Accurate Measurement of Argon Isotope Composition of Air by Argus Multi-collector Noble Gas Mass Spectrometer
-
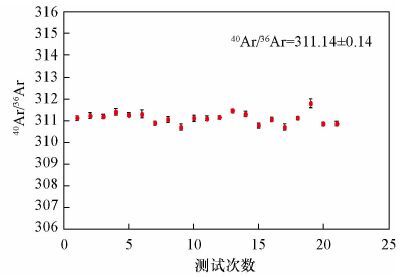
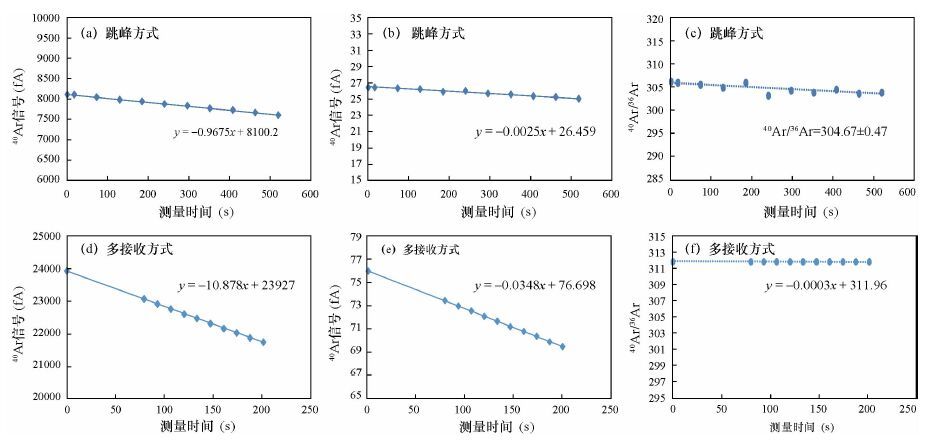
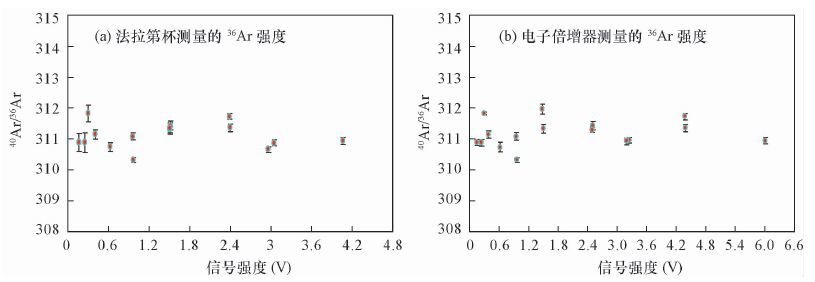
摘要: 稀有气体质谱仪准确测量氩同位素组成是Ar-Ar法高精度定年的前提,目前测量氩同位素主要应用单接收或多接收质谱仪,其中多接收稀有气体质谱仪在数据准确性和重现性等方面具备优势。本文研究了Argus多接收稀有气体质谱仪应用于测量Ar同位素过程中一些主要因素对测量结果准确度和重现性的影响情况。结果表明,整套系统在静态模式下不同时间段的本底值极低,不影响测定;仪器电子倍增器的接收效率优于99.67%,可显著提高Ar低含量样品测量精度,当40Ar信号强度低于0.5 V时,用电子倍增器测量40Ar/36Ar组成的标准偏差仅为0.11%,而用法拉第杯测量40Ar/36Ar组成的标准偏差为0.53%;仪器的质量歧视效应可通过多次循环测量并采用指数定律获得稳定的质量歧视校正因子(此值相对标准偏差为0.0434%),实现对Ar同位素组成的准确校正。本文以测量空气中的氩同位素组成为例,证明了Argus多接收稀有气体质谱仪的测试效率比单个接收器跳峰方式的测试效率高,测试结果更精确,因此适合年轻样品或含钾量极低的样品的Ar-Ar高精度定年工作。Abstract: Accurate measurement of Argon isotopes is the premise of Ar-Ar dating with high precision. Two main kinds of instruments for Ar isotope measurement are Single-collector and Multi-collector Mass Spectrometers, among which the Multi-collector Noble Gas Mass Spectrometer can produce data with better accuracy and reproducibility. Some main factors affecting the accuracy and reproducibility of the results during the measurement of the Ar isotopes by the Argus Multi-collector Noble Gas Mass Spectrometer are discussed in this paper. Results show that the background of the whole system in static mode is very low and has little effect on the measurement of Ar isotope composition. The efficiency of the multiplier of the instrument is better than 99.67%, which can improve the measurement precision of low Ar samples. When the signal of 40Ar is less than 0.5 V, the standard error is only 0.11% for the 40Ar/36Ar ratios measured by the CDD, while the standard error is 0.53% when the ratios are measured using a Faraday cup. The mass discrimination effect of the instrument could be calibrated with the logarithmic law through the repeated measurement of argon isotopes in air and the relative standard error of the mass discrimination is only 0.0434%. Using the example of the determination of argon isotopes in air, it can be demonstrated that the efficiency of the measurement by Argus Multi-collector Mass Spectrometer is higher than that of the Single-collector Mass Spectrometer with higher precision and accuracy. Therefore, the Multi-collector Mass Spectrometer is highly suitable for the high-precision Ar-Ar dating of young and potasium-poor samples.
-

-
表 1 法拉第杯之间增益系数确定
Table 1. The determination of the gain between the Faraday cups
法拉第杯名称 UFC 补偿(fA) 增益系数 校正因子 H2 -13.9771985 0.0001179 1 H1 -0.7418739 0.0020749 1 AX -6.7486484 0.0019324 1 L1 -3.354546 0.0010854 1 L2 -1.6338639 0.0017126 1 表 2 电子倍增器的接收效率
Table 2. The receiving efficiency of the CDD SEM
循环次数 中心杯测量质量数:43.288 电子倍增器测量质量数:39.962 第一个法拉第杯测量质量数:39.962 中心杯测量质量数:38.962 电子倍增器的接收效率(%) 1 -0.147734 56.513159 56.635510 -0.154347 99.78 2 -0.131512 56.824269 56.905517 -0.099949 99.86 3 -0.064739 57.069140 57.321538 -0.099247 99.56 4 -0.095934 57.380536 57.502257 -0.066231 99.79 5 -0.149298 57.602783 57.887258 -0.068898 99.51 6 -0.160772 57.960536 57.994782 -0.037516 99.94 7 -0.009275 58.261207 58.384115 -0.082337 99.79 8 -0.093395 58.524347 58.599753 -0.165132 99.87 9 -0.114019 58.863647 58.937859 -0.179805 99.871 10 -0.119440 59.107328 59.381736 -0.110706 99.54 11 -0.151464 59.489227 59.584644 -0.086769 99.84 12 -0.115166 59.744958 59.899836 -0.116371 99.74 注:法拉第杯和离子倍增器信号强度均已扣除信号噪音值。AX代表中心法拉第杯,CCD SEM代表电子倍增器,H1代表第一个法拉第杯。 -
[1] Turrin B D,Swisher C C,Dieno A L.Mass Discrimination Monitor and Intercalibration of Dual Collectors in Noble Gas Mass Spectrometer Systems[J].Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystems,2010,11:doi:10.1029/2009GC003013.
[2] Mark D F,Stuart F M,de Podesta M.New High Precision Measurement of the Isotopic Composition of Atmospheric Argon[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2011,75:7494-7501.
[3] Renne P R,Sharp W D,Dieno A L,et al.The Isotopic Composition of Atmospheric Argon and Ar/Ar Geochronology:Time for a Change?[J].Quarternary Geochronology,2009,4(4):288-298.
[4] Kim J,Jeon S.40Ar/39 Ar Age Determination Using Argus Ⅵ Multiple-collector Noble Gas Mass Spectrometer:Performance and Its Application to Geosciences[J].Journal of Analytical Science and Technology,2015,6:4-11.
[5] McDougall I,Harrison T M.Geochronology and Thermo-chronology by the 40Ar/39 Ar Method[M].Oxford:Oxford University Press,1999:89-90.
[6] Alexsander E C,Ozima M.Terrestrial Rare Gas[M].Tokyo:Center for Academic Publications,1978.
[7] Mark D F,Barfod D B,Stuart F M,et al.The Argus Multicollector Noble Gas Mass Spectrometer:Performance for Ar/Ar Geochronology[J].Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystem,2009,10(2):1-9.
[8] 李军杰,李剑,刘汉彬,等.Helix SFT惰性气体质谱仪分析矿物包裹体中氦同位素组成[J].地质学报,2015,89(10):1826-1831.
Li J J,Li J,Liu H B,et al.The Analysis of Helium Isotope of Inclusions in Minernal Using Helix SFT Noble Gas Mass Spectrometer[J].Acta Geologica Sinica,2015,89(10):1826-1831.
[9] Eiler J M,Clog M, Magyar P,et al.A High-resolution Gas-source Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometer[J].International Journal of Mass Spectrometry[J].http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijms.2012.10.014.2012.
[10] Turrin B D,Swisher C C,Deino A L.Mass Discrimination Monitoring and Intercalibration of Dual Collectors in Noble Gas Mass Spectrometer Systems[J].Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystem,2010,11.doi:10.1029/2009GC003013.
[11] Burnard P G,Farley K A.Calibration of Pressure-dependent Sensitivity and Discrimination in Nier-type Noble Gas Ion Sources[J].Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystem,2000,1:33-38.
[12] Baur H A.Noble-gas Mass Spectrometer Compressor Source with Two Orders of Magnitude Improvement in Sensitivity[J].EOS,1999,80:1118.
[13] Reynolds J H.High Sensitivity Mass Spectrometer for Noble Gas Analysis[J].Review of Scientific Instrument,1956,27(11):928-934.
[14] Ryuji O,Tomoki N,Nobuo T,et al.Noble Gases in Ureilites Released by Crushing[J].Meteoritics and Planetary Science,2003,5:767-781.
[15] Ozima M,Podosek F A.Noble Gas Geochemistry[M].Cambridge:Cambridge University Press,2002:286.
[16] Baski A K,Archibald D A,Farrar E.Intercalibration of 40Ar/39 Ar Dating Standards[J].Chemical Geology,1996,129:307-324.
[17] Rudenhauer F G.Gas Scattering as a Limit to Partial-pressure Sensitivity[J].Vacuum Science Technology,1972,9:215.
[18] Lee J Y,Marti K,Severinghaus K,et al.A Redeter-mination of the Isotopic Abundances of Atmospheric Ar[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2006,70:4507-4512.
[19] Holst B,Buckland J R,Allison W.Spatial Mapping in the Electron Impact Ion Source of a Residual Gas Analyser[J].Vacuum,1999,53:207-210.
[20] Nier A O.A Redetermination of the Relative Abundances of the Isotopes of Carbon,Nitrogen,Oxygen,Argon and Potassium[J].Physics Review,1950,77:789-793.
[21] Young E D,Galy A,Nagahara H.Kinetc and Equilibrium Mass-dependent Isotope Fractionation Laws in Nature and Their Geochemical and Cosmochemical Significance[J].Geochmica et Cosmochimica Acta,2002,66(6):1095-1104.
[22] Valkiers S,Vendelbo D,Berglund M,et al.Preparation of Argon Primary Measurement Standards for the Calibration of Ion Current Ratios Measured in Argon[J].International Journal of Mass Spectrometry,2010,291:41-47.
-



 下载:
下载: