Research Progress of Organochlorine Pesticides in Breast Milk of Biological Samples in the Last Twenty Years
-
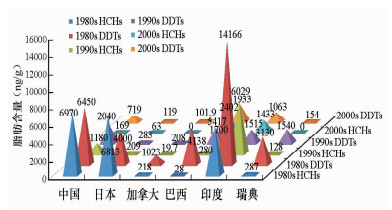
摘要: 有机氯农药(OCPs)至今是人体内残留浓度和检出率最高的有机污染物,母乳作为一种生物介质,被广泛用于人体中OCPs蓄积量、母乳中OCPs浓度的影响因素、婴幼儿母乳喂养期OCPs摄入量、人体中OCPs排泄动力学等研究领域。近二十年的研究表明:母乳中残留的OCPs主要有六氯苯(HCB)、滴滴涕(DDTs)和六六六(HCHs),浓度持续下降,总体上发展中国家高于发达国家,沿海地区高于内陆地区,热带地区高于其他地区;母乳中OCPs浓度主要受饮食习惯、年龄和分娩次数等因素的影响,在哺乳期浓度并不是持续下降,其排泄速度呈波动性变化趋势;不同国家和地区婴幼儿母乳喂养时OCPs日摄入量普遍低于WHO/FAO建议值,但在一些仍然使用OCPs的热带地区,婴幼儿OCPs日摄入量比WHO/FAO建议值高出几十倍。未来有关母乳中OCPs的研究将主要集中于:继续开展母乳中OCPs方法学研究,推进分析方法的标准化,提高评价方法和统计学方法的应用范围和可靠性;研究高暴露区和污染区OCPs对婴幼儿早期发育和未来生长健康的影响;研究OCPs在人体内的蓄积和排泄规律;结合统计学方法,开展母乳中OCPs与新生儿或成年人各种疾病相关性的统计流行病学研究。Abstract: Hitherto, organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) have been reported with the highest residue level and the highest detection rate in human beings. Breast milk is the earliest biological medium used to research OCPs in humans and provides an effective way to study the exposure pathway of OCPs for humans, factors affecting OCPs concentration in breast milk, infant breastfeeding intake of OCPs, and OCPs excretion in humans. The conclusions of research in the last 20 years are as follows. First, the concentration of OCPs in breast milk continues to show a downward trend in world. p, p'-DDE, β-HCH and HCB are dominated OCPs in breast milk. In general, the residue levels of total OCPs in breast milk of developing countries show that in coastal areas and tropical regions they are higher than in developed countries, inland areas, and other regions, respectively. Second, concentration of OCPs in breast milk is affected primarily by age, delivery times and eating habits, and will not decrease during the breastfeeding period with waved drain mode. Finally, acceptable daily intake (ADI) of OCPs for infants is usually lower than the recommended value of WHO/FAO during the breastfeeding period. For infants of tropical regions where some OCPs are still used, the ADIs are obviously higher than the values recommended by WHO/FAO. In the future, the research of OCPs in breast milk will focus on these aspects. First, research on analytical or detecting methods of OCPs in breast milk will be carried out, the standardization of analytical methods will be promoted to expand the applied range of research data and improve the reliability and evaluation of the exposure risk for OCPs of humans, especially infants living in OCPs polluted areas. Second, research about the effect of OCPs on early development and future health of those infants, the excretion and accumulation rules of dominated OCPs in the human body such as metabolite DDE, β-HCH and HCB with multiple emission source, and statistical epidemiological studies using statistical method to reveal the relationship between OCPs in breast milk and disease of adult diseases will also be carried out.
-
Key words:
- biological sample /
- breast milk /
- persistent organic pollutants /
- organochlorine pesticides /
- inflant
-

-
[1] Tsydenova O V, Agus S, Natsuk K, et al.Organohalogen Compounds in Human Breast Milk from Republic of Buryatia, Russia[J].Environmental Pollution, 2007, 146(1):225-232. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2006.04.036
[2] Rambhatla A, Mills J N.Impact of the Environment on Male Sexual Health[J].Current Sexual Health Reports, 2016, 8:1-8. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/291385900_Impact_of_the_Environment_on_Male_Sexual_Health
[3] Li Y F.Global Technical Hexachlorocyclohexane Usage and Its Contamination Consequences in Environment:From 1988 to 1997[J].Science of the Total Environment, 1999, 232(3):121-158. doi: 10.1016/S0048-9697(99)00114-X
[4] Safi J M.Certain Organochlorine and Organochlorine Contaminants in Swedish Human Milk in Perspective of Past 20-30 Years[J].Chemosphere, 2000, 40(9-11):1111-1123. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(99)00360-4
[5] Iscan M, Coban T I, Cok I, et al.The Organochlorine Pesticides Residues and Antioxidant Enzyme Activities in Human Breast Tumors:Is There Any Association?[J].Breast Cancer Research and Treatment, 2002, 72(2):173-182. doi: 10.1023/A:1014828705281
[6] Vos J G, Dybing E H A, Ladefoged O, et al.Health Effects of Endocrine-disrupting Chemicals on Wildlife, with Special Reference to European Situation[J].Critical Reviews in Toxicology, 2000, 30(1):71-133. doi: 10.1080/10408440091159176
[7] Pathak R, Ahmed R S, Tripathi A K, et al.Maternal and Cord Blood Levels of Organochlorine Pesticides:Association with Preterm Labor[J].Clinical Biochemistry, 2009, 42(7-8):746-749. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2008.11.007
[8] Galetin-Smith R, Pavkov S, Roncevic N.DDT and PCBs in Human Milk:Implication for Breast Feeding Infants[J].Bulletin Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 1990, 45(6):811-818. doi: 10.1007/BF01701076
[9] Waliszewski S M, Melo-Santiesteban G, Villalobos-Pietrini R.Breast Milk Exrection Kinetic of β-HCH, p, p'-DDE and p, p'-DDT[J].Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2009, 83(6):869-873. doi: 10.1007/s00128-009-9796-3
[10] Laug E P, Kunze F M, Prickett C S.Occurrence of DDT in Human Fat and Milk[J].Archives of Industrial Hygiene and Occupational Medicine, 1951, 3(3):245-246.
[11] Kalra R L, Chawla R P.Occurrence of DDT and BHC Residues in Human Milk in India[J].Experientia, 1981, 37(4):404-405. doi: 10.1007/BF01959888
[12] Cok I, D nmez M K, Karakaya A E.Levels and Trends of Chlorinated Pesticides in Human Breast Milk from Ankara Residents:Comparison of Concentrations in 1984 and 2002[J].Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2004, 72(3):522-529. doi: 10.1007/s00128-004-0275-6
[13] Konishi Y, Kuwabara K, Hori S.Continuous Surveillance of Organochlorine Compounds in Human Breast Milk from 1972 to 1998 in Osaka, Japan[J].Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2001, 40(4):571-578. doi: 10.1007/s002440010212
[14] Krauthacker B, Votava-Raic A, Romanic H S, et al.Persistent Organochlorine Compounds in Human Milk Collected in Croatia over Two Decades[J].Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2009, 57(3):616-622. doi: 10.1007/s00244-009-9301-3
[15] Fang J, Nyberg E, Winnber U, et al.Spatial and Temporal Treads of the Stockholm Convention POPs in Mothers's Milk-A Global Review[J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(12):8989-9041. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-4080-z
[16] Zhou P P, Wu Y N, Yin S, et al.National Survey of the Levels of Persistent Organochlorine Pesticides in the Breast Milk of Mothers in China[J].Environmental Pollution, 2011, 159(2):524-531. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2010.10.014
[17] Raab U, Preiss U, Albrecht M, et al.Concentrations of Polybrominateddiphenyl Ethers, Organochlorine Compounds and Nitro Musks in Mother's Milk from Germany (Bavaria)[J].Chemosphere, 2008, 72(1):87-94. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.01.053
[18] Kumar A, Baroth A, Soni I, et al.Organochlorine Pesticide Residues in Milk and Blood of Women from Annpgarh, Rajasthan, India[J].Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2006, 116(1-3):1-7. doi: 10.1007/s10661-006-7463-2
[19] Kunisue T, Someya M, Monirith I, et al.Occurrence of PCBs, Organochlorine Insecticides, Tris(4-Chlorophenyl)Methane, and Tris(4-Chlorophenyl)Methanol in Human Breast Milk Collected from Cambodia[J].Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2004, 46(3):405-412. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15195813
[20] Fujii Y, Ito Y, Harada K H, et al.Comparative Survey of Levels of Chlorinated Cyclodiene Pesticides in Breast Milk from Some Cities of China, Korea and Japan[J].Chemosphere, 2012, 89(4):452-457. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.05.098
[21] Rodas-Ortíz J P, Ceja-Moreno V, González-Navarrete R L, et al.Organochlorine Pesticides and Polychlorinated Biphenyls Levels in Human Milk from Chelem, Yucatńn, México[J].Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2008, 80(3):255-259. doi: 10.1007/s00128-007-9356-7
[22] Okonkwo J O, Mutshatshi T N, Ben B, et al.DDT, DDE and DDD in Human Milk from South Africa[J].Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2008, 81(4):348-354. doi: 10.1007/s00128-008-9495-5
[23] Davies D, Mes J.Comparison of the Residue Levels of Some Organochlorine Compounds in Breast Milk of the General and Indigenous Canadian Populations[J].Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 1987, 39(5):743-749. doi: 10.1007/BF01855849
[24] Craan A G, Haines D A.Twenty-five Years of Surve-illance for Contaminants in Human Breast Milk[J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 1998, 35(35):702-710.
[25] Jarrell J, Chan S, Hauser R, et al.Longitudinal Assess-ment of PCBs and Chlorinated Pesticides in Pregnant Women from Western Canada[J].Environmental Health:A Global Access Science Source, 2005, 4(10):1-8. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/7815079_Longitudinal_assessment_of_PCBs_and_chlorinated_pesticides_in_pregnant_women_from_Western_Canada
[26] Yu H F, Zhao X D, Zhao J H, et al.Continuous Surveillance of Organochlorine Pesticides in Human Milk from 1983 to 1998 in Beijing, China[J].International Journal of Environmental Health Research, 2006, 16(1):21-26. doi: 10.1080/09603120500397615
[27] Yao Z, Zhang Y, Jiang G.Residues of Organochlorine Compounds in Human Breast Milk Collected from Beijing, People's Republic of China[J].Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2005, 74(1):155-161. doi: 10.1007/s00128-004-0562-2
[28] Matuo Y K, Lopes J N C, Casanova I C, et al.Organochlorine Pesticides Residues in Human Milk in the Ribeirão Preto Region, State of São Paulo, Brazil[J].Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 1992, 22(2):167-175. doi: 10.1007/BF00213281
[29] Paumgartten F J R, Cruz C M, Chahoud I, et al.PCDDs, PCDFs, PCB and Other Organochlorine Compounds in Human Milk from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil[J].Environmental Research, 2000, 83(3):293-297. doi: 10.1006/enrs.2000.4062
[30] Barra R, Colombo J C, Eguren G, et al.Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) in Eastern and Western South American Countries[J].Review of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2006, 185:1-33. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/223716690_Persistent_Organic_Pollutants_(POPs)_in_Eastern_and_Western_South_American_Countries
[31] Tanabe S, Gondaira F, Subramanian A, et al.Specific Pattern of Persistent Organochlorine Residues in Human Breast Milk from South India[J].Journal of Agricultural Food and Chemistry, 1990, 38(3):899-903. doi: 10.1021/jf00093a066
[32] Devanathan G, Subramanian A, Someya M, et al.Persistent Organochlorines in Human Breast Milk from Major Metropolitan Cities in India[J].Environmental Pollution, 2009, 157(1):148-154. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2008.07.011
[33] Martins J G, Chávez A A, Waliszewski S M, et al.Extraction and Clean-up Methods for Orgnocholorine Pesticides Determination in Milk[J].Chemosphere, 2013, 92:233-246. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.04.008
[34] Poon B H T, Leung C K M, Wong C K C, et al.Polychlorinated Biphenyls and Organochlorine Pesticides in Human Adipose Tissue and Breast Milk Collected in Hong Kong[J].Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2005, 49(2):274-282. doi: 10.1007/s00244-004-0111-3
[35] Zhao G F, Xu Y, Li W, et al.PCBs and OCPs in Human Milk and Selected Foods from Luqiao and Pingqiao in Zhejiang, China[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2007, 378(3):281-292. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.03.008
[36] Manaca M N, Grimalt J O, Sunyer J, et al.Concentration of DDT Compounds in Breast Milk from African Women (Manhi, Mozambique) at the Early Stages of Domestic Indoor Spraying with This Insecticide[J].Chemosphere, 2011, 85(3):307-314. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.06.015
[37] Kunisue T, Someya M, Kayama F, et al.Persistent Organochlorines in Human Breast Milk Collected from Primiparae in Dalian and Shenyang, China[J].Environmental Pollution, 2004, 131(3):381-392. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2004.03.008
[38] Sun S J, Zhao J H, Koga M, et al.Persistent Organic Pollutants in Human Milk in Women from Urban and Rural Areas in Northern China[J].Environmental Research, 2005, 99(3):285-293. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2005.05.007
[39] Leng J H, Kayama F, Wang P Y, et al.Levels of Persistent Organic Pollutants in Human Milk in Two Chinese Coastal Cities, Tianjin and Yantai:Influence of Fish Consumption[J].Chemosphere, 2009, 75(5):634-639. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.01.008
[40] 史蓉婕, 仲岳桐, 雷毅雄, 等.深圳市母乳中六六六和滴滴涕蓄积水平与影响因素分析[J].卫生研究, 2013, 42(2):205-210. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/236662328_Accumulative_levels_of_organochlorine_pesticides_of_HCHs_DDTs_in_breast_milk_and_risk_factors_analysis_in_Shenzhen
Shi R J, Zhong Y T, Lei Y X, et al.Accumulative Levels of Organochlorine Pesticides of HCHs, DDTs in Breast Milk and Risk Factors Analysis in Shenzhen[J].Journal of Hygiene Research, 2013, 42(2):205-210. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/236662328_Accumulative_levels_of_organochlorine_pesticides_of_HCHs_DDTs_in_breast_milk_and_risk_factors_analysis_in_Shenzhen
[41] Polder A, Skaare J U, Skjerve E, et al.Levels of Chlorinated Pesticides and Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Norwegian Breast Milk (2002-2006), and Factors that May Predict the Level of Contamination[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2009, 407(16):4584-4590. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.04.032
[42] Mishra K, Sharma R C.Assessment of Organochlorine Pesticides in Human Milk and Risk Exposure to Infants from North-East India[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2011, 409(23):4939-4949. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.07.038
[43] Tue N M, Sudaryanto A, Tu M B, et al.Kinetic Differences of Legacy Organochlorine Pesticides and Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Vietnamese Human Breast Milk[J].Chemosphere, 2010, 81(8):1006-1011. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.09.013
[44] LaKind J S, Berlin C M J, Sj din A, et al.Do Human Milk Concentrations of Persistent Organic Chemicals Really Decline during Lactation? Chemical Concentrations during Lactation and Milk/Serum Partitioning[J].Environmental Health Perspectives, 2009, 117(10):1625-1631. doi: 10.1289/ehp.0900876
[45] Harris C A, Woolridge M W, Hay A W M.Factors Affecting the Transfer of Organochloine Pesticides Residues to Breast Milk[J].Chemosphere, 2001, 43(2):243-256. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(00)00149-1
[46] Bates M N, Hannah D J, Buckland S J, et al.Chlorinated Organic Contaminants in Breast Milk of New Zealand Women[J].Environmental Health and Perspectives, 1994, 102(1):211-217. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/15010976_Chlorinated_organic_contaminants_in_breast_milk_of_New_Zealand_women
[47] Song S L, Ma J, Tian Q, et al.Hexachlorobenzene in Breast Milk from Beijing, China[J].Chemosphere, 2013, 91(2):145-149. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.12.019
[48] Ruuska T.Occurrence of Acute Diarrhoea in Atopic and Nonatopic Infants:The Role of Prolonged Breast-feeding[J].Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition, 1992, 14(1):27-33. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199201000-00006
[49] EggesbØ M, Stigum H, Longnecker M P, et al.Levels of Hexachlorobenzene (HCB) in Breast Milk in Relation to Birth Weight in a Norwegian Cohort[J].Environmental Research, 2009, 109(5):559-566. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2009.04.001
[50] WHO.Fourth WHO-Coordinated Survey of Human Milk for Persistent Organic Pollutants-A Protocol for Collection, Handling and Analysis of Samples at the Country Level[S].2005.
[51] Fujii Y, Haraguchi K, Harada K H, et al.Detection of Dicofol and Related Pesticides in Human Breast Milk from China, Korea and Japan[J].Chemosphere, 2011, 82(1):25-31. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.10.036
[52] Tian L, Li J, Xu Y.et al.Organochlorine Pesticides in Seawater and the Surrounding Atmosphere of the Marginal Seas of China:Spatial Distribution, Sources and Air-Water Exchange[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2012, 435-436(7):244-252. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22858532
[53] Hardell L, van Bavel B, Lindstr m G, et al.Increased Concentrations of Polychlorinated Biphenyls, Hexachloro-benzene and Chlordanes in Mothers of Men with Testicular Cancer[J].Environmental Health Perspectives, 2003, 111(7):930-934. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/7101334_Increased_Concentrations_of_Polychlorinated_Biphenyls_Hexachlorobenzene_and_Chlordanes_in_Mothers_of_Men_with_Testicular_Cancer
[54] Siddiqui M K J, Srivastava S, Srivastava S P, et al.Persistent Chlorinated Pesticides and Intrauterine Foetal Growth Retardation:A Possible Association[J].International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health, 2003, 76(1):75-80. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12592586
[55] Fenster L, Eskenazi B, Anderson M, et al.Association of in Utero Organochlorine Pesticide Exposure and Fetal Growth and Length of Gestation in an Agricultural Population[J].Environmental Health and Perspect, 2006, 114(5):597-602. http://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/31162/Share
[56] ATSDR.Addendum to the DDT/DDD/DDE Toxicologi-cal Profile[R].Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry.Division of Toxicology and Environmental Medicine, 2008.
-



 下载:
下载: