Progress in Microwave-assisted Recovery of Valuable Metals from Spent Lithium Battery Cathode Materials
-
摘要:
在国际前沿和国家战略性关键金属保护的大背景下, 废旧锂电池正极材料中的高价值材料如镍、钴、锰和锂等的回收利用已成为当前的研究热点。论文概述了锂电池正极废弃物有价金属回收工艺, 介绍了微波技术的原理及在冶金过程中的应用, 重点讨论了微波辅助火法—湿法联合工艺在焙烧还原过程、浸出过程、萃取过程的发展态势, 微波的参与节约了碳热还原时间、提高了金属离子的浸出率以及加快萃取过程的传质速率, 最终实现目标金属的产率和品质的提高。最后, 对未来废旧锂电池回收市场的发展前景进行了展望。
Abstract:Recycling of high-value materials such as Ni, Co, Mn, and Li from used lithium battery cathode materials has become a current research hotspot, resulting from the requirements on the protection of the national strategic key metal and the development of the international frontier. This paper summarized the valuable metals recovery process for waste lithium battery positive electrode, and introduced the principle and application of microwave technology in the metallurgical process. The applications of microwave-assisted heat and humidity combined process in the roasting reduction process, leaching process, and extraction process were studied emphatically. With the involvement of microwave energy, the carbon thermal reduction time was saved, the leaching rate of metal ions was increased and the mass transfer rate of the extraction process was accelerated, ultimately achieving an increase in yield and quality of the target metal. Finally, we prospected the development prospect of waste lithium battery recovery market in the future.
-
Key words:
- waste lithium battery /
- valuable metals /
- recycling process /
- microwave /
- Li /
- Co
-

-
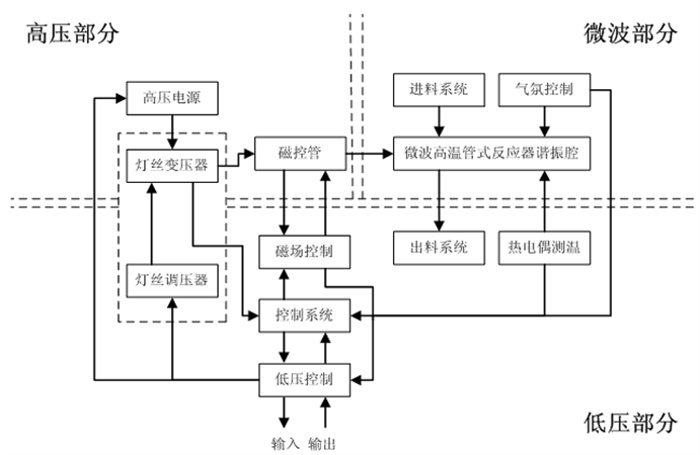
图 1 典型的微波加热系统[26]
Figure 1.
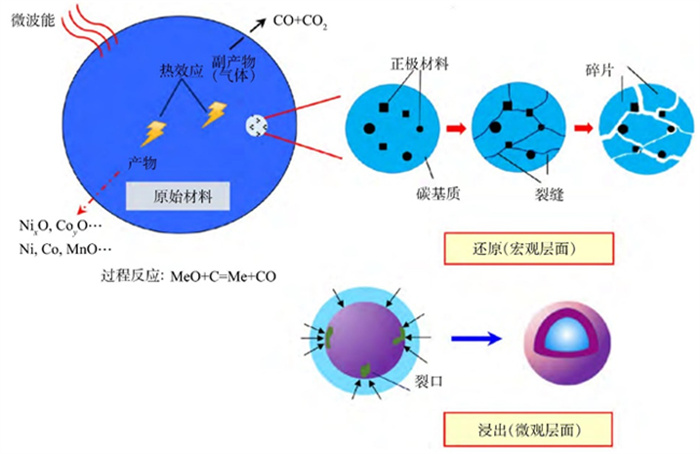
图 2 微波增强还原反应模型示意图[32]
Figure 2.
表 1 锂电池的主要结构及常用材料
Table 1. The main structures and common materials of lithium batteries
电池部件 作用 常用材料 外壳 保护性,成型 铝壳,铝塑复合膜,不锈钢,聚合物软壳 正极 活性物质 LiCoO2, LiMn2O4, LiNiO2, LiFePO4, LiV2O3, (NiCoMn)O2, LiNixMnyCozO2 负极 活性物质 石墨等碳材料,Li4Ti5O12等非碳材料 集电器 负极或正极的集流体 铜箔(负极),铝箔(正极) 电解质 传输电极之间的离子 电解质盐:LiPF6, LiBF4, LiClO4, LiSO2, LiCF3SO3, Li(SO2CF3);溶剂:碳酸丙烯酯(PC),二甲基亚砜(DMSO),碳酸乙烯酯(EC) 分隔器微膜 防止电极直接接触造成短路 微孔聚丙烯(PP),聚乙烯(PE) 黏合剂 黏结和导电 聚偏二氟乙烯(PVDF),聚四氟乙烯(PTFE) 表 2 微波还原和传统的碳热还原的比较[31]
Table 2. Comparison of microwave reduction and conventional carbon thermal reduction
还原方法 反应条件 反应时间 质量损失 锂的回收率 马弗炉 885 ℃, 30%还原碳 59 min 21.1% 83% 微波 870 W, 24.4%还原碳 7.8 min 31.6% 82% 表 3 不同操作条件下的正极有价金属回收情况
Table 3. Recovery of valuable metals from positive electrodes under different operating conditions
-
[1] ZHENG M, TANG H, LI L, et al. Hierarchically nanostructured transition metal oxides for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Science, 2018, 5(3): 1700592. doi: 10.1002/advs.201700592
[2] FAN M, CHANG X, MENG Q, et al. Progress in the sustainable recycling of spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. SusMat, 2021, 1(2): 241-254. doi: 10.1002/sus2.16
[3] LI W, SONG B, MANTHIRAM A. High-voltage positive electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017, 46(10): 3006-3059. doi: 10.1039/C6CS00875E
[4] TAO R, XING P, LI H, et al. Recovery of spent LiCoO2 lithium-ion battery via environmentally friendly pyrolysis and hydrometallurgical leaching[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2022, 176: 105921. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105921
[5] SCHMUCH R, WAGNER R, HÖRPEL G, et al. Performance and cost of materials for lithium-based rechargeable automotive batteries[J]. Nature Energy, 2018, 3(4): 267-278. doi: 10.1038/s41560-018-0107-2
[6] DUAN X, ZHU W, RUAN Z, et al. Recycling of lithium batteries-a review[J]. Energies, 2022, 15(5): 1611. doi: 10.3390/en15051611
[7] YANG Y, OKONKWO E G, HUANG G, et al. On the sustainability of lithium ion battery industry-a review and perspective[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 36: 186-212. doi: 10.1016/j.ensm.2020.12.019
[8] MAKUZA B, TIAN Q, GUO X, et al. Pyrometallurgical options for recycling spent lithium-ion batteries: a comprehensive review[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 491: 229622. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2021.229622
[9] CHEN X, GUO C, MA H, et al. Organic reductants based leaching: a sustainable process for the recovery of valuable metals from spent lithium ion batteries[J]. Waste Management, 2018, 75: 459-468. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2018.01.021
[10] 王芳, 张邦胜, 刘贵清, 等. 废旧动力电池资源再生利用技术进展[J]. 中国资源综合利用, 2018, 36(10): 106-111. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9500.2018.10.034
WANG F, ZHANG B S, LIU G Q, et al. Progress in recycling technology of waste power battery resources[J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization, 2018, 36(10): 106-111. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9500.2018.10.034
[11] MA Y Y, TANG J J, WANALDI R, et al. A promising selective recovery process of valuable metals from spent lithium ion batteries via reduction roasting and ammonia leaching[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 402: 123491. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123491
[12] ZHANG Y C, WANG W Q, FANG Q, et al. Improved recovery of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries by efficient reduction roasting and facile acid leaching[J]. Waste Management, 2020, 102: 847-855. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2019.11.045
[13] 张超, 廖青云, 路璐, 等. 锂电池回收产业发展报告[J]. 高科技与产业化, 2019(3): 36-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GKFC201903009.htm
ZHANG C, LIAO Q Y, LU L, et al. Report on the development of lithium battery recycling industry[J]. High Technology and Industrialization, 2019(3): 36-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GKFC201903009.htm
[14] 靳星, 贾美丽, 杜浩, 等. 废旧磷酸铁锂正极材料回收再生研究进展[J]. 有色金属工程, 2020, 10(11): 64-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2020.11.010
JIN X, JIA M L, DU H, et al. Research progress on recycling of waste lithium iron phosphate cathode materials[J]. Nonferrous Metal Engineering, 2020, 10(11): 64-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2020.11.010
[15] LIU C, LIN J, CAO H, et al. Recycling of spent lithium-ion batteries in view of lithium recovery: A critical review[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 228: 801-813. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.304
[16] MENG F, LIU Q, KIM R, et al. Selective recovery of valuable metals from industrial waste lithium-ion batteries using citric acid under reductive conditions: leaching optimization and kinetic analysis[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2020, 191: 105160. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2019.105160
[17] GUAN J, LI Y, GUO Y, et al. Mechanochemical process enhanced cobalt and lithium recycling from wasted lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2017, 5(1): 1026-1032.
[18] HUANG B, WANG J. Bio-hydrometallurgically treatment of spent Lithium-ion batteries[M]. Recycling of Spent Lithium-ion Batteries, 2019: 85-92.
[19] 李之钦, 庄绪宁, 宋小龙, 等. 废锂离子电池正极材料的火法资源化技术研究进展[J]. 环境工程, 2021, 39(4): 115-122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJGC202104018.htm
LI Z Q, ZHUANG X N, SONG S L, et al. Research progress of pyrogenic resource recovery technology for waste lithium-ion battery cathode materials[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2021, 39(4): 115-122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJGC202104018.htm
[20] DIAZ F, WANG Y, MOORTHY T, et al. Degradation mechanism of nickel-cobalt-aluminum (NCA) cathode material from spent lithium-ion batteries in microwave-assisted pyrolysis[J]. Metals, 2018, 8(8): 565. doi: 10.3390/met8080565
[21] 庞建明, 潘聪超, 马永宁, 等. 微波冶炼低品位锰矿制备含锰生铁的试验研究[J]. 中国有色冶金, 2020, 49(3): 83-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSYL202003020.htm
PANG J M, PAN C C, MA Y N, et al. Experimental study of microwave smelting of low-grade manganese ore for the preparation of pig iron containing manganese[J]. China Nonferrous Metallurgy, 2020, 49(3): 83-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSYL202003020.htm
[22] MIZUNO N, KOSAI S, YAMASUE E. Microwave-based extractive metallurgy to obtain pure metals: A review[J]. Cleaner Engineering and Technology, 2021, 5: 100306. doi: 10.1016/j.clet.2021.100306
[23] 庞建明, 赵沛, 郭培民. 红土镍矿低温还原+微波冶炼镍铁新技术[J]. 中国冶金, 2017, 27(9): 70-76. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYE201709015.htm
PANG J M, ZHAO P, GUO P M. New technology for low-temperature reduction + microwave smelting of ferronickel from laterite nickel ore[J]. China Metallurgy, 2017, 27(9): 70-76. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYE201709015.htm
[24] FERRARI-JOHN R S, BATCHELOR A R, KATRIB J, et al. Understanding selectivity in radio frequency and microwave sorting of porphyry copper ores[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2016, 155: 64-73. doi: 10.1016/j.minpro.2016.08.011
[25] MISHRA R R, SHARMA A K. Microwave-material interaction phenomena: heating mechanisms, challenges and opportunities in material processing[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2016, 81: 78-97. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2015.10.035
[26] 陈菓. 微波法制备人造金红石新工艺及设备研制[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2012.
CHEN G. New process and equipment development for the preparation of artificial rutile by microwave method[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Technology, 2012.
[27] ZHAO Y, LIU B, ZHANG L, et al. Microwave-absorbing properties of cathode material during reduction roasting for spent lithium-ion battery recycling[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 384: 121487. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121487
[28] 昝文宇, 马北越, 刘国强. 动力锂电池回收利用现状与展望[J]. 稀有金属与硬质合金, 2020, 48(5): 5-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYJY202005002.htm
ZAN W Y, MA B Y, LIU G Q. Status and prospects of power lithium battery recycling[J]. Rare Metals and Cemented Carbides, 2020, 48(5): 5-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYJY202005002.htm
[29] ZHANG J H, GAO L H, HE Z J, et al. Separation and recovery of iron and nickel from low-grade laterite nickel ore by microwave carbothermic reduction roasting[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2020, 9(6): 12223-12235. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.08.036
[30] LI K Q, CHEN J, PENG J H, et al. Pilot-scale study on enhanced carbothermal reduction of low-grade pyrolusite using microwave heating[J]. Powder Technology, 2020, 360: 846-854. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2019.11.015
[31] PINDAR S, DHAWAN N. Comparison of microwave and conventional indigenous carbothermal reduction for recycling of discarded lithium-ion batteries[J]. Transactions of the Indian Institute of Metals, 2020, 73(8): 2041-2051. doi: 10.1007/s12666-020-01956-2
[32] FU Y P, HE Y Q, YANG Y, et al. Microwave reduction enhanced leaching of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 832: 154920. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154920
[33] ZHAO Y Z, LIU B G, ZHANG L B, et al. Microwave pyrolysis of macadamia shells for efficiently recycling lithium from spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 396: 122740. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122740
[34] JIN H, ZHANG J, WANG D, et al. Facile and efficient recovery of lithium from spent LiFePO4 batteries via air oxidation-water leaching at room temperature[J]. Green Chemistry, 2022, 24(1): 152-162. doi: 10.1039/D1GC03333F
[35] DANDIA A, PAREWA V, GUPTA S L, et al. Microwave-assisted Fe3O4 nanoparticles catalyzed synthesis of chromeno[1, 6] naphthyridines in aqueous media[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2015, 61: 88-91.
[36] PINDAR S, DHAWAN N. Evaluation of carbothermic processing for mixed discarded lithium-ion batteries[J]. Metallurgical Research & Technology, 2020, 117(3): 302.
[37] PINDAR S, DHAWAN N. Carbothermal reduction of spent mobile phones batteries for the recovery of lithium, cobalt, and manganese values[J]. JOM, 2019, 71(12): 4483-4491.
[38] MUSARIRI B, AKDOGAN G, DORFLING C, et al. Evaluating organic acids as alternative leaching reagents for metal recovery from lithium ion batteries[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2019, 137: 108-117.
[39] PINDAR S, DHAWAN N. Recycling of mixed discarded lithium-ion batteries via microwave processing route[J]. Sustainable Materials and Technologies, 2020, 25: 157.
[40] PATIL D, CHIKKAMATH S, KENY S, et al. Rapid dissolution and recovery of Li and Co from spent LiCoO2 using mild organic acids under microwave irradiation[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2020, 256: 109935.
[41] PINDAR S, DHAWAN N. Evaluation of in-situ microwave reduction for metal recovery from spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Sustainable Materials and Technologies, 2020, 25: 201.
[42] LIE J, LIU J C. Closed-vessel microwave leaching of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) using dual-function leaching agent: Ascorbic acid[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 266: 118458.
[43] SHIH Y J, CHIEN S K, JHANG S R, et al. Chemical leaching, precipitation and solvent extraction for sequential separation of valuable metals in cathode material of spent lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2019, 100: 151-159.
[44] 王斌, 梁精龙, 李慧, 等. 废旧锂离子电池金属离子回收技术综述[J]. 电源技术, 2019, 43(1): 165-167. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DYJS201901053.htm
WANG B, LIANG J L, LI H, et al. A review of metal ion recovery technologies for waste lithium-ion batteries[J]. Power Technology, 2019, 43(1): 165-167. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DYJS201901053.htm
[45] MAO Y, ROBINSON J, BINNER E. Understanding heat and mass transfer processes during microwave-assisted and conventional solvent extraction[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2021, 233: 116418.
[46] MARTíN A, NAVARRETE A. Microwave-assisted process intensification techniques[J]. Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, 2018, 11: 70-75.
[47] GRüTZKE M, KRüGER S, KRAFT V, et al. Investigation of the storage behavior of shredded lithium-ion batteries from electric vehicles for recycling purposes[J]. Chemistry Sustainability Energy Materials, 2015, 8(20): 3433-3438.
[48] NAYL A A, HAMED M M, RIZK S E. Selective extraction and separation of metal values from leach liquor of mixed spent Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2015, 55: 119-125.
[49] 李之钦, 李商略, 庄绪宁, 等. 微波焙烧强化废锂离子电池中的金属回收研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(10): 4712-4719. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ202110035.htm
LI Z Q, LI S L, ZHUANG X N, et al. Study on microwave roasting for enhanced metal recovery from waste lithium-ion batteries[J]. China Environmental Science, 2021, 41(10): 4712-4719. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ202110035.htm
[50] WINDISCH-KERN S, GEROLD E, NIGL T, et al. Recycling chains for lithium-ion batteries: A critical examination of current challenges, opportunities and process dependencies[J]. Waste Management, 2022, 138: 125-139.
[51] 孙静, 江镇宇, 于冠群, 等. 微波技术在锂离子电池正极材料高效回收再利用中的研究进展[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(7): 2191-2217. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJJZ202107002.htm
SUN J, JIANG Z Y, YU G Q, et al. Research progress of microwave technology in efficient recycling of lithium-ion battery cathode materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2021, 15(7): 2191-2217. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJJZ202107002.htm
-



 下载:
下载: