The Leaching Technology of Rare Earth Polishing Powder Waste in Thiourea-Hydrochloric Acid System and Recovery of Rare Earth Oxides from the Lixivium Through Oxalic Acid Precipitation
-
摘要:
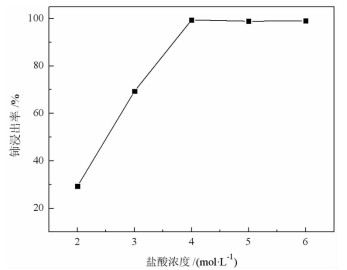
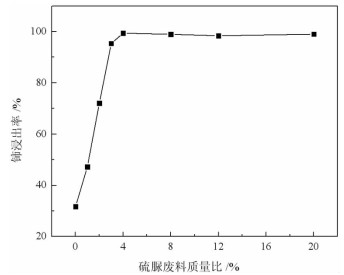
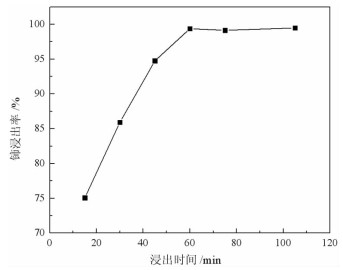
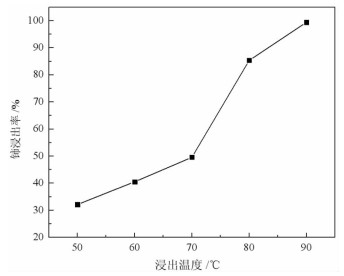
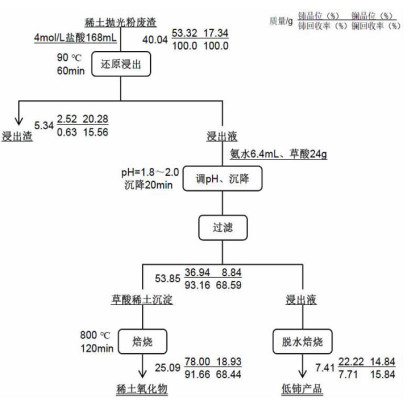
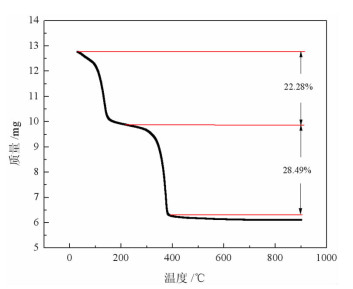
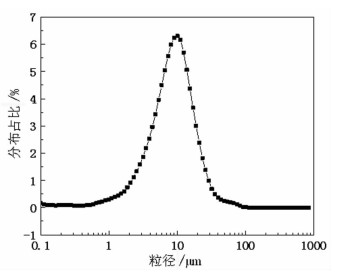
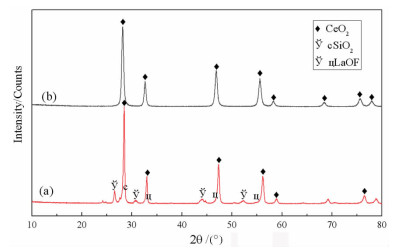
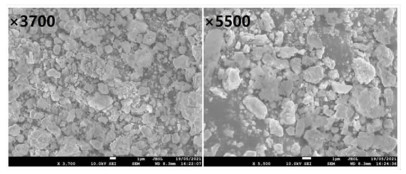
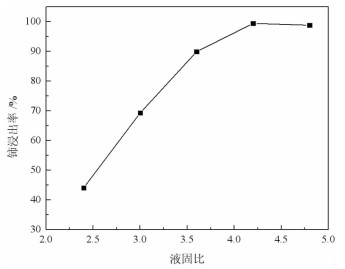
基于稀酸溶液中Ce(Ⅳ)难溶而Ce(Ⅲ)易溶的特点,采用硫脲-稀盐酸体系还原浸出稀土抛光粉废料中稀土氧化物。考察了浸出温度、浸出时间、液固比(L/S)、盐酸浓度和硫脲用量对稀土抛光粉废料中铈浸出率的影响。结果表明:在盐酸浓度为4 mol/L、L/S为4.2、浸出温度90 ℃、浸出时间60 min、硫脲用量0.04 g/g给料的优选条件下,铈浸出率达99.37%。然后对浸出液采用草酸沉淀法分离和回收稀土氧化物,经氨水调pH至1.8~2.0,草酸沉淀,氧化焙烧,得到稀土氧化物产物,总REO含量约为97%,其中CeO2 78.00%、La2O3 18.93%,回收率分别为91.66%和68.44%。激光粒度分析、XRD、SEM等研究表明,稀土氧化物产物粒度分布均匀,主要为CeO2晶体,方形颗粒表面平整,棱角分明。
Abstract:The solubility of Ce(Ⅲ) is far greater than that of Ce(Ⅳ). Thus, the thiourea was used to reduce Ce(Ⅳ) into Ce(Ⅲ) in dilute hydrochloric acid solutions to promote the recovery of rare earth oxides from a rare earth polishing powder waste. The effects of leaching temperature, leaching time, liquid-to-solid ratio (L/S), hydrochloric acid concentration and thiourea dosage on the leaching ratio of cerium from the rare earth polishing powder waste were investigated. The results showed that under the optimal technologies, hydrochloric acid concentration of 4 mol/L, L/S of 4.2, leaching temperature of 90 ℃, leaching time of 60 min, and thiourea dosage of 0.04 g/g, the cerium leaching ratio reached 99.37%. Then, the rare earth ions in leaching solutions were separated and recovered by oxalic acid precipitation approach. After adjusting pH to 1.8-2.0 by ammonia water, oxalic acid was added to deliver rare earth oxalate precipitates which were subsequently roasted under air to obtain the rare earth oxide (REO) product. The total REO content in the REO product was about 97% with 78.00% CeO2 and 18.93% La2O3, and their recovery ratio was 91.66% and 68.44%, respectively. In addition, the findings of laser particle size analysis, XRD and SEM showed that the rare earth oxide products were mainly composed by CeO2 square particles, and exhibited a narrow particle size distribution with a flat and angular surface.
-
Key words:
- rare earth polishing powder waste /
- reduction leaching /
- cerium /
- lanthanum /
- oxalic acid
-

-
表 1 稀土抛光粉废料的化学组成
Table 1. Chemical composition of rare earth polishing powder waste
/% 成分 Ce La O Al Si F Ca 含量 43.40 14.79 23.90 5.00 4.37 3.85 0.80 注:Ce和La为化学滴定法分析结果,其余元素为XRF分析结果。 表 2 稀土氧化物产品的化学组成
Table 2. Chemical composition of rare earth oxide products
/% 成分 Ce La O F Cl Al Ca Si 含量 63.49 16.14 17.6 2.21 0.152 0.041 0.035 0.02 注:Ce和La为化学滴定法分析结果,其余元素为XRF分析结果。 -
[1] BORRA C, VLUGT T, YANG Y, et al. Recovery of cerium from glass polishing waste: A critical review[J]. Metals, 2018, 8(10): 801-817. doi: 10.3390/met8100801
[2] UM N, HIRATO T. A hydrometallurgical method of energy saving type for separation of rare earth elements from rare earth polishing powder wastes with middle fraction of ceria[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2016, 34(5): 536-542. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0721(16)60059-5
[3] 罗天纵, 吴希桃, 包新军, 等. 废弃稀土抛光粉回收再利用研究进展[J]. 稀土, 2020, 41(3): 95-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTZZ202003015.htm
LUO T Z, WU X T, BAO X J, et al. Research process in recovering and reutilizing of rare earth polishing powder wastes[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2020, 41(3): 95-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTZZ202003015.htm
[4] OH M, NHO J, CHO S, et al. Polishing behaviors of ceria abrasives on silicon dioxide and silicon nitride CMP[J]. Powder Technology, 2011, 206(3): 239-245. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2010.09.025
[5] BINNEMANS K, JONES P T, BLANPAIN B, et al. Recycling of rare earths: a critical review[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2013, 51: 1-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2012.12.037
[6] MESHRAM P, ABHILASH. Recovery and recycling of cerium from primary and secondary resources- a critical review[J]. Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy Review, 2020, 41(4): 279-310. doi: 10.1080/08827508.2019.1677647
[7] 李振民, 王勇, 牛京考. 中国稀土资源开发的生态环境影响及维护政策[J]. 稀土, 2017, 38(6): 144-154. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTZZ201706019.htm
LI Z M, WANG Y, NIU J K. The influence of rare earth resources exploitation on ecology and environment and the protection plicy[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2017, 38(6): 144-154. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTZZ201706019.htm
[8] TING M H, SEAMAN J. Rare earths: future elements of conflict in asia[J]. Asian Studies Review, 2013, 37(2): 234-252. doi: 10.1080/10357823.2013.767313
[9] 涂雅洁. 废弃稀土抛光渣梯级循环利用的研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2012.
TU Y J. The study for step recycling of easte rare earth polishing powder[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2012.
[10] KIM J, KIM U, BYEON M, et al. Recovery of cerium from glass polishing slurry[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2011, 29(11): 1075-1078. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0721(10)60601-1
[11] WANG L, LIU P, CHEN Y. Recovery of cerium oxide abrasive from an abrasive-glass polishing waste through alkaline roasting followed by water leaching[J]. Metals, 2020, 10(6): 752-767. doi: 10.3390/met10060752
[12] 刘晓杰, 于亚辉, 许涛, 等. 碱焙烧法从稀土抛光粉废渣中回收稀土[J]. 稀土, 2015, 36(4): 75-80. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTZZ201504013.htm
LIU X J, YU Y H, XU T, et al. Recovery of RE from waste RE polishing powder by Alkali roasting[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2015, 36(4): 75-80. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTZZ201504013.htm
[13] ZOU D, LI H, DENG Y, et al. Recovery of lanthanum and cerium from rare earth polishing powder wastes utilizing acid baking-water leaching-precipitation process[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 261: 118244. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2020.118244
[14] 罗磊. 从废弃稀土抛光粉中回收稀土金属的工艺条件研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2015.
LUO L. Technological conditions of recovering rare earth metals from an abandoned rare earth polishing power[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2015.
[15] POSCHER A, LUIDOLD S, ANTREKOWITSCH H. Extraction of cerium and lanthanum from spent glass polishing agent: rare earth elements symposium[C]. Montreal, 2013.
[16] JANOŠ P, KURÁÑ P, EDERER J, et al. Recovery of cerium dioxide from spent glass-polishing slurry and its utilization as a reactive sorbent for fast degradation of toxic organophosphates[J]. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2015(22): 1-8.
[17] LU S, SUN S, HUANG X, et al. Optimization of recovering cerium from the waste polishing powder using response surface methodology[J]. Green Processing and Synthesis, 2017, 6(2): 217-224.
[18] JING-YING L, XIU-LI X, WEN-QUAN L. Thiourea leaching gold and silver from the printed circuit boards of waste mobile phones[J]. Waste Management, 2012, 32(6): 1209-1212. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2012.01.026
[19] SADRI F, RASHCHI F, AMINI A. Hydrometallurgical digestion and leaching of Iranian monazite concentrate containing rare earth elements Th, Ce, La and Nd[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2017, 159: 7-15. doi: 10.1016/j.minpro.2016.12.003
[20] 全国稀土标准化技术委员会. 稀土抛光粉化学分析方法第1部分: 氧化铈量的测定滴定法[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2012.
National rare earth standardization technical committee. GB/T 20166.1-2012, Chemical analysis methods of rare earth polishing powder-Part1: Determination of cerium oxide content-Titrimetry[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2012.
[21] 赵林治, 杨书廷. 硫脲稳定性研究[J]. 河南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 1992(1): 98-102. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNSX199201018.htm
ZHAO L Z, YANG S T. Study on the stability of thiourea[J]. Journal of Henan Normal University (Natural Science), 1992(1): 98-102. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNSX199201018.htm
[22] CALLA-CHOQUE D, LAPIDUS G T. Acid decomposition and silver leaching with thiourea and oxalate from an industrial jarosite sample[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2020, 192: 105289. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2020.105289
[23] GABAL M A, ELROBY S A K, OBAID A Y. Synthesis and characterization of nano-sized ceria powder via oxalate decomposition route[J]. Powder Technology, 2012, 229: 112-118. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2012.06.017
[24] 李梅, 杨来东, 柳召刚, 等. 粒度及粒度分布对铈基稀土抛光粉性能影响的研究[J]. 稀土, 2016, 37(4): 144-147. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTZZ201604026.htm
LIM, YANG L D, LIU Z G, et al. The study of the ipact of particle size and particle size distribution of the Ce-based rare earth polishing powder on its performance[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2016, 37(4): 144-147. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTZZ201604026.htm
[25] YU B, JIANG J, YANG C. Conversion of lanthanum and cerium recovered from hazardous waste polishing powders to hazardous ammonia decomposition catalysts[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 379: 120773. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120773
[26] 周筱桐, 肖汉宁, 刘井雄, 等. 草酸沉淀法制备稀土抛光粉及其抛光性能[J]. 机械工程材料, 2014, 38(8): 57-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXGC201408013.htm
ZHOU X T, XIAO H N, LIU J X, et al. Preparation of polishing powders by oxalate deposition and its polishing performance[J]. Materials of Mechanical Engineering, 2014, 38(8): 57-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXGC201408013.htm
[27] ZHAN G, YU J, XU Z, et al. Kinetics of thermal decomposition of lanthanum oxalate hydrate[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(4): 925-934. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61266-1
[28] ANJANEYA K C, NAYAKA G P, MANJANNA J, et al. Studies on structural, morphological and electrical properties of Ce0.8Ln0.2O2-δ (Ln=Y3+, Gd3+, SM3+, Nd3+ and La3+) solid solutions prepared by citrate complexation method[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014, 585: 594-601. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.09.101
-



 下载:
下载: