Process Mineralogy Investigations and Processabilities of Kaolinite in Lower Permian Liangshan Formation of Enshi
-
摘要:
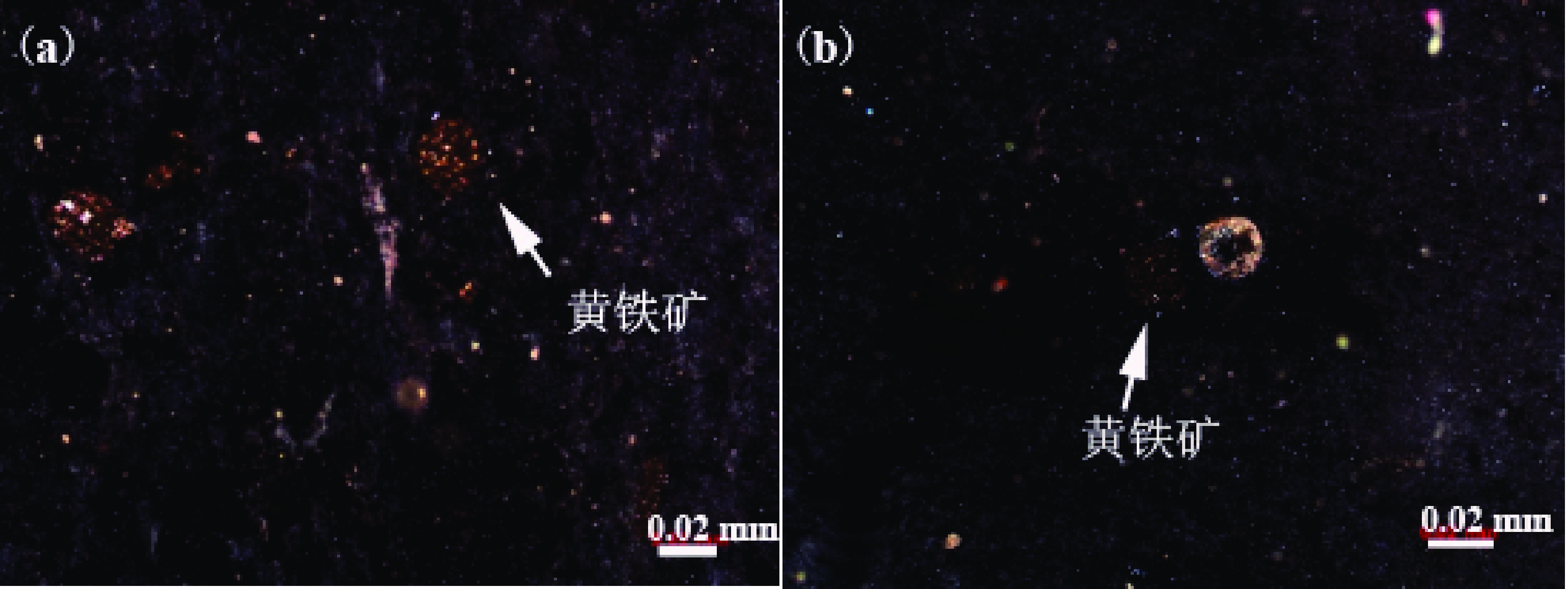
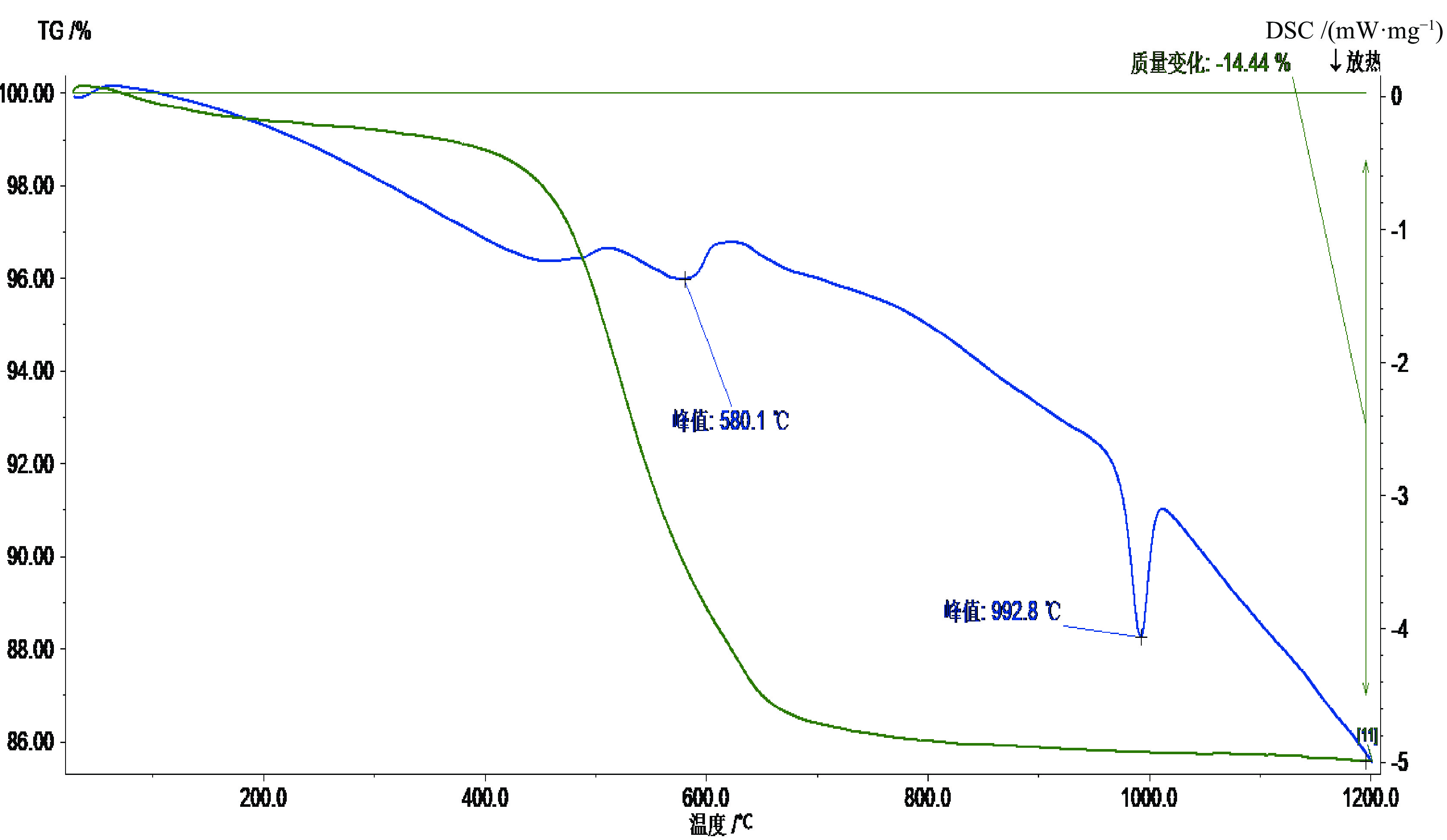
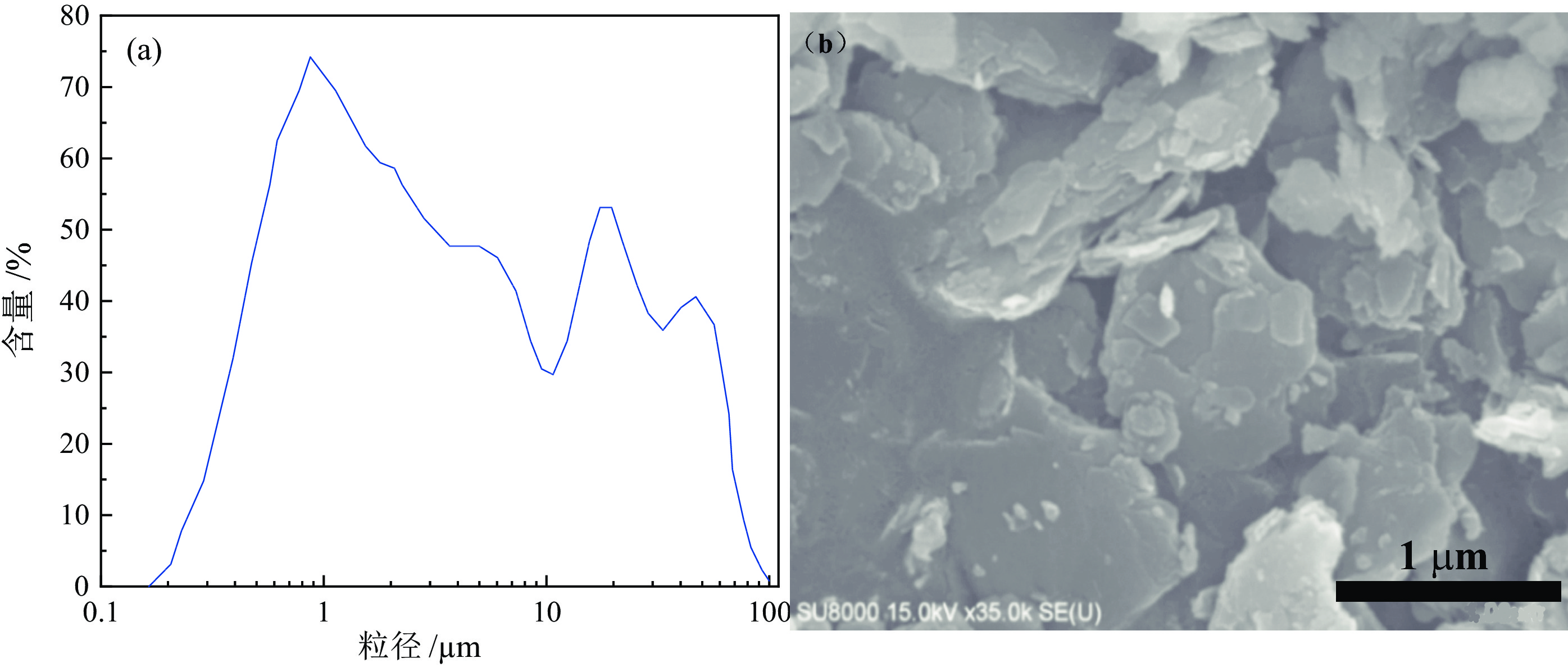
以湖北恩施下二叠统梁山组高岭土作为研究对象,利用XRD、XRF、SEM/EDS、ICP-MS、TG/DSC、光学显微镜、白度仪、粒度仪等分析手段,解析物相、主成分和微量锂含量、杂质赋存状态、白度、粒径分布、吸油值及热解特征,进行干法初加工和煅烧实验研究其加工特性。结果表明该矿石工业类型为硬质高岭土,部分层位高岭石含量86.79%~99.45%,结晶程度不高,结构无序;微量Li有待开发;黄铁矿杂质呈现出鲕粒状,分布于高岭石颗粒粒隙间。高岭石干法初加工后,<1 μm占比32.35%,筛下物含铁量和化学需氧量(COD)会同时降低,可考虑分选加工用作玻纤原料、水泥、复合肥等添加料等;950 ℃煅烧后白度可达79.1%,750 ℃煅烧后吸油值48.23 g/100g,其应用可扩展至偏高岭石、莫来石及陶瓷釉料原料。本研究为恩施高岭土资源加工及潜在应用指出了方向,为其他同类型资源开发提供了研究基础。
Abstract:The objects studied in this paper were the kaolin samples collected from Huashiban mining area of the Lower Permian Liangshan Formation in Enshi, Hubei province. The phase compositions, principal components, trace lithium contents, impurity states, whitenesses, particle sizes, values of oil adsorption and pyrolysis characteristics of these samples were studied by the methods like XRD, XRF, SEM/EDS, ICP-MS, TG/DSC, optical microscope, whiteness and particle-size analyzer. The experiments of the preliminary processing and the calcination were operated to research their processabilities. The results show that the ore in the industry type is hard kaolin. The content of kaolinite is 86.79%~99.45% in some layers. The crystallizations of kaolinite in these samples are not high and they have disorder structures. The trace Li in kaolin needs subsequent researches. The pyrite is in oolitic-shape and distributes between the kaolinite particles. After the preliminary processing of kaolinite, the proportion of less than 1 μm particles is 32.35%. The contents of Fe and chemical oxygen demand (COD) in the undersize material both decreased. The samples were considered to be used as the raw materials for glass fibers and other additives in cements and fertilizers. After the calcination, the whiteness of a sample can reach 79.1% at 950 ℃, and the oil absorption value is 48.23 g/100g after calcination at 750 ℃. Their applications can be extended to be metakaolinite, the raw materials for the mullite and ceramic glazes. Therefore, the researches in this paper propose possible processing methods and potential applications for Enshi kaolinite resources, which can provide references for other similar resources.
-
Key words:
- kaolin /
- process mineralogy /
- preliminary process /
- calcination /
- application
-

-
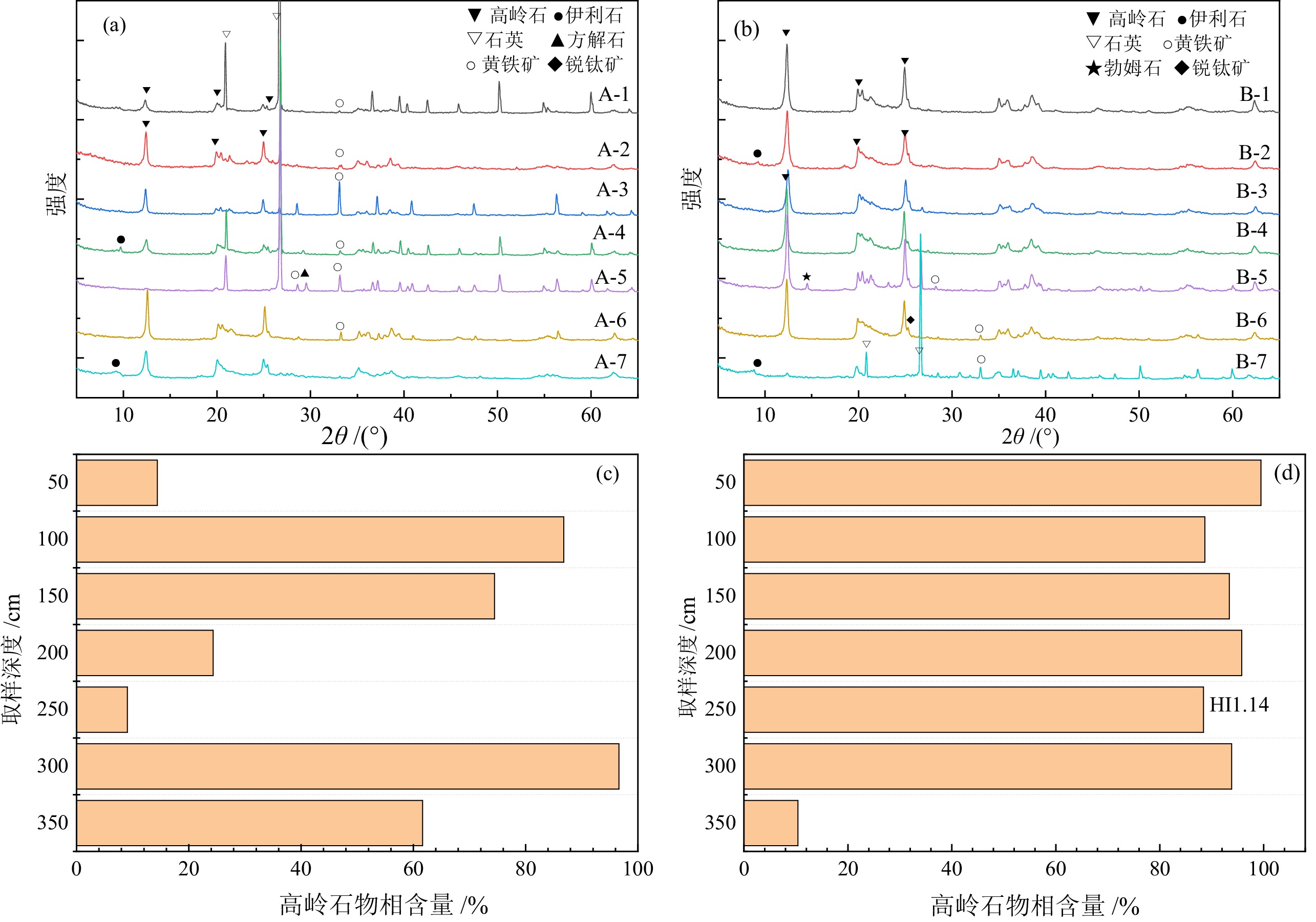
表 1 恩施花石板矿样物相组成和HI参数
Table 1. XRD analysis results of ores from Huashiban of Enshi
/% 取样点 样品编号 高岭石 /% 黄铁矿/% 石英 /% 锐钛矿 /% 伊利石 /% 勃姆石 /% 方解石 /% HI 巷道口距845 m,由顶板至下层 A−1 14.38 1.05 83.44 1.13 0.40 A−2 86.79 5.76 7.44 0.53 A−3 74.47 20.62 4.91 0.89 A−4 24.32 2.02 53.57 20.08 0.59 A−5 9.04 7.72 79.5 3.74 − A−6 96.6 3.41 0.74 A−7 61.63 1.05 3.5 29.45 4.37 − A点平均值 52.46 5.95 33.19 0.16 7.08 0.00 1.16 0.45 巷道口距810 m,由顶板至下层 B−1 99.45 0.55 0.62 B−2 88.7 0.91 2.43 7.95 0.20 B−3 93.41 0.72 3.02 2.86 0.31 B−4 95.76 0.25 4 0.54 B−5 88.41 7.2 2.45 1.93 1.14 B−6 93.84 2.24 3.92 0.38 B−7 10.38 4.93 46.29 38.4 0.52 B点平均值 81.42 1.21 8.24 2.24 6.62 0.28 0.00 0.53 表 2 恩施花石板矿区矿样化学成分分析结果
Table 2. Chemical compositions of ores from Huashiban of Enshi
样品编号 SiO2 /% Al2O3 /% Fe2O3 /% MgO /% CaO/% Na2O /% K2O/% MnO/% TiO2/% P2O5/% 烧失量/% Li/(μg·g−1) A−1 75.52 15.7 0.97 0.20 0.11 0.48 0.53 0.01 1.25 0.02 5.14 86.8 A−2 28.27 25.56 4.21 0.30 0.07 0.09 0.16 0.01 0.87 0.02 40.40 170 A−3 44.06 37.07 1.22 0.56 0.23 0.20 0.42 0.01 1.55 0.02 14.60 492 A−4 49.03 14.34 2.31 0.17 0.10 0.29 0.28 0.01 1.17 0.01 32.24 126 A−5 68.50 5.84 12.01 0.65 2.36 0.16 0.82 0.01 0.33 0.03 9.12 20.3 A−6 38.93 29.63 4.71 0.84 0.45 0.21 0.84 0.02 1.14 0.05 23.13 654 A−7 45.00 35.42 1.84 0.63 0.21 1.06 1.40 0.01 2.80 0.05 11.39 254 A点平均值 49.90 23.37 3.90 0.48 0.50 0.36 0.64 0.01 1.30 0.03 19.43 257.59 B−1 55.25 19.09 6.29 2.55 2.80 0.47 2.87 0.02 0.95 0.74 8.84 43.9 B−2 44.05 38.38 0.85 0.31 0.16 0.19 0.19 0.01 1.70 0.02 14.04 500 B−3 44.11 38.13 1.04 0.59 0.20 0.56 0.43 0.01 1.42 0.06 13.39 534 B−4 44.02 39.53 0.53 0.17 0.10 0.12 0.09 0.01 1.34 0.02 14.00 639 B−5 43.95 39.14 0.41 0.18 0.11 0.12 0.12 0.01 1.22 0.02 14.67 605 B−6 43.64 39.19 0.80 0.19 0.10 0.09 0.12 0.01 1.43 0.02 14.37 646 B−7 42.32 37.81 2.76 0.17 0.10 0.09 0.10 0.01 1.47 0.03 15.07 568 B点平均值 45.33 35.90 1.81 0.59 0.51 0.23 0.56 0.01 1.36 0.13 13.48 505.13 表 3 破碎、研磨、筛分两组实验样品的Al2O3、Fe2O3和COD值
Table 3. The content of Al2O3, Fe2O3 and COD values of the samples by crushing, grinding and sieving
样品 原矿 1#筛下物 1#筛上物 2#筛下物 2#筛上物 Al2O3 /% 38.13 39.88 38.90 39.76 37.75 Fe2O3 /% 1.04 0.80 1.56 0.74 1.95 COD /10−6 14654 8959 17310 8838 18303 -
[1] 鞠建华, 张照志, 潘昭帅, 等. 我国战略性新兴产业矿产厘定与“十四五”需求分析[J]. 中国矿业, 2022, 31(9): 1−11. doi: 10.12075/j.issn.1004-4051.2022.09.025
JU J H, ZHANG Z Z, PAN Z S, et al. Determinationof mineral resources in China’s strategice merging industries and analysis of the demand of the ‘14th five year plan’[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2022, 31(9): 1−11. doi: 10.12075/j.issn.1004-4051.2022.09.025
[2] WANG S, GAINEY L, D. R. MACKINNON I, et al. High- and low-defect kaolinite for brick making: Comparisons of technological properties, phase evolution and microstructure[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 366: 130250. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.130250
[3] 肖万山. 大同煤田煤系高岭土矿地质特征及成因探讨[J]. 中国非金属矿工业导刊, 2023(1): 20−23+34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9386.2023.01.005
XIAO W S. Geological characteristics and genesis of coal-series kaolinite deposits in Datong coalfield[J]. China Non-metallic Mining Industry, 2023(1): 20−23+34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9386.2023.01.005
[4] 冯雪茹, 邓建, 严伟平, 等. 我国高岭土开发现状及综合利用进展[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2022(6): 1−10.
FENG X R, DENG J, YAN W P, et al. Development status and comprehensive utilization of kaolin[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2022(6): 1−10.
[5] 陈漫, 陈肖汀, 黄腾, 等. 我国煤系高岭土应用现状研究与展望[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2022(6): 11−16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2022.06.002
CHEN M, CHEN X T, HUANG T, et al. Application status of coal series kaolin in china[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2022(6): 11−16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2022.06.002
[6] 肖金凯. 贵州高岭土中铁钛的赋存状态研究[J]. 贵州地质, 1997(3): 235−243.
XIAO J K. A study on occurrence of iron and titanium in kaoline of Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Geology, 1997(3): 235−243.
[7] 陈开旭, 姚书振, 沈上越, 等. 鄂西下二叠统梁山组煤系高岭岩铁、钛赋存状态研究[J]. 华南地质与矿产, 2005(3): 1−5.
CHEN K X, YAO S Z, SHEN S Y, et al. Fe-Ti occurrence in kaolinitie of lower permian liangshan formation, western Hubei[J]. Province Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 2005(3): 1−5.
[8] 袁新军. 云南省上二叠统宣威组硬质高岭土矿地质特征及成矿规律研究[J]. 建材发展导向, 2022, 20(8): 32−35.
YUN X J. A study on the geological characteristics and metallogenic laws of hard kaolin deposits in the Xuanwei formation of the upper permian in Yunnan Province[J]. Development Guide to Building Materials, 2022, 20(8): 32−35.
[9] LIU D, ZHANG Y, ZHOU A, et al. The kaolinite crystallinity and influence factors of coal-measure kaolinite rock from Datong coalfield, China[J]. Minerals (Basel), 2022, 12(1): 54.
[10] MBEY J, SIÉWÉ J M, NGALLY SABOUANG C J, et al. DMSO intercalation in selected kaolinites: influence of the crystallinity[J]. Chem Engineering, 2020, 4(4): 66. doi: 10.3390/chemengineering4040066
[11] 王新富, 秦云虎, 王彦君, 等. 华丰煤矿矸石理化特征分析及分级分质利用[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2023, 35(1): 19−24+31.
WANG X F, QIN Y H, WANG Y J, et al. Analysis of physical and chemical characteristics and utilization by grading and quality separation of Gangue in Huafeng coal mine[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2023, 35(1): 19−24+31.
[12] 温汉捷, 罗重光, 杜胜江, 等. 碳酸盐黏土型锂资源的发现及意义[J]. 科学通报, 2020, 65(1): 53−59. doi: 10.1360/TB-2019-0179
WEN H J, LUO C G, DU S J, et al. Carbonate-hosted clay-type lithium deposit and its prospecting significance[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2020, 65(1): 53−59. doi: 10.1360/TB-2019-0179
[13] GU H, GUO T, WEN H, et al. Leaching efficiency of sulfuric acid on selective lithium leachability from bauxitic claystone[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2020, 145: 106076. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2019.106076
[14] 周冬冬, 朱继华, 何斌. 湖南风化残积型高岭土矿分布及成矿机理分析[J]. 中国非金属矿工业导刊, 2023(1): 28−30+54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9386.2023.01.007
ZHOU D D, ZHU J H, HE B. Distribution and metallogenic mchanism of weathered residual kaolin deposit in Hu’nan Province[J]. China Non-metallic Mining Industry, 2023(1): 28−30+54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9386.2023.01.007
[15] VALÁšKOVÁ M, KLIKA Z, JOZEF V, et al. Alkali-activated metakaolins: mineral chemistry and quantitative mineral composition[J]. Minerals, 2022, 12(11): 1342. doi: 10.3390/min12111342
[16] DOU W, FAN J, LIN Q, et al. Study on the adsorption performance of La(Ⅲ) and Y(Ⅲ) on malic acid-kaolinite nanocomposite[J]. Materials Letters, 2023(330): 133254.
[17] 孙涛, 周春宇, 陈洁渝, 等. 煤系煅烧高岭土吸油值的影响因素[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2013, 32(2): 232−238.
SUN T, ZHOU C Y, CHEN J Y, et al. Factors influencing oil adsorption of calcined coal-series kaolin[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2013, 32(2): 232−238.
[18] ALALI A F, WANG S, ZHU Z, et al. Formation of oil-particle aggregates with motor oil and kaolinite clay in cold and warm freshwater[J]. Environmental Science Processes & Impacts, 2023, 25(3): 566−576.
[19] ZHENG D, LIANG X, CUI H, et al. Study of performances and microstructures of mortar with calcined low-grade clay[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022(327): 126963.
[20] 孙悦, 刘小青, 何峰, 等. 煅烧温度对低品位煅烧黏土物相和结构的影响[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2023(3): 1−8.
SUN Y, LIU X Q, HE F, et al. Effects of calcination temperature on phase and structure of low-grade calcined clay[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2023(3): 1−8.
-



 下载:
下载: