Research on the Sedimentary and Paleoclimate Environment of the Xiaoheba Formation in Southeastern Sichuan Based on the Trace Elements Ratio Method
-
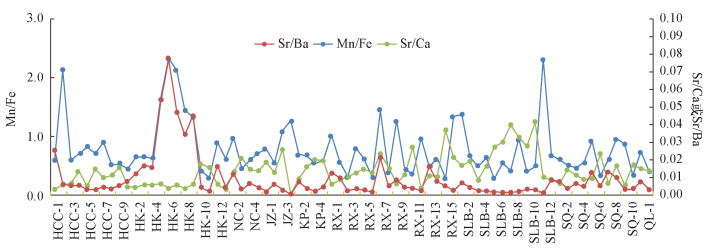
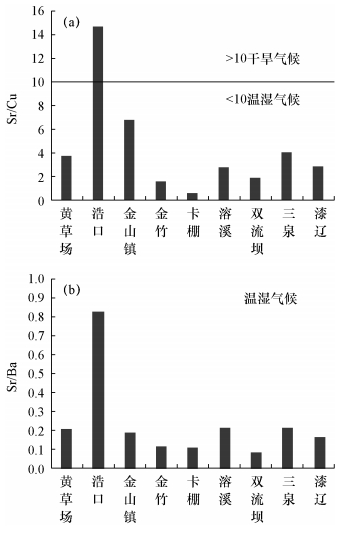
摘要: 川东南地区下志留统小河坝组砂岩具有较好的生储盖组合条件,油气地质条件优越,但对其沉积环境为陆相还是海相沉积三角洲的厘定尚不明确。本文针对川东南地区小河坝组亟需解决的沉积环境问题,系统采集了该地区9条典型剖面的74个样品,通过微量元素比值分析方法分析其元素组成,并结合沉积构造特征分析其沉积环境及古气候环境。利用X射线荧光光谱法测试了能判别海陆相沉积环境的Sr、Ba、Mn、Cu等微量元素。结果显示,Sr/Ba平均值为0.2790,最大值为2.31,Mn/Fe值为0.0093~0.0778,Sr/Ca值为0.0005~0.0414,表现为三角洲淡水沉积特征;Sr/Ba平均值小于1,Sr/Cu平均值为4.8758,8.1%样品的Sr/Cu值大于10,总体上反映了小河坝组沉积环境为温润潮湿的古气候环境。Abstract: Lower Silurian sandstone of the Xiaoheba formation in Southeastern Sichuan has a good reservoir seal combination, and an oil and gas geological condition, but the hypothesis that the sedimentary environment belongs to continental or marine sedimentary deltas remains a matter of debate. In order to solve this problem, 74 samples were collected from 9 typical sections. The elemental composition was determined by the trace element ratio method. Combined with the tectonic background and source characteristics, the sedimentary and paleoclimatic environment were discussed. X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry (XRF) was used to analyze Ba, Mn, Sr, Cu and other trace elements, which are useful in discriminating between the sea and land facies sedimentary environment. The results show that the average Sr/Ba value is 0.2790 with the maximum of 2.31, the Mn/Fe value is 0.0093 to 0.0778, and the Sr/Ca value is 0.0005 to 0.0414, typical of freshwater delta sedimentary characteristics. The average Sr/Ba is less than 1, the average Sr/Cu is 4.8758, and more than 8.1% samples have Sr/Cu values greater than 10, reflecting the warm, moist, ancient climate environment.
-

-
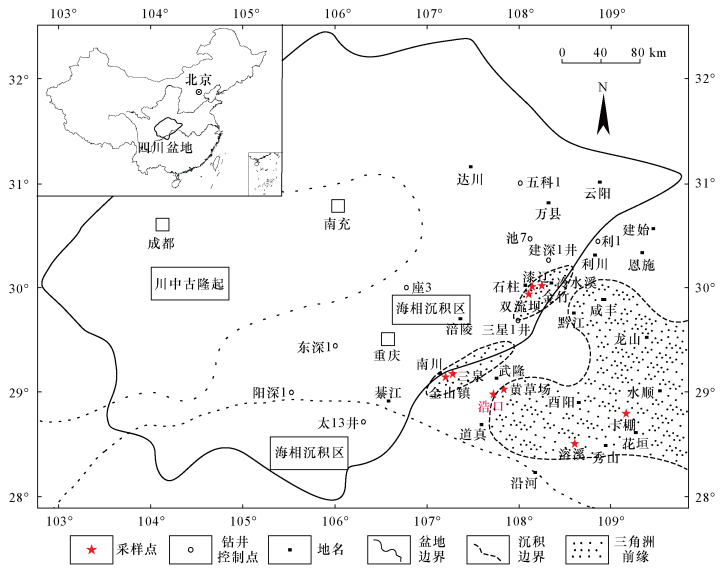
图 1 采样点分布位置特征图(据朱志军等[1]改编)
Figure 1.
表 1 元素XRF分析测试条件
Table 1. Analytical conditions of the elements by XRF
元素 晶体 检测器 测量角度
(°)测量时间
(s)电压
(kV)电流
(mA)脉冲高度调节 分析上限 分析下限 Ti-U LiF SC 10~90 240 40 95 25 75 K, Ca, Sn-Cs LiF FPC 90~140 150 40 95 25 75 Cl Ge FPC 90~96 18 40 95 25 75 S Ge FPC 108~114 18 40 95 25 75 P Ge FPC 138~144 18 40 95 25 75 Si PET FPC 106~112 18 40 95 25 75 Al PET FPC 142~148 18 40 95 25 75 Mg TAP FPC 42~48 18 40 95 25 75 Na TAP FPC 52~58 18 40 95 25 75 表 2 XRF法与化学分析法结果比较
Table 2. Comparison of analytical results between XRF and chemical methods
样品 分析方法 SiO2
(%)Al2O3
(%)Fe2O3
(%)CaO
(%)MnO
(%)BaO
(%)SrO
(%)HCC-S1X-2 压片法 78.20 13.30 3.04 3.15 0.19 0.07 0.02 化学法 78.15 13.20 3.02 3.12 0.17 0.07 0.02 HK-S1X-4 压片法 61.8023 16.5877 4.8052 7.4275 0.0950 0.0706 0.0383 化学法 61.7044 16.5426 4.7512 7.4177 0.0807 0.0655 0.0267 JZ-S1X-03 压片法 70.2663 17.1618 4.0065 0.3753 0.0947 0.0802 0.0059 化学法 70.2431 17.1446 4.0089 0.3917 0.0917 0.0601 0.0031 KP-S1X-3 压片法 72.0475 18.7829 4.7761 0.3927 0.0959 0.0426 0.0053 化学法 72.0876 18.7347 4.7226 0.3911 0.0853 0.0436 0.0051 SLB-S1X-9 压片法 71.6791 16.2985 3.6895 0.2511 0.0311 0.0976 0.0058 化学法 71.6603 16.2687 3.6367 0.2412 0.0304 0.0964 0.0053 注:HCC代表重庆武隆黄草场,HK代表重庆武隆浩口,JZ代表重庆石柱金竹,KP代表湖南花垣卡棚,SLB代表石柱双流坝。 表 3 不同采样点元素比值平均值数据
Table 3. Data of average trace element ratios for different sampling point
采样地点 Mn/Fe Sr/Ba Sr/Ca Sr/Cu 黄草场 0.027806 0.211277 0.00959 3.726602 浩口 0.035684 0.82998 0.00722 14.69682 金山镇 0.022522 0.187635 0.013203 6.761095 金竹 0.027013 0.118283 0.019193 1.542298 卡棚 0.025147 0.109539 0.013158 0.57519 溶溪 0.022036 0.216467 0.014179 2.711468 双流坝 0.027497 0.083117 0.024333 1.852628 三泉 0.020757 0.215158 0.011712 4.01708 漆辽 0.01907 0.167818 0.014374 2.81459 -
[1] 朱志军, 陈洪德.川东南地区早志留世晚期沉积特征及沉积模式分析[J].中国地质, 2012, 39(1):64-76. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201201008.htm
Zhu Z J, Chen H D.An analysis of sedimentary characteristics and model of Silurian Xiaoheba Formation in southeastern Sichuan Province[J].Geology in China, 2012, 39(1):64-76. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201201008.htm
[2] 王国茹, 陈洪德, 朱志军, 等.川东南-湘西地区志留系小河坝组砂岩稀土元素特征及其地质意义[J].成都理工大学学报, 2011, 38(1):7-14. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201005017.htm
Wang G R, Chen H D, Zhu Z J, et al.The characteristics and geological implications of rare earth elements in sandstone of lower Silurian Xiaoheba Formation in the southeastern Sichuan-western Hunan[J].Journal of Chengdu University of Technology, 2011, 38(1):7-14. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201005017.htm
[3] 张欣平, 张纯臣, 王大任.湘西北地区志留系泥盆系的痕迹化石[J].湖南地质, 1986, 5(2):49-61. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNDZ198602005.htm
Zhang X P, Zhang C C, Wang D R.The trace fossils of Silurian and Devonian systems of the northwest region, Hunan Province[J].Hunan Geology, 1986, 5(2):49-61. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNDZ198602005.htm
[4] 王正和, 谭钦银, 何利, 等.川东南-黔北志留系石牛栏组沉积与层序地层[J].石油与天然气地质, 2013, 34(4):499-507. doi: 10.11743/ogg20130411
Wang Z H, Tan Q Y, He L, et al.Deposition and sequence stratigraphy of the Silurian Shiniulan Formation in southeastern Sichuan-northern Guizhou Province[J].Oil & Gas Geology, 2013, 34(4):499-507. doi: 10.11743/ogg20130411
[5] 杨明太, 唐慧.能量色散X射线荧光光谱仪现状及其发展趋势[J].核电子学与探测技术, 2011, 31(12):1307-1311. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0934.2011.12.001
Yang M T, Tang H.The actualities and trend of energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometry[J].Nuclear Electronics & Detection Technology, 2011, 31(12):1307-1311. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0934.2011.12.001
[6] 杨明太.放射性核素迁移研究的现状[J].核电子学与探测技术, 2006, 26(6):1025-1028. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGAN200411001023.htm
Yang M T.Recent developments in studies for migration of radionuclides[J].Nuclear Electronics & Detection Technology, 2006, 26(6):1025-1028. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGAN200411001023.htm
[7] 吉昂.X射线荧光光谱三十年[J].岩矿测试, 2012, 31(3):383-398. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/ykcs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20120302&flag=1
Ji A.Development of X-ray fluorescence spectrometry in the 30 years[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2012, 31(3):383-398. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/ykcs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20120302&flag=1
[8] Andrew T, Montserrat F.Field-portable-XRF reveals the ubiquity of antimony in plastic consumer products[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 584-585:982-989. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.01.149
[9] 孔芹, 陈磊, 汪灵.非金属矿二级标样配制及其粉末样品的XRF分析方法[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2012, 32(5):1405-1409. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201205067.htm
Kong Q, Chen L, Wang L.Preparation of sub-standard samples and XRF analytical method of powder non-metallic minerals[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2012, 32(5):1405-1409. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201205067.htm
[10] 高拉凡, 王长城, 杨海欧, 等.XRF法四川盆地须家河组沉积相研究中的应用[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2016, 36(6):1904-1909. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201606059.htm
Gao L F, Wang C C, Yang H O, et al.Application of X-ray fluorescence spectrometry in Xujiahe Formation of Sichuan basin for the study of sedimentary facies[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2016, 36(6):1904-1909. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201606059.htm
[11] 王国平, 刘景双, 翟正丽.沼泽沉积剖面特征元素比值及其环境意义——盐碱化指标及气候干湿变化[J].地理科学, 2005, 25(3):335-339. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX200503013.htm
Wang G P, Liu J S, Zhai Z L.Ratio of elements and their implications within typical sedimentation profile in the marsh-Slinization indicators and climatic change between the arid and the humid[J].Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2005, 25(3):335-339. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX200503013.htm
[12] 熊小辉, 肖加飞.沉积环境的地球化学示踪[J].地球与环境, 2011, 39(3):405-414. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201103021.htm
Xiong X H, Xiao J F.Geochemical indicators of sedimentary environments-A summary[J].Earth and Environment, 2011, 39(3):405-414. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201103021.htm
[13] 金艳, 傅强.东海盆地某油气田井层沉积体系研究[J].海洋石油, 2013(4):19-23. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYSY201304007.htm
Jin Y, Fu Q.Study on sedimentary system of formation in Well A in and gas field of East China Sea[J].Offshore Oil, 2013(4):19-23. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYSY201304007.htm
[14] 朱志军, 陈洪德, 林良彪, 等.黔北-川东南志留系层序格架下的沉积体系演化特征及有利区带预测[J].地质科技情报, 2010, 29(2):24-32. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201002006.htm
Zhu Z J, Chen H D, Lin L B, et al.Depositional system evolution characteristics in the frame work of sequences of Silurian and prediction of favorable zones in the Northern Gui Zhou-Southeastern Sichuan[J].Geological Science and Technology Information, 2010, 29(2):24-32. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201002006.htm
[15] 刘刚, 周东升.微量元素分析在判别沉积环境中的应用——以江汉盆地潜江组为例[J].石油实验地质, 2007, 29(3):307-314. doi: 10.11781/sysydz200703307
Liu G, Zhou D S.Application of microelements analysis in identifying sedimentary environment-Taking Qianjiang Formation in the Jianghan basin as an example[J].Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2007, 29(3):307-314. doi: 10.11781/sysydz200703307
[16] 钱利军, 陈洪德, 林良彪, 等.四川盆地西缘地区中侏罗统沙溪庙组地球化学特征及其环境意义[J].沉积学报, 2012, 30(6):1061-1071. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201206007.htm
Qian L J, Chen H D, Lin L B, et al.Geochemical characteristics and environmental implications of middle Jurassic Shaximiao Formation, western margin of Sichuan basin[J].Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2012, 30(6):1061-1071. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201206007.htm
[17] 宋明水.东营凹陷南斜坡沙四段沉积环境的地球化学特征[J].矿物岩石, 2005, 25(1):67-73. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS200501013.htm
Song M S.Sedimentary environment geochemistry in the Shasi section of Southern Ramp, Dongying depression[J].Journal of Mineral Petrology, 2005, 25(1):67-73. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS200501013.htm
[18] 邓平.微量元素在油气勘探中的应用[J].石油勘探与开发, 1993, 20(1):27-32. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201105020.htm
Deng P.The application of trace amount of elements in the exploration of oil and gas[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1993, 20(1):27-32. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201105020.htm
[19] 孙顺才.长江三角洲全新世沉积特征[J].海洋学报, 1981, 3(1):97-113. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ198704008.htm
Sun S C.Deltaic sediments of the Changjiang Delta and its characteristics[J].Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1981, 3(1):97-113. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ198704008.htm
[20] 马光祖, 梁国立.地质样品的X射线荧光光谱分析[J].岩矿测试, 1992, 11(1-2):37-43. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/ykcs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19920105&flag=1
Ma G Z, Liang G L.X-ray fluorescence spectrometric analysis of geological samples[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 1992, 11(1-2):37-43. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/ykcs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=19920105&flag=1
[21] 王随继, 黄杏珍, 妥进才, 等.泌阳凹陷核桃园组微量元素演化特征及其古气候意义[J].沉积学报, 1997, 15(1):65-70. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB701.011.htm
Wang S J, Huang X Z, Tuo J C, et al.Evolutional characteristics and their paleoclimate significance of trace elements in the Hetaoyuan Formation, Biyang depression[J].Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1997, 15(1):65-70. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB701.011.htm
[22] 安凤桐, 高善明, 李元芳.用微量元素分析法研究滦河三角洲沉积环境[J].海洋湖沼通报, 1982(2):24-31. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYFB198202004.htm
An F T, Gao S M, Li Y F.A research on depositional environment of delta by analyzed method of trace elements in Luanher River[J].Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 1982(2):24-31. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYFB198202004.htm
-



 下载:
下载: