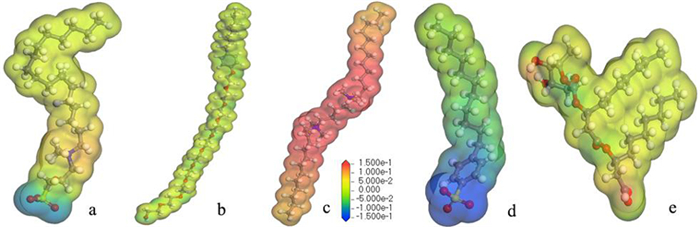
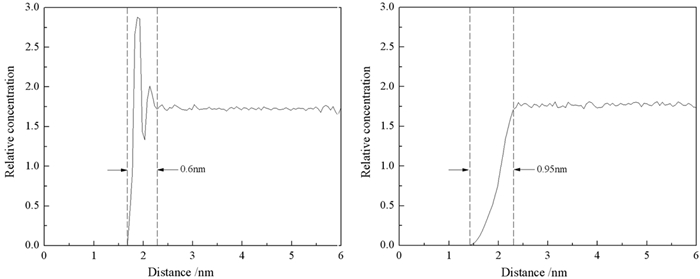
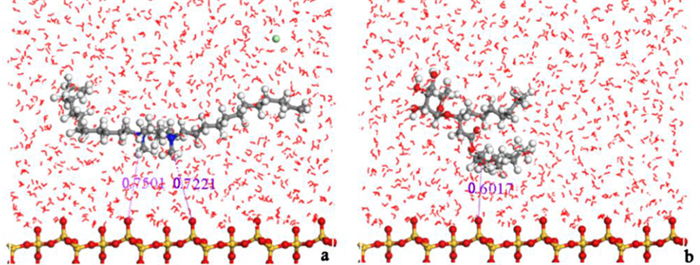
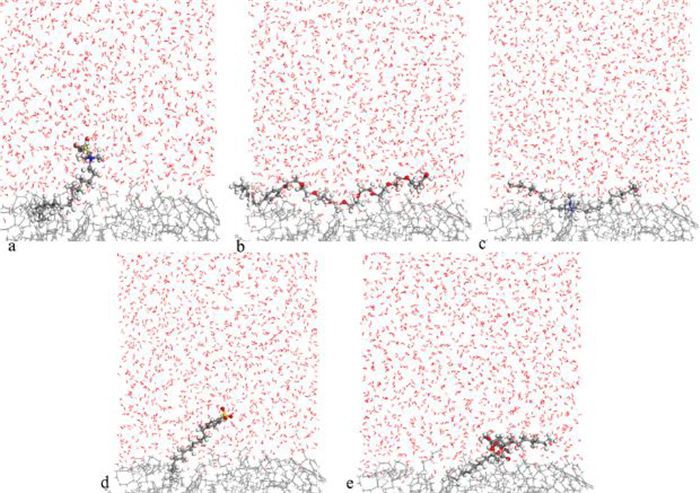
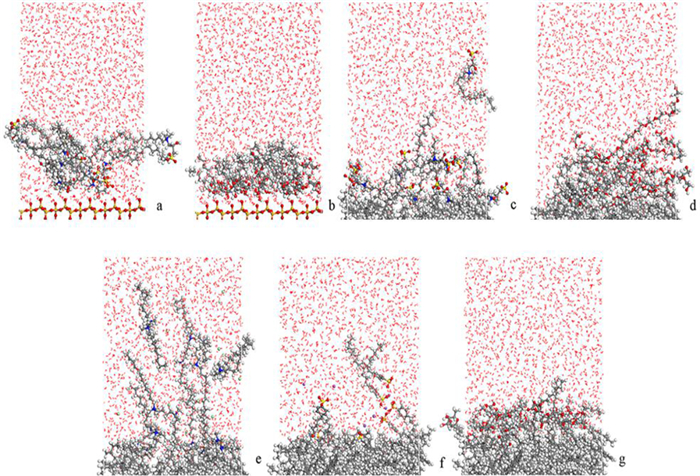
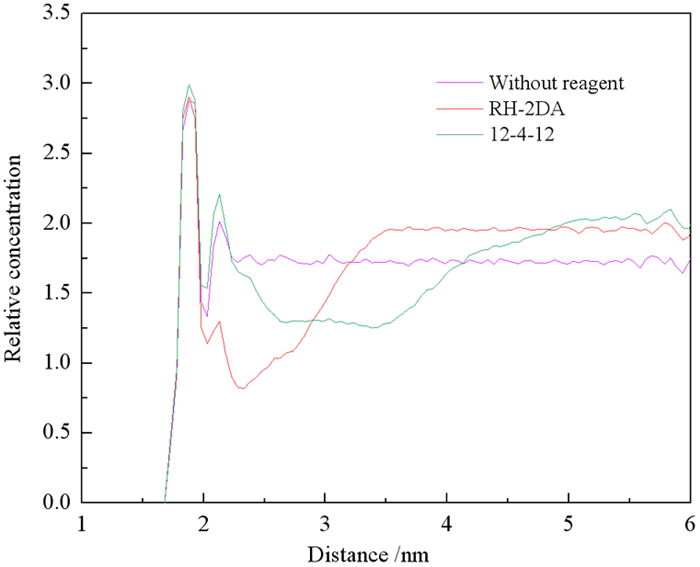
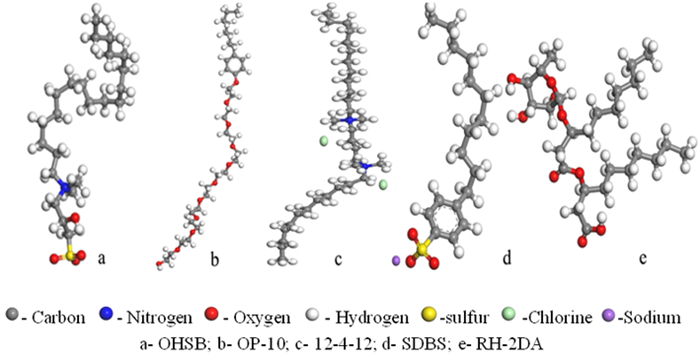
Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Adsorption Behavior of Different Surfactants on Quartz Surface and Oil/water Interface
-
摘要:
低渗透油藏开采中表面活性剂在岩石和油/水界面的吸附对岩石表面和油/水界面性质的影响,是低渗透油藏渗吸增强驱油技术的关键问题。本文运用分子动力学模拟方法研究了十八烷基二甲基羟丙基磺基甜菜碱(OHSB)、聚氧乙烯辛基苯酚醚-10(OP-10)、阳离子双子表面活性剂(12-4-12)、十二烷基苯磺酸钠(SDBS)和鼠李糖脂(RH-2DA)5种表面活性剂在石英(101)面和油/水界面的吸附行为。研究结果表明:12-4-12双子阳离子表面活性剂与带负电荷的石英表面之间的静电吸引作用最强,SDBS与石英表面之间的静电排斥作用最强,12-4-12和RH-2DA能够自发吸附在石英表面并降低石英表面的润湿性;5种表面活性剂在石英表面吸附能数值由小至大的顺序为12-4-12 < RH-2DA < OHSB < OP-10 < SDBS;5种表面活性剂均能自发吸附到油相表面,在油相表面吸附强弱的大小顺序为OP-10 > RH-2DA > OHSB > 12-4-12 > SDBS;5种表面活性剂在油/水界面的吸附均能增强油水界面的稳定性。
Abstract:The adsorption behavior of surfactants on the rock and oil/water interface and its influence on the properties of the rock surface and the oil/water interface are the key issues in producing low permeability reservoirs of imbibition enhanced oil displacement technology in low permeability reservoirs. In this paper, molecular dynamics simulation methods are used to study the octadecyl dimethyl hydroxypropyl sultaine (OHSB), polyoxyethylene octyl phenol ether-10 (OP-10), Gemini surfactant (12-4-12), sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate (SDBS), and rhamnolipid (RH-2DA), five types of surfactants adsorption behavior of on the quartz (101) surface and the oil/water interface. The study results show that among the five surfactants, the electrostatic attraction between the Gemini surfactant12-4-12 and the negatively charged quartz surface is the strongest, and the electrostatic repulsion between the SDBS and the quartz surface is the strongest. 12-4-12 and RH-2DA can spontaneously adsorb on the quartz surface and reduce the wettability of the quartz surface. The adsorption energy of five surfactants on the quartz surface from small to large is 12-4-12 < RH-2DA < OHSB < OP -10 < SDBS. All five surfactants can be adsorbed on the surface of the oil phase spontaneously, and the order of adsorption strength on the surface of the oil phase is OP-10 > RH-2DA > OHSB > 12-4-12 > SDBS. The adsorption of the five surfactants at the oil/water interface can all enhance the oil/water interface's stability.
-
Key words:
- surfactant /
- quartz surface /
- oil/water interface /
- molecular dynamic
-

-
表 1 水分子润湿石英和油相表面时体系的能量/(kJ·mol-1)
Table 1. Energy of the system when water wet the surface of quartz and oil phase
体系 体系总能量 水分子的能量 表面的能量 能量变化 石英-水 -851 582.30 120 990.68 -600 738.26 -371 834.76 油-水 -3 631.19 -19 061.75 15 482.50 51.94 表 2 表面活性剂分子/离子在石英表面的吸附能
Table 2. Adsorption energy of surfactant molecules/ions on the surface of quartz
/(kJ·mol-1) 表面活性剂 吸附后体系的总能量 表面活性剂的能量 吸附前体系的能量 吸附能 OHSB -599 744.65 136.53 -600 738.24 857.07 OP-10 -598 701.60 944.65 -600 738.24 1 091.99 12-4-12 -601 320.76 551.64 -600 738.24 -1 134.16 SDBS -597 538.33 101.70 -600 738.24 3 098.21 RH-2DA -600 880.60 -84.42 -600 738.24 -57.94 表 3 表面活性剂分子/离子在油相表面的吸附能
Table 3. Adsorption energy of surfactant molecules/ions on the surface of oil phase
/(kJ·mol-1) 表面活性剂 吸附后体系的总能量 表面活性剂的能量 吸附前体系的能量 吸附能 OHSB 15 411.29 14.46 15 482.50 -85.67 OP-10 16 168.38 808.36 15 482.50 -122.48 12-4-12 16 001.46 590.36 15 482.50 -71.39 SDBS 15 593.59 158.52 15 482.50 -47.43 RH-2DA 15 251.70 -139.81 15 482.50 -90.99 表 4 表面活性剂在油/水界面的界面形成能/(kJ·mol-1)
Table 4. Interface formation energy of surfactants at the oil/water interfaces
Reagent Etotal Esurfactant IFE OHSB -6248.59 -20.56 -270.26 OP-10 -2437.35 668.98 -536.80 12-4-12 -8848.49 301.86 -882.49 SDBS -8638.60 -227.29 -330.49 RH-2DA -7697.93 -141.06 -312.66 Eref=-3 614.43 -
[1] SCHECHTER D S, ZHOU D, JR FMO. Low IFT drainage and imbibition[J]. Journal Of Petroleum Science & Engineering, 1994, 11(4): 283-300. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0920410594900477
[2] 李继山. 表面活性剂体系对渗吸过程的影响[D]. 廊坊市: 中国科学院研究生院(渗流流体力学研究所), 2006.
[3] 李振泉, 何秀娟, 李英, 等. 烷基苯磺酸盐在油水界面行为的介观模拟[J]. 化学学报, 2015, 64(24): 2803-2808. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXXB200724003.htm
[4] 肖红艳, 甄珍, 孙焕泉, 等. 阴离子表面活性剂在水/正烷烃界面的分子动力学模拟[J]. 物理化学学报, 2010, 26(2): 422-428. doi: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB20100216
[5] 夏柳荫. 双季铵盐型Gemini捕收剂对铝硅酸盐矿物的浮选特性与机理研究[D]. 天津市: 天津大学, 2009.
[6] 王东方, 葛际江, 张贵才, 等. 新型阴离子-非离子表面活性剂界面张力的研究[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 23(6): 70-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-064X.2008.06.017
[7] 郑倩, 潘睿, 向卉, 等. MS分子模拟软件在有机化学立体异构教学中的应用[J]. 广州化工, 2020, 48(4): 108-110. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZHA202004042.htm
[8] SUN H, JIN Z, YANG C, et al. COMPASS Ⅱ: extended coverage for polymer and drug-like molecule databases, Journal of Molecular Modeling, 2016, 22(2): 1-10. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00894-016-2909-0
[9] 周继凯, 黄俊凯, 林成欢. 水化硅酸钙力学性能分子动力学模拟方法对比研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2015, 15(28): 179-183. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2015.28.034
[10] 王丽娟, 石静, 赵方剑. 气液界面上磺基甜菜碱两性表面活性剂分子动力学模拟[J]. 山东大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(6): 83-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDGY201406013.htm
[11] 王业飞, 于维钊, 胡松青. 羟基取代双烷烃链苯磺酸盐水气界面单层膜的分子动力学模拟[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 35(2): 153-163. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201106029.htm
[12] 牛艳萍, 李亚, 许洪峰, 等. 红柱石与石英之间浮选交互影响研[J]. 有色金属工程, 2020, 10(12): 69-74+89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2020.12.011
[13] 罗思岗, 王福良. 分子力学在研究浮选药剂与矿物表面作用中的应用[J]. 矿冶, 2009, 18(1): 1-4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYZZ200901001.htm
[14] 杨阳, 朱辰, 王洪涛, 等. 醇羟基对碳酸钙矿物成核物相及界面能影响研究[J]. 高校地质学报, 2020, 26(6): 617-627.
[15] 彭陈亮, 闵凡飞, 赵晴, 等. 微细矿物颗粒表面水化膜研究现状及进展综述[J]. 矿物学报, 2012, 32(4): 515-522. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201204008.htm
[16] 刘晓阳. 表面活性剂吸附对褐煤润湿性影响及其调控机制研究[D]. 太原市: 太原理工大学, 2017.
[17] 康志红. "拟双子"表面活性剂的分子动力学模拟[D]. 大庆市: 东北石油大学, 2019.
-



 下载:
下载: