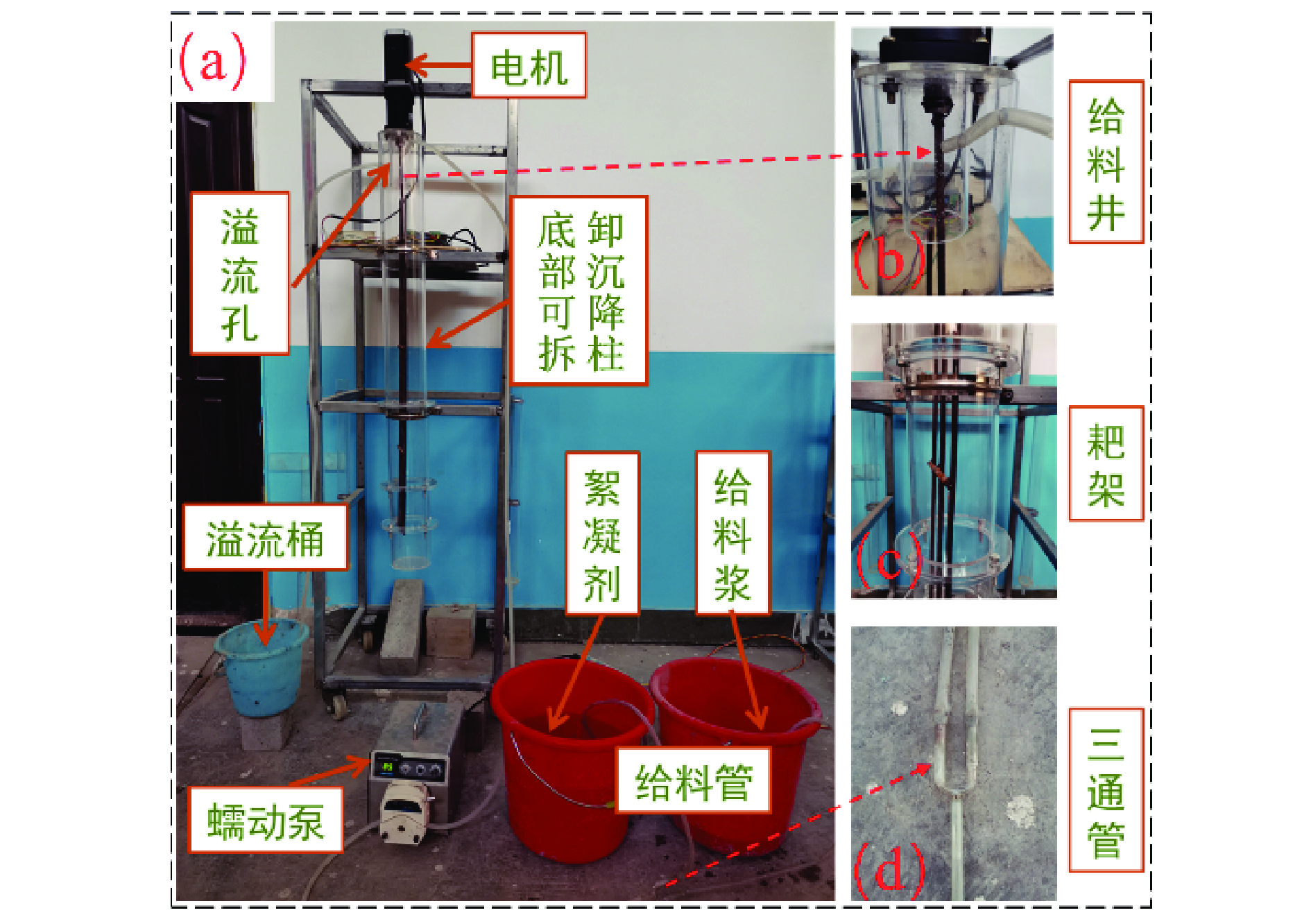
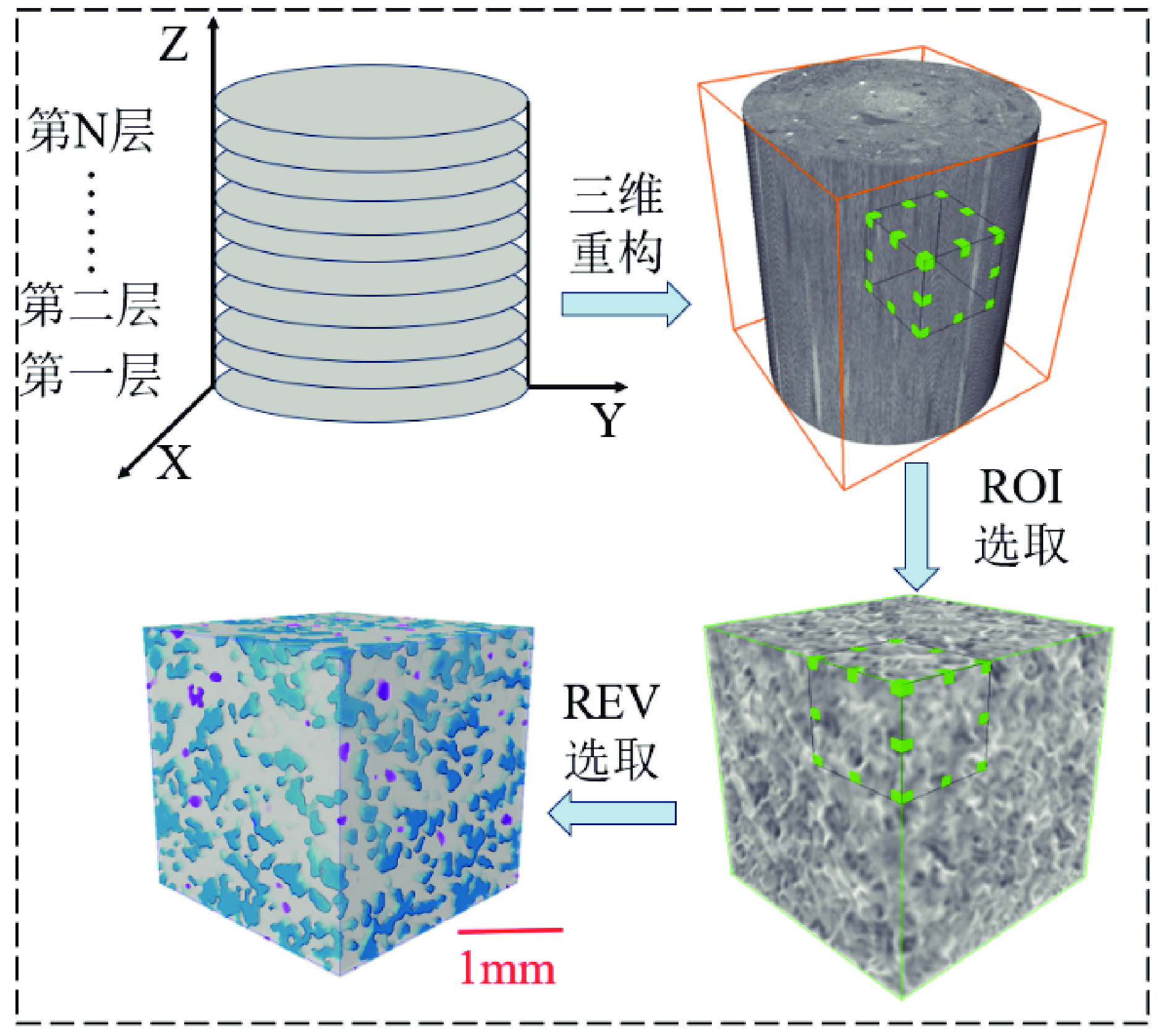
Study on Meso-mechanism of Deep Dewatering of Mine Filling Materials Based on CT Scanning
-
摘要:
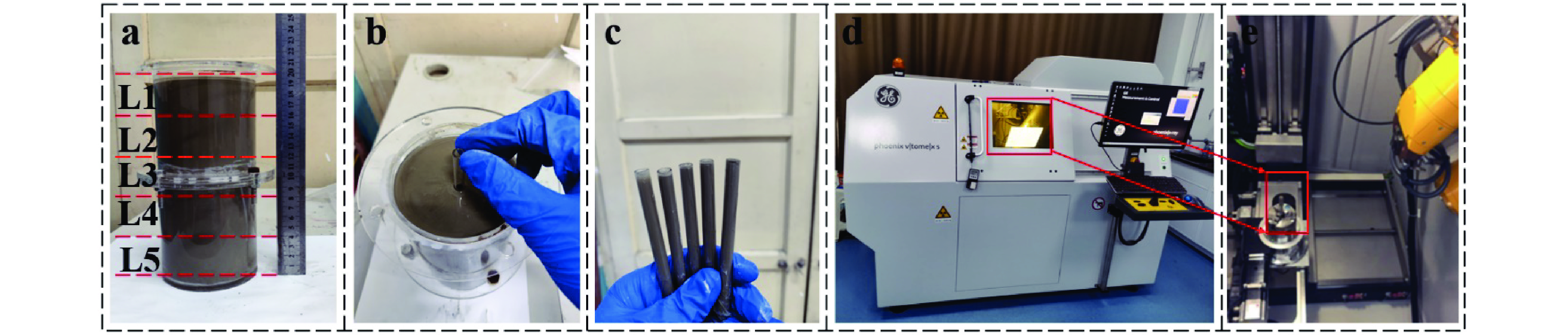
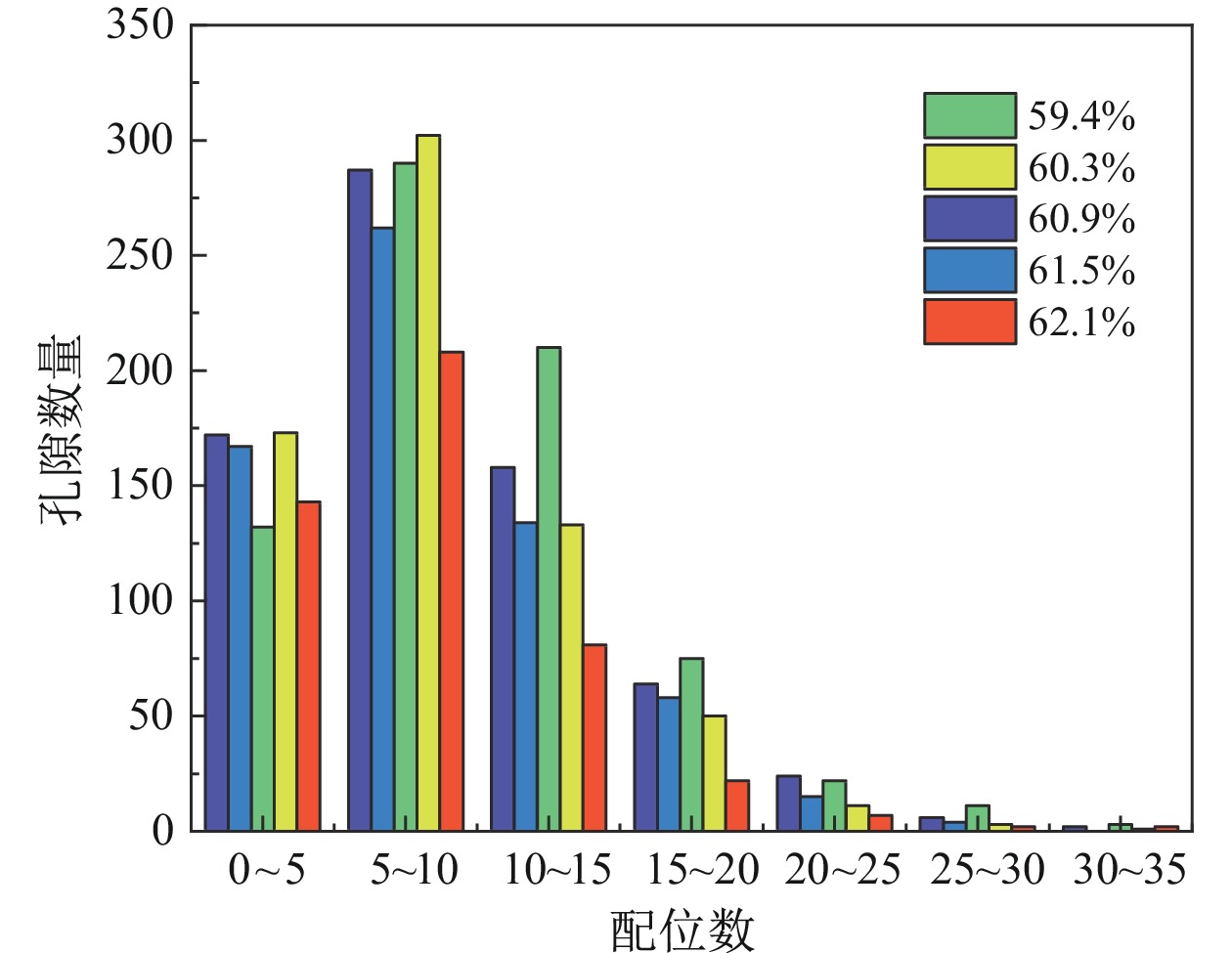
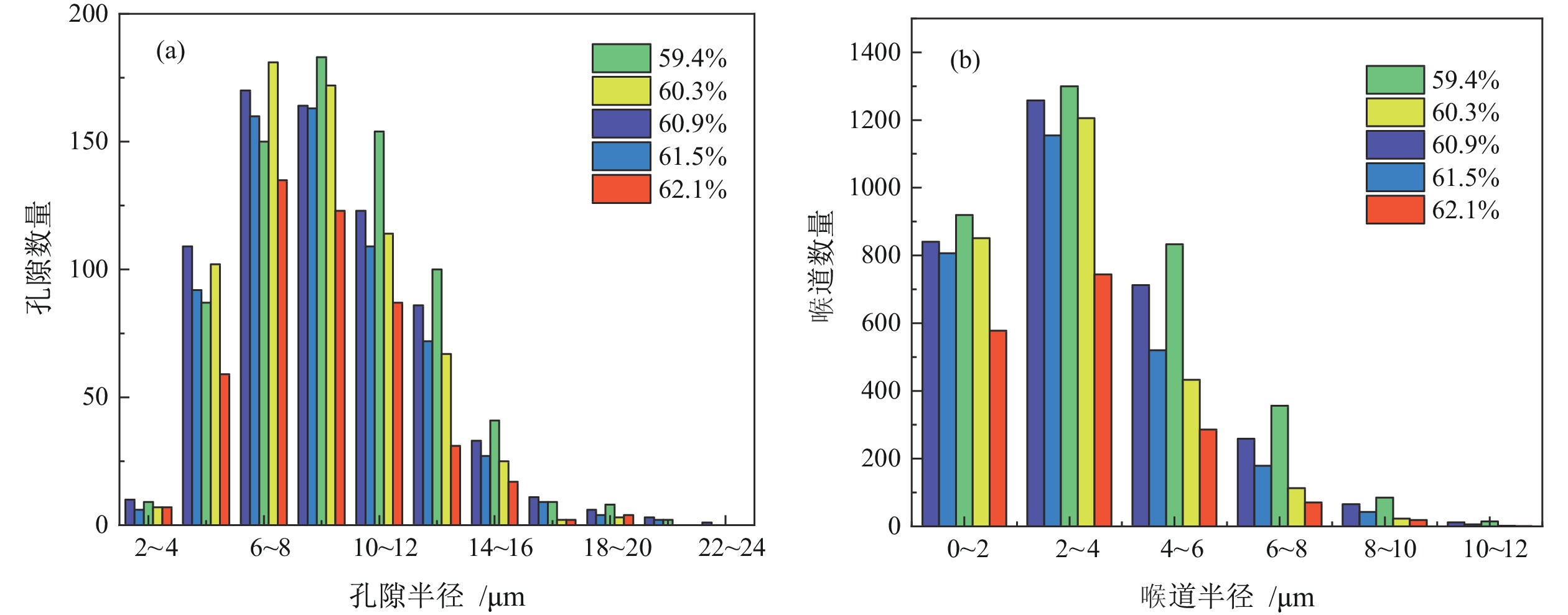
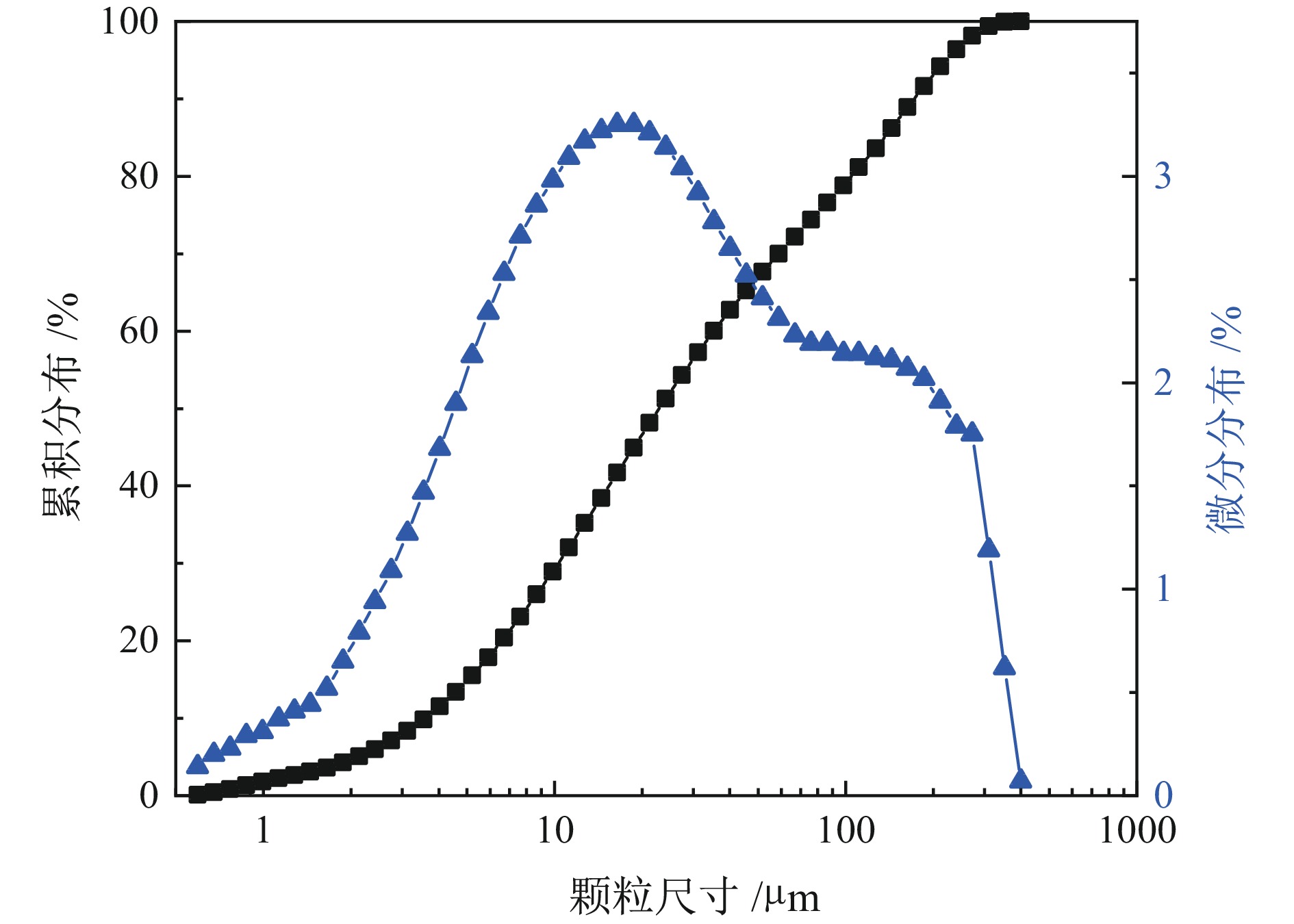
针对全尾砂浓密脱水困难、底流质量浓度低的问题,开展了基于压缩床层不同高度处料浆絮团细观结构深度浓密脱水研究。通过对全尾砂进行动态浓密实验获取压缩床层料浆样品,借助SEM及高精度CT扫描设备,对获取的絮团结构进行扫描及三维重构处理分析沿压缩床层方向孔隙结构变化规律。结果表明:沿着床层向下,五组料浆内部孔隙平均半径分别为9.58 μm、9.23 μm、8.76 μm、8.63 μm及8.31 μm。床层顶部料浆质量浓度为59.4%,絮团呈现松散无规则状,底部料浆质量浓度为62.1%,絮团呈现致密规则状。对比顶部和底部料浆,孔隙率下降3.7个百分点,连通孔隙比下降了35.53%,孔隙平均配位数减小了22.73%,孔隙连通性大大降低。本文从细观角度定量表征了微观孔隙结构特征,为矿山充填材料进一步脱水提供理论依据。
Abstract:Aiming at the problems of difficult thickening and dewatering of total tailings and low underflow mass concentration, the deep thickening and dewatering of slurry flocs based on the meso−structure of slurry flocs at different heights of the compressed bed was studied.Through the dynamic thickening experiment of the whole tailings, the slurry sample of the compressed bed layer was obtained. With the help of SEM and high−precision CT scanning equipment, the obtained floc structure was scanned and three−dimensionally reconstructed to analyze the pore structure variation along the direction of the compressed bed layer. The results show that the average pore radius of the five groups of slurry is 9.58 μm, 9.23 μm, 8.76 μm, 8.63 μm and 8.31 μm respectively. The mass concentration of slurry at the top of the bed is 59.4%, and the flocs are loose and irregular. The mass concentration of slurry at the bottom is 62.1%, and the flocs are dense and regular. Compared with the top and bottom slurry, the porosity decreased by 3.7 percentage points, the connected pore ratio decreased by 35.53%, the average coordination number of pores decreased by 22.73%, and the pore connectivity was greatly reduced. This thesis the microscopic pore structure characteristics are quantitatively characterized from the microscopic point of view, which provides a theoretical basis for further dehydration of mine filling materials.
-
Key words:
- unclassified tailings /
- compressed bed /
- floc structure /
- CT scanning /
- porosity
-

-
表 1 1800万分子量阴离子型絮凝剂基本特性表
Table 1. Basic characteristics of 18 million molecular weight anionic flocculants
聚丙烯酰胺 单位
分子量/万固相
质量分数/%粘度/(mPa·s) 溶解
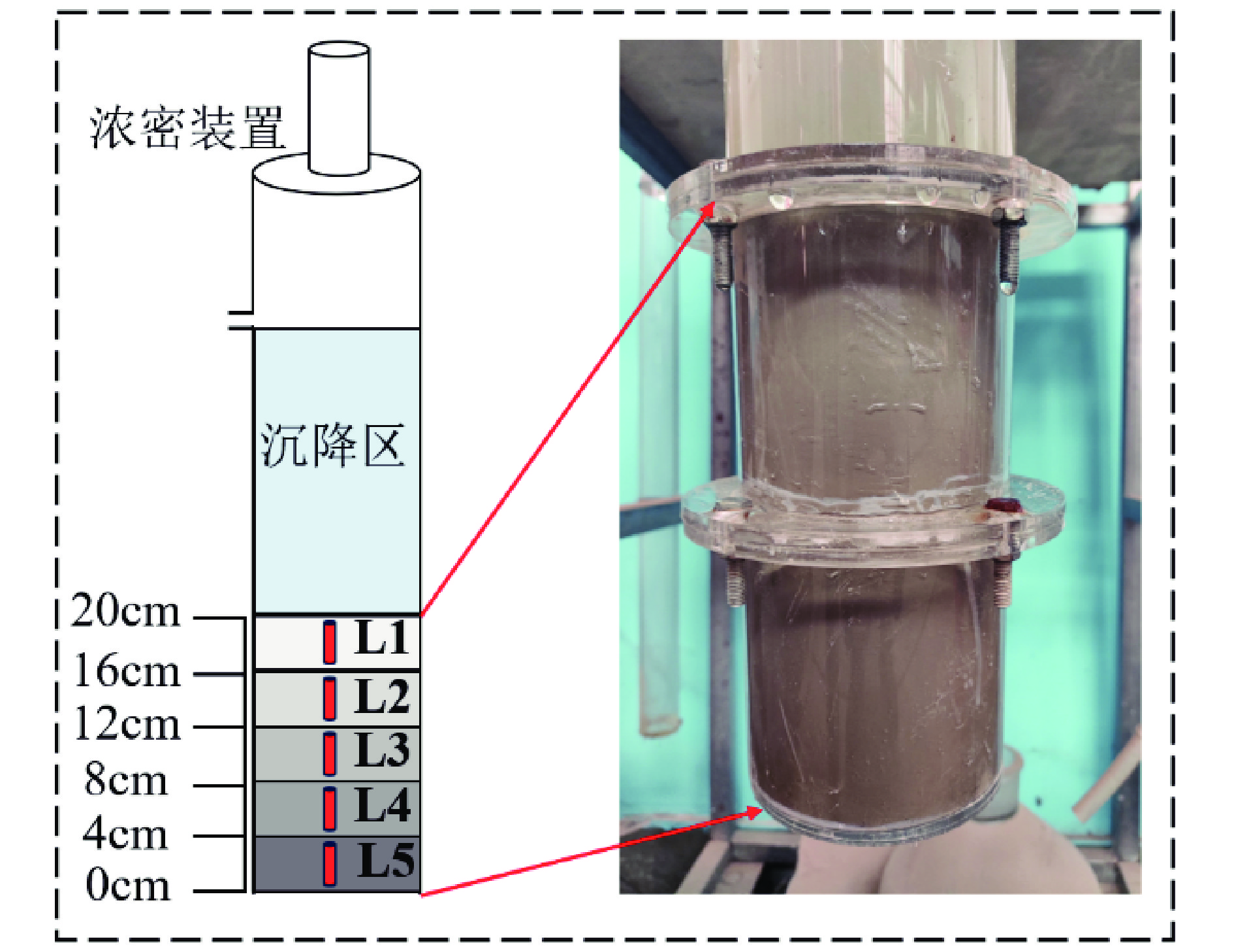
速度/h阴离子型 1800 88~92 3~4 ≤1 表 2 压缩床层不同高度处样品质量浓度
Table 2. Mass concentration of samples at different heights of compressed bed
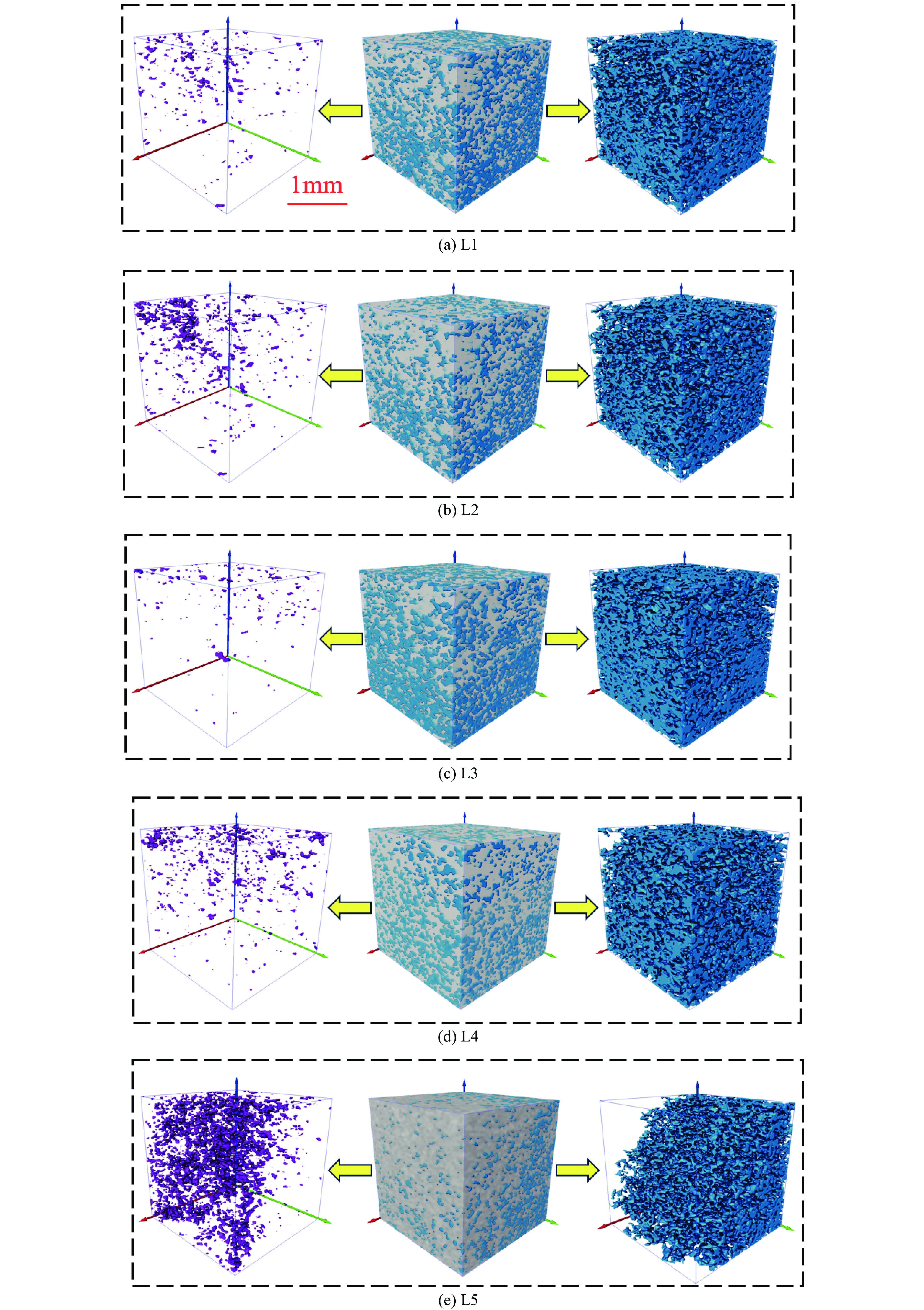
样品编号 L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 样品料浆取样高度/ cm 16~20 12~16 8~12 4~8 0~4 平均质量浓度/% 59.4 60.3 60.9 61.5 62.1 表 3 孔隙连通性结果统计表
Table 3. Statistical table of pore connectivity results
样品 L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 总孔隙率/% 41.6 39.7 39.1 38.5 37.9 孤立孔隙数量/ 个 454 696 301 839 1829 连通孔隙比 fp 0.76 0.71 0.64 0.58 0.49 表 4 孔隙网络模型结构参数统计
Table 4. Statistics of structural parameters of pore network model
样品 值 孔隙数量 孔隙半径/μm 喉道数量 喉道半径/μm 配位数 (a)L1 大 742 20.84 3510 15.43 48 平均 9.58 3.56 9.46 最小 2.73 0.27 1 (b)L2 最大 715 22.41 3150 13.04 46 平均 9.23 3.40 8.81 最小 3.09 0.27 1 (c)L3 最大 672 18.98 2627 10.73 33 平均 8.76 2.91 8.43 最小 2.68 0.27 1 (d)L4 最大 643 21.77 2708 11.73 31 平均 8.63 3.17 7.82 最小 3.09 0.30 1 (e)L5 最大 464 19.61 1697 10.82 32 平均 8.31 2.91 7.31 最小 2.86 0.27 1 -
[1] 白俊豪, 祝朝辉, 时永志, 等. 河南省金矿山尾矿金属资源调查及综合利用分析[J]. 矿物学报, 2022, 42(5): 683−691.
BAI J H, ZHU C H, SHI Y Z, et al. Investigation and comprehensive utilization analysis of metal resources in tailings of gold mines in He’nan Province, China[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2022, 42(5): 683−691.
[2] SUN W, JI B, KHOSO S A, et al. An extensive review on restoration technologies for mining tailings[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25: 33911−33925. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-3423-y
[3] ARAUJO F S M, TABORDA−LLANO I, NUNES E B, SANTOS R M. Recycling and reuse of mine tailings: a review of advancements and their implications[J]. Geosciences, 2022, 12: 319. doi: 10.3390/geosciences12090319
[4] 吴爱祥, 李红, 杨柳华, 等. 深地开采, 膏体先行[J]. 黄金, 2020, 41(9): 51−57.
WU A X, LI H, YANG L H, et al. Cemented paste backfill paves the way for deep mining[J]. Gold, 2020, 41(9): 51−57.
[5] 阮竹恩, 吴爱祥, 焦华喆, 等. 我国全尾砂料浆浓密研究进展与发展趋势[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2022, 32(1): 286−301.
RUAN Z E, WU A X, JIAO H Z, et al. Advances and trends on thickening of full−tailings slurry in China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2022, 32(1): 286−301.
[6] WU A X, YANG Y, CHENG H Y, et al. Status and prospects of paste technology in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2018, 40(5): 517−525.
[7] KIVENTERÄ J, PERUMAL P, YLINIEMI J, et al. Mine tailings as a raw material in alkali activation: A review[J]. International Journal of Minerals Metallurgy and Materials, 2020, 27: 1009−1020. doi: 10.1007/s12613-020-2129-6
[8] 张雷, 郭利杰, 许文远, 等. 细尾砂在矿山充填应用中关键工艺与材料的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2023, 37(23): 102−112.
ZHANG L, GUO L J, XU W Y, et al. Research on crucial technological and material issues of applying fine tailings to mine filling: a review[J]. Materials Reports, 2023, 37(23): 102−112.
[9] Yang Y, Zhou X, CHEN X, et al. Numerical simulation of tailings flow from dam failure over complex terrain[J]. Materials, 2022, 15: 2288. doi: 10.3390/ma15062288
[10] KINNUNEN P H M, KAKSONEN A H. Towards circular economy in mining: Opportunities and bottlenecks for tailings valorization[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 228: 153−160. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.171
[11] 丁冉伟. 浅析尾矿库扬尘综合治理[J]. 中国金属通报, 2022, (13): 162−164.
DING R W. Analysis of Comprehensive Dust Control in Tailings Ponds, China Metal Bulletin, 2022, (13): 162−164.
[12] GOU M F, ZHOU L F, THEN N, et al. Utilization of tailings in cement and concrete: A review[J]. Science and Engineering of Composite Materials, 2019, 26(1): 449−464. doi: 10.1515/secm-2019-0029
[13] RI L G, LIANG Y S, QIN W, et al. Exploration on comprehensive utilization technology of mine tailings[J]. E3S Web of Conferences, 2020, 165(12): 03003−03011.
[14] KYNCH G J. A theory of sedimentation[J]. Transactions of the Faraday society, 1952, 48: 166−176. doi: 10.1039/tf9524800166
[15] RAIMUND B, KENNETH H K, JOHN D. Towers. Mathematical model and numerical simulation of the dynamics of flocculated suspensions in clarifier−thickeners[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2005, 111(2): 119−134.
[16] STEPHENS D W, FAWELL P D. Process equipment optimization using CFD and surrogate models[J]. Progress in Computational Fluid Dynamics, An International Journal, 2015, 15(2): 102. doi: 10.1504/PCFD.2015.068818
[17] 牛永辉, 程海勇, 吴顺川, 等. 动态剪切环境超细全尾砂絮凝沉降特性[J]. 有色金属工程, 2022, 12(8): 139−148. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2022.08.019
NIU Y H, CHENG H Y, WU S C, et al. Flocculation and sedimentation characteristics of ultra‐fine full tailing sand in dynamic shear environment[J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering, 2022, 12(8): 139−148. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2022.08.019
[18] 王勇, 那庆, 杨军, 等. 深锥浓密机泥层高度与压力关系研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2022, 51(2): 257−262.
WANG Y, NA Q, YANG J, et al. Research on the relationship between mud height and pressure of deep cone thickener[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2022, 51(2): 257−262.
[19] 焦华喆, 王树飞, 吴爱祥, 等. 剪切浓密床层孔隙网络模型与导水通道演化[J]. 工程科学学报, 2019, 41(8): 987−996.
JIAO H Z, WANG S F, WU A X, et al. Pore network model of tailings thickener bed and water drainage channel evolution under the shearing effect[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2019, 41(8): 987−996.
[20] 位乐, 王登科, 陈旭, 等. 煤的孔隙结构分形特征研究[J]. 科技创新与应用, 2023, 13(9): 53−56.
WEI L, WANG D K, CHEN X, et al. Research on fractal characteristics of coal pore structure[J]. Technology Innovation and Application, 2023, 13(9): 53−56.
-



 下载:
下载: