Quantum Chemical Study of Adsorption of Calcium (Magnesium) Ions on Smithsonite Surface
-
摘要:
与菱锌矿伴生的高可溶性碳酸盐类矿物方解石、白云石会导致矿浆中含有大量钙(镁)离子, 从而影响菱锌矿的浮选。采用密度泛函理论对钙(镁)离子在菱锌矿(101)表面吸附进行模拟。计算结果表明, 钙离子和镁离子会与清洁菱锌矿(101)表面发生较强的化学吸附, 并且钙离子的吸附比镁离子更强。水化后的菱锌矿(101)表面也会与钙离子和镁离子发生吸附, 但是吸附强度明显减弱。另外, 钙离子在水化菱锌矿(101)表面的吸附会削弱菱锌矿(101)表面的水化作用。研究结果可为消除菱锌矿浮选过程中难免离子的影响提供理论指导。
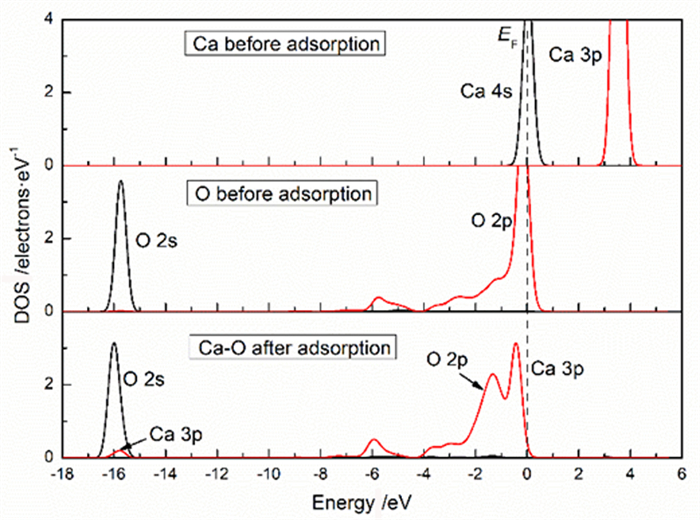
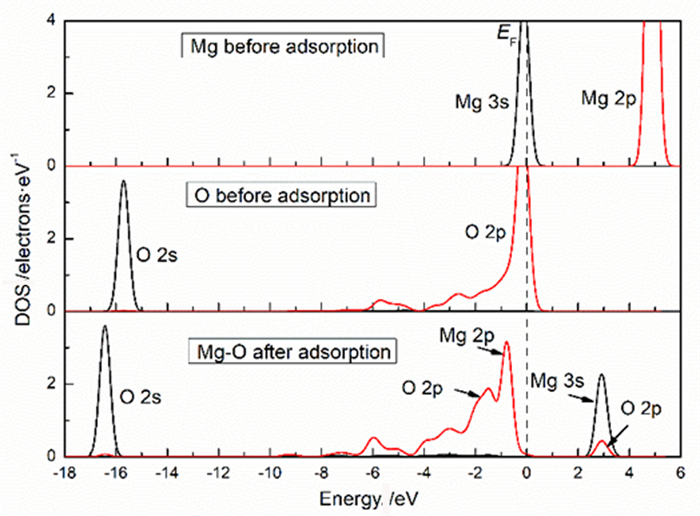
Abstract:The high soluble carbonate minerals calcite and dolomite associated with the smithsonite will lead to amounts of calcium (magnesium) ions in the pulp, which will affect the flotation of smithsonite. In this work, Density Functional Theory calculations are conducted to investigate the adsorption of calcium (magnesium) ions on smithsonite (101) surface. The calculation results indicate that calcium ions and magnesium ions have strong chemisorption with the surface of clean smithsonite (101), and the adsorption of calcium ions is stronger than magnesium ions. The hydrated smithsonite (101) surface also adsorbed calcium and magnesium ions, but the adsorption intensity was obviously weakened. In addition, the adsorption of calcium ions on hydrated smithsonite surface (101) weakens the hydration of smithsonite (101). The results can provide theoretical guidance for eliminating the influence of unavoidable ions in the flotation process of smithsonite.
-
Key words:
- DFT /
- flotation /
- smithsonite /
- calcium(magnesium)ions /
- adsorption /
- hydrated surface
-

-
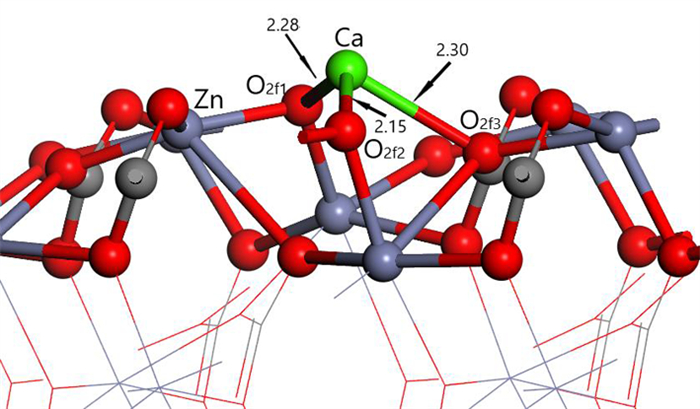
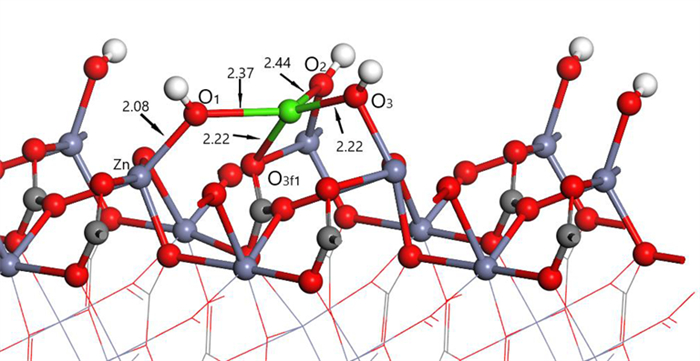
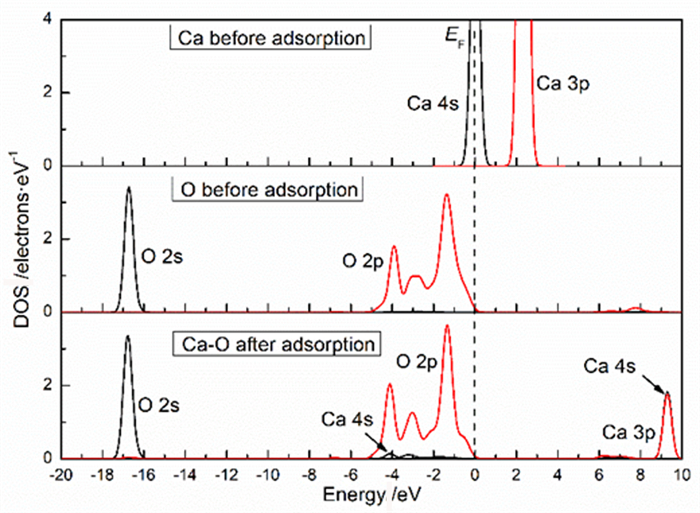
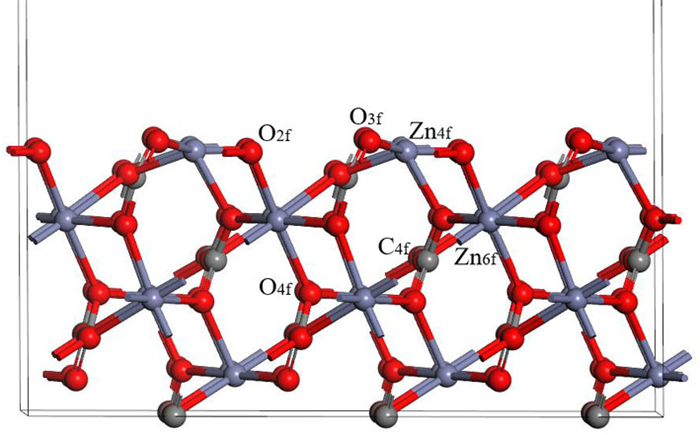
表 1 钙离子在清洁菱锌矿(101)表面吸附前后的电荷
Table 1. Mulliken charge of atoms before and after Ca2+ adsorption on clean smithsonite(101)surface
原子序号 吸附状态 电子数 电荷/e s p Ca 吸附前 7.56 12.00 0.44 吸附后 6.08 12.10 1.56 O2f1 吸附前 3.91 4.68 -0.59 吸附后 3.89 5.00 -0.89 O2f2 吸附前 3.91 4.68 -0.59 吸附后 3.88 5.06 -0.96 O2f3 吸附前 3.83 4.72 -0.58 吸附后 3.85 4.86 -0.75 表 2 镁离子在清洁菱锌矿(101)表面吸附的电荷
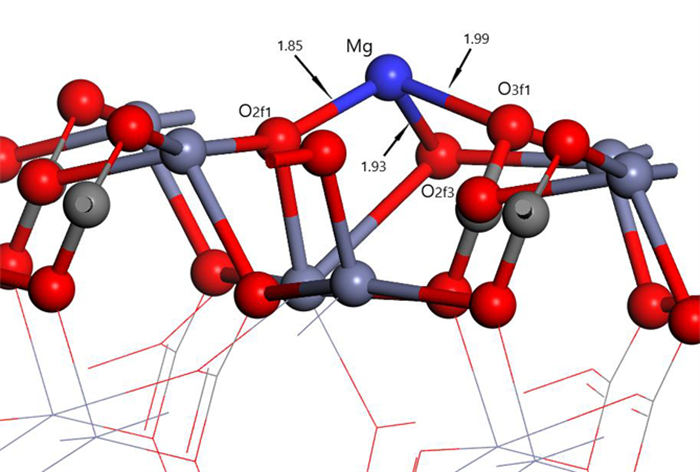
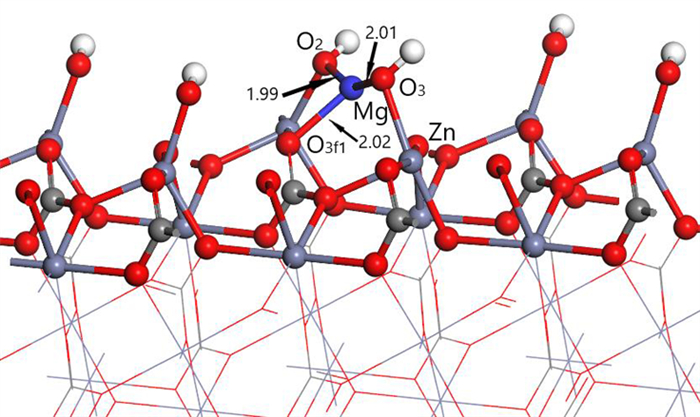
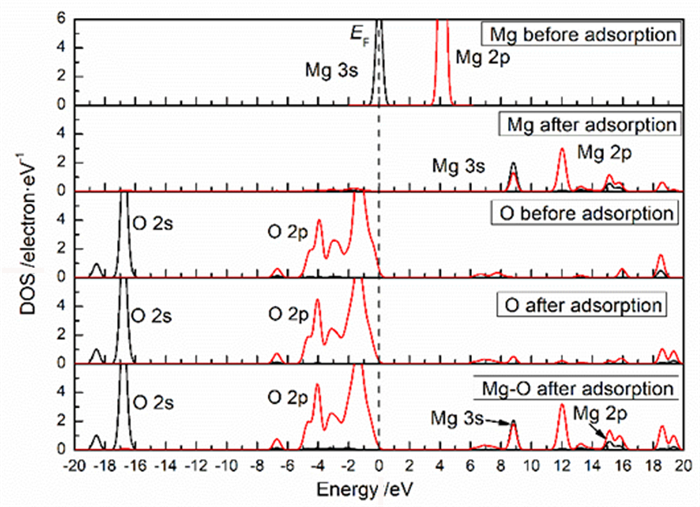
Table 2. Mulliken charge of atoms before and after Mg2+ adsorption on clean smithsonite(101)surface
原子序号 吸附状态 电子数 电荷/e s p Mg 吸附前 5.69 6.00 0.31 吸附后 4.25 6.39 1.13 O2f1 吸附前 3.91 4.68 -0.59 吸附后 3.85 5.02 -0.89 O2f2 吸附前 3.91 4.68 -0.59 吸附后 3.82 4.84 -0.68 O3f1 吸附前 3.83 4.72 -0.49 吸附后 3.84 4.83 -0.70 -
[1] 尚衍波, 陈经华, 何发钰. 中国铅锌选矿技术新进展[J]. 世界有色金属, 2016(6): 11-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COLO201606001.htm
SHANG Y B, CHEN J H, HE F Y. The new progress of China's lead-zinc mineral processing technology[J]. World Nonferrous Metal, 2016(6): 11-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COLO201606001.htm
[2] 田尤, 刘廷, 曾祥婷, 等. 我国锌资源产业形势及对策建议[J]. 现代矿业, 2015, 31(4): 5-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2015.04.002
TIAN Y, LIU T, ZENG X T, et al. Situation and suggestion of China's zinc resources industry[J]. Express Information of Mining Industry, 2015, 31(4): 5-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2015.04.002
[3] 刘红召, 杨卉芃, 冯安生. 全球锌矿资源分布及开发利用[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2017(1): 113-118. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=8c635d74-95a7-4338-bd4b-7df9f58a90ec
LIU H Z, YANG H P, FENG A S. The distribution and utilization of global zinc resource[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2017(1): 113-118. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=8c635d74-95a7-4338-bd4b-7df9f58a90ec
[4] 杜五星, 戴惠新, 何东祥, 等. 氧化铅锌矿的选矿研究现状及进展[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2016(4): 11-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2016.04.003
DU W X, DAI H X, HE D X, et al. Research status and progress of beneficiation for a lead-zinc oxide ore[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2016(4): 11-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2016.04.003
[5] LIU C, ZHANG W, SONG S, et al. Flotation separation of smithsonite from calcite using 2-phosphonobutane-1, 2, 4-tricarboxylic acid as a depressant[J]. Powder Technology, 2019, 352: 11-15. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2019.04.036
[6] 罗利萍, 徐龙华, 巫侯琴, 等. 氧化锌矿物的表面性质与浮选关系研究综述[J]. 金属矿山, 2020(6): 24-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS202006005.htm
LUO L P, XU L H, WU H Q, et al. A review on the relationship between surface properties and flotation of zinc oxide ore[J]. Metal Mine, 2020(6): 24-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS202006005.htm
[7] 李想, 林诗鸿, 陈佳, 等. 氧化锌矿石浮选研究进展[J]. 金属矿山, 2018(10): 98-103. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS201810019.htm
LI X, LIN S H, CHEN J, et al. Research status of zinc oxide ore flotation[J]. Metal Mine, 2018(10): 98-103. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS201810019.htm
[8] 沈智豪, 张谦, 方健, 等. 菱锌矿表面硫化研究进展[J]. 有色金属(选矿部分), 2021(1): 37-46+59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXK202101007.htm
SHEN Z H, ZHANG Q, FANG J, et al. Research progress in surface sulfidization of smithsonite[J]. Nonferrous Metals(Mineral processing section), 2021(1): 37-46+59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXK202101007.htm
[9] 刘小奇, 张鑫. 菱锌矿浮选基础理论研究[J]. 金属材料与冶金工程, 2013, 41(6): 30-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6084.2013.06.007
LIU X Q, ZHANG X. Flotation basic theory research of smithsonite[J]. Metal Materials and Metallurgy Engineering, 2013, 41(6): 30-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6084.2013.06.007
[10] 冯程, 祁忠旭, 孙大勇, 等. 氧化锌矿选矿技术现状与进展[J]. 矿业研究与开发, 2019, 39(9): 105-109. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYYK201909023.htm
FENG C, QI Z X, SUN D Y, et al. Current status and overview of zinc oxide ore beneficiation technology[J]. Mining Research and Development, 2019, 39(9): 105-109. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYYK201909023.htm
[11] 杨柳毅, 黄光耀, 曹玉川, 等. 菱锌矿和异极矿的晶体结构差异对其分选性的影响[J]. 矿冶, 2018, 27(6): 22-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYZZ201806005.htm
YANG L Y, HUANG G Y, CAO Y C, et al. Influence of crystal sctructure of hemimorphite and smithsonite on their floatability[J]. Mining and Metallurgy, 2018, 27(6): 22-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYZZ201806005.htm
[12] 蒋世鹏, 张国范, 常永强, 等. 金属离子对菱锌矿硫化浮选影响研究[J]. 有色金属(选矿部分), 2016(2): 23-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9492.2016.02.005
JIANG S P, ZHANG G F, CHANG Y Q, et al. Effect of metal ions on sulfiding flotation of smithsonite[J]. Nonferrous Metals(Mineral processing section), 2016(2): 23-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9492.2016.02.005
[13] ANA CAROLINA ARANTES ARAúJO, ROSA MALENA FERNANDES LIMA. Influence of cations Ca2+, Mg2+ and Zn2+ on the flotation and surface charge of smithsonite and dolomite with sodium oleate and sodium silicate[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2017: 35-41
[14] 韩玉光. 菱锌矿与方解石浮选分离试验研究及机理探讨[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2018.
HAN Y G. Experimental study and mechanism of flotation separation of calcite from zinc ore[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2018.
[15] SHI Q, ZHANG G, FENG Q, et al. Effect of solution chemistry on the flotation system of smithsonite and calcite[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2013, 119: 34-39. doi: 10.1016/j.minpro.2012.12.011
[16] 何晓太, 王杰, 崔伟勇, 等. 胶磷矿-白云石体系中离子的溶液化学行为研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2015, 35(3): 55-57+62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2015.03.015
HE X T, WANG J, CUI W Y, et al. Solution chemistry of dissolved ions in collophane-dolomite system[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2015, 35(3): 55-57+62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2015.03.015
[17] 刘忠义. 金属离子对菱锌矿和方解石分散行为的影响研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2019.
LIU Z Y. Study on the influence of metal ions on dispersion of smithsonite and calcite[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2019.
[18] 崔萌萌. 菱锌矿与石英浮选分离中难免离子的影响及消除[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2012.
CUI M M. Effect and elimination of inevitable ions in selective flotation between smithsonite and quartz[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2012.
[19] 杨少燕. 菱锌矿浮选的理论与工艺研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2010.
YANG S Y. Study on theory and process of flotation of calamine[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2010.
[20] 刘长青. 氧化锌矿浮选体系金属离子对矿物浮选行为影响[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2017.
LIU C Q. Effect of ions on mineral flotation behavior in zinc oxide mineral flotation system[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2017.
[21] 邓荣东. 氧化锌矿矿浆中离子存在行为及吸附机理研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2015.
DENG R D. Study on the existence behavior and adsorption mechanism of ions in zinc oxide ore pulp[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2015.
[22] POPOV SR, VUINI DR, KAANIK JV. Floatability and adsorption of ethyl xanthate on sphalerite in an alkaline medium in the presence of dissolved lead ions[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 1989, 27(3/4): 205-219.
[23] A. HUNG, J. MUSCAT, I. YAROVSKY, et al. Density functional theory studies of pyrite FeS2(100) and(110) surfaces[J]. Surf. Sci., 2002, 520: 111-119. doi: 10.1016/S0039-6028(02)02294-X
[24] C.H. ZHAO, J.H. CHEN, Y.Q. Li, et al. DFT study of interactions between calcium hydroxyl ions and pyrite, marcasite, pyrrhotite surfaces, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2015, 355: 577-581. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.07.081
[25] Y. CHEN, J.H. CHEN. The first-principle study of the effect of lattice impurity on adsorption of CN on sphalerite surface[J]. Miner. Eng., 2010: 23 676-684. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2010.04.002
[26] REICH M, Becker U. First-principles calculations of the thermodynamic mixing properties of arsenic incorporation into pyrite and marcasite[J]. Chemical Geology, 2006, 225(3/4): 278-290.
[27] 周泳. 量子化学方法在矿物表面研究中的应用[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学, 2006.
ZHOU Y. Applicafion of mineral surface studying by quantum chemistry method[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2006.
[28] DANIEL JOUBERT. Density functionals: theory and applications[M]. Springer Berlin Heidelberg; Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg: 2007-05-01.
[29] HOSSEINI S H, FORSSBERG E. Smithsonite flotation using potassium amyl xanthate and hexylmercaptan[J]. Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy, 2006, 115(2): 107-112. doi: 10.1179/174328506X109077
[30] NUNES A P L, PERES A E C, DE ARAUJO A C, et al. Electrokinetic properties of wavellite and its floatability with cationic and anionic collectors[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2011, 361(2): 632-638. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2011.06.014
[31] L. ROTTMANNOVá, J. RIMARík, T. VESELY, et al. Applicability of DFTB+ method for the calculations of O-H bond dissociation enthalpies of phenols[J]. Acta Chimica Slovaca, 2010, 3: 12-19.
[32] SUN F, ZHANG J X, TIAN Y. Calculation of alloying effect of ruthenium in Ni-based single-crystal super alloys[J]. Computational Mate-rials Science, 2012, 60(10): 163-167.
[33] XU SHUN, WANG GANG, LIU HONGMIN, et al. A DMol3 study on the reaction between trans-resveratrol and hydroperoxyl radical: dissimilarity of antioxidant activity among O-H groups of trans-resveratrol[J]. Journal of Molecular Structure: Theochem, 2007, 809(1): 79-85.
[34] PERDEW J P, CHEVARY J A, VOSKO S H, et al. Atoms, molecules, solids, and surfaces: applications of the generalized gradient approximation for exchange and correlation[J]. Physical Review B, 1992, 46(11): 6671-6687. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.46.6671
[35] MONKHORST H J, PACK J D. Special points for brillouin-zone integrations[J]. Physical Review B, 1976, 13(12): 5188-5192. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.13.5188
[36] Z. WANG, L.H. XU, J.M. WANG, et al. A comparison study of adsorption of benzohydroxamic acid and amyl xanthate on smithsonite with dodecylamine as co-collector[J]. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2017, 426: 1141-1147. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.07.271
[37] HAN C, LI T, ZHANG W, et al. Density functional theory study on the surface properties and floatability of hemimorphite and smith sonite[J]. Minerals, 2018, 8(12): 56-60.
[38] N.H. MOREIRA, G. DOLGONOS, B. ARADI, A.L. DA ROSA. Frauenheim Th. Toward an accurate density-functional tight-binding description of zinc-containing compounds, J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2009(5): 605-614. doi: 10.1021/ct800455a
[39] H.J. MONKHORST, J.D. PACK. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations[J]. Phys. Rev. B, 1976, 13: 5188-5192. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.13.5188
[40] 沈智豪, 张谦, 方健, 等. 菱锌矿表面硫化研究进展[J]. 有色金属(选矿部分), 2021(1): 37-46+59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXK202101007.htm
SHEN Z H, ZHANG Q, FANG J, et al. Research progress in surface sulfidization of smithsonite[J]. Nonferrous Metals(Mineral processing section), 2021(1): 37-46+59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXK202101007.htm
[41] LIU M, CHEN J H, CHEN Y, et al. Interaction between smithsonite and carboxyl collectors with different molecular structure in the presence of water: a theoretical and experimental study[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 510: 145410.1-145410.10.
[42] CHEN Y, LIU M, CHEN J H, et al. A density functional based tight binding(DFTB+) study on the sulfidization-amine flotation mechanism of smithsonite[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 458: 454-463.
-



 下载:
下载: