J]. Computer Systems & Applications, 2023, 32(4): 141-148.
[20] 于营, 王春平, 付强, 等. 语义分割评价指标和评价方法综述[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2023, 59(6): 57-69.
Yu Y, Wang C P, Fu Q, et al. Survey of evaluation metrics and methods for semantic segmentation[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2023, 59(6): 57-69.
[21] 王茂桢, 王冰洁, 郝轶伟, 等. 辽中凹陷南洼中深层储层孔隙度分布特征及影响因素分析[J]. 长江大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 20(3): 23-32.
Wang M Z, Wang B J, Hao Y W, et al. Analysis of porosity distribution characteristics and influencing factors of middle-deep reservoirs in the southern subsag of Liaozhong Sag[J]. Journal of Yangtze University (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 20(3): 23-32.
[22] 刘毅, 林承焰, 林建力, 等. 东海盆地西湖凹陷深层低渗-致密砂岩孔隙结构特征及成因分析[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2024, 35(3): 405-422.
Liu Y, Lin C Y, Lin J L, et al. Pore structure characteristics and genesis analysis of deep tight sandstone in Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2024, 35(3): 405-422.
[23] 龚建涛, 白艳军. 致密砂岩储层微观孔隙结构表征研究——以鄂尔多斯盆地东南部地区延长组为例[J]. 地质与资源, 2024, 33(5): 662-670. DOI: 10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2024.05.006shu
Gong J T, Bai Y J. Characterization of microscopic pore structure in tight sandstone reservoir: A case study of Yanchang Formation in southeastern Ordos Basin[J]. Geology and Resources, 2024, 33(5): 662-670. DOI: 10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2024.05.006
[24] 方梦阳, 何建宁, 王万虎, 等. 一种基于MATLAB的碎屑岩粒度分析方法[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2020, 39(4): 504-510.
Fang M Y, He J N, Wang W H, et al. A particle size analysis method for clastic rock based on MATLAB[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2020, 39(4): 504-510.
-



 下载:
下载: