Recovery of Tin on the Surface of Waste Copper-based Tinplate by H2SO4-CuSO4-Cl- Zero Emission System
-
摘要:
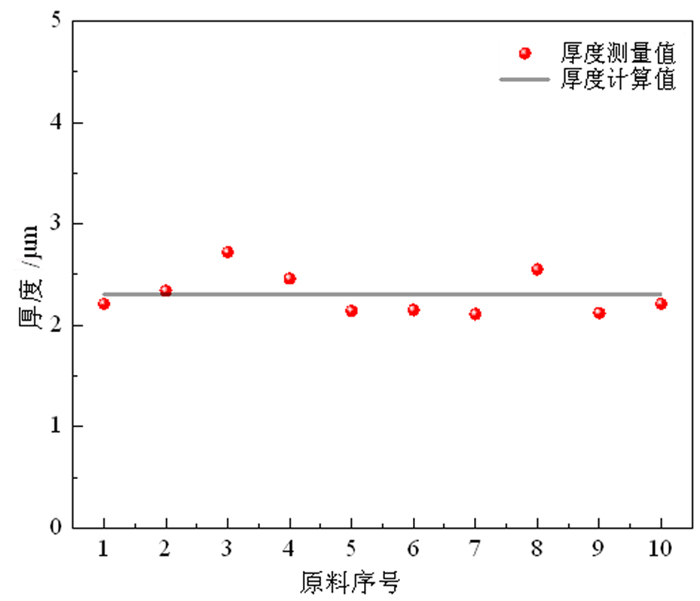
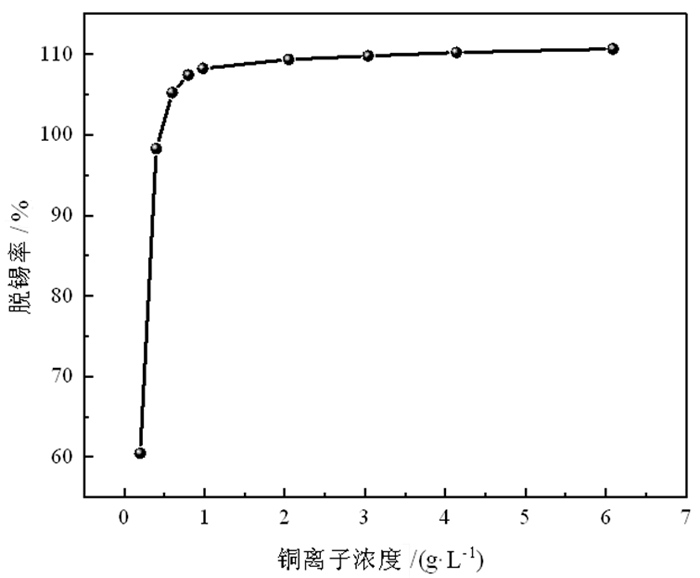
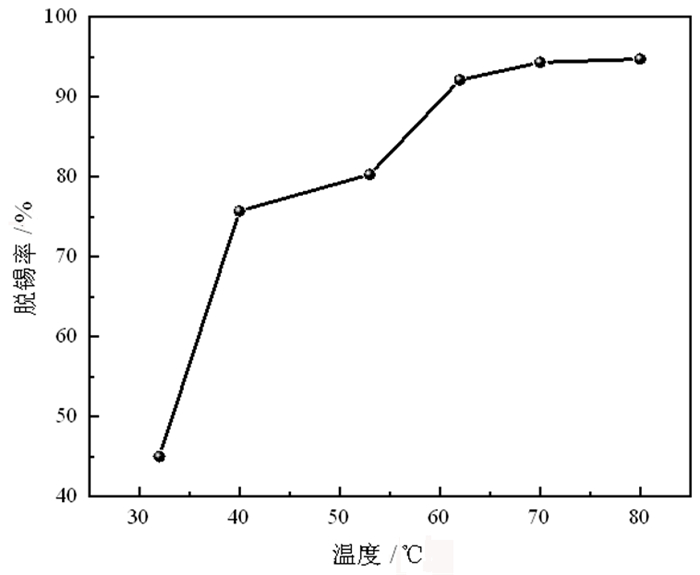
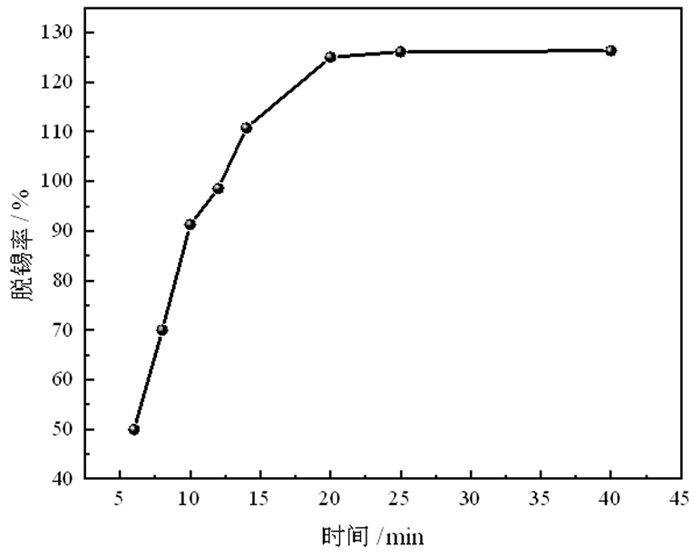
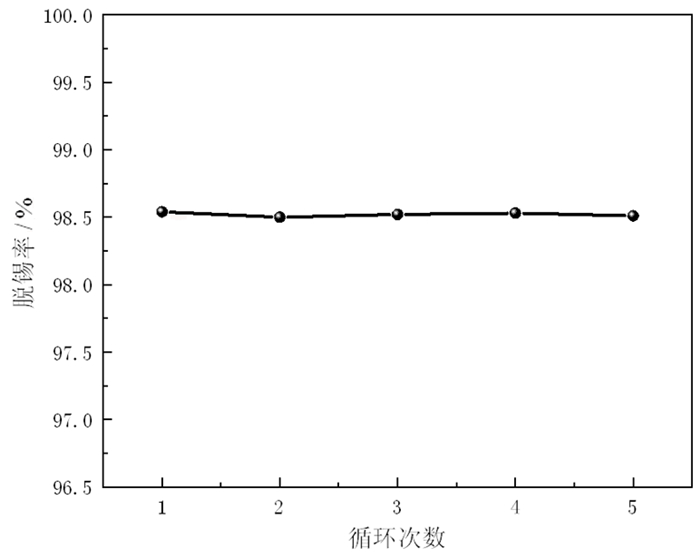
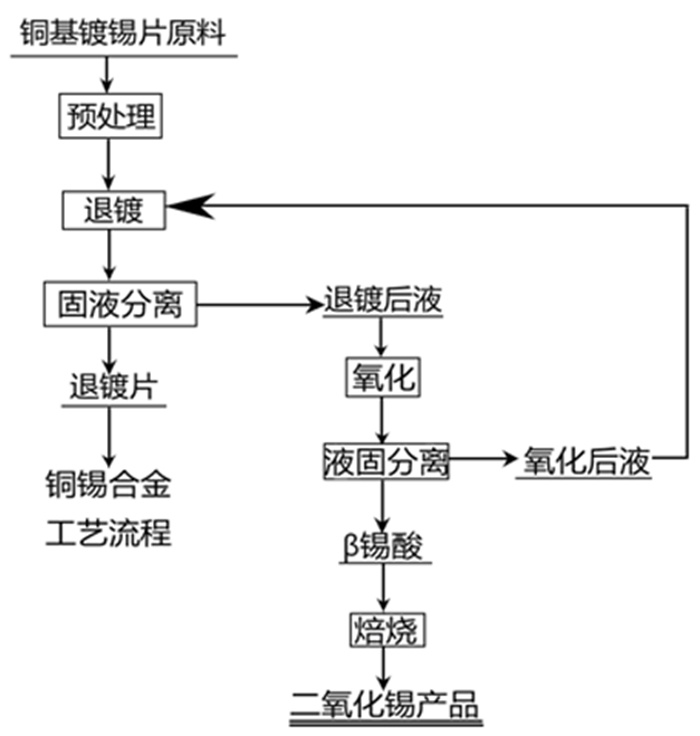
为了有效回收废弃铜基镀锡电路板表面的锡金属, 试验采用H2SO4-CuSO4-Cl-体系进行退镀处理, 详细考察了铜离子质量浓度、初始硫酸浓度、温度、时间等因素对脱锡率的影响, 并进行了循环试验。试验结果表明, 在铜离子质量浓度0.4 g/L、液固比为57 mL/g、硫酸浓度50 g/L、氯离子浓度3.65 g/L、搅拌速度600 r/min、反应温度70℃、反应时间为12 min的条件下取得了较优的脱锡效果, 镀层锡的脱锡率达到98.54%, 锡进入溶液中转化成Sn2+、Sn4+, 退镀后液添加H2O2进一步氧化变成Sn4+, 溶液中的Sn4+大部分水解以β-锡酸沉淀形式分离, 获得干燥的β-锡酸产物, 含锡量高69.34%~69.89%;五次循环试验的脱锡率在98.5%左右, 检测结果表明Cu2+基本没有损失, 退镀液能够形成循环。该体系解决了置换过程中金属铜覆盖在表层从而影响脱锡效果的问题, 提高了脱锡效率, 可高效剥离镀锡层和基板; 该方法能够能循环利用退镀液, Cu2+置换脱锡后变为Cu+, 通过添加H2O2, 将退镀后液中的Cu+氧化为Cu2+后能再次脱锡。
Abstract:In order to effectively recover the tin metal in the waste copper-based tin plating circuit board, the H2SO4-CuSO4-Cl- system was used for treatment in the experiment. The effects of copper ion concentration, initial sulfuric acid concentration, temperature, time and other factors on the tin removal rate were investigated in detail, and the cycle test was carried out. The experimental results show that the optimal tin removal effect is achieved under the conditions of 0.4 g/L copper ion concentration, 57 mL/g liquid-solid ratio, 50 g/L sulfuric acid concentration, 3.65 g/L chlorine ion concentration, 600 r/min stirring speed, 70℃ reaction temperature and 12 min reaction time. The tin removal rate of the coating reached 98.54%, and tin was transformed into Sn2+ and Sn4+ in the solution. After deplating, H2O2 was added to the solution to further oxidize it into Sn4+. Most of the Sn4+ in the solution was separated in the form of β-tinic acid precipitation, and the tin content of the dried β-tinic acid product was 69.34%-69.89% higher. The tin removal rate after five cycles is about 98.5%, the test results show that Cu2+ basically has no loss, and the deplating solution can form a cycle. The system solves the problem that metal copper covers on the surface during the replacement process, which affects the effect of tin removal, improves the efficiency of tin removal, and can effectively strip the tin coating and substrate. Cu2+ is changed into Cu+ after displacement and tin removal. By adding hydrogen peroxide, Cu+ in the deplating solution is oxidized to Cu2+, so this method can recycle the tin removal solution.
-
Key words:
- copper based tinned circuit board /
- tin /
- β- stannic acid /
- recycling /
- copper
-

-
表 1 主要试验仪器及试剂
Table 1. Main test instruments and reagents
名称 型号 生产公司 集热式恒温加热磁力搅拌器 DF-101S 巩义市予华仪器有限责任公司 高精度电子天平 Adventure AR1140 梅特勒-托利多仪器(上海)有限公司 X射线荧光分析仪 XRF-1800 日本岛津 自动三重蒸馏水器 SZ-97 上海亚荣生化仪器厂 原子吸收分光光谱仪 AA-6300 日本岛津 电热鼓风干燥箱 DHG-9035A 上海一恒科学仪器有限公司 循环水式真空泵 SHZ-D(Ⅲ) 巩义市予华仪器有限责任公司 超声波清洗仪 SK6210HP 上海科导超声仪器有限公司 硫酸 AR 成都市科龙化工试剂厂 硫酸铜 AR 天津市致远化学试剂有限公司 盐酸 GR 汕滇药业有限公司 30%过氧化氢 AR 重庆创导化工有限公司 表 2 初始硫酸浓度对镀层锡脱除率的影响
Table 2. Effect of initial sulfuric acid concentration on tin removal rate of coating
初始硫酸浓度/(g·L-1) 0.131 20.131 40.131 50.131 60.131 脱锡率/% 79.87 77.63 76.04 75.78 75.62 表 3 退镀前及氧化后溶液中的铜浓度/(g·L-1)
Table 3. Copper concentration in solution before stripping and after oxidation
退镀前铜浓度 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 2 氧化后铜浓度 0.198 0.397 0.608 0.81 1.12 2.13 表 4 β-锡酸产物的含锡量
Table 4. Tin content of β- stannic acid products
产物编号 1 2 3 4 5 含锡量/% 69.89 69.34 69.49 69.80 69.53 -
[1] 陈丛林, 张伟. 全球锡矿资源现状及供需分析[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2021, 41(4): 172-178. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=26b189c1-bd28-47eb-b176-834f7b840891
CHEN C L, ZHANG W. Study on the current situation and analysis of supply and demand of global tin resource[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021, 41(4): 172-178. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=26b189c1-bd28-47eb-b176-834f7b840891
[2] 中国Sn资源分布情况[J]. 能源与节能, 2021(2): 6.
Distribution of Sn resources in China[J]. Energy and Energy Conservation, 2021(2): 6.
[3] 杨繁明, 申培, 龚志强, 等. 我国镀锡板产业的发展现状及未来发展趋势[C]//第十四届中国科协年会第8分会场: 钢材深加工研讨会论文集. 中国金属学会, 2012: 48-51.
YANG F M, SHEN P, GONG Z Q, et al. Progresses of tinplate industry in China and its development tendency[C]//The 8th Sub Venue of the 14th Annual Conference of China Association for Science and Technology: Proceedings of seminar on steel deep processing. China Metal Society, 2012: 48-51.
[4] 周益辉, 曾毅夫, 龙桂花, 等. 废弃电路板电子元件和焊锡的分离回收技术[J]. 资源再生, 2011(2): 64-67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSZS201102022.htm
ZHOU Y H, ZENG Y F, LONG G H, et al. Separating and recycling of electronic components and solder from waste printed circuit boards[J]. Resource Regenerating, 2011(2): 64-67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSZS201102022.htm
[5] 付嘉琦, 陈小平, 林敏, 等. 废镀锡铜料中铜锡分离回收技术[J]. 能源研究与管理, 2020(3): 6-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXLY202003002.htm
FU J Q, CHEN X P, LIN M, et al. Separation and recovery of copper and tin of scrapped tinned copper materials[J]. Energy Research and Management, 2020(3): 6-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXLY202003002.htm
[6] 陈亮, 王勇, 熊振坤, 等. 从电子脚镀锡铜针中回收锡和铜[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2013(9): 15-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-METE201309005.htm
CHEN L, WANG Y, XIONG Z K, et al. Recovery of tin and copper from electronic foot tin plated copper needle[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2013(9): 15-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-METE201309005.htm
[7] RUDNIK E, BAYARAA E. Electrochemical dissolution of smelted low-grade electronic scraps in acid sulfate-chloride solutions[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2015, 159: 110-119.
[8] KIZAKI Y, HIGUCHI K, HONMA S, et al. Ni-solder (Pb/Sn) selective wet-etching method in acidic solutions[J]. Journal of Japan Institute of Electronics Packaging, 1999, 2(1): 29-34.
[9] AHN J W, SEO J S. Nitric acid leaching of electronic scraps and the removal of free nitric acid from the leaching solution for the recovery of copper and tin[J]. 2009, 18(5): 44-51.
[10] 李元山, 李德良. 印制板循环再生型退锡剂的研制[J]. 电子工艺技术, 2001(5): 211-213. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZGY200105005.htm
LI Y S, LI D L. Study and development of recycled tin-lead stripper for PCB[J]. Electronics Process Technology, 2001(5): 211-213. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZGY200105005.htm
[11] LEE M S. AHN J G, AHN J W. Recovery of copper, tin and lead from the spent nitric etching solutions of printed circuit board and regeneration of the etching solution[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2003, 65(1/2/3): 23-29.
[12] KERR C. Sustainable technologies for the regeneration of acidic tin stripping solutions used in PCB fabrication[J]. Circuit World, 2004, 30(3): 51-58.
[13] TIINA K, TANSKANEN J, KUOKKANEN T. Analysis of key patents of the regeneration of acidic cupric chloride etchant waste and tin stripping waste[J]. Resources, Conservation&Recycling, 2007, 49(3): 217-243.
[14] ROY S, BUCKLE R. The recovery of copper and tin from waste tin stripping solution part Ⅱ: kinetic analysis of synthetic and real process waste[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2009, 68: 185-192.
[15] 彭准, 伍泽广, 万炜, 等. 废旧镀锡覆铜板表面锡回收及其制备二氧化锡的试验研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(4): 141-146. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCZL202004024.htm
PENG Z, WU Z, WAN W, et al. Experimental study on the recovery of Tin on the surface of scrap Tin-coated copper plate and the preparation of Tin dioxide[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(4): 141-146. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCZL202004024.htm
[16] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 金属覆盖层锡电镀层技术规范和试验方法: GB/T 12599-2002[S]. 北京: 中国机械工业联合会, 2002.
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China. Technical specifications and test methods for tin Electrodeposited coatings of metal coatings: GB/T 12599-2002[S]. Beijing: China Machinery Industry Federation, 2002.
-



 下载:
下载: