Review on the Strategic Metals Recovery from Electrolytic Manganese Anode Slime (EMAS)
-
摘要:
电解锰行业每年产生7.5~12万t的锰阳极泥固废, 其矿物组成与结构复杂, 有价金属组分多、含量高, 综合利用难度大, 目前大部分厂家廉价销售或大量堆存, 造成了严重的资源浪费和环境污染。文章分析了阳极泥的产生机理和资源特点, 综述了阳极泥中主要有价战略金属元素Mn、Pb、Sn、Se的分离回收技术, 对比了还原浸出法、焙烧浸出法、碱熔—浸出法等阳极泥处理方法的优缺点, 提出了硫转化综合回收锰铅锡硒新思路, 可为电解锰阳极泥固废的资源化利用提供技术参考。
Abstract:75 000-120 000 tons of electrolytic manganese anode slime (EMAS) are produced in the electrolytic manganese industry every year. The EMAS has high content of strategic metals, complex mineral compositions and complicated structure, and thus the comprehensive utilization is difficult. At present, most manufacturers sell the EMAS cheaply or take the stockpiling disposal, causing serious waste of resources and environmental pollution. This paper analyzed the production mechanism and resource characteristics of the EMAS, and also summarized the separation and recovery technologies of the valuable metals including Mn, Pb, Sn, and Se from the EMAS. The advantages and disadvantages of the reduction leaching method, roasting-leaching method, and alkali melting-leaching method were reviewed and compared. This paper puts forward a novel technique solution for the comprehensive recovery of Mn, Pb, Sn, and Se by sulfur conversion, which can provide technical reference for utilization of EMAS.
-

-
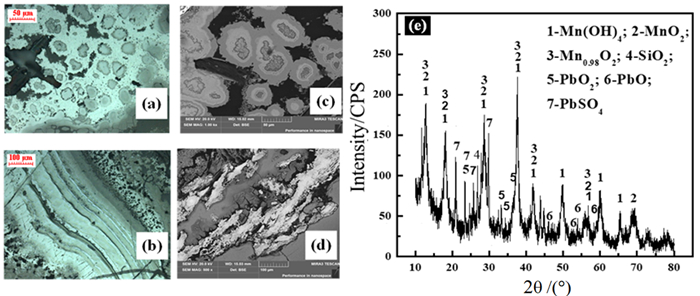
图 2 电解锰阳极泥原料分析:(a), (b)光学显微镜;(c), (d)SEM;(e)XRD[64]
Figure 2.
表 1 典型电解锰阳极泥主要化学成分
/% Table 1. Chemical constituents of the typical electrolytic manganese anode slime
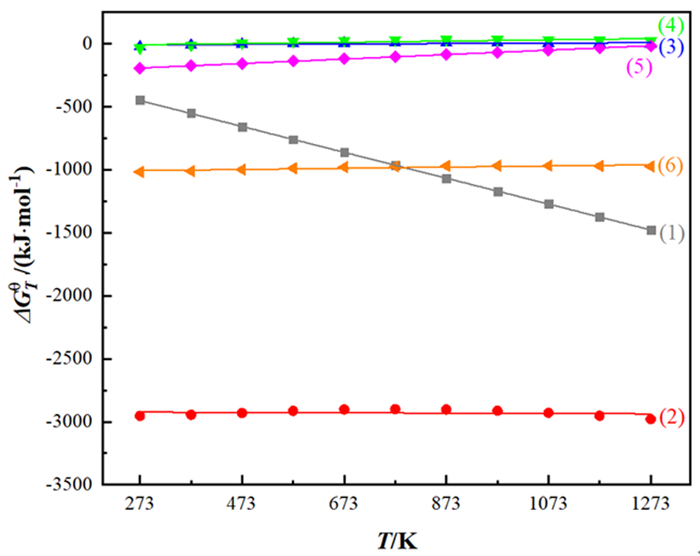
Mn (NH4)2SO4 Fe CaO Pb MgO Sn Se 40~50 5~10 0.1~6 0.1~6 3~6 0.1~6 0.1~0.5 0.1~0.4 表 2 不同还原剂与MnO2的反应方程式以及对应的ΔGθ-T方程式
Table 2. Reactions of different reducing agents and MnO2 and corresponding ΔGθ-T equations
编号 反应方程式 ΔGθ-T/(kJ·mol-1) 自发反应温度范围/K (1) 11MnO2+2FeS2=11MnO+Fe2O3+4SO2(g) ΔGTθ=-170.92-1.026T 自发反应 (2) 15MnO2+2FeS2+14H2SO4=15MnSO4+Fe2(SO4)3+14H2O ΔGθT=-2918.36-0.014T 自发反应 (3) 2MnO2+SO2(g)=Mn2O3+SO3(l) ΔGTθ=-15.01+0.018T T<834 (4) 3MnO2+2SO2(g)=Mn3O4+2SO3(l) ΔGTθ=-22.22+0.049T T<453 (5) MnO2+SO2(g)=MnSO4 ΔGTθ=-240.98+0.177T T<1361 (6) 3MnO2+2Fe+6H2SO4=3MnSO4+Fe2(SO4)3+6H2O ΔGTθ=-1020.13+0.047T 自发反应 表 3 电解锰阳极泥中锰铅分离方法
Table 3. Separation methods of manganese and lead from electrolytic manganese anode slime
分离方法 基本原理 优点 缺点 无机还原浸出法 采用低价硫化物将Mn4+还原为Mn2+进入溶液,铅富集于渣中 锰浸出率高,操作简单 产生酸性废水和废渣,产生SO2和H2S气体 有机还原浸出法 利用有机物的还原性将锰还原为低价进入溶液,铅不发生反应 锰铅分离效果好,原料价格低廉,易获得 操作复杂,反应周期长 固态焙烧浸出法(空气气氛) 高温焙烧活化,乙酸铵浸出铅,锰则不发生反应 铅浸出率高,操作简单 能耗高,反应时间长 固态焙烧浸出法(还原气氛) 利用还原性气体还原锰和铅,硫酸浸出后,固液分离 分离效果好,反应周期短 能耗高,会产生二次污染 碱熔浸出法 高温下碱溶液与MnO2反应生成锰酸根进入溶液,铅不发生反应,锰酸盐经还原得到初级二氧化锰 产品收率高,分离效果好 操作复杂,能耗高 表 4 SnO2转化过程中发生的主要反应[73]及对应的ΔGθ-T方程式
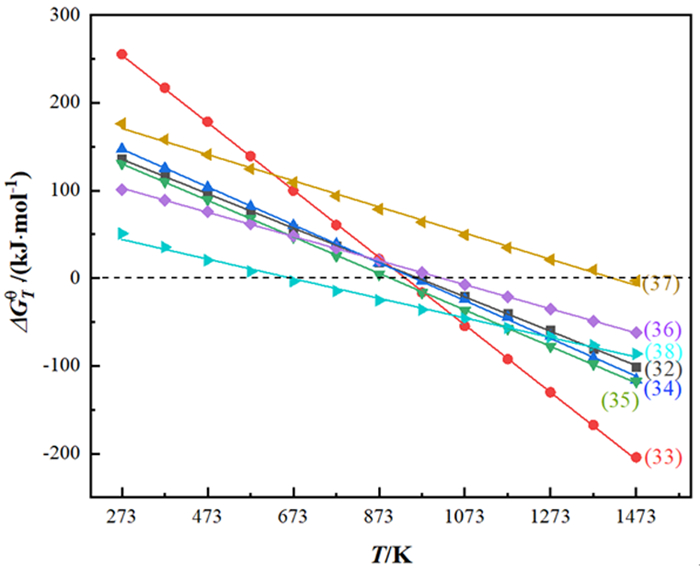
Table 4. Main chemical reactions[73] during the conversion of SnO2and corresponding ΔGθ-Tequations
编号 反应方程式 ΔGθ-T/(kJ·mol-1) 自发反应温度范围/K (32) SnO2+C=SnO+CO(g) ΔGθ-T=188.98-0.196T T>964 (33) SnO2+2C=Sn+2CO(g) ΔGθ-T=359.06-0.384T T>935 (34) 2SnO2+C=2SnO+CO2(g) ΔGθ-T=206.00-0.216T T>954 (35) SnO2+C=Sn+CO2(g) ΔGθ-T=187.10-0.208T T>900 (36) FeS2=FeS+0.5S2(g) ΔGθ-T=140.15-0.138T T>1 016 (37) SnO+FeS=FeO+SnS(g) ΔGθ-T=211.46-0.149T T>1 419 (38) 2Sn+S2=2SnS(g) ΔGθ-T=74.53-0.112T T>665 -
[1] JOO S, CHOI Y, SHIN H. Hierarchical multi-porous copper structure prepared by dealloying electrolytic copper-manganese alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 900: 163423. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.163423
[2] HE D, SHU J, WANG R, et al. A critical review on approaches for electrolytic manganese residue treatment and disposal technology: reduction, pretreatment, and reuse[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 418: 126235. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126235
[3] LI P, LUO S, WANG X, et al. Study on the high-efficiency separation of Fe and Mn from low-grade pyrolusite and the preparation of LiMN2O4 materials for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 278: 119611. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119611
[4] HE D, SHU J, ZENG X, et al. Synergistic solidification/stabilization of electrolytic manganese residue and carbide slag[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 810: 152175. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152175
[5] YANG T, XUE Y, LIU X, et al. Solidification/stabilization and separation/extraction treatments of environmental hazardous components in electrolytic manganese residue: a review[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2022, 157: 509-526. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2021.10.031
[6] HUANG L. Q, BI Y. F, MU L. L, et al. The process and mechanism of electrolytic manganese anode slime lead removal[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2014, 878: 163-170. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.878.163
[7] WANG Y, GAO S, LIU X, et al. Preparation of non-sintered permeable bricks using electrolytic manganese residue: Environmental and NH3-N recovery benefits[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 378: 120768. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120768
[8] SHU J, WU Y, DENG Y, et al. Enhanced removal of Mn2+ and NH4+-N in electrolytic manganese metal residue using washing and electrolytic oxidation[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 270: 118798. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2021.118798
[9] 黄良取, 黄升谋, 唐疆蜀, 等. 电解锰阳极泥的利用研究进展[J]. 武汉工程大学学报, 2015, 37(10): 5-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHHG201510002.htm
HUANG L, HUANG S, TANG J, et al. Research progress on utilization of electrolytic manganese anode slime[J]. Journal of Wuhan University, 2015, 37(10): 5-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHHG201510002.htm
[10] 夏熙. 二氧化锰及相关锰氧化物的晶体结构、制备及放电性能(1)[J]. 电池, 2004(6): 411-414. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1579.2004.06.009
XIA X. Crystal structure, preparation and discharge performance for manganese dioxides and related manganese oxides (Ⅰ). Battery Bimonthly, 2004(6): 411-414. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1579.2004.06.009
[11] SONG J, ZHU J, ZHANG P, et al. Reduction of low-grade manganese oxide ore by biomass roasting[J]. ActaMetallurgicaSinica-English Letters, 2010(3): 223-229.
[12] WU Y, SHI B, LIANG H, et al. Magnetic properties of low grade manganese carbonate ore[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2014, 664: 38-42. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.664.38
[13] DUAN N, FAN W, CHANGBO Z, et al. Analysis of pollution materials generated from electrolytic manganese industries in China[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2010, 54(8): 506-511. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2009.10.007
[14] ZHANG H, BI Y, CHEN X, et al. Treatment and characterization analysis of electrolytic manganese anode slime[J]. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2016, 31: 683-690. doi: 10.1016/j.proenv.2016.02.125
[15] ZHU R, LONG H, WANG Y, et al. Microwave-assisted recovery of lead from electrolytic manganese anode sludge using tartaric acid and NaOH[J]. Environmental Technology, 2021: 1-15.
[16] TAO C, LI D, LIU Z, et al. Activation and purification of electrolytic-manganese anode slime and its application[J]. Battery Bimonthly, 2011, 41: 121-124.
[17] GUO P, TANG J, WANG S, et al. Synergistic effect of reduction leaching of manganese anode slime and oxidation pretreatment of gold concentrate[J]. Materials Research Express, 2019(6): 1065.
[18] LI K, CHEN J, PENG J, et al. Dielectric properties and thermal behavior of electrolytic manganese anode mud in microwave field[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 384: 121227. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121227
[19] ZHOU X, LUO C, WANG J, et al. Recycling application of modified waste electrolytic manganese anode slag as efficient catalyst for PMS activation[J]. SCIENCE of the Total Environment, 2021, 762: 143120. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143120
[20] WU Y, SHEN H. Comprehensive recycling of manganese anode slime with modified reductant[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2016, 36(5): 69-72+75.
[21] FAN X, XI S, SUN D, et al. Mn-Se interactions at the cathode interface during the electrolytic-manganese process[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2012, 127/128: 24-29. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2012.07.006
[22] 左小红. 高纯电解锰生产工艺设计探讨[J]. 湖南有色金属, 2003(1): 17-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5540.2003.01.006
ZUO X. Discussion on production process design of high purity electrolytic manganese[J]. Hunan Nonferrous Metals, 2003(1): 17-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5540.2003.01.006
[23] ZHANG W, CHENG C Y. Manganese metallurgy review. Part Ⅱ: manganese separation and recovery from solution[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2007, 89: 160-177. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2007.08.009
[24] 黄健, 李武斌, 张谊, 等. 一体化组合体电解槽电解锰阳极泥控制机理研究[J]. 广州化工, 2020, 48(15): 76-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2020.15.026
HUANG J, LI W, ZHANG Y, et al. Research on control mechanism of anode mud producing manganese by combined electrolytic device[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry, 2020, 48(15): 76-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2020.15.026
[25] 孙俊. 富铅电解锰渣中锰和铅回收工艺研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2021.
SUN J. Recovery of Mn and Pb from containing lead electrolytic manganese residues[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2021.
[26] 陈玉亮. 电解锰阳极泥中MnO2晶型调控规律及放电性能研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2016.
CHEN Y. Study on crystal shape control rule of MnO2 and discharge performance for electrolytic manganese anode slime[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2016.
[27] XIE Z, CHANG J, TAO C, et al. Polyacrylonitrile-based carbon fiber as anode for manganese electrowinning: anode slime emission reduction and metal dendrite control[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2021, 168: 013501. doi: 10.1149/1945-7111/abd608
[28] SHU J, LIU R, LIU Z, et al. Leaching of manganese from electrolytic manganese residue by electro-reduction[J]. Environmental Technology, 2017, 38: 2077-2084. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2016.1245789
[29] 魏汉可, 杨勇, 罗豆, 等. 电解金属锰阳极泥的综合回收利用研究[J]. 中国锰业, 2017, 35(S1): 55-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMM2017S1016.htm
WEI H, YANG Y, LUO D, et al. A research on comprehensive recycling of electrolytic manganese anode slime[J]. China's manganese industry, 2017, 35(S1): 55-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMM2017S1016.htm
[30] 严超, 杨勇, 黄冠汉, 等. 电解金属锰阳极泥资源化工程应用研究[J]. 中国锰业, 2017, 35(3): 135-137. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMM201703039.htm
YAN C, YANG Y, HUANG G, et al. A study on resource engineering utilization of electrolytic manganese anode slime[J]. China's manganese industry, 2017, 35(3): 135-137. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMM201703039.htm
[31] LUO S, GUO H, WANG Z, et al. The electrochemical performance and reaction mechanism of coated titanium anodes for manganese electrowinning[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2019, 166: E502-E511. doi: 10.1149/2.1071914jes
[32] LUO S, GUO H, ZHANG S, et al. Comprehensive utilization of metallurgic waste in manganese electrowinning: Towards high performance LiMn2O4[J]. Ceramics International, 2019, 45: 8607-8615. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.01.180
[33] 刘建本, 陈上. 用电解锰阳极泥和含SO2工业尾气制备硫酸锰[J]. 化工环保, 2009, 29(6): 538-540. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2009.06.014
LIU J, CHEN S. Preparation of manganese sulfate using anode slurry from electrolytic manganese production and industrial exhaust gas containing SO2[J]. Environmental Protection of Chemical Industry, 2009, 29(6): 538-540. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2009.06.014
[34] 黄良取. 电解锰阳极泥制备锰酸锂电池正极材料的工艺研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉工程大学, 2014: 83.
HUANG L. Research on preparation of manganate cathode materials for lithium batteries with electrolytic manganese anode slime[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan Institute of Technology, 2014: p83.
[35] 陈炳翰, 丁建华, 叶会寿, 等. 中国硒矿成矿规律概要[J]. 矿床地质, 2020, 39(6): 1063-1077. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ202006007.htm
CHEN B, DING J, YE H, et al. Metallogenic regularity of selenium ore in China[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2020, 39(6): 1063-1077. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ202006007.htm
[36] FUNARI V, GOMES H I, COPPOLA D, et al. Opportunities and threats of selenium supply from unconventional and low-grade ores: a critical review[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2021, 170: 105593. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105593
[37] ABOUTALEBI MR, ISAC M, GUTHRIE R I L. The behaviour of selenium impurities during the addition of Se-containing manganese to steel melt[J]. Steel Research International, 2004, 75: 366-372. doi: 10.1002/srin.200405782
[38] 鲜金利, 童湖云, 蔡正杰, 等. 硒与新型冠状病毒研究进展[J]. 保健医学研究与实践, 2020, 17(5): 12-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXBJ202005004.htm
XIAN J, DONG H, CAI Z, et al. Research progress of selenium and novelcoro navirus[J]. Health Medicine Research and Practice, 2020, 17(5): 12-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXBJ202005004.htm
[39] 张栋. 铜阳极泥蒸硒过程中含硒物相变化的研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2021.
ZHANG D. Study on the change of selenium phase in copper anode slime during selenium evaporation[D]. Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2021.
[40] 曾宪日, 王雨红, 屈欣轲, 等. 碱浸回收电解锰阳极泥中硒的研究[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2016(8): 48-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7545.2016.08.011
ZENG X, WANG Y, QU X, et al. Seleniumre covery from manganese anode slime by alkaline leaching. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2016(8): 48-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7545.2016.08.011
[41] 彭思尧, 杨建广, 陈冰, 等. 含锡二次资源隔膜电积回收锡新工艺试验[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(12): 2656-2667. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ201612022.htm
PENG S, YANG J, CHEN B, et al. Novel process for tin recovery from stannous secondary resources based on membrane electrodeposition[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2016, 26(12): 2656-2667. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ201612022.htm
[42] 韦栋梁, 何绘宇, 夏斌. 对我国锡矿业发展的几点思考[J]. 中国矿业, 2006(1): 58-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2006.01.017
WEI D, HE H, XIA B. Some views on the development of tin industry in China[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2006(1): 58-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2006.01.017
[43] 马娟, 秦德先, 薛传东. 世界锡矿资源形势预测[J]. 昆明理工大学学报(理工版), 2002(6): 13-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-855X.2002.06.004
MA J, QIN D, XUE C. Prediction of the situation for the world tin mines[J]. Journal of Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2002(6): 13-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-855X.2002.06.004
[44] 崔凤平. 电解锰用阳极材料中锡的示波极谱法测定[J]. 冶金分析, 2003(4): 72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7571.2003.04.030
CUI F. Determination of tin in anode material by oscillopolarography for electrolytic manganese[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2003(4): 72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7571.2003.04.030
[45] TENG Y, HAN F, ZHAO S, et al. Preparation of manganese sulfate by reduction of electrolytic manganese mud with corn straws[J]. Singapore: Springer Singapore, 2018, pp 627-636.
[46] DU B, ZHOU C, LI X, et al. A kinetic study of Mn (Ⅱ) precipitation of leached aqueous solution from electrolytic manganese residues[J]. Toxicological&Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 97: 349-357.
[47] 王强. 玉米秆还原浸出电解锰阳极泥制备化学二氧化锰研究[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2015.
WANG Q. Study on preparation ofchemicalmanganese dioxide leaching of electrolytic mangane seanode slimer eduction for corn stalk[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2015.
[48] 符磊, 满瑞林, 扶强, 等. 电解锰阳极泥制备锰酸锂[J]. 广东化工, 2018, 45(8): 13-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDHG201808009.htm
FU L, MAN R, FU Q, et al. Preparation of lithium manganate from electrolytic manganese anode slime[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2018, 45(8): 13-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDHG201808009.htm
[49] 伍永国. 电解锰阳极渣回收制备一氧化铅和活性二氧化锰[D]. 吉首: 吉首大学, 2020.
WU Y. Preparation oflead oxide and active manganese dioxide from electrolyticmanganese anode slag[D]. Jishou: Jishou University, 2020.
[50] 严浩, 彭文杰, 王志兴, 等. 响应曲面法优化电解锰阳极渣还原浸出工艺[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(2): 528-534. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ201302033.htm
YAN H, PENG W, WANG Z, et al. Reductive leaching technology of manganese anode slag optimized by response surface methodology[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(2): 528-534. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ201302033.htm
[51] 沈慧庭, 覃华, 黄晓毅, 等. 某含锰冶金渣中锰和铅的综合回收研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2009(6): 171-176. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS200906055.htm
SHEN H, TAN H, HUANG X, et al. Research on the comprehensive recovery of manganese and an Mn-bearing metallurgical residue[J]. Metal mine, 2009(6): 171-176. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS200906055.htm
[52] ZHANG Y, YOU Z, LI G, et al. Manganese extraction by sulfur-based reduction roasting-acid leaching from low-grade manganese oxide ores[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2013, 133: 126-132. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2013.01.003
[53] 汤集刚, 韩至成. 锰阳极泥的工艺矿物学及杂质的脱除研究[J]. 矿冶, 2005(3): 75-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYZZ200503019.htm
TANG J, HAN Z. Investigation on process mineralogy of manganese anode slime and impurity removal[J]. Mining&Metallurgy, 2005(3): 75-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYZZ200503019.htm
[54] 申永强, 符智荣, 黄养逢, 等. 电解金属锰阳极泥回收制备化学二氧化锰工艺研究[J]. 中国锰业, 2007(3): 14-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMM200703006.htm
SHEN Y, FU Z, HUANG Y, et al. The research on manganese anode slime recycle to produce into chemical manganese dioxide[J]. China's Manganese Industry, 2007(3): 14-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMM200703006.htm
[55] 陈晓亮, 王海峰, 尤晓宇, 等. 两矿法浸出电解锰阳极渣中锰的研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2021, 41(3): 92-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYGC202103022.htm
CHEN X, WANG H, YOU X, et al. Leaching of manganese in anode residue from manganese electrolysis[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2021, 41(3): 92-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYGC202103022.htm
[56] 吴焱, 沈慧庭. 改性无机还原剂还原浸出电解锰阳极泥综合回收锰铅研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2016, 36(5): 69-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYGC201605021.htm
WU Y, SHEN H. Comprehensive recycling of manganese anode slime with modified reductant[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2016, 36(5): 69-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYGC201605021.htm
[57] 赵世珍, 韩凤兰, 滕於江, 等. 木纤维还原电解锰阳极泥制备硫酸锰工艺研究[J]. 无机盐工业, 2017, 49(6)63-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WJYG201706016.htm
ZHAO S, HAN F, TENG Y, et al. Study on preparation of manganese sulfate by reduction of electrolytic manganese anode slime with wood fiber[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2017, 49(6): 63-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WJYG201706016.htm
[58] 刘贵扬, 沈慧庭, 王强. 电解锰阳极泥有机还原浸出回收锰和铅的研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2014(4): 92-98. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYGC201404023.htm
LIU G, SHEN H, WANG Q. Recovery of manganese and lead from manganese electrowinning anode slimeby reduction leaching with organic reductants[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2014(4): 92-98. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYGC201404023.htm
[59] XIE H, ZHANG L, CHEN G, et al. High temperature roasting combined with ultrasonic enhanced extracting lead from electrolytic manganese anode mud[J]. Materials Research Express, 2019, 6(10): 105530.
[60] 黎应芬, 李祥, 叶华, 等. 硫磺还原焙烧-酸浸法提取锰阳极泥[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2017(8): 13-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-METE201708004.htm
LI Y, LI X, YE H, et al. Recovery of manganese anode slimes by sulfur reduction roasting-acid leaching process[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2017(8): 13-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-METE201708004.htm
[61] SHU J, LIU R, LIU Z, et al. Enhanced discharge performance of electrolytic manganese anode slime using calcination and pickling approach[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2017, 806: 15-21.
[62] WANG B, MU L, GUO S, et al. Lead leaching mechanism and kinetics in electrolytic manganese anode slime[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2019, 183: 98-105.
[63] XIE H, LI S, GUO Z, et al. Extraction of lead from electrolytic manganese anode mud by microwave coupled ultrasound technology[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 407: 124622.
[64] ZHANG Y, WANG J, LIU B, et al. Extraction and separation of Mn and Pb from electrolytic manganese anodic slime (EMAS) via SO2 roasting followed by acid leaching process[J]. JOM, 2020, 72(2): 925-932.
[65] 王晖, 王重庆, 符剑刚. 硒的资源、提取及应用研究现状[J]. 稀有金属与硬质合金, 2013, 41(2): 1-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYJY201302002.htm
WANG H, WANG C, FU J. Research on resource situation, extraction and application of selenium[J]. Rare Metals and Cemented Carbides, 2013, 41(2): 1-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYJY201302002.htm
[66] KILIC Y, KARTAL G, TIMUR S. An investigation of copper and selenium recovery from copper anode slimes[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2013, 124: 75-82.
[67] ZHENG Y, CHEN K. Leaching kinetics of selenium from selenium-tellurium-rich materials in sodium sulfite solutions[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(2): 536-543.
[68] LIU W, YANG T, ZHANG D, et al. Pretreatment of copper anode slime with alkaline pressure oxidative leaching[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2014, 128: 48-54.
[69] 覃兆财, 明宪权, 李春霞, 等. 亚硫酸铵还原浸出电解锰阳极泥中锰和硒的研究[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2020(10): 55-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-METE202010011.htm
TAN Z, MING X, LI C, et al. Leaching of manganese and selenium from electrolytic manganese anode slime with ammonium sulfiteas reducing agent[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2020(10): 55-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-METE202010011.htm
[70] 王雨红, 覃兆财, 黄丽燕, 等. 从电解锰阳极泥中两段浸出锰富集硒试验研究[J]. 湿法冶金, 2020, 39(2): 118-122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SFYJ202002010.htm
WANG Y, TAN Z, HUANG L, et al. Two-stage leaching of manganese and enrichment of selenium from electrolytic manganese anode slime[J]. Hydrometallurgy of China, 2020, 39(2): 118-122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SFYJ202002010.htm
[71] 韦成果. 含锡富渣烟化炉硫化挥发[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2002(4): 21-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-METE200204005.htm
WEI C. Sulphurationvolatilization of rich tin slag on fuming furnace[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2002(4): 21-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-METE200204005.htm
[72] P. HALSALL P. HODGKINS. 从副产品中回收锡和中低品位锡精矿的综合利用[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 1982(8): 31-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSYL198208005.htm
P. HALSALL P. HODGKINS. Comprehensive utilization of tin recovery from by-products and medium and low grade tin concentrate[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 1982(8): 31-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSYL198208005.htm
[73] 后宝明. 碳热还原硫化挥发法从锡中矿回收金属锡的试验研究[J]. 矿冶, 2015, 24(4): 39-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYZZ201504011.htm
HOU B. Experiment study on tin recovery from tin middling product by carbothermic reduction and sulfidizing volatilization[J]. Mining&Metallurgy, 2015, 24(4): 39-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYZZ201504011.htm
[74] 钟晨, 陈淑瑜, 梁惠珠. 用低品位锡矿制取锡酸钠的研究[J]. 广东有色金属学报, 1999(1): 37-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDYS901.006.htm
ZHONG C, CHEN S, LIANG H. Study on preparation of sodium stannate from the tin ore of low grade[J]. Journal of guangdong non-ferrous metals, 1999(1): 37-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDYS901.006.htm
[75] 傅其华. 从低品位锡渣中制取锡酸钠[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 1983(8): 10-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSYL198308003.htm
FU Q. Sodium stannate is prepared from low-grade tin slag[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 1983(8): 10-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSYL198308003.htm
[76] LIU W, GU K, HAN J, et al. Innovative methodology for comprehensive use of tin anode slime: preparation of CaSnO3[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2019, 143: 105945.
-



 下载:
下载: