Soilization Improvement and Cultivation Experiment of Molybdenum Tailings in Hebei Province
-
摘要:
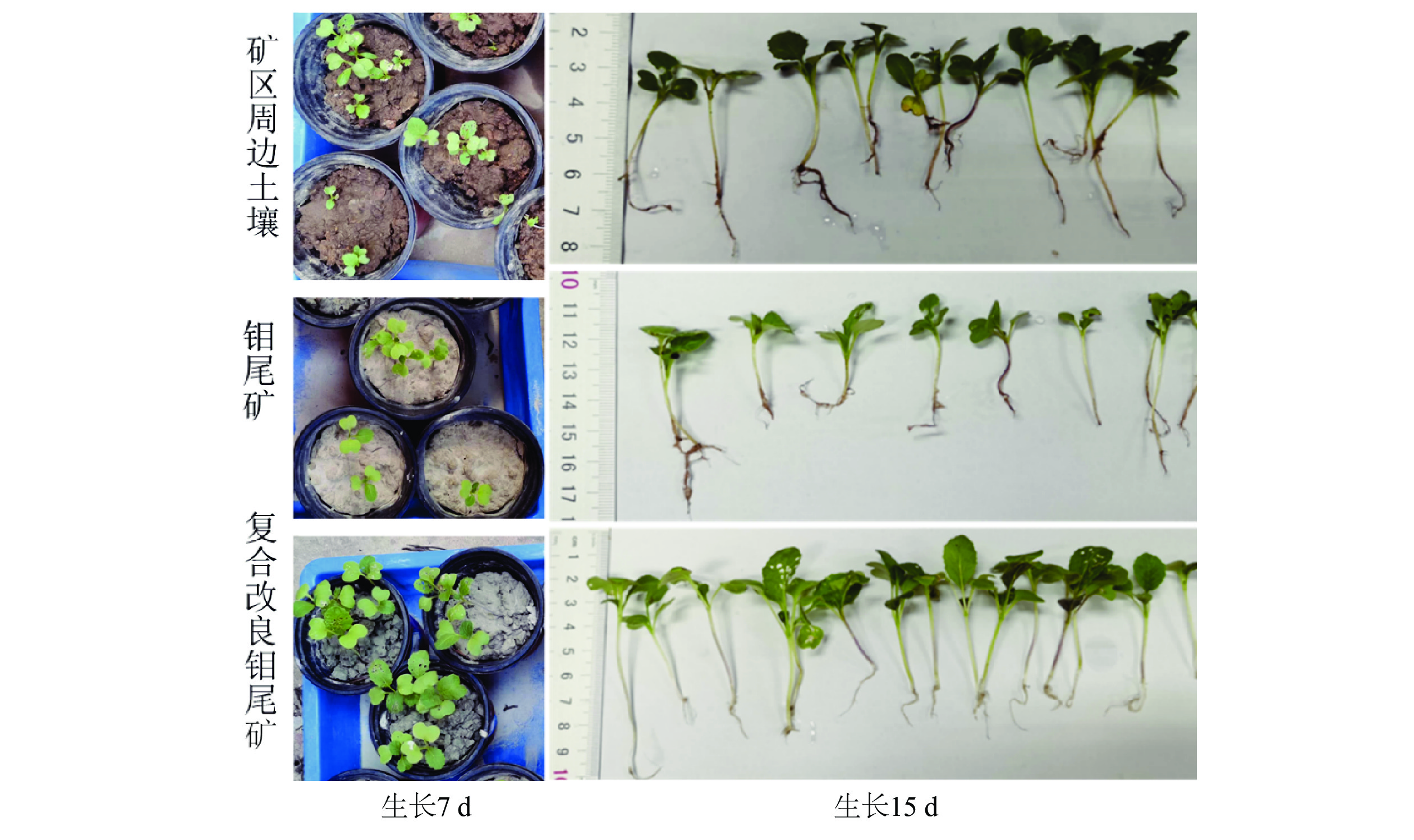
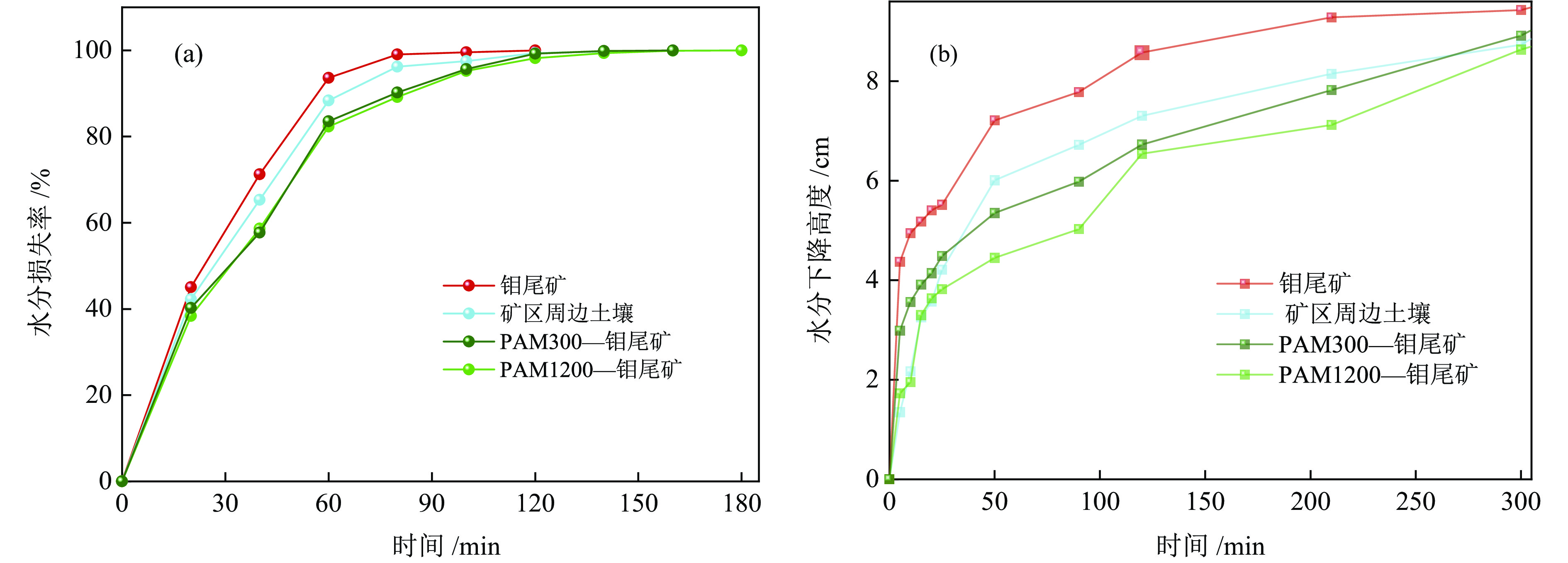
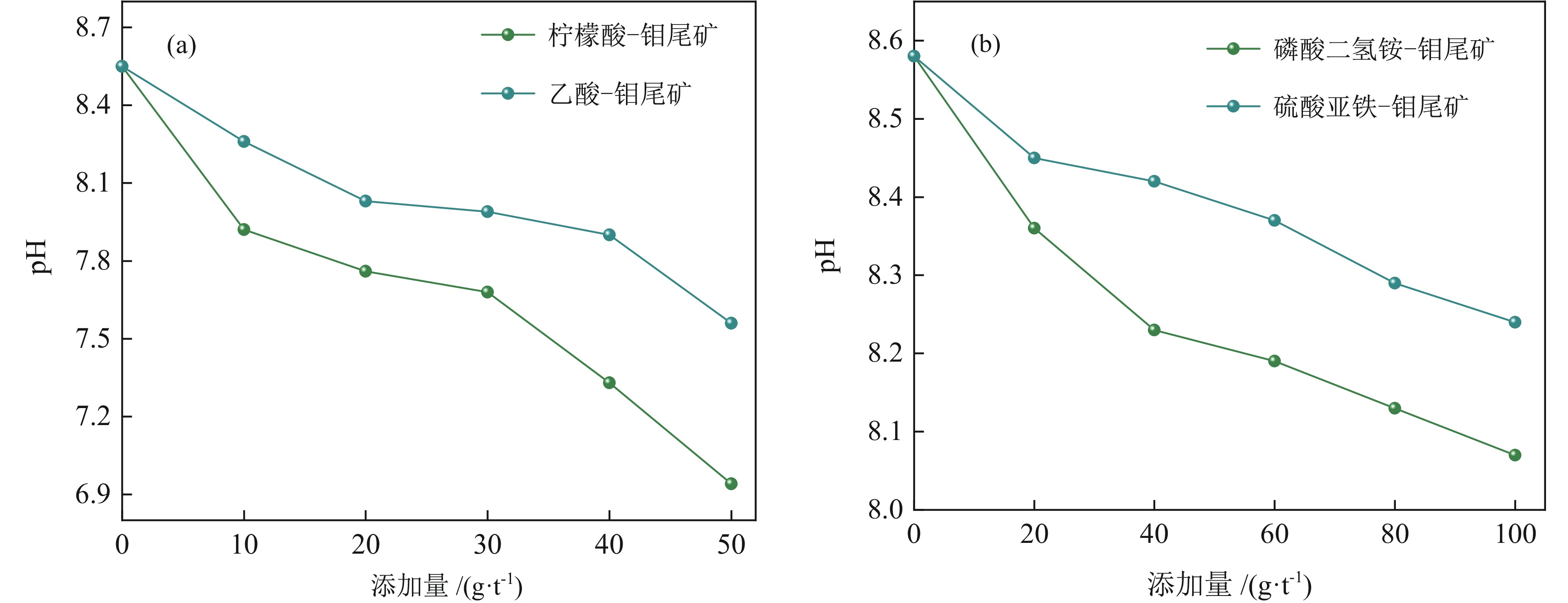
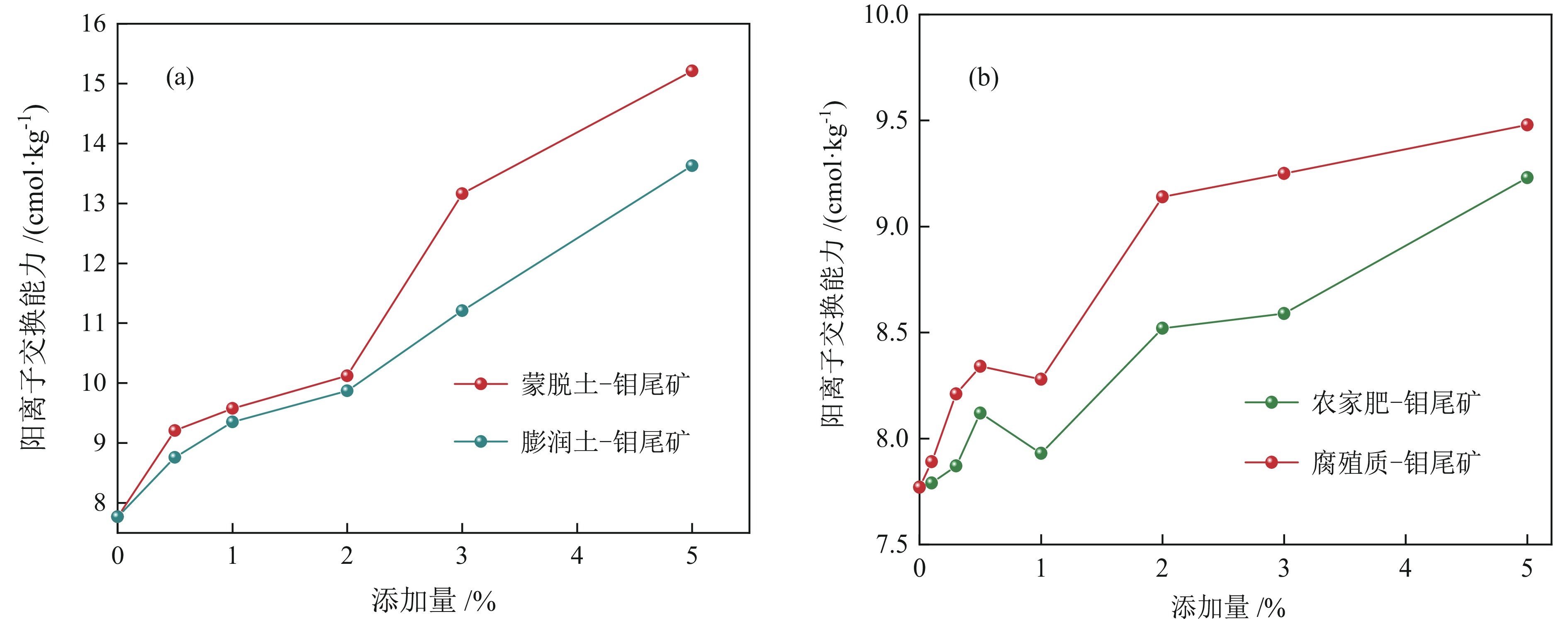
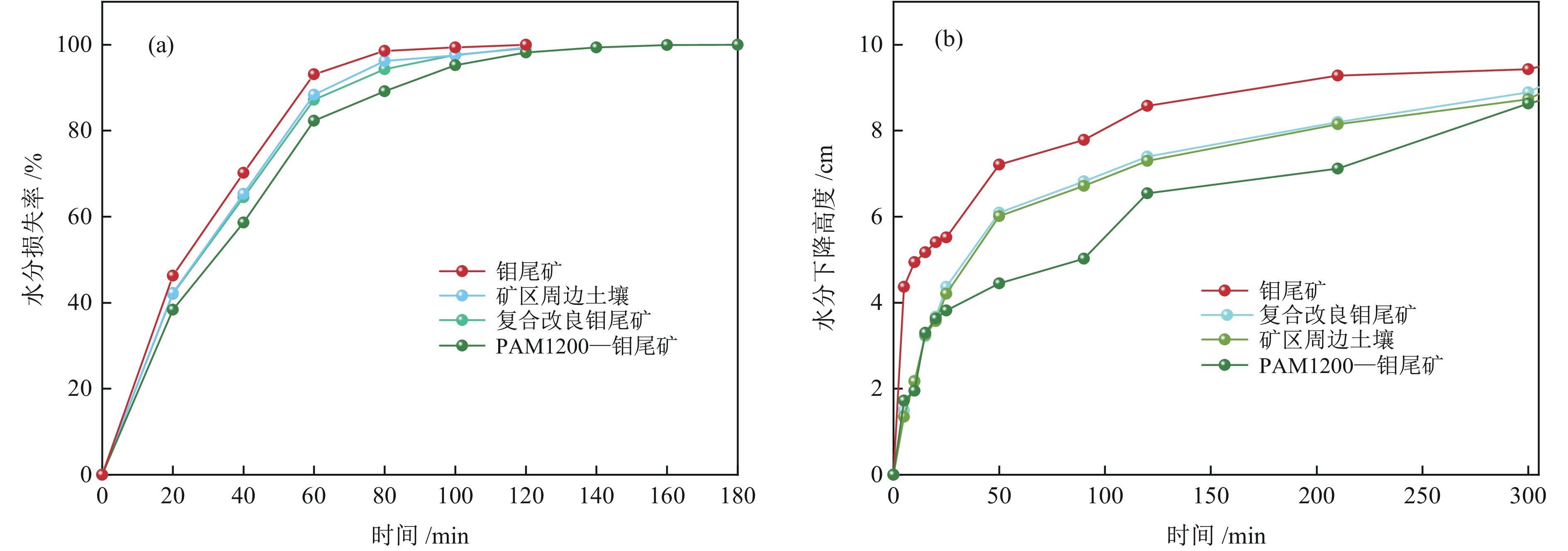
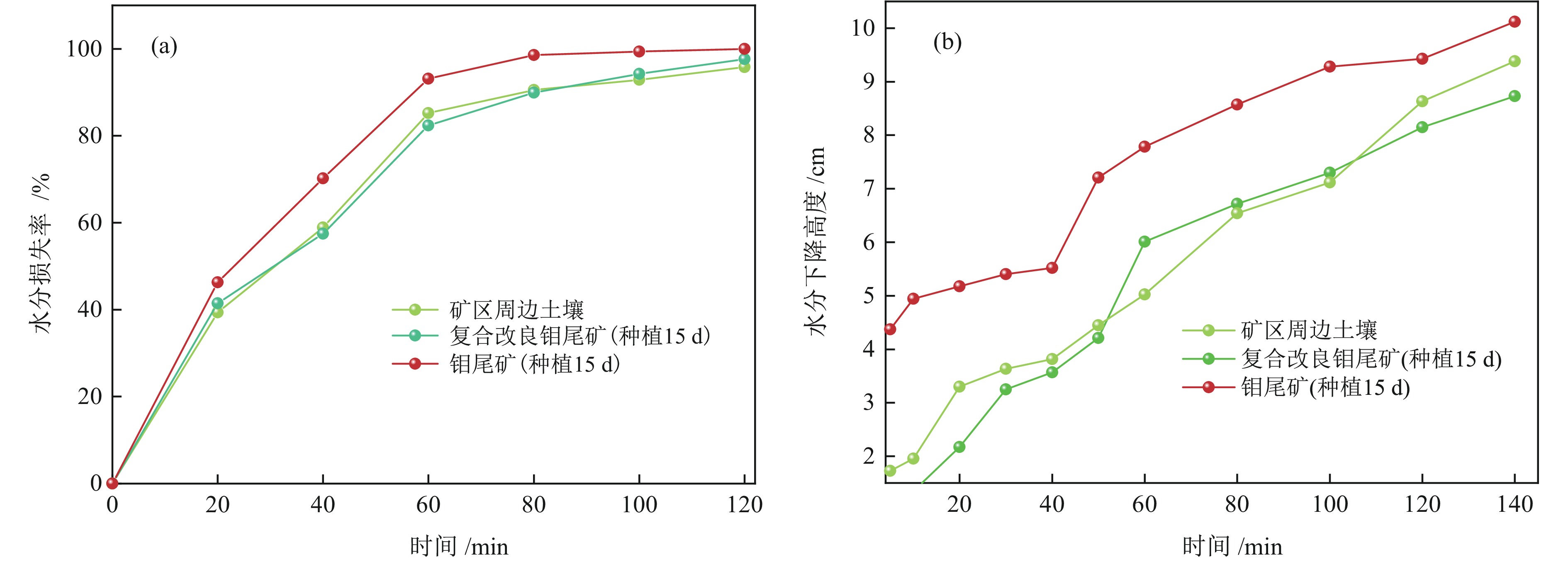
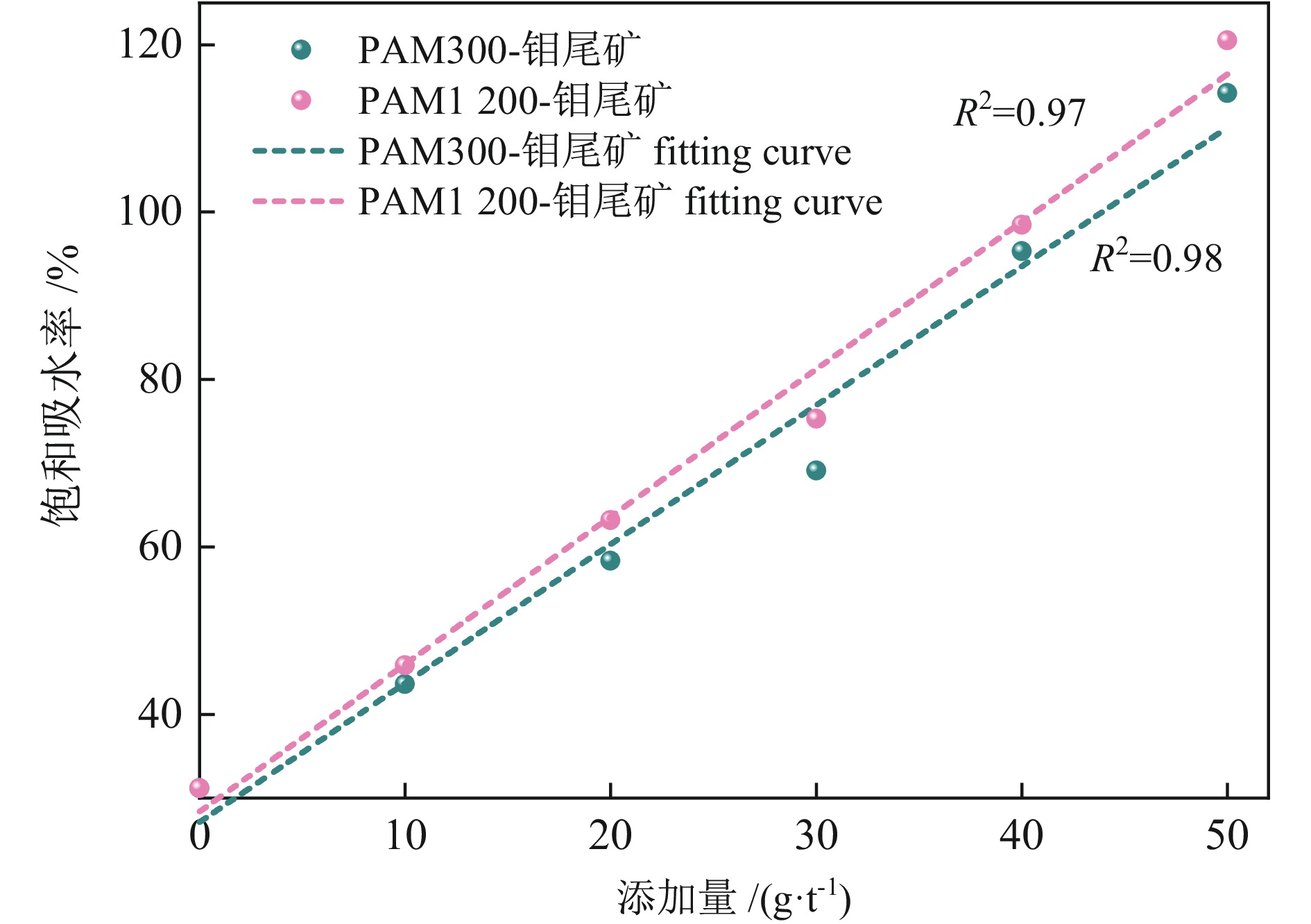
以河北省某钼尾矿为研究对象,采用低成本添加剂与机械混合方法对钼尾矿进行土壤化改良。针对钼尾矿的保水性、酸碱性及阳离子交换能力,开展了单因素改良实验及复合改良实验。结果表明,利用农家肥、蒙脱土、聚丙烯酰胺及柠檬酸复合改良剂对钼尾矿进行改良,钼尾矿的饱和吸水率提高至61.1%,水分挥发速率和渗滤速率明显降低;阳离子交换能力达到了10.15 cmol/kg,pH值降低至8.08,达到了适宜种植的水平。此外,通过盆栽实验验证了复合改良后钼尾矿的植物生长效应,与原始钼尾矿相比,复合改良后钼尾矿中的小白菜生长状态良好,植株的高度和质量分别提高了77.4%和98.1%。经过15 d的小白菜种植后,改良钼尾矿的保水性、pH值及阳离子交换能力达到了正常土壤的水平,实现了钼尾矿向可种植土壤的转化。
Abstract:The molybdenum tailings in Hebei Province had been improved through simple mechanical mixing with low−cost additives, facilitating their utilization for soilization. Through single−factor and composite−amended tests, the water retention rate, pH value, and cation exchange capacity (CEC) of molybdenum tailings were significantly enhanced. Results indicated the application of a composite amendment agent, consisting of farmyard manure, montmorillonite, polyacrylamide (PAM), and citric acid, to the molybdenum tailings has significantly enhanced their properties. The saturated water absorption rate of the molybdenum tailings increased to 61.1%, and both the evaporation rate and decline rate of the moisture was significantly reduced. The cation exchange capacity (CEC) reached 10.15 cmol/kg, and the pH value was lowered to 8.08, achieving a level suitable for agricultural cultivation. Additionally, a pot experiment was conducted to assess the growth effect of improved molybdenum tailings on plants. Compared to the initial molybdenum tailings, the height and quality of plant growth in composite−amended molybdenum tailings increased by 77.4% and 98.1%, respectively. Furthermore, after 15 days of plant growth, the water retention, pH value, and CEC of the composite−amended molybdenum tailings reached levels comparable to those of normal soil, confirming the successful transformation of molybdenum tailings into plantable soil.
-
Key words:
- molybdenum tailings /
- compound amendments /
- water retention /
- pH /
- cation exchange capacity /
- plant growth effect
-

-
表 1 钼尾矿的化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of molybdenum tailings
/% 元素 O F Na Mg Al Si P S K 含量 50.11 1.41 0.28 10.41 2.66 19.83 0.028 0.42 1.98 元素 Ca Mn Fe Cu Zn Mo Pb Rb Ti 含量 7.82 0.22 4.68 0.015 0.048 0.004 0.012 0.006 0.061 表 2 钼尾矿的理化性质
Table 2. Physical and chemical properties of molybdenum tailings
性质 pH值 CEC
/(cmol·kg−1)电导率
/(mS·cm−1)全氮
/(g·kg−1)全磷
/(g·kg−1)全钾
/(g·kg−1)有机质
/(g·kg−1)数值 8.58 7.77 0.21 0.37 0.43 19.80 10.10 表 3 钼尾矿浸出毒性(浸出浓度)
Table 3. Leaching toxicity of molybdenum tailings
/(mg·L−1) 元素 F Mn Cu Pb Zn Mo 水平振荡法 1.04 0.15 0.018 0.015 0.18 0.11 硫酸硝酸法 1.01 0.12 0.011 0.016 0.19 0.18 毒性结果 合格 合格 合格 合格 合格 合格 表 4 复合改良后钼尾矿的CEC、pH值及饱和吸水率
Table 4. CEC, pH value, and saturated water absorption rate of composite-amended molybdenum tailings
样品 CEC/(cmol·kg−1) pH值 饱和吸水率/% 复合改良钼尾矿 10.15 8.08 61.1 表 5 钼尾矿、矿区周边土壤和复合改良钼尾矿中生长15 d后小白菜的参数
Table 5. Parameters of plant grown for 15 days in molybdenum tailings, normal soil, and composite-amended molybdenum tailings
土壤样品 发芽率/% 平均株高/cm 10株质量/g 叶片数 正常土壤 86 4.58 5.86 3~4 钼尾矿 58 2.74 3.12 3 复合改良钼尾矿 92 4.86 6.18 3~4 表 6 种植15 d后钼尾矿和复合改良钼尾矿的理化性质
Table 6. Physical and chemical properties of molybdenum tailings and composite-amended molybdenum tailings after 15 days of cultivation
样品 自然含水率/% pH值 CEC/
(cmol·kg−1)电导率/(mS·cm−1) 有机质/(g·kg−1) 碱解氮/(g·kg−1) 有效磷/(g·kg−1) 有效钾/(g·kg−1) 钼尾矿 19.70 8.38 8.78 0.23 8.92 0.015 0.047 2.43 复合改良钼尾矿 24.30 7.54 12.56 0.44 14.30 0.063 0.087 3.45 -
[1] 王长龙, 叶鹏飞, 张凯帆, 等. 钼尾矿复合胶凝材料的制备及其水化机理研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2020(9): 41−47.
WANG C L, YE P F, ZHANG K F, et al. Study on preparation and hydration mechanism of composite cementitious materials using molybdenum tailings[J]. Metal Mine, 2020(9): 41−47.
[2] 伍红强, 刘诚, 陈延飞. 我国钼尾矿资源综合利用研究进展[J]. 金属矿山, 2018(8): 169−174.
WU H Q, LIU C, CHEN Y F. Research progress of and comprehensive utilized on molybdenum tailings resources in China[J]. Metal Mine, 2018(8): 169−174.
[3] 马伟鸣, 柴文翠, 马鹏举, 等. 钼尾矿中有价矿物综合回收研究进展[J/OL]. 化工矿物与加工: 1−11[2024−03−19]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/32.1492.TQ.20240112.1435.002.html.
MA W M, CAI W C, MA P J, et al. Research progress of comprehensive recovery of valuable minerals from molybdenum tailing[J]. Industrial Minerals & Processing: 1−11[2024−03−19]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/32.1492.TQ.20240112.1435.002.html.
[4] 张艳佳, 付士峰, 张广田, 等. 钼尾矿粉对水泥基材料强度和微观结构影响研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2023(4): 253−259.
ZHANG Y J, FU S F, ZHANG G T, et al. Study on the influence of molybdenum tailings powder on the strength and microstructure of cement−based materials[J]. Metal Mine, 2023(4): 253−259.
[5] 徐晓萍, 高玉德, 孟庆波. 利用某钼尾矿回收钼及制备硅肥的研究[J]. 材料研究与应用, 2018, 12(1): 55−58+63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9981.2018.01.011
XU X P, GAO Y D, MENG Q B. Research and application of new technology of wolframite and scheelite mixed flotation[J]. Materials Research and Application, 2018, 12(1): 55−58+63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9981.2018.01.011
[6] 魏伟明, 邱建锋, 汪磊, 等. 尾矿基发泡水泥隔热材料性能增强工艺研究[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2021, 41(4): 119−123.
WEI W M, QIU J F, WANG L, et al. Study on performance enhancement process of tailings−based foamed cement insulation material[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021, 41(4): 119−123.
[7] 宗传娇. 铁尾矿土壤化利用物理化学改良技术研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2018.
ZONG C J. Study on physical and chemical improvement of iron tailings in soil utilization[D]. Ji’nan: Shandong university, 2018.
[8] 王艳超, 李玉灵, 王辉, 等. 不同植被恢复模式对铁尾矿微生物和酶活性的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2008(10): 1826−1829.
WANG Y C, LI Y L, WANG H. Effect of vegetation restoration pattern on microbial quantity and enzyme activity in iron tailings[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2008(10): 1826−1829.
[9] 石娟华, 袁玉欣, 李玉灵, 等. 铁尾矿坝沙棘、桑树人工林生物量分配及根系分布研究[J]. 河北农业大学学报, 2008, 31(4): 30−35+46.
SHI J H, YUAN Y X, LI Y L, et al. Study on biomass and root distribution of the mixed plantations composed of hippophae rhamnoides L. and Morus alba L. planted on iron tailing[J]. Journal of agricultural university of Hebei, 2008, 31(4): 30−35+46.
[10] 艾艳君, 谷海红. 尾矿生态修复研究进展[J]. 世界有色金属, 2016(3): 88−90.
AI Y J, GU H H. Progress of ecological remediation of tailings[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2016(3): 88−90.
[11] 朱丽瑶, 许永利, 张俊英, 等. 不同改良剂修复铁尾矿的研究[J]. 广东化工, 2023, 50(15): 126−130.
ZHU L Y, XU Y L, ZHANG J Y, et al. Study on repairing iron tailings with different amendments[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2023, 50(15): 126−130.
[12] 盘丽珍, 许中坚, 伍泽广, 等. 大豆秸秆生物炭对铅锌尾矿污染土壤的修复作用[J]. 水土保持学报, 2018, 32(5): 325−329+334.
PAN L Z, XU Z J, WU Z G, et al. Remediation of soil polluted by lead−zinc tailings using soybean straw biochar[J]. Journal of soil and water conservation, 2018, 32(5): 325−329+334.
[13] 张东, 龙军, 杨微, 等. 萤石型铅锌尾矿渣的基质改良与矿山修复应用[J]. 环境工程, 2023, 41(2): 156−165.
ZHANG D, LONG J, YANG W, et al. Subestrate amelioration of fluorite−type lead−zinc tailings and its application in mine restoration[J]. Environmental engineering, 2023, 41(2): 156−165.
[14] 孙波. 聚丙烯酰胺对铁尾矿砂水分运移及物理性质的影响[D]. 太原: 山西农业大学, 2023.
SUN B. Effects of polyacrylamide on water transport and physical property of iron tailings[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi Agricultural University, 2023.
[15] 刘目兴, 聂艳, 于婧. 不同初始含水率下粘质土壤的入渗过程[J]. 生态学报, 2012, 32(3): 871−878. doi: 10.5846/stxb201103300412
LIU M X, NIE Y, YU J. The infiltration process of clay soil under different initial soil water contents[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 32(3): 871−878. doi: 10.5846/stxb201103300412
[16] 周涛, 谌芸, 王润泽, 等. 种草和施用聚丙烯酰胺对荒坡紫色土抗剪和抗蚀性能的影响研究[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(3): 62−73. doi: 10.11686/cyxb2018196
ZHOU T, CHEN Y, WANG R Z, et al. Effect of planting grasses and adding polyacrylamide on the shear performance and erodibility−resistance of purple soil in barren hill sides[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2019, 28(3): 62−73. doi: 10.11686/cyxb2018196
[17] HU X, LIU L Y, LI S J, et al. Development of soil crusts under simulated rainfall and crust formation on a loess soil as influenced by polyacrylamide[J]. Pedosphere, 2012, 22(3): 415−424. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0160(12)60027-7
[18] YANG K, TANG Z J, FEH J Z. Effect of Co−use of fly ash and granular polyacrylamide on infiltration, runoff, and sediment yield from sandy soil under simulated rainfall[J]. Agronomy, 2020, 10(3): 344−344. doi: 10.3390/agronomy10030344
[19] 张根柱. 外源柠檬酸对塿土养分、酶活性及微生物活性的影响[D]. 西安: 西北农林科技大学, 2011.
ZHANG G Z. Effects of exogenous citric on soil nutrients and enzyme activities and microbial activity of old manured loessal soil[D]. Xi’an: Northwest A & F university, 2011.
[20] LI M, SHI L. Construction of a bridging network structure by citric acid for environmental heavy metal extraction[J]. ACS Earth and Space Chemistry, 2023, 7(4): 676−684. doi: 10.1021/acsearthspacechem.2c00389
[21] 邱德勋, 尹殿胜, 穆兴民, 等. 聚丙烯酰胺施用量、初始含水率和容重对土壤水分入渗特性的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 2022, 53(2): 333−340.
QIU D X, YIN D S, MU X M, et al. Effects of polyacrylamide application amounts, initial water contents and bulk densities on soil infiltration characteristics[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2022, 53(2): 333−340.
[22] 朱本国, 王丽娟, 胡艳燕, 等. 不同土壤改良材料对碱性土壤pH值的影响试验[J]. 南方农业, 2021, 15(25): 68−71.
ZHU B G, WANG L J, HU Y Y, et al. Effect tests of different soil improvement materials on pH value of alkaline soil[J]. Southern Agriculture, 2021, 15(25): 68−71.
[23] 于耀泓, 刘悦, 顾晓娟, 等. 2种人工林对土壤碳氮磷化学计量特征及阳离子交换量的影响[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 168−177.
YU Y H, LIU Y, GU X J, et al. Effects of two plantations on soil carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus stoichiometry and cation exchange capacity[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2023, 43(6): 168−177.
[24] 杨树俊, 韩张雄, 王思远, 等. 土壤阳离子交换量与有机质、机械组成的关系[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2023, 23(7): 2799−2805. doi: 10.12404/j.issn.1671-1815.2023.23.07.02799
YANG S J, HAN Z X, WANG S Y, et al. The relationship between cation exchange capacity and organic matter, mechanical composition in soil[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2023, 23(7): 2799−2805. doi: 10.12404/j.issn.1671-1815.2023.23.07.02799
-



 下载:
下载: