Recovery of Titanium and Iron from Titanium Rough Concentrate in Malawi by Reduction Roasting-Magnetic Separation Process
-
摘要:
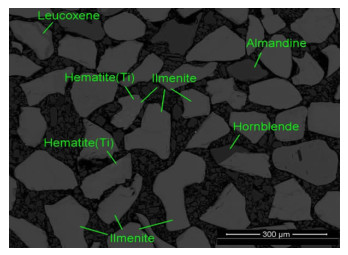
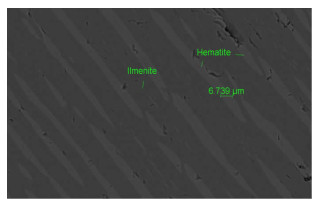
由于马拉维钛铁矿资源中铁和钛矿物关系复杂,用常规的重选、磁选和电选方法难以直接分离,不能选出合格的钛精矿,仅能获得低品级的钛粗精矿。本研究用MLA(矿物定量自动检测系统)和SEM(扫描电镜)等测试手段对钛粗精矿进行了工艺矿物学研究,研究结果表明,该钛粗精矿中钛赤铁矿和赤铁矿合计含量为16.33%,钛铁矿含量为79.49%,由于钛与铁呈固溶分离或氧化蚀变形成了钛赤铁矿,导致钛粗精矿中钛、铁难以有效分离,因此,采用焙烧工艺将赤铁矿还原成磁铁矿,利用磁铁矿与钛铁矿的磁性差异特征进行磁选分离,有效回收利用钛粗精矿中的铁和钛。钛粗精矿经过还原焙烧—磁选工艺处理后获得铁精矿和钛精矿,铁精矿中Fe含量为56.71%、回收率13.50%,钛精矿中的TiO2含量为49.10%、产率为65.57%、回收率为77.57%。该试验使钛粗精矿中钛铁矿与赤铁矿得到高效分离,为马拉维钛铁矿资源高效综合回收利用提供了技术途径。
Abstract:Due to the complexity of iron and titanium minerals in Malawian, only low grade titanium concentrate can be obtained by conventional gravity separation, magnetic separation and electric separation. Through MLA (automatic quantitative analysis system of mineral parameters) and SEM (scanning electron microscope), the process mineralogy of titanium rough concentrate was studied. The results showed that the content of Ti-hematite and hematite in Ti rough concentrate was 16.33%, ilmenite content was 79.49%. It is difficult to effectively separate titanium and iron in titanium rough concentrate due to hematite formed by oxidation and alteration. Therefore hematite is reduced to magnetite by roasting and then magnetic separation is carried out in virtue of magnetic difference between magnetite and ilmenite. Iron and titanium in titanium rough concentrate can be effectively recovered and utilized. Iron concentrate and titanium concentrate were obtained by reduction roasting and magnetic separation process. At the same time, secondary iron concentrate and secondary titanium concentrate were comprehensively recycled. Fe content in iron concentrate was 56.71%, recovery rate was 13.50%. TiO2 content in titanium concentrate was 49.10%, yield was 65.57%. Fe content in secondary iron concentrate was 51.08%, recovery rate was 10.29%. TiO2 content in secondary titanium concentrate was 41.51%, yield was 10.57%。The tests solved the technical problem of separating ilmenite from hematite in titanium rough concentrate, and provided a technical way for comprehensive and effective recovery and utilization of Malawian ilmenite.
-
Key words:
- ilmenite /
- hematite /
- magnetite /
- process mineralogy /
- reduction roasting
-

-
表 1 钛粗精矿化学多元素分析结果
Table 1. Results of chemical multi-element analysis of Ti rough concentrate
/% TiO2 Fe P S CaO MgO Al2O3 SiO2 Mn 42.20 38.76 0.03 <0.005 0.20 0.62 0.82 2.29 0.83 表 2 钛粗精矿矿物组成分析结果
Table 2. Results of mineral phase analysis of Ti rough concentrate
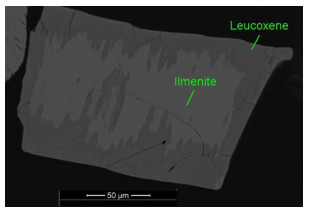
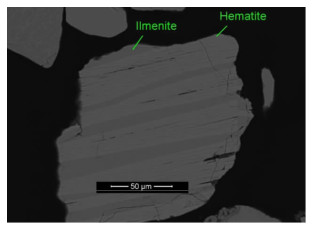
/% Mineral phase Content Content of TiO2 Distibution of TiO2 Content of Fe Distibution of Fe Ilmenite 79.49 48.84 93.49 34.00 72.28 Haplotypite 11.09 17.8 4.75 56.04 16.62 Hematite 5.24 1.88 0.24 66.78 9.35 Rutile 0.04 97.13 0.10 1.18 <0.01 Leucoxene 0.75 71.01 1.28 16.34 0.33 Sphene 0.01 36.18 0.01 2.22 <0.01 Pyroxene 0.39 1.17 0.01 21.50 0.22 Hornblende 0.86 3.33 0.07 15.50 0.36 Garnet 1.61 1.14 0.05 19.43 0.84 Other 0.52 - - - - Total 100 41.53 100.00 37.39 100.00 表 3 钛铁矿的能谱分析结果
Table 3. Energy spectrum analysis results of ilmenite
/% TiO2 FeO MnO Na2O MgO Al2O3 SiO2 Nb2O5 48.84 48.57 1.57 0.02 0.44 0.12 0.36 0.07 表 4 其他主要矿物的能谱分析
Table 4. Energy spectrum analysis of other main minerals
/% Constituent Fe2O3 Fe3O4 TiO2 MnO MgO Al2O3 SiO2 V2O5 Cr2O3 Hematite 95.41 - 1.88 0.18 - 1.03 1.14 0.35 0.01 Haplotypite 80.05 - 17.80 0.18 0.09 0.86 0.47 0.47 0.08 Titano-magnetite - 77.21 20.13 0.31 0.15 0.71 0.84 0.58 0.06 表 5 主要矿物的解离度测定
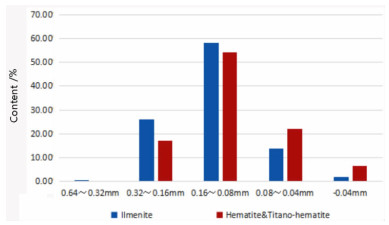
Table 5. Determination of liberation degree of main minerals
/% Size class/mm +0.150 -0.150 合计 yield 59.54 40.46 100.00 Content Ilmenite 80.77 77.61 79.49 Hematite 3.552 7.77 5.24 Titano-hematite 12.74 8.67 11.09 Liberation degree Ilmenite 84.32 85.68 84.87 Hematite 90.40 91.92 91.00 Titano-hematite 7.25 16.04 10.76 表 6 钛粗精矿中铁和钛元素在不同场强磁性产物中分布情况
Table 6. Distribution of Fe and Ti element in magnetic products with different field strengths in Ti rough concentrate
/% Magnetic field intensity/T yield TiO2 Fe Main minerals 0.10 1.43 29.80 47.92 Ilmenite, hematite and titano-hematite 0.12 11.89 37.08 41.64 0.23 45.73 43.00 40.18 Ilmenite, hematite, titano-hematite 0.42 12.06 44.40 36.80 a few leucoxene, garnet and monazite 0.48 20.74 37.54 36.04 Ilmenite, hematite, titano-hematite 0.52 7.85 35.37 37.38 a few leucoxene, garnet, monazite and gangue Nonmagnetic minerals 0.31 16.10 11.76 Gangue Total 100.00 40.46 38.89 表 7 焙烧方式对比试验结果
Table 7. Comparison tests of roasting methods
/% Calcination mode Product Yield Content Rate of recovery TiO2 Fe TiO2 Fe Direct magnetic separation Iron concentrate 0.02 27.34 51.32 0.01 0.02 Ilmenite concentrate 99.98 42.63 39.08 99.99 99.98 Oxidation roasting test Iron concentrate 8.19 37.22 37.51 7.15 7.94 Ilmenite concentrate 91.81 43.08 38.79 92.85 92.06 Reduction roasting /Iron concentrate 28.67 29.44 49.35 19.75 35.89 Ilmenite concentrate 71.33 48.07 35.43 80.25 64.11 Feed of titanium rough concentrate 100.00 42.65 39.10 100.00 100.00 表 8 还原焙烧的冷却方式对比试验结果
Table 8. Comparison tests of cooling methods for reduction roasting
/% Cooling mode Product Yield Content rate of recovery Slow-air cooling Iron concentrate 28.74 29.29 19.73 Ilmenite concentrate 71.26 48.08 80.27 Water quenching Iron concentrate 28.67 29.44 19.75 Ilmenite concentrate 71.33 48.07 80.25 Feed of titanium rough concentrate 100.00 42.66 100.00 表 9 还原焙烧的还原剂种类试验结果
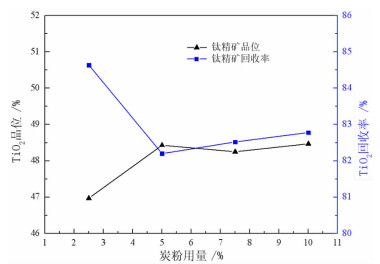
Table 9. Type tests of reducing agents
/% Type of reducing agent Product Yield Content Rate of recovery Lignite Iron concentrate 13.00 29.20 8.88 Ilmenite concentrate 87.00 44.75 91.12 Anthracite (0.5~1 mm) Iron concentrate 18.71 29.90 13.11 Ilmenite concentrate 81.29 45.62 86.89 Anthracite (<0.5 mm) Iron concentrate 20.13 30.61 14.41 Ilmenite concentrate 79.87 45.85 85.59 Carbon powder Iron concentrate 27.51 27.63 17.80 Ilmenite concentrate 72.49 48.43 82.20 Feeding of crude titanium concentrate 100.00 42.68 100.00 表 10 干式和湿式弱磁选机对比试验结果
Table 10. Comparison tests of dry and wet weak magnetic separators
/% Type of magnetic separator Product Yield Content rate of recovery Wet drum type weak magnet separator Iron concentrate 28.67 29.44 19.75 Ilmenite concentrate 71.33 48.07 80.25 Dry drum type weak magnet separator Iron concentrate 28.91 29.56 19.99 Ilmenite concentrate 71.09 48.11 80.01 表 11 磁选机机型试验结果
Table 11. Test results of magnetic separator model
/% Type of magnetic separator Product Yield Content rate of recovery Concurrent Iron concentrate 27.51 27.63 17.80 Ilmenite concentrate 72.49 48.43 82.20 Counter-Current Iron concentrate 28.85 27.53 18.60 Ilmenite concentrate 71.15 48.85 81.40 表 12 扫选磁场强度试验结果
Table 12. Test results of scanning magnetic field strength
/% Magnetic field intensity/T Product Yield Content Rate of recovery 0.20 Iron concentrate 27.45 27.74 17.84 Secondary titanium concentrate 0.53 39.17 0.49 Ilmenite Concentrate 72.02 48.40 81.67 Iron concentrate 27.53 27.67 17.83 0.30 Secondary titanium concentrate 1.75 39.62 1.62 Ilmenite Concentrate 70.72 48.67 80.55 Iron concentrate 27.51 27.63 17.80 0.45 Secondary titanium concentrate 5.31 40.55 5.04 Ilmenite Concentrate 67.18 49.05 77.16 表 13 合并铁粗精矿磨矿细度试验结果
Table 13. Grinding fineness test results of combined iron coarse concentrates
/% Grinding fineness Product Yield Content rate of recovery TiO2 Fe TiO2 Fe Iron concentrate 64.54 25.10 54.52 52.13 70.81 -0.075 mm Secondary iron concentrate 8.73 38.65 43.33 10.86 7.61 90% Secondary titanium concentrate 26.73 43.04 40.14 37.01 21.58 Iron concentrate 42.16 21.73 56.73 29.86 48.23 -0.045 mm Secondary iron concentrate 25.14 27.65 51.45 20.65 23.76 90% Secondary titanium concentrate 32.70 43.12 39.45 49.49 28.01 Feed of titanium rough concentrate 100.00 30.84 49.58 100.00 100.00 表 14 全流程试验结果
Table 14. Test results of the whole process
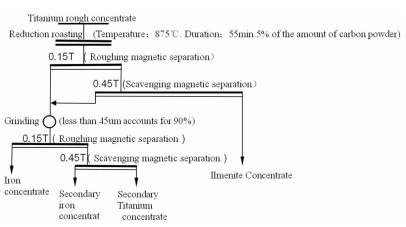
/% Product Yield Content Rate of recovery TiO2 Fe TiO2 Fe Iron concentrate 13.50 21.40 56.71 6.75 19.16 Secondary iron concentrate 8.05 27.16 51.08 5.11 10.29 Secondary titanium concentrate 10.88 41.51 39.16 10.57 10.67 Ilmenite Concentrate 67.57 49.10 35.40 77.57 59.88 Feeding of crude titanium concentrate 100.00 42.77 39.95 100.00 100.00 Combined iron concentrate 21.55 23.55 54.61 11.86 29.45 Combined titanium concentrate 78.45 48.05 35.92 88.14 70.55 表 15 钛精矿的化学分析
Table 15. Chemical analysis of titanium concentrate
/% Constituent TiO2 P CaO MgO S Fe2O3 MnO Content 49.10 0.022 0.27 0.76 <0.005 5.37 1.56 表 16 钛精矿矿物组成分析结果
Table 16. Mineral phase analysis results of titanium concentrate
/% Minerals Content Minerals Content Minerals Content Ilmenite 92.869 Titano-hematite 0.628 Garnet 2.213 Leucoxene 1.365 Hematite 0.006 Hornblende 1.444 Pyroxene 0.835 Limonite 0.007 Zircon 0.101 表 17 铁精矿的化学分析
Table 17. Chemical analysis of iron concentrate
/% Constituent TFe SiO2 S P Cu Pb Zn Sn As Content 56.71 0.54 0.006 0.019 0.005 <0.001 0.03 0.05 <0.005 -
[1] 喻连香, 周吉奎, 刘军, 等. 马拉维含难分离赤铁矿的钛锆粗精矿工艺矿物学及分离新技术的研究[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2019(12): 171-178. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=8711e9c5-2a7d-405c-ba10-3b6efad3257a
YU L X, ZHOU J K, LIU J, et al. Study on process mineralogy and separation technology of titanium-zirconium rough concentrate with refractory hematite in Malawi[J]. Conservation and utilization of Mineral Resource. 2019 (12): 171-178. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=8711e9c5-2a7d-405c-ba10-3b6efad3257a
[2] 王利珍, 刘洋, 曹佳宏, 等. 某钛铁矿石的工艺矿物学特征[J]. 金属矿山, 2016(5): 91-93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1250.2016.05.020
WANG L Z, LIU Y, CAO J H, et al. Mineralogical characteristics features of an ilmenite ore[J]. Metal Mine, 2016(5): 91-93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1250.2016.05.020
[3] 刘星, 李成秀, 刘飞燕, 等. 甘肃大滩某低品位钛铁矿石选矿试验[J]. 金属矿山, 2014(12): 75-78.
LIU X, LI C X, LIU F Y, et al. Beneficiation technology for a low-grade ilmenite ore in Datan of Gansu Province[J]. Metal Mine, 2014(12): 75-78.
[4] 吴雪红. 攀西某超细粒级钛铁矿选矿试验[J]. 金属矿山, 2015(7): 56-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1250.2015.07.013
WU X H. Beneficiation experiments on a ultra fine grained ilmenite in western Panzhihua[J]. Metal Mine, 2015(7): 56-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1250.2015.07.013
[5] 余永富. 国内外铁矿选矿技术进展及对炼铁的影响[J]. 矿冶工程, 2004(5): 25-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYGC200401007.htm
YU Y F. Advance in iron ore dressing technology at home and abroad and their influence on iron-smelting[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004(5): 25-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYGC200401007.htm
[6] 杨佳, 李奎, 汤爱涛, 等. 钛铁矿资源综合利用现状与发展[J]. 材料导报, 2003(8): 44-46.
YANG J, LI K, TANG A T, et al. Comprehensive utilization of ilmenite: resources present status and future prospects[J]. Materials Review, 2003(8): 44-46.
[7] 杨耀辉, 惠博, 严伟平, 等. 攀西微细粒钛铁矿工艺矿物学研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(6): 131-135.
YANG Y H, HUI B, YAN W P, et al. Research on process mineralogy of fine ilmenite in Panxi Area[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(6): 131-135.
[8] 刘建国, 张军, 于丽丽, 等. 陕西某难选原生钛铁矿选矿工艺研究[A]. 矿产综合利用, 2014(6): 24-27.
LIU J G, ZHANG J, YU L L, et al. Technological research on beneficiation for a refractory primary ilmenite in Shaanxi[A]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2014(6): 24-27.
[9] 董天颂. 钛选矿[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2009.
DONG T S. Titanium beneficiation[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2009.
-



 下载:
下载: