Study on the Partition Behaviors of Germanium During the Carbonization of Germanium-rich Lignite
-
摘要:
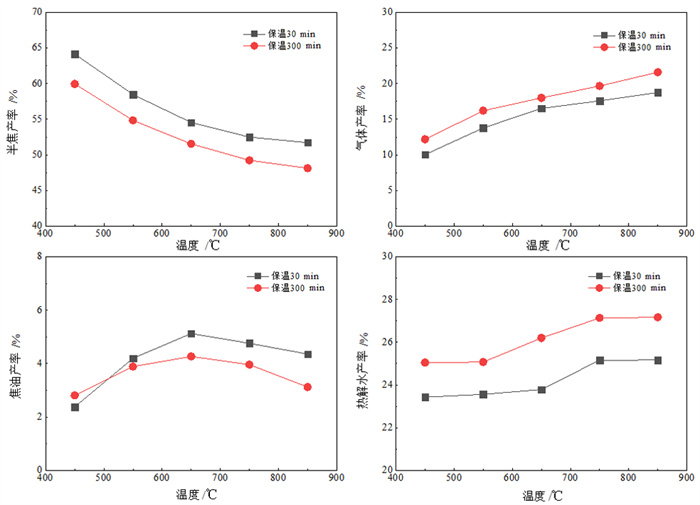
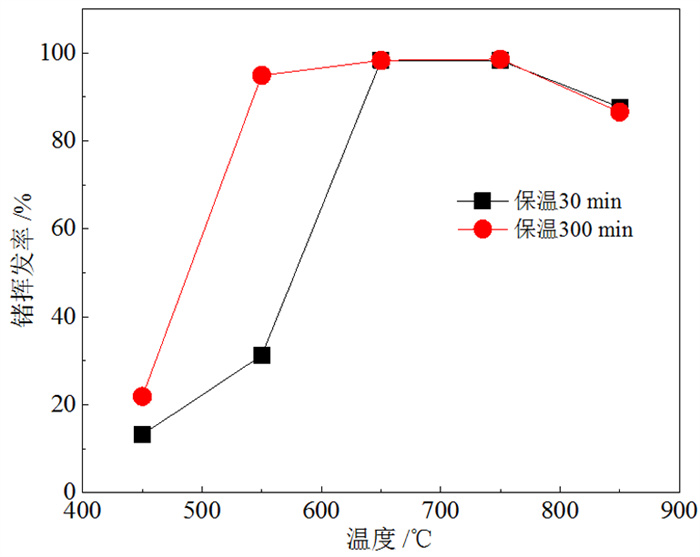
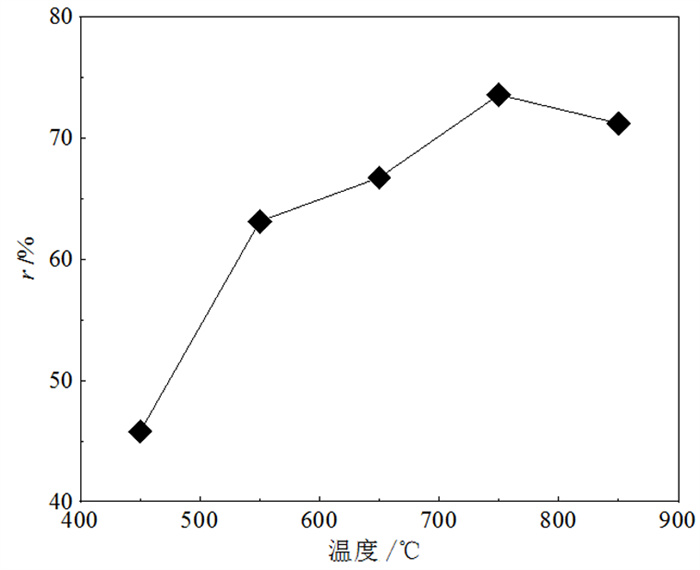
为了研究不同干馏条件下富锗褐煤干馏产物分布及锗在各产物中的配分, 采用逐级化学提取法和SEM-EDX首先测定了褐煤中锗的赋存形态, 又采用钢甑反应器进行了不同热解终温(450~850℃)和保温时间(30 min和300 min)下的褐煤干馏试验。结果表明: 褐煤中锗主要以腐殖质结合态存在(占比93.64%)。影响锗挥发的主要因素是干馏温度, 高温(> 650℃)下锗挥发率受保温时间影响较小。绝大部分(>95%)锗迁移到煤气中, 焦油和热解水中锗回收率极低, 褐煤中的锗可进一步从煤气中分离获取。从锗挥发率并兼顾焦油产率的角度考虑, 较好的干馏条件为终温650℃、保温30 min, 此时锗挥发率为98.29%, 焦油产率为5.13%。另外, 还采用TG-MS研究了干馏煤气主要组分的释放行为, 初步探讨了煤气还原性组分与锗挥发率的关系。结果表明: 干馏煤气的还原性组分(CO、H2和H2S)体积浓度与锗挥发率存在明显的正相关性, 煤气还原性越强, 锗挥发率越高, 但高温(850℃)下可能发生过还原反应, 造成锗挥发率的降低。
Abstract:In order to study the distribution of dry distillation products from germanium-rich lignite retorting and germanium partition in each product under different conditions, the occurrence form of germanium in lignite was firstly determined by sequential chemical extraction and SEM-EDX. Then, lignite retorting experiments were carried out at different pyrolysis temperatures (450~850℃) and holding time (30 min and 300 min) in steel retort reactor. The results showed that germanium in lignite mainly existed in the form of humus-bound state (accounting for 93.64%). The main factor affecting the volatilization of germanium was the pyrolysis temperature, and the holding time had little effect on the volatilization of germanium at high temperature (> 650℃). Most of the germanium(95%) migrated to coal gas, and germanium could be further separated from the gas, while the recovery rate of germanium in coal tar and pyrolysis water was extremely low. Considering the maximum volatilization rate of germanium and tar yield, the best retorting condition was the final temperature of 650℃ for 30 min, when the volatilization rate of germanium was 98.29% and the tar yield was 5.13%. In addition, TG-MS was used to study the release behavior of the main components of retorting gas, and the relationship between the reducing components of gas and the volatilization of germanium was discussed. The results showed that the concentration of reducing components (CO, H2 and H2S) of dry distillation gas was positively correlated with the volatilization of germanium. The stronger the reducing nature of gas, the higher the volatilization of germanium. However, over-reduction reaction may occur at high temperature (850℃), resulting in the decrease of the volatilization of germanium.
-
Key words:
- lignite /
- germanium /
- dry distillation /
- tar /
- coal gas /
- humic substances /
- occurrence state
-

-
表 1 煤样的工业分析和元素分析
Table 1. Proximate and ultimate analysis of coal sample
工业分析/% 元素分析/% Mad Aad Vad FCad* Cad Had Oad* Nad Sad Gead# 15.99 9.7 32.27 42.04 72.18 5.31 19.33 1.00 2.18 91.3 注:Mad、Aad、Vad和FCad分别是指空气干燥基准下煤的水分、灰分、挥发分和固定碳含量。ad:空气干燥基;*由差减法得到;#单位为g/t。 表 2 逐级化学提取步骤
Table 2. Sequential chemical extraction procedure
步骤 提取方法 赋存形态 1 将0.50 g样品加入20 mL 0.1 mol/L CH3COONa溶液,室温下振荡5 h,4 200 r/min转速离心30 min,取上清液;10 mL去离子水冲洗沉淀,振荡15 min,两次洗涤清液混合 水溶态及可交换态 2 残渣用0.04 mol/L NH4OH·HCl+25% CH3COOH(V/V)溶液提取,室温下振荡5 h,4 200 r/min转速离心30 min,取上清液;10 mL去离子水冲洗沉淀,振荡15 min,两次洗涤清液混合 碳酸盐及铁锰氧化物结合态 3 残渣用1% NaOH+0.1 mol/L Na4P2O7提取,80 ℃下恒温振荡2 h,离心提取同前。提取液蒸干后灰化处理,再将灰用HNO3-HF-HClO4混酸消解 腐植质结合态 4 残渣用30% H2O2提取,85 ℃下恒温振荡5 h,离心提取步骤同前。提取液蒸干后灰化处理,再将灰用HNO3-HF-HClO4混酸消解 其他有机结合态 5 残渣转移至聚四氟乙烯坩埚中,用HNO3-HF-HClO4混酸湿法消解 残渣态 表 3 煤中锗的形态分布
Table 3. Speciation distribution of germanium in coal
赋存形态 水溶及离子交换态 碳酸盐及铁锰氧化物结合态 腐殖质结合态 其他有机物结合态 残渣态 占比/% 0.19 0.61 93.64 1.95 3.61 表 4 不同干馏条件下各挥发相中锗的回收率
Table 4. Ge recovery rates of each volatile phase under different retorting conditions
终温/℃ 保温时间30 min 保温时间300 min 焦油 热解水 煤气 焦油 热解水 煤气 450 4.96% 0.04% 8.20% 4.65% 0.10% 17.08% 550 4.91% 0.06% 26.20% 3.70% 0.07% 91.09% 650 3.03% 0.14% 95.12% 1.37% 0.12% 96.86% 750 1.79% 0.06% 96.42% 2.36% 0.04% 96.16% 850 2.19% 0.20% 85.25% 3.07% 0.21% 83.24% -
[1] JIANG T, ZHANG T, LIU Z H. Review on resources and recycling of germanium, with special focus on characteristics, mechanism and challenges of solvent extraction[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 294: 126217. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126217
[2] 叶霖, 韦晨, 胡宇思, 等. 锗的地球化学及资源储备展望[J]. 矿床地质, 2019, 38(4): 711-728. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201904003.htm
YE L, WEI C, HU T S, et al. Geochemistry of germanium and its resources reserves[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2019, 38(4): 711-728. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201904003.htm
[3] DAI S F, YAN X Y, WARD C R, et al. Valuable elements in Chinese coals: a review[J]. International Geology Review, 2018, 60(5/6): 590-620.
[4] 李国娟, 曹洪杨. 褐煤中伴生低品位锗资源化利用研究进展[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2021(2): 52-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.02.011
LI G J, CAO H Y. Research process in resource utilization of associated low-grade germanium in lignite[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(2): 52-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.02.011
[5] PATEL M, KARAMALIDIS A K. Germanium: a review of its US demand, uses, resources, chemistry, and separation technologies[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 275: 118981. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2021.118981
[6] 雷霆, 张玉林, 王少龙. 锗的提取方法[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2007.
LEI T, ZHANG Y L, WANG S L. Extraction of germanium[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2007.
[7] 冯林永, 雷霆, 张家敏, 等. 从褐煤中提取锗及洗选焦炭[J]. 有色金属, 2009, 61(3): 98-100+108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2009.03.024
FENG L Y, LEI T, ZHANG J M, et al. Ge recovery and char floatation from lignite[J]. Nonferrous Metals, 2009, 61(3): 98-100+108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2009.03.024
[8] 张家敏, 雷霆, 张玉林, 等. 从含锗褐煤中干馏提锗和制取焦炭的试验研究[J]. 稀有金属, 2007(3): 371-376. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7076.2007.03.019
ZHANG J M, LEI T, ZHANG Y L, et al. Distilling of germanium and preparation of coke from lignite containing germanium[J]. Rare Metals, 2007(3): 371-376. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7076.2007.03.019
[9] 张志昊, 徐冬, 刘汉强, 等. 温度及气氛对褐煤热转化过程中锗元素迁移的影响[J]. 洁净煤技术, 2016, 22(3): 69-73+89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JJMS201603015.htm
ZHANG Z H, XU D, LIU H Q, et al. Influence of temperature and atmosphere on transformation of ge during lignite thermal transition[J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2016, 22(3): 69-73+89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JJMS201603015.htm
[10] 张淑苓, 尹金双, 王淑英. 云南帮卖盆地煤中锗存在形式的研究[J]. 沉积学报, 1988(3): 29-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB198803003.htm
ZHANG S L, YIN J S, WANG S Y. Study on existent froms of germanium in coal, Bangmai Basin, Yunnan[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1988(3): 29-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB198803003.htm
[11] 邹本东, 李晓燕, 陈圆圆, 等. 褐煤中锗的连续化学提取及形态分布研究[J]. 中国检验检测, 2017, 25(1): 20-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDJL201701010.htm
ZHOU B D, LI X Y, CEHN Y Y, et al. Study on sequential extraction and speciation distribution of germanium from lignite[J]. China Inspection Body Laboratory, 2017, 25(1): 20-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDJL201701010.htm
[12] ZHOU C C, DU J, ZHANG Y L, et al. Redistribution and transformation mechanisms of gallium and germanium during coal combustion[J]. Fuel, 2021, 305: 121532.
[13] POKROVSKI G S, MARTIN F, HAZEMANN J L, et al. An X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy study of germanium-organic ligand complexes in aqueous solution[J]. Chemical Geology, 2006, 163(1/2/3/4): 151-165.
[14] 杜刚, 夏斌, 秦胜利, 等. 内蒙古胜利煤田共生锗矿与成煤沼泽微环境的成因关系[J]. 煤炭学报, 2008(4): 405-409. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2008.04.011
DU G, XIA B, QIN S L, et al. Genetic relationship of Ge-coal deposit in Shengli coal field and micro-environment of coal-froming swamp[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2008(4): 405-409. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2008.04.011
[15] ETSCHMANN B, LIU W H, LI K, et al. Donna Falconer. Enrichment of germanium and associated arsenic and tungsten in coal and roll-front uranium deposits[J]. Chemical Geology, 2017, 463: 29-49.
[16] SARLAKI E, PAGHALEH A S, KIANMEHR M H, et al. Extraction and purification of humic acids from lignite wastes using alkaline treatment and membrane ultrafiltration[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 235: 712-723.
[17] 李艳红, 庄锐, 张政, 等. 褐煤腐殖酸的结构、组成及性质的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2015, 34(8): 3147-3157.
LI Y H, ZHUANG R, ZHANG Z, et al. Research on the structure, chemical composition and characterization of humic acid from lignite[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2015, 34(8): 3147-3157.
[18] LI C Z. Advances in the science of victorian brown coal[M]. Oxford: Elsevier, 2004.
[19] 王娜. 提质低阶煤热解特性及机理研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京), 2010.
WANG N. Pyrolysis characteristics and mechanism of upgraded low-rank Coal[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining Technology, Beijing, 2010.
[20] SHPIRT M Y, STOPANI O I, LEBEDEVA L N, et al. Germanium production technology based on the conversion of germanium-bearing lignites[J]. Solid Fuel Chemistry, 2020, 54(1): 1-10.
-



 下载:
下载: