Application of thermal infrared remote sensing technology in geothermal resource survey in Jinzhai County, Anhui Province
-
摘要:
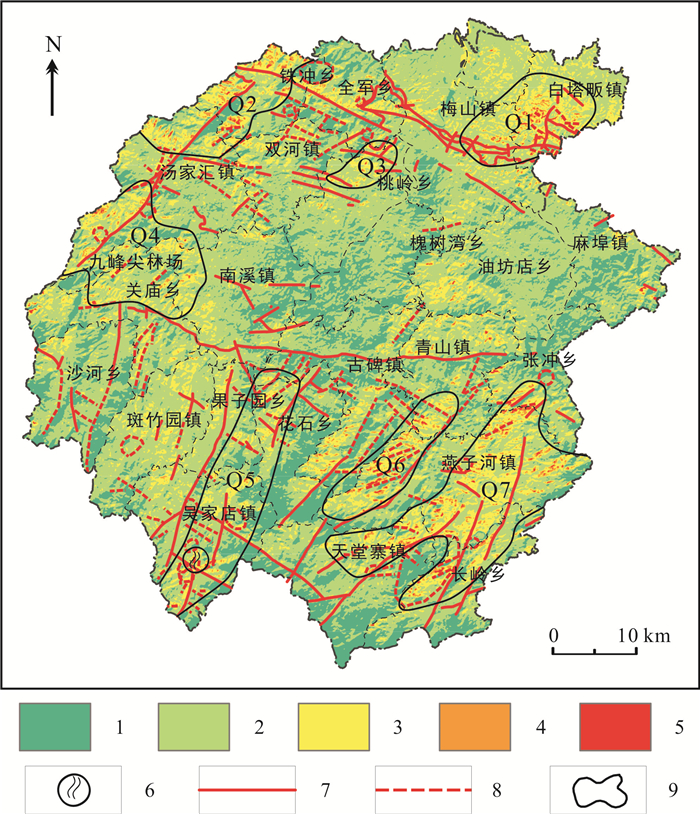
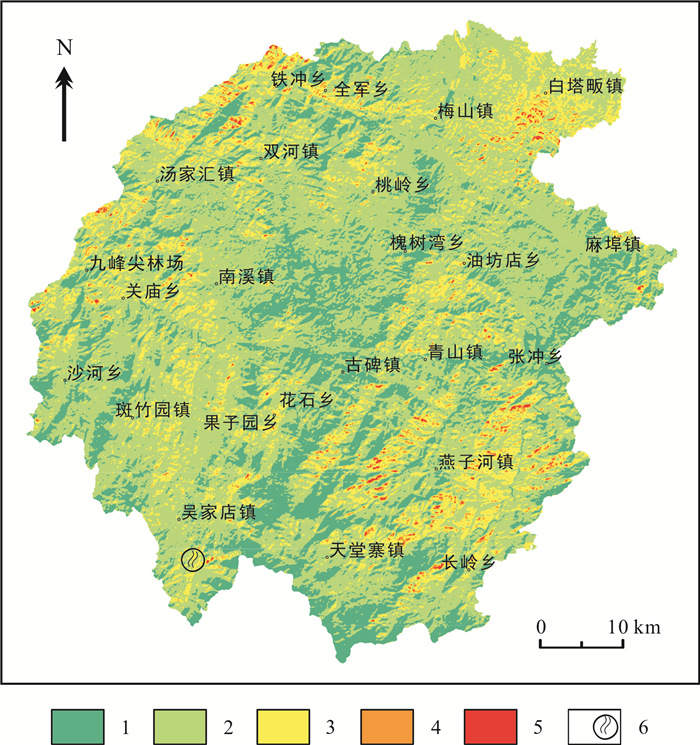
利用热红外遥感技术进行地热异常信息的提取可以为地热资源调查提供重要的依据.在充分掌握金寨县区域地质背景的基础上, 采用Landsat 8热红外TIRS10波段数据通过大气校正法进行地表温度反演, 采用高分一号和高分二号数据进行线环构造遥感解译, 再将遥感反演的地表温度、解译的线环构造和其他地质条件、已知地热资料进行综合分析, 建立地热异常区圈定依据, 圈定地热异常区, 并结合相关判定因子剔除假异常.最终在研究区共圈定7个潜在地热异常区, 为下一步地热资源实地调查提供先导支持.
Abstract:The extraction of geothermal anomaly information with thermal infrared remote sensing technology can provide important basis for geothermal resource survey. Based on the regional geological background of Jinzhai County, the Landsat 8 TIRS10 band data are adopted for surface temperature inversion by atmospheric correction method, and the GF-1 and GF-2 data for remote sensing interpretation of linear and ring structures. Then, the surface temperature obtained from remote sensing inversion, interpreted linear and ring structures, and other geological conditions as well as the known geothermal data are comprehensively analyzed to delineate geothermal anomaly areas and eliminate false anomalies in combination with relevant judgment factors. Finally, a total of 7 potential geothermal anomaly areas are recognized in the study area, providing a guiding support for the next field survey of geothermal resources.
-

-
表 1 遥感数据源信息
Table 1. Information of remote sensing data source
产品名称 空间分辨率/m 获取时间 云量/% 主要用途 Landsat 8 15 2015-01-03 0.91 地表温度反演 GF-1 2 2020-04—2020-10 < 2 线环构造解译 GF-2 0.8 2020-01—2020-09 < 1 线环构造解译 表 2 研究区地表温度热异常区判定表
Table 2. Determination of surface thermal anomaly areas in the study area
编号 范围 判定结果 特征 Q1 白塔畈与梅山镇交界部位 地热异常区 地表温度异常明显,范围较大,为非城镇区域,异常分布均匀,不受地形影响,且构造发育密集 Q 2 汤家汇镇北部尧铁冲乡西北部 地热异常区 地表温度异常明显,分布较广,局部受地形影响阴阳坡温度差异较大,其余部分分布较均匀,且处于金寨断裂与金刚台断裂的交汇处 Q 3 桃岭乡西北部 地热异常区 地表温度异常明显,分布均匀,临近金寨大断裂,且各方向小断裂发育 Q 4 汤家汇镇南侧及关庙乡北侧 地热异常区 地表温度异常分布不均,范围较大,金刚台断裂穿插其中,影像上局部线性构造明显,且两侧都有异常分布 Q 5 吴家店镇东部及花石乡西侧,果子园东侧小部分地区 地热异常区 地表温度异常明显,局部分布不均,阳坡和阴坡都存在异常,断裂构造呈格状发育,局部发生位移,区域内有西庄温泉一处 Q 6 燕子河镇西部 伪地热异常区 阳坡地温异常分布范围明显比阴坡大,且温度差异较大,线性构造发育不明显,认为地温异常为太阳辐射造成的 Q 7 燕子河东部分布最广,其次为天堂寨和长岭乡北部 地热异常区 断裂构造较为发育,延伸较长,地温异常分布多数不受地形影响,阴阳坡均有高温异常,也较为集中 -
[1] 王贵玲, 张薇, 梁继运, 等. 中国地热资源潜力评价[J]. 地球学报, 2017, 38(4): 449-459.
Wang G L, Zhang W, Liang J Y, et al. Evaluation of geothermal resources potential in China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2017, 38(4): 449-459.
[2] 王贵玲, 陆川. 碳中和目标驱动下干热岩和增强型地热系统增产技术发展[J]. 地质与资源, 2023, 32(1): 85-95, 126. DOI: 10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2023.01.011shu
Wang G L, Lu C. Stimulation technology development of hot dry rock and enhanced geothermal system driven by carbon neutrality target[J]. Geology and Resources, 2023, 32(1): 85-95, 126. DOI: 10.13686/j.j.cnki.dzyzy.2023.01.011
[3] 边宇, 杨永鹏, 李萌, 等. 热红外遥感技术在地热资源调查中的应用[J]. 中国矿业, 2021, 30(S2): 153-157.
Bian Y, Yang Y P, Li M, et al. Application of thermal infrared remote sensing techniques in geothermal resources surveying[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2021, 30(S2): 153-157.
[4] 任正情, 方泓锦, 王学平. 热红外遥感技术在江西寻乌地区地热勘查中的应用[J]. 地质学刊, 2021, 45(3): 277-282.
Ren Z Q, Fang H J, Wang X P. Application of thermal infrared remote sensing in exploration of geothermal resources in Xunwu area, Jiangxi Province[J]. Journal of Geology, 2021, 45(3): 277-282.
[5] 郭宝东, 孙中任, 石玉学, 等. MT法在鄂尔多斯盆地北部地热资源勘查中的应用[J]. 地质与资源, 2023, 32(1): 64-69. doi: 10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2023.01.008
Guo B D, Sun Z R, Shi Y X, et al. Application of magnetotelluric sounding method in geothermal resources exploration in northern Ordos Basin[J]. Geology and Resources, 2023, 32(1): 64-69. doi: 10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2023.01.008
[6] 林伟, 王清晨, Faure M, 等. 从北淮阳构造带的多期变形透视大别山构造演化[J]. 中国科学(D辑: 地球科学), 2005, 35(2): 127-139.
Lin W, Wang Q C, Faure M, et al. Tectonic evolution of the Dabieshan orogen: In the view from polyphase deformation of the Beihuaiyang metamorphic zone[J]. Science in China (Series D), 2005, 48(7): 886-899.
[7] 王龙平, 魏永霞, 程宏超, 等. 安徽长江经济带地热资源赋存特征及潜力评价[J]. 中国地质, 2022, 49(6): 1765-1777.
Wang L P, Wei Y X, Cheng H C, et al. Characteristics and potential evaluation of geothermal resources in Anhui of Yangtze River Economic Zone[J]. Geology in China, 2022, 49(6): 1765-1777.
[8] 宋挺, 段峥, 刘军志, 等. Landsat 8数据地表温度反演算法对比[J]. 遥感学报, 2015, 19(3): 451-464.
Song T, Duan Z, Liu J Z, et al. Comparison of four algorithms to retrieve land surface temperature using Landsat 8 satellite[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2015, 19(3): 451-464.
[9] 赵珍, 李贵仁, 陈刚. ArcGIS和RS技术在高植被覆盖率地区地热资源勘查中的应用[J]. 勘察科学技术, 2019(2): 44-48.
Zhao Z, Li G R, Chen G. Application of ArcGIS and RS technology in exploration of geothermal resources at high vegetation coverage ratio area[J]. Site Investigation Science and Technology, 2019(2): 44-48.
[10] 冯鹏, 岳昊, 刘晓源. 基于Landsat 8数据的地表温度反演研究——以哈尔滨主城区为例[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息, 2018, 41(9): 223-225.
Feng P, Yue H, Liu X Y. Land surface temperature inversion based on Landsat 8 data: Take the main city of Harbin as an example[J]. Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology, 2018, 41(9): 223-225.
[11] Sheng L, Tang X L, You H Y, et al. Comparison of the urban heat island intensity quantified by using air temperature and Landsat land surface temperature in Hangzhou, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2017, 72: 738-746.
[12] Guo Y B, Zhang C H. Analysis of driving force and driving mechanism of the spatial change of LST based on Landsat 8[J]. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 2022, 50(9): 1787-1801.
[13] 周传芳, 陈卓, 孙彦峰, 等. 遥感在大兴安岭森林覆盖区地质矿产调查中的应用——以黑龙江洛古河1: 5万区域地质矿产调查工作为例[J]. 地质与资源, 2022, 31(5): 632-641, 613.
Zhou C F, Chen Z, Sun Y F, et al. Remote sensing applied in geological and mineral survey in forest-covered area of Daxinganling Mountains: A case study of 1: 50000 regional geological and mineral survey in Luoguhe, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geology and Resources, 2022, 31(5): 632-641, 613.
[14] 韩乐乐, 丁伟翠, 陈宣华, 等. 西准噶尔地区多源遥感信息的线性构造提取与定量分析[J]. 中国地质, 2019, 46(5): 1209-1223.
Han L L, Ding W C, Chen X H, et al. Linear structure extraction and quantitative analysis of multi-source remote sensing information in West Junggar Basin[J]. Geology in China, 2019, 46(5): 1209-1223.
[15] 卢克轩, 刘新星, 张娟, 等. 京津冀地区线环构造遥感地质解译与控矿规律分析[J]. 地质与资源, 2022, 31(2): 175-182. doi: 10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2022.02.007
Lu K X, Liu X X, Zhang J, et al. Remote sensing geological interpretation and ore-controlling regularity of line-ring structures in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region[J]. Geology and Resources, 2022, 31(2): 175-182. doi: 10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2022.02.007
[16] 张焜, 马世斌, 李宗仁, 等. 高分一号卫星数据遥感地质解译[J]. 遥感信息, 2016, 31(1): 115-123.
Zhang K, Ma S B, Li Z R, et al. Geological interpretation of GF-1 satellite imagery[J]. Remote Sensing Information, 2016, 31(1): 115-123.
[17] 梁树能, 魏红艳, 甘甫平, 等. "高分二号"卫星数据在遥感地质调查中的初步应用评价[J]. 航天返回与遥感, 2015, 36(4): 63-72.
Liang S N, Wei H Y, Gan F P, et al. Preliminary application evaluation of GF-2 satellite data in remote sensing geological survey [J]. Spacecraft Recovery & Remote Sensing, 2015, 36(4): 63-72.
[18] 龙登红, 周小龙, 杨坤光, 等. 青藏高原东北缘深部地质构造与地热资源分布关系研究[J]. 中国地质, 2021, 48(3): 721-731.
Long D H, Zhou X L, Yang K G, et al. Research on relationship between the deep structure and geothermal resource distribution in the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geology in China, 2021, 48(3): 721-731.
[19] Nishar A, Richards S, Breen D, et al. Thermal infrared imaging of geothermal environments and by an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV): A case study of the Wairakei-Tauhara geothermal field, Taupo, New Zealand[J]. Renewable Energy, 2016, 86: 1256-1264.
[20] 豆保娜, 王安东, 万建军, 等. 安徽金寨地区花岗岩类放射性地球化学特征及岩石圈热结构研究[J]. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 45(3): 234-242.
Dou B N, Wang A D, Wan J J, et al. Radioactive geochemical characteristics of granitoids and thermal structure of lithosphere in Jinzhai area, Anhui Province[J]. Journal of East China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 45(3): 234-242.
-



 下载:
下载: