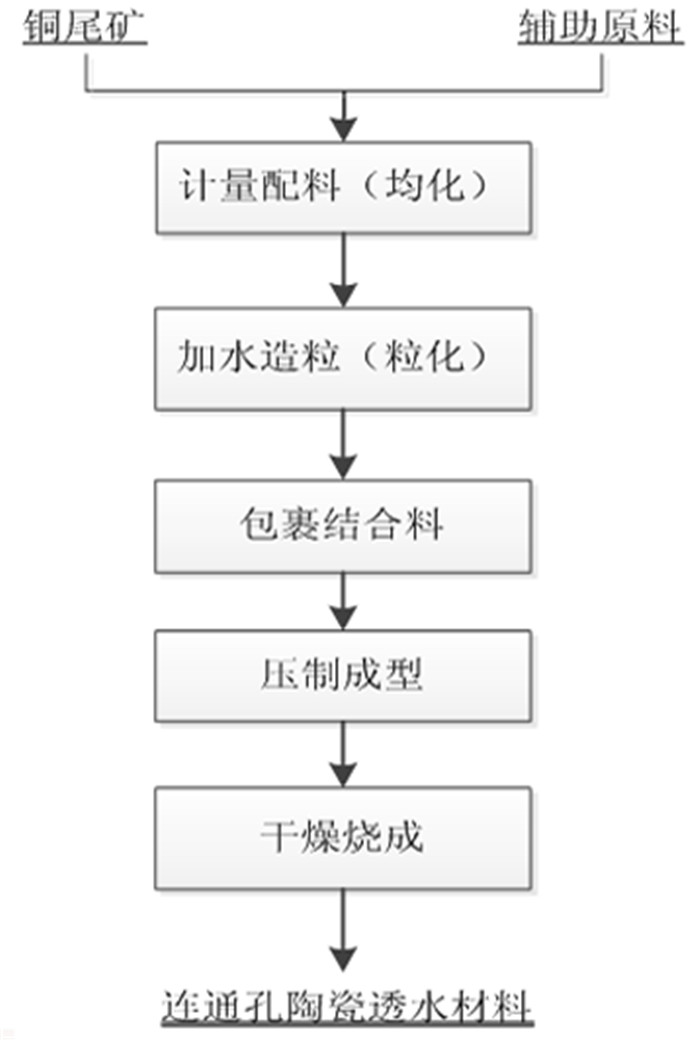
Preparation of the Connected Porous and Water-permeable Ceramic Materials by Porphyry Copper Tailings
-
摘要:
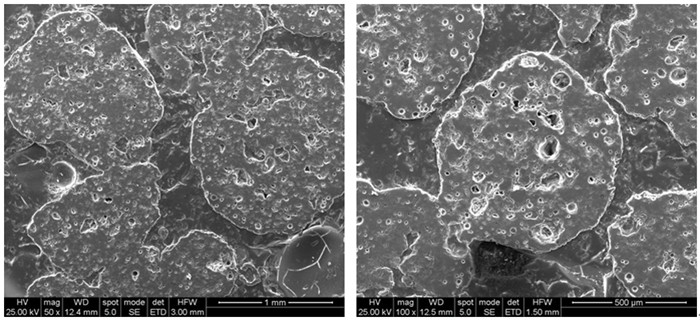
以斑岩型铜矿尾矿、高岭土、玻璃粉为主要原料,制备连通孔陶瓷透水材料。研究了骨料配比、结合料用量、成型压力和烧成制度对连通孔陶瓷透水材料抗折强度和透水系数的影响。当m(铜尾矿):m(高岭土):m(玻璃粉)为7:3:2、成型压力为1 MPa、烧成温度为1 150 ℃、保温时间为90 min时,工艺流程最佳。此时,连通孔陶瓷透水材料抗折强度为3.9 MPa,透水系数为2.7×10-2 cm/s,劈裂抗拉强度为3.7 MPa,耐磨性磨坑长度为25.2 mm,抗冻性为D50。
Abstract:The connected porous and water-permeable ceramic materials were prepared with porphyry copper tailings, kaolin and glass powder as main raw materials. The flexural strength and water permeability coefficient of the connected porous and water-permeable ceramic materials were studied at different aggregate ratio, binder dosage, molding pressure and firing system. The results showed that when the ratio of copper tailings, kaolin and glass powder was 7 : 3 : 2, molding pressure was 1 MPa, sintering temperature was 1 150 ℃, and holding time was 90 min, the flexural strength, water permeability coefficient, splitting tensile strength, the wear-resistant pit length, and frost resistance of the prepared connected porous and water-permeable ceramic materials were 3.9 MPa, 2.7×10-2 cm/s, 3.7 MPa, 25.2 mm, and D50, respectively.
-

-
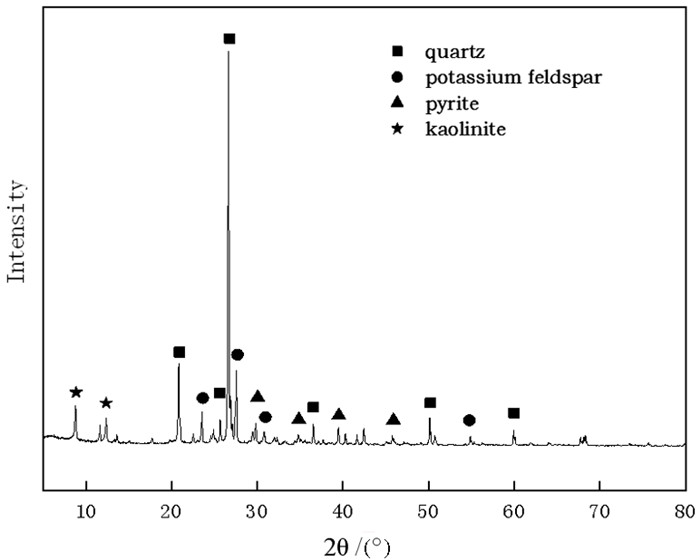
表 1 主要原料的X射线荧光光谱分析
Table 1. X-ray fluorescence spectrum analysis of the copper tailings
/% 化学成分 SiO2 Al2O3 CaO MgO K2O Na2O Fe2O3 SO3 Loss 铜尾矿 63.38 11.51 0.68 0.21 6.45 0.34 2.03 3.63 3.56 高岭土 45.71 40.32 0.77 0.66 2.53 0.18 7.27 0.16 2.14 玻璃粉 73.14 0.88 8.12 3.88 1.88 12.36 0.21 0.02 - 表 2 骨料配比试验结果
Table 2. Test results of the aggregate ratio
试验编号 铜尾矿用量/% 高岭土用量/% 抗折强度/MPa 透水系数/(10-2cm·s-1) 1 100 0 3.01 2.23 2 80 20 3.46 2.25 3 70 30 3.93 2.71 4 60 40 4.38 2.44 表 3 结合料外掺量试验结果
Table 3. Test results of the binder dosage
试验编号 结合料外掺量/% 抗折强度/MPa 透水系数/(×10-2cm·s-1) H1 10 3.45 1.84 H2 15 3.78 1.67 H3 20 3.93 2.71 H4 25 4.92 0.99 表 4 正交试验因素水平表
Table 4. Orthogonal test factor level table
水平 因素 成型压力(A)/MPa 烧成温度(B)/℃ 保温时间(C)/min 1 0.5 1100 30 2 1 1150 60 3 1.5 1200 90 表 5 正交试验结果
Table 5. Results of the orthogonal test
水平 因素 测试结果 A B C 抗折强度/MPa 透水系数/(10-2cm·s-1) 1 A1 B1 C1 1.28 2.87 2 A1 B2 C2 2.34 2.36 3 A1 B3 C3 2.53 1.75 4 A2 B1 C2 2.42 1.53 5 A2 B2 C3 3.97 2.46 6 A2 B3 C1 3.12 1.44 7 A3 B1 C3 4.12 1.14 8 A3 B2 C1 3.96 0.96 9 A3 B3 C2 3.32 0.79 k11 2.05 2.61 2.79 k12 3.17 3.42 2.69 k13 3.80 2.99 3.54 R1 1.75 0.82 0.85 优方案 A3 B2 C3 k21 2.33 1.85 1.76 k22 1.81 1.93 1.56 k23 0.96 1.33 1.78 R2 1.36 0.60 0.22 优方案 A1 B2 C3 表 6 最优产品性能测试结果
Table 6. Results the optimal product performance test
项目 抗折强度/MPa 透水系数/(10-2cm·s-1) 劈裂抗拉强度/MPa 耐磨性/mm 抗冻性 产品性能 3.9 2.7 3.7 25.2 D50 标准要求 ≥3.0 2.0 ≥3.0 ≤35 ≥D30 -
[1] 蔚美娇, 孔祥云, 黄劲松, 等. 我国尾矿固废处置现状及建议[J]. 化工矿物与加工, 2022, 51(1): 34-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGKJ202201007.htm
WEI M J, KONG X Y, HUANG J S, et al. Present situation and suggestions of tailings solid waste disposal in China[J]. Chemical Minerals and Processing, 2022, 51(1): 34-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGKJ202201007.htm
[2] 郑竞, 程波, 杨武, 等. 尾矿减量化、资源化和无害化实践状况与思考[J]. 矿山机械, 2022, 50(1): 38-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KSJX202201009.htm
ZHENG J, CHENG B, YANG W, et al. Practice situation and thinking of tailings reduction, resource utilization and harmlessness[J]. Mining Machinery, 2022, 50(1): 38-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KSJX202201009.htm
[3] 敖顺福. 有色金属矿山尾矿综合利用进展[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2021, 41(3): 94-103. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=7384e697-ffa3-481e-a1bf-1a9eac4ee847
AO S F. Progress of comprehensive utilization of nonferrous metal mine tailings[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021, 41(3): 94-103. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=7384e697-ffa3-481e-a1bf-1a9eac4ee847
[4] 杜艳强, 段文峰, 赵艳. 金属尾矿处置及资源化利用技术研究[J]. 中国矿业, 2021, 30(8): 57-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA202108011.htm
DU Y Q, DUAN W F, ZHAO Y. Research on metal tailings disposal and resource utilization technology[J]. China Mining Industry, 202130(8): 57-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA202108011.htm
[5] 赵宇翔, 张茜, 刘碧雯, 等. 尾矿制备建筑材料的研究进展[J]. 中国资源综合利用, 2021, 39(9): 120-124. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWZS202109037.htm
ZHAO Y X, ZHANG Q, LIU B W, et al. Research progress of tailings preparation of building materials[J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization, 2021, 39(9): 120-124. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWZS202109037.htm
[6] 颜凡, 金强, 王文君, 等. 钢渣协同建筑再生骨料制备透水材料[J]. 中国建材科技, 2020, 29(5): 46-48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JCKJ202005018.htm
YAN F, JIN Q, WANG W J, et al. Preparation of permeable materials with steel slag and recycled building aggregate[J]. China Building Materials Science and Technology, 2020, 29(5): 46-48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JCKJ202005018.htm
[7] 刘恒源, 唐莉, 李倩, 等. 微孔生态透水材料的制备及性能研究[J]. 新型建筑材料, 2020, 47(5): 63-67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXJZ202005017.htm
LIU H Y, TANG L, LI Q, et al. Preparation and properties of microporous ecological permeable materials[J]. New Building Materials, 2020, 47(5): 63-67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXJZ202005017.htm
[8] 曾宪沂, 彭红涛, 卞立波, 等. 砂基多孔隙透水材料探析[J]. 施工技术, 2018, 47(S1): 1278-1279. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SGJS2018S1346.htm
ZENG X Y, PENG H T, BIAN L B, et al. Analysis of porous porous sand-based materials[J]. Construction Technology, 2018, 47(S1): 1278-1279. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SGJS2018S1346.htm
[9] 王恬君, 刘立伟, 李国峰, 等. 焙烧尾矿制备透水砖的孔隙特征研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2021(6): 85-90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCZL202106015.htm
WANG T J, LIU L W, LI G F, et al. Study on the pore characteristics of permeable brick prepared by roasting tailings[J]. Mineral Comprehensive Utilization, 2021(6): 85-90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCZL202106015.htm
[10] 李志新, 马先伟, 牛季收, 等. 铝矾土尾矿烧结透水砖的性能调控[J]. 河南城建学院学报, 2021(1): 60-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJGZ202101009.htm
LI Z X, MA X W, NIU J S, et al. Performance regulation of bauxite tailings sintered permeable brick[J]. Journal of Henan Urban Construction University, 2021(1): 60-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJGZ202101009.htm
[11] 祖彬, 王天瑞, 王超杰, 等. 风积沙基烧结透水材料的制备[J]. 新型建筑材料, 2019, 46(2): 145-147. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXJZ201902037.htm
ZU B, WANG T R, WANG C J, et al. Preparation of sintered permeable materials based on aeolian sand[J]. New Building Materials, 2019, 46(2): 145-147. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXJZ201902037.htm
[12] 钟艳梅, 张国涛, 杨景琪, 等. 利用尾矿和陶瓷废料制备烧结型透水砖的技术现状[J]. 佛山陶瓷, 2019, 29(2): 40-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FSTC201902018.htm
ZHONG Y M, ZHANG G T, YANG J Q, et al. Technical Status of Sintered Water Permeable Brick with Tailings and Ceramic Waste[J]. Foshan Ceramics, 2019, 29(2): 40-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FSTC201902018.htm
[13] 夏溢, 程寒飞, 刘克权, 等. 铁尾矿粉烧结透水砖的制备及其性能[J]. 安徽工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 38(3): 237-241. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDYX202103001.htm
XIA Y, CHENG H F, LIU K Q, et al. Preparation and properties of iron tailings sintered permeable brick[J]. Journal of Anhui University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 38(3): 237-241. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDYX202103001.htm
[14] 周忠华. 高强烧结污泥黏土透水砖的研制[J]. 砖瓦, 2018(4): 17-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XUWA201804007.htm
ZHOU Z H. Development of high-strength sintered clay permeable brick[J]. Brick and Tile, 2018(4): 17-19 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XUWA201804007.htm
[15] 武晓宇, 魏东, 王正, 等. 烧结透水砖用低温高强粘结剂的研制[J]. 新型建筑材料, 2018, 45(7): 89-92. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXJZ201807029.htm
WU X Y, WEI D, WANG Z, et al. Development of low-temperature and high-strength binder for sintered permeable brick[J]. New Building Materials, 2018, 45(7): 89-92. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXJZ201807029.htm
-



 下载:
下载: