Dealkalization of Red Mud by Mild Acid Leaching and Comprehensive Utilization
-
摘要:
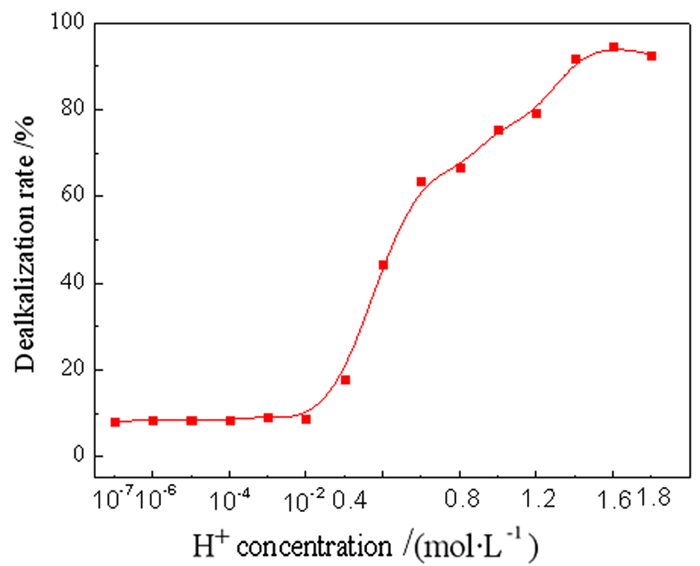
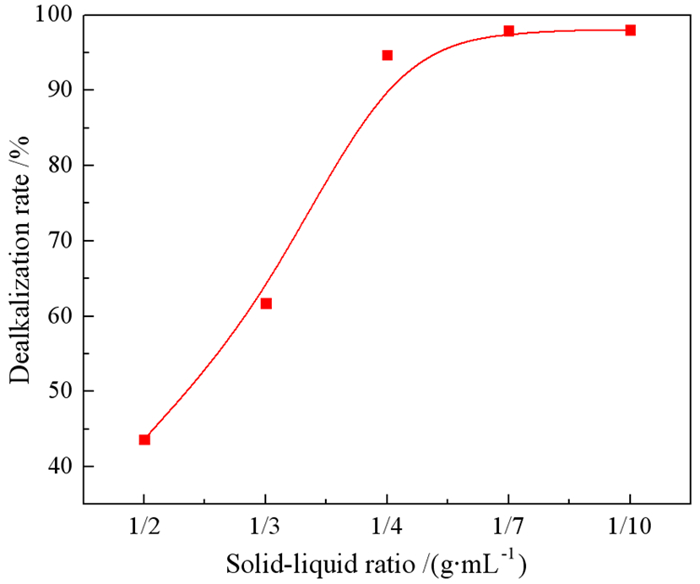
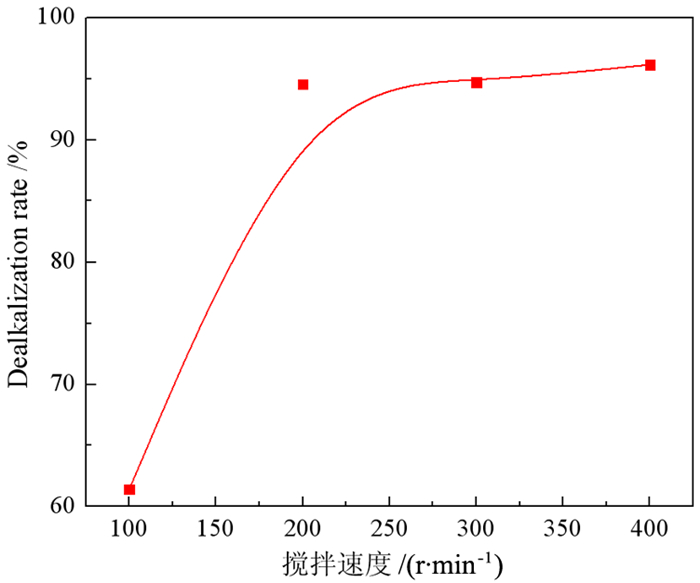
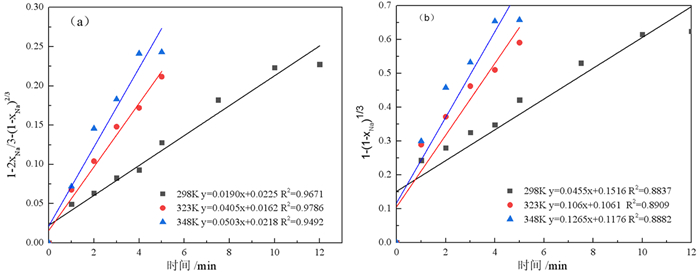
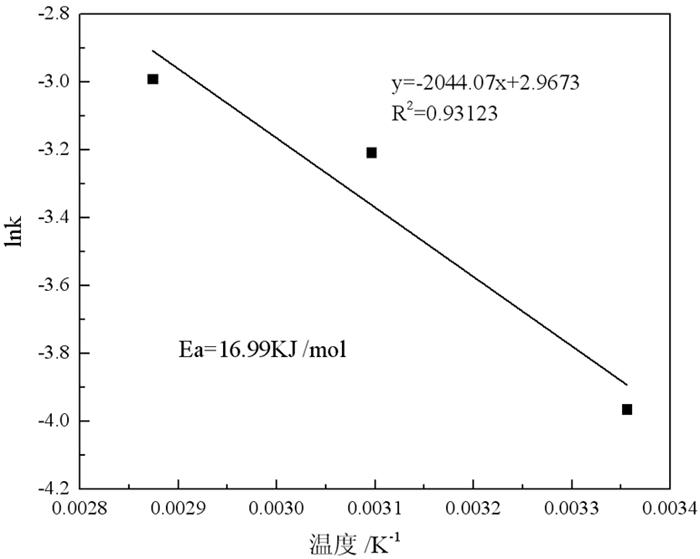
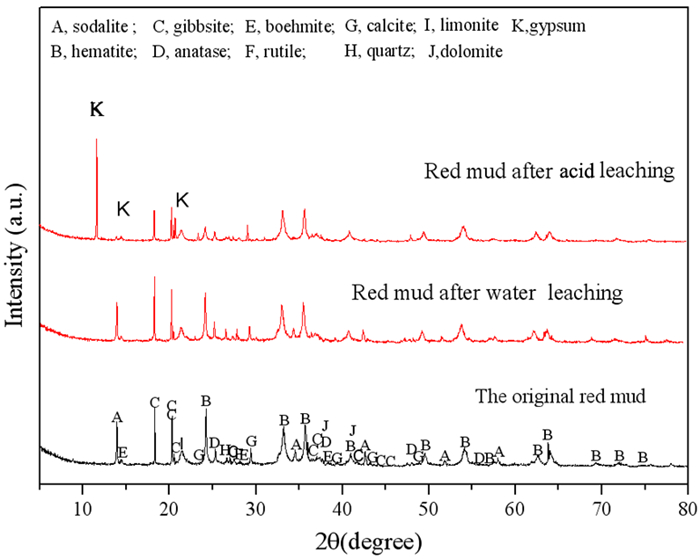
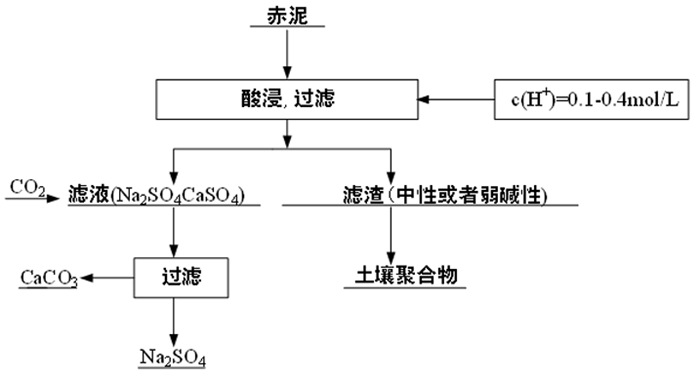
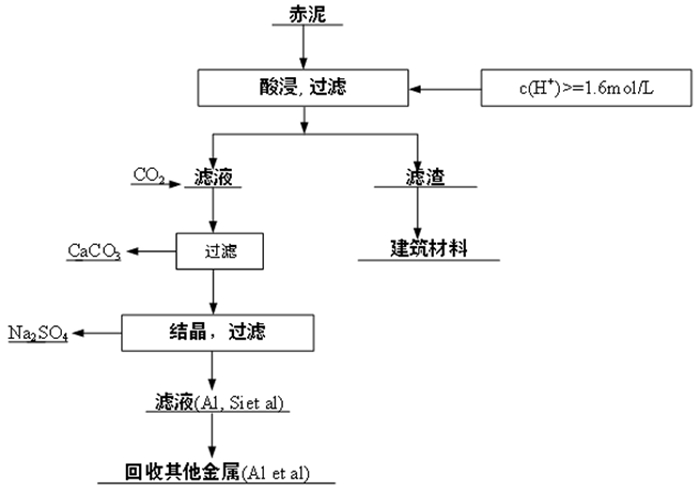
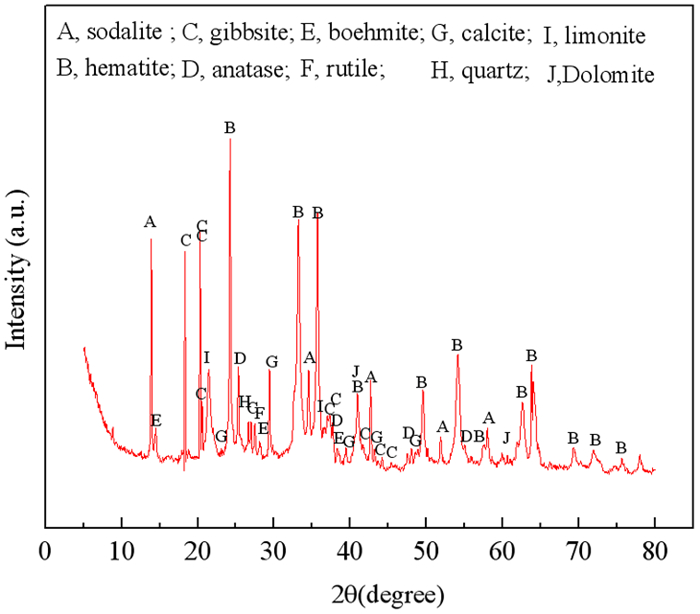
强碱性是制约赤泥综合利用的关键因素,酸浸是实现赤泥脱碱的有效方法。大部分研究采用强酸浸出赤泥实现重金属的回收,忽略了低浓度酸对赤泥脱碱化的影响。本文研究了低浓度的硫酸浸出赤泥过程中钠的浸出行为,同时考察了硫酸浓度、液固比、搅拌速度、浸出温度和浸出时间对赤泥脱碱化的影响。结果表明:采用pH 1的酸性溶液可以浸出赤泥中17.84%的钠。采用H+浓度为0.5 mol/L的酸性溶液可以浸出赤泥中大于60%的钠,这使得浸出液处理工艺相对简单,同时滤渣的pH值为8.5,为弱碱性,可直接用于土壤。在H+浓度为1.6 mol/L、固液比为1/4 g/mL、搅拌速度为300 r/min、浸出温度为298 K和浸出时间为10 min的最佳条件下,钠的浸出率为94.70%,滤渣中只剩下0.6% 的钠,可以用于建筑材料。并对硫酸浸出动力学进行了研究。结果表明:在较低浓度的硫酸介质中,钠的浸出过程主要受产物层扩散模型控制,浸出过程的表观活化能为16.99 kJ/mol。XRD分析结果证实方解石与硫酸反应生成硫酸钙微溶物质是形成产物层的主要原因。基于上述结果,提出了一种新型多级酸浸脱碱工艺,为赤泥的综合利用奠定了基础。
Abstract:Strong alkalinity is the key factor restricting the comprehensive utilization of red mud and acid leaching is an effective method for the dealkalization of red mud. Most studies have focused on the recovery of metals in this extreme alkaline waste by strong acid leaching, ignoring the dealkalization and stabilization of red mud with low concentrations of acid. In this study, the leaching behavior of Na in red mud with low concentration of sulfuric acid was carefully investigated and the effects of sulfuric acid concentration, liquid-solid ratio, stirring speed, leaching temperature and leaching time on red mud dealkalization were investigated. The results show that treatment with an acidic solution at pH 1 removed 17.84% of Na. Greater than 60% Na was leached by an acidic solution with H+ concentration of 0.5 mol/L, resulting in a relatively simple leaching liquid treatment process. And the pH of the leaching residue was 8.5 which slightly alkaline so the residual RM could be used as soil aggregates. Under the optimal conditions of H+ concentration 1.6 mol/L, solid-liquid ratio 1/4 g/mL, stirring speed 300 r/min, leaching temperature 298K and leaching time 10 min, the dissolution efficiency of Na reached at 94.70%, leaving only 0.6% Na in the residue, which makes it possible to meet the demand of application for construction materials. We also investigated the sulfuric acid leaching kinetics. The results show that the sodium leaching process is mainly controlled by the product layer diffusion model and the apparent activation energy of the leaching process is 16.99 kJ/mol in low concentration sulfuric acid medium. XRD analysis shows that calcite reacts with sulfuric acid to form calcium sulfate microsoluble substance is the main reason for the formation of product layer. Based on the above results, a new multistage acid leaching process was proposed, which laid a foundation for the comprehensive utilization of red mud.
-
Key words:
- red mud /
- sulfuric leaching /
- dealkalization /
- kinetics mechanism
-

-
表 1 赤泥的主要化学组成
Table 1. Main chemical compositions of red mud
/% 元素 Al2O3 CaO Fe2O3 TiO2 Na2O SiO2 含量 20.49 2.46 48.01 5.77 9.14 14.66 表 2 浸出渣的主要化学成分
Table 2. The main chemical composition of the leached residue
元素 Na Al Si Ca 含量/% 0.60 9.60 1.54 2.17 表 3 水泥和赤泥滤渣成分对比
Table 3. The composition of cement and red mud residual
物质 Na2O/% Al2O3/% SiO2/% CaO/% 水泥 < 1 4-7 20-24 62-67 赤泥滤渣 0.47 17.8 12.8 2.5 -
[1] ZHANG Y, SHI Q, LUO M, et al. Improved bauxite residue dealkalization by combination of aerated washing and electrodialysis[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019. 364: 682-690. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.10.023
[2] LU F, XIAO T, LIN J, et al. Recovery of gallium from Bayer red mud through acidic-leaching-ion-exchange process under normal atmospheric pressure[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2018, 175: 124-132. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2017.10.032
[3] CHUN T, ZHU D, PAN J, et al. Recovery of Alumina from Magnetic Separation Tailings of Red Mud by Na2CO3 Solution Leaching[J]. Metallurgical & Materials Transactions B, 2014, 45(3): 827-832. doi: 10.1007/s11663-014-0023-1
[4] WANG Q, YU H, BEN T, et al. Preparation of lightweight high-strength thermal insulation and decoration integration porous ceramics using red mud[J]. Journal of the Australian Ceramic Society, 2019: 91-98. doi: 10.1007/s41779-019-00374-y
[5] CHUN S, H RAI, M NISHIYAMA, et al. Using Organic Matter with Chemical Amendments to Improve Calcareous Sodic Soil[J]. Communications in Soil Science & Plant Analysis, 2007. 38(1): 205-216. http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/00103620601094163?cookieSet=1
[6] YI R R, CAO W. Current Situation and Prospect of Comprehensive Utilization of Red Mud[J]. Applied Mechanics & Materials, 2014, 522/523/524: 811-816. http://www.scientific.net/AMM.522-524.811
[7] DAVRIS P, BALOMENOS E, PANIAS D, et al. Selective leaching of rare earth elements from bauxite residue (red mud), using a functionalized hydrophobic ionic liquid[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2016, 164: 125-135. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2016.06.012
[8] HE H, YUE Q, QI Y, et al. The effect of incorporation of red mud on the properties of clay ceramic bodies[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2012, 70(DEC. ): 67-73. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169131712002396
[9] KANG S P, KWON S J. Effects of red mud and Alkali-Activated Slag Cement on efflorescence in cement mortar[J]. Construction & Building Materials, 2017, 133: 459-467. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S095006181632044X
[10] KANFMAN, E N., LITTLE M H., SELVARAJ PT. Recycling of FGD gypsum to calcium carbonate and elemental sulfur using mixed sulfate-reducing bacteria with sewage digest as a carbon source[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 2010. 66(4): 365-374. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/229775892_Recycling_of_FGD_gypsum_to_calcium_carbonate_and_elemental_sulfur_using_mixed_sulfatereducing_bacteria_with_sewage_digest_as_a_carbon_source
[11] ZHU X, LI W, GUAN X. An active dealkalization of red mud with roasting and water leaching[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 286: 85-91. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.12.048
[12] CHEN L B, ZHANG Y F, ZHANG Y. Dealkalization of red mud generated in alumina production by sub-molten salt process under atmospheric pressure[J]. Chinese journal of process engineering, 2010, 10(3): 470-475. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HGYJ201003010.htm
[13] ZHAO B L, HONG X L, MENG M L. Effects of cooling method on removal of sodium from active roasting red mud based on water leaching[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2017, 167: 92-100. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2016.10.021
[14] LUO M, QI X, ZHANG Y, et al. Study on dealkalization and settling performance of red mud[J]. Environmental ence and Pollution Research, 2016, 24(2): 1-9. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27796987
[15] U ROHDE, F RUTHE, PG JONES, et al. Formation and Structure of the First 7-Aza-1-phosphanorbornadiene Complex[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2010. 38(1/2): 215-217. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/264741427_Formation_and_Structure_of_the_First_7-Aza-1-phosphanorbornadiene_Complex
[16] LUO M, Y REN, J TONG, et al. Study on dealkalization and settling performance of red mud[J]. Environmental Science & Pollution Research International, 24(2): 1794-1802. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27796987
[17] WANG Y, ZHANG T A, LYU G, et al. Recovery of alkali and alumina from bauxite residue (red mud) and complete reuse of the treated residue[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 188(1): 456-465. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959652618310217
[18] JIAO J, LANG L, RUOHUA L, et al. Preparation and thermal performance of binary fatty acid with diatomite as form-stable composite phase change material for cooling asphalt pavements[J], Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 226(30): 616-642
[20] BORRA C R, PONTIKES Y, BINNEMANS K, et al. Leaching of rare earths from bauxite residue (red mud)[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2015, 76: 20-27. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-WJYG201601019.htm
[21] HONG L C, TING W, YANG K, et al. Technology conditions and mechanism discussion of sodium and iron extraction from red mud by acid[J]. inorganic chemicals industry, 2016, 1: 44-48. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ201112029.htm
[22] HUANG K, LI Y F, JIAO S Q, et al. Adsorptive removal of methylene blue dye wastewater from aqueous solution using citric acid activated red mud[J]. Zhongguo Youse Jinshu Xuebao/Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(12): 3182-3188. doi: 10.1007/s40831-016-0082-4
[23] ALHARTHI A I, HARGREAVES J S J, PULFORD I D, et al. Hydrocarbon cracking over red mud and modified red mud samples[J]. Sustain. Metall. 2016, 2: 387-393. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/279655007_Dissolution_kinetics_of_iron_and_aluminium_from_red_mud_in_sulphuric_acid_solution
[24] UZUN D, MUSTAFA G. Dissolution kinetics of iron and aluminium from red mud in sulphuric acid solution[J]. Indian Journal of Chemical Technology, 2007, 14(3): 263-268. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2013.02.006
[25] TUNCUK A, CIFTLIK S, AKCIL A. Factorial experiments for iron removal from kaolin by using single and two-step leaching with sulfuric acid[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2013, 134/135: 80-86. doi: 10.1007/s40831-016-0103-3
[26] BORRA C R, BLANPAIN B, PONTIKES Y, et al. Recovery of Rare Earths and Major Metals from Bauxite Residue (Red Mud) by Alkali Roasting, Smelting, and Leaching[J]. Journal of Sustainable Metallurgy, 2017, 3(2): 393-404. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0002601
[27] JIAO J, YaANQING T, RUO H L, et al. Synergy Effect of Attapulgite, Rubber, and Diatomite on Organic Montmorillonite Modified Asphalt[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2019, 31(2): 04018388.1-04018388.8. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2019.05.019
[28] ZHANG Y, HU Y, SUN N, et al. A novel precipitant for separating lithium from magnesium in high Mg/Li ratio brine[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2019, 187: 125-133. http://europepmc.org/articles/PMC4727973
[29] EDWIN C. Microscopical and elemental FESEM and Phenom ProX-SEM-EDS analysis of osteocyte- and blood vessel-like microstructures obtained from fossil vertebrates of the Eocene Messel Pit, Germany[J]. Peerj, 2016, 4(5). doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.10.073
[30] KONG X, LI M, LI X, et al. Acid transformation of bauxite residue: conversion of its alkaline characteristics[J]. Journal of Hazardous Material, 2017, 324: 382-390. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.10.073
[31] SAHU M. K, PATEL R K J R A. Removal of safranin-O dye from aqueous solution using modified red mud[J]. Kinetics and equilibrium studies. 2015. 5(96): 78491-78501.
[32] LI X F, YE Y Z, XUE S G, et al. Leaching optimization and dissolution behavior of alkaline anions in bauxite residue[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 28(6). doi: 10.1007/s11771-019-4000-3
[33] XUE S G, WU Y J, LI Y W, et al. Application of industrial waste to alkaline regulation of red mud[J]. Journal of central south university, 2019, 26(2): 268-288(in Chinese). http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22176227
-



 下载:
下载: