Application of X-ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy in Identification and Classification of Marble
-
摘要: 大理岩的鉴定与分类主要依靠岩石薄片鉴定及X射线衍射(XRD)矿物半定量检测技术。工作中发现,岩石薄片鉴定技术及XRD矿物半定量检测技术所测得矿物组分含量很少一致,这就需要引入其他技术对岩石薄片鉴定及XRD矿物半定量检测结果加以验证。本文利用X射线荧光光谱仪(XRF)对野外采集的32件大理岩样品进行全岩化学成分分析,以岩石化学成分为基础,分析岩石杂质系数、镁质系数和钙质系数特征,对大理岩进行分类。结果表明:方解石大理岩、白云石大理岩、菱镁矿大理岩的镁质系数值分别为0.01~0.13、0.40~0.46、0.97~0.98,钙质系数值分别为0.78~0.84、0.30~0.49和0.01~0.02,不同类型大理岩的钙质系数和镁质系数明显不同,可以作为划分大理岩类型的主要依据。当岩石中SiO2+Al2O3含量大于35%(杂质系数大于为1.20),不能定为大理岩,只有岩石中SiO2+Al2O3含量小于30%(杂质系数小于1.00)时,可定为大理岩。杂质系数、镁质系数和钙质系数的应用,能够校正岩石薄片鉴定法及XRD矿物半定量法矿物含量检测不一致的问题,使大理岩分类定名更加准确。Abstract: The identification and classification of marble depended mainly on the identification of rock slices and the semi-quantitative detection of minerals by X-ray Diffraction (XRD). It was found that the results of identification of rock slices were not always consistent with those of the semi-quantitative detection by XRD. Therefore, it is necessary to introduce other techniques to verify the results of thin section observation and XRD semi-quantitative analysis. 32 marble samples were analyzed by X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometer, the results and finding of which are reported in this paper. Based on the chemical composition of rock, rock impurity, magnesite, and calcareous coefficients are used to classify the marble. The results show that magnesite coefficients of calcite marble, dolomite marble, and magnesite marble are 0.01-0.13, 0.40-0.46 and 0.97-0.98, respectively. Calcareous coefficients are 0.78-0.84, 0.30-0.49 and 0.01-0.02, respectively. Different types of marble have various magnesia and calcareous coefficients, which can be used as the main basis for the division of marble types. Only the contents of SiO2+Al2O3 in rocks are less than 30% (impurity coefficient less than 1.00), then can be classified as marbles. The establishment and application of impurity, magnesia and calcareous coefficients in marble can be used to correct the inconsistent results between thin section observation and X-ray Powder Diffraction mineral semi-quantitative analysis, making marble classification more accurate.
-

-
表 1 X射线荧光光谱仪分析大理岩化学成分含量
Table 1. Analytical results of chemical components in marble samples by XRF
样品编号 含量(%) Na2O MgO Al2O3 SiO2 P2O5 K2O CaO TiO2 MnO TFe2O3 b26 0.10 1.34 0.71 6.71 0.023 <0.05 47.19 0.028 <0.005 0.20 b27 0.06 2.85 0.38 6.67 0.024 <0.05 45.55 0.023 <0.005 0.22 b28 0.06 1.19 0.28 4.99 0.021 <0.05 48.97 0.021 <0.005 0.14 b31 0.09 0.61 0.62 5.32 0.017 <0.05 48.82 0.030 <0.005 0.12 b32 0.05 3.67 0.74 7.87 0.029 <0.05 44.57 0.038 0.010 0.50 b33 <0.01 19.74 0.53 9.27 0.027 0.16 26.04 0.048 0.012 0.63 b34 0.03 18.91 1.55 9.77 0.030 0.80 25.35 0.079 0.015 0.71 b35 0.01 18.87 0.95 9.06 0.031 0.46 25.65 0.064 0.013 0.69 b40 <0.01 19.83 2.34 14.88 0.037 0.97 23.42 0.110 0.034 1.23 b43 1.48 8.90 6.16 33.64 0.063 0.86 22.19 0.280 0.008 1.34 b45 0.06 3.17 0.77 8.65 0.038 0.35 44.96 0.041 0.006 0.43 b46 0.01 18.93 0.47 8.88 0.025 0.34 26.54 0.042 0.023 0.61 b47 0.01 18.93 0.64 7.97 0.021 0.55 26.70 0.053 0.013 0.59 P77 <0.01 33.18 0.49 19.63 0.053 <0.05 0.74 0.080 <0.005 0.92 P79 <0.01 35.15 1.63 14.37 0.150 <0.05 0.97 0.170 <0.005 0.65 P80 <0.01 33.08 2.03 18.60 0.190 0.05 0.99 0.210 <0.005 0.90 P94 <0.01 18.47 1.29 10.31 0.061 0.32 24.74 0.070 <0.005 1.10 P95 0.65 7.50 7.20 45.43 0.094 1.81 15.13 0.340 <0.005 2.86 P96 0.47 4.88 3.49 26.29 0.085 0.68 32.36 0.180 <0.005 1.20 P139 0.15 3.72 1.10 9.03 0.068 0.34 43.53 0.046 <0.005 0.30 P140 0.27 2.45 2.97 21.25 0.140 1.48 37.12 0.130 <0.005 1.07 P141 <0.01 5.30 4.72 32.90 0.120 1.54 25.54 0.170 <0.005 1.69 P142 <0.01 5.33 1.28 10.73 0.084 0.49 40.91 0.058 <0.005 0.41 P144 <0.01 5.51 2.85 16.34 0.045 1.07 36.23 0.100 <0.005 0.85 P152 <0.01 5.72 14.47 49.80 0.120 4.71 7.45 0.590 <0.005 0.63 P153 <0.01 9.13 9.77 42.17 0.057 3.54 12.15 0.390 <0.005 0.99 P154 <0.01 14.36 3.85 26.48 0.057 2.27 19.10 0.160 <0.005 1.39 P155 <0.01 15.17 3.29 17.70 0.034 1.04 22.50 0.140 <0.005 1.16 P156 <0.01 17.27 3.79 20.68 0.045 0.53 20.19 0.160 <0.005 1.15 P196 <0.01 19.64 0.79 11.71 0.023 <0.05 24.06 0.045 <0.005 0.49 P197 <0.01 19.71 1.08 11.61 0.016 <0.05 24.75 0.047 <0.005 0.79 P198 <0.01 19.93 0.84 9.40 0.021 <0.05 24.85 0.043 <0.005 0.71 注:检测单位为沈阳地质调查中心实验室。 表 2 大理岩32件岩石薄片定名与X射线粉晶衍射分析定名对比
Table 2. A comparison of 32 marble named by slice identification and X-ray powder diffraction analysis
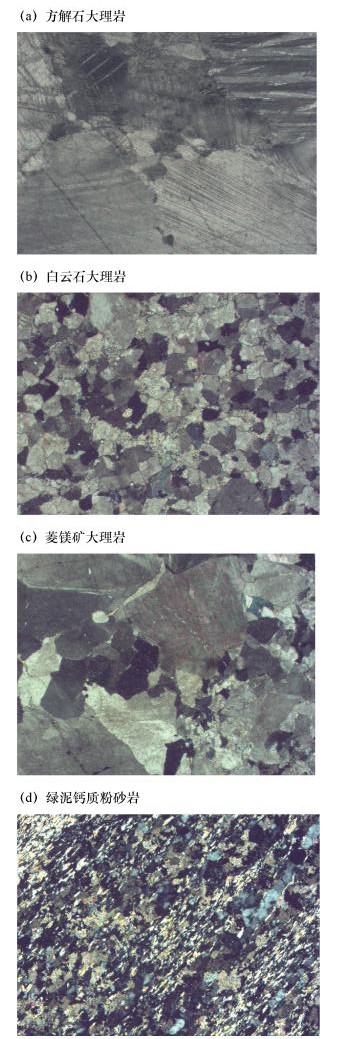
样品编号 岩石薄片定名 岩石薄片+XRD定名 b26 大理岩 大理岩 b27 大理岩 含白云石大理岩 b28 大理岩 大理岩 b31 大理岩 大理岩 b32 大理岩 含绿泥石大理岩 b33 白云石大理岩 白云石大理岩 b34 白云石大理岩 含云白云石大理岩 b35 白云石大理岩 含云白云石大理岩 b40 含云母白云石大理岩 方解滑云白云石大理岩 b43 长英质大理岩 钙质粉砂岩 b45 大理岩 大理岩 b46 白云石大理岩 滑石白云石大理岩 b47 白云石大理岩 云滑方解白云石大理岩 P77 菱镁矿大理岩 滑石菱镁矿大理岩 P79 白云石大理岩 菱镁矿大理岩 P80 白云石大理岩 绿泥滑石菱镁大理岩 P94 含石英白云石大理岩 含石英白云石大理岩 P95 云英质白云石大理岩 钙质粉砂岩 P96 云英质大理岩 粉砂质方解石大理岩 P139 含石英大理岩 含白云石云母大理岩 P140 硅砂泥质大理岩 含云母白云石粉砂大理岩 P141 石英大理岩 钙质粉砂岩 P142 大理岩 含石英白云石质大理岩 P144 含石英大理岩 云英白云石质大理岩 P152 云英质白云石大理岩 绿泥钙质粉砂岩 P153 云英质白云石大理岩 绿泥钙质粉砂岩 P154 云英质白云石大理岩 云母长英质白云石大理岩 P155 云英质白云石大理岩 云英白云石大理岩 P156 绿泥石英白云石大理岩 绿泥云英白云石大理岩 P196 石英白云石大理岩 含滑石石英白云石大理岩 P197 含绿泥石英白云石大理岩 含石英白云石大理岩 P198 含石英白云石大理岩 含石英白云石大理岩 表 3 大理岩化学成分指数特征
Table 3. Index characteristics of chemical compositions in marble
样品编号 CaO+MgO SiO2+Al2O3 SiO2+Al2O3+CaO+MgO 杂质系数 镁质系数 钙质系数 b26 48.53 7.42 55.95 0.15 0.03 0.84 b27 48.40 7.05 55.45 0.15 0.06 0.82 b28 50.16 5.27 55.43 0.11 0.02 0.88 b31 49.43 5.94 55.37 0.12 0.01 0.88 b32 48.24 8.61 56.85 0.18 0.08 0.78 b33 45.78 9.80 55.58 0.21 0.43 0.47 b34 44.26 11.32 55.58 0.26 0.43 0.46 b35 44.52 10.01 54.53 0.22 0.42 0.47 b40 43.25 17.22 60.47 0.40 0.46 0.39 b43 31.09 39.80 70.89 1.28 0.29 0.31 b45 48.13 9.42 57.55 0.20 0.07 0.78 b46 45.47 9.35 54.82 0.21 0.42 0.48 b47 45.63 8.61 54.24 0.19 0.41 0.49 P77 33.92 20.12 54.04 0.59 0.98 0.01 P79 36.12 16.00 52.12 0.44 0.97 0.02 P80 34.07 20.63 54.70 0.61 0.97 0.02 P94 43.21 11.60 54.81 0.27 0.43 0.45 P95 22.63 52.63 75.26 2.33 0.33 0.20 P96 37.24 29.78 67.02 0.80 0.13 0.48 P139 47.25 10.13 57.38 0.21 0.08 0.76 P140 39.57 24.22 63.79 0.61 0.06 0.58 P141 30.84 37.62 68.46 1.22 0.17 0.37 P142 46.24 12.01 58.25 0.26 0.12 0.70 P144 41.74 19.19 60.93 0.46 0.13 0.59 P152 13.17 64.27 77.44 4.88 0.43 0.10 P153 21.28 51.94 73.22 2.44 0.43 0.17 P154 33.46 30.33 63.79 0.91 0.43 0.30 P155 37.67 20.99 58.66 0.56 0.40 0.38 P156 37.46 24.47 61.93 0.65 0.46 0.33 P196 43.70 12.50 56.20 0.29 0.45 0.43 P197 44.46 12.69 57.15 0.29 0.44 0.43 P198 44.78 10.24 55.02 0.23 0.45 0.45 -
[1] 汤艳, 张云鹏, 齐先茂, 等.很低级变质作用研究及其在沉积盆地中的应用[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2015, 34(3):353-364. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/YSKW201503008.htm
Tang Y, Zhang Y P, Qi X M, et al.A study of the very low-grade metamorphism and its application to the sedimentary basin[J].Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2015, 34(3):353-364. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/YSKW201503008.htm
[2] 刘昌伟, 胡煜昭, 任涛, 等.塔里木盆地西缘阿克苏群变质岩岩相学特征与原岩恢复[J].矿物学报, 2017, 37(5):617-624. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=kwxb201705012&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
Liu C W, Hu Y Z, Ren T, et al.Study on the petrographic features and protoliths reconstruction of Akesu group metamorphic rocks from the Northwestern Margin of Tarim Basin, the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China[J].Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2017, 37(5):617-624. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=kwxb201705012&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[3] 和志鹏, 刘继顺, 康亚龙.新疆塔什库尔干岩群变质岩原岩及产出构造环境研究[J].矿物学报, 2017, 37(3):314-320. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=kwxb201703008&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
He Z P, Liu J S, Tang Y L.Research on protolith and tectonic setting of tashenkuergan group metamorphic rocks in Tatulugou area, Xinjiang Autonomous Region, China[J].Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2017, 37(3):314-320. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=kwxb201703008&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[4] 唐梦奇, 罗明贵, 韦彦强, 等.铜冶炼炉渣的X射线衍射Rietveld全谱图拟合物相定量分析[J].冶金分析, 2016, 36(11):11-16. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=yjfx201611002&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
Tang M Q, Luo M G, Wei Y Q, et al.Quantitative analysis of phases in copper smelting slag by Rietveld full spectrum fitting of X-ray diffraction[J].Metallurgical Analysis, 2016, 36(11):11-16. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=yjfx201611002&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[5] 严俊, 刘晓波, 王巨安, 等.应用FTIR-XRD-XRF分析测试技术研究新型仿制绿松石的矿物学特征[J].岩矿测试, 2015, 34(5):544-549. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2015.05.008
Yan J, Liu X B, Wang J A, et al.Determination of mineral compositions of new kinds of imitated turquoise by FTIR-XRD-XRF[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(5):544-549. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2015.05.008
[6] 张志丹, 罗香丽, 王继红, 等.吉林省主要土壤胶散复合体粘土矿物XRD物相研究[J].矿物学报, 2016, 36(1):97-102. https://www.doc88.com/p-9933542180727.html
Zhang Z D, Luo X L, Wang J H, et al.Research on XRD phase for clay minerals in organo-mineral complex of major soil from Jilin Province, China[J].Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2016, 36(1):97-102. https://www.doc88.com/p-9933542180727.html
[7] 乔蓉, 郭钢.X射线荧光光谱法测定白云石、石灰石中氧化钙、氧化镁和二氧化硅[J].冶金分析, 2014, 34(1):75-78. http://www.doc88.com/p-2925311161292.html
Qiao R, Guo G.Determination of calcium oxide, magnesium oxide and silicon dioxide in dolomite and limestone by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry[J].Metallurgical Analysis, 2014, 34(1):75-78. http://www.doc88.com/p-2925311161292.html
[8] 曲月华, 王翠艳, 王一凌, 等.熔融制样-X射线荧光光谱法测定石灰石中5种组分[J].冶金分析, 2013, 33(2):230-235. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=yjfx201312006&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
Qu Y H, Wang C Y, Wang Y L, et al.Determination of five components in limestone by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry with fusion sample preparation[J].Metallurgical Analysis, 2013, 33(2):230-235. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=yjfx201312006&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[9] 罗学辉, 苏建芝, 鹿青, 等.高倍稀释熔融制样-X射线荧光光谱法测定铅锌矿中主次组分[J].冶金分析, 2014, 34(1):50-54. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YJFX201507001.htm
Luo X H, Su J Z, Lu Q, et al.Determination of major and minor components in lead-zinc ores by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry with high dilution fusion sample preparation[J].Metallurgical Analysis, 2014, 34(1):50-54. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YJFX201507001.htm
[10] 陈静, 高志军, 陈冲科, 等.X射线荧光光谱法分析地质样品的应用技巧[J].岩矿测试, 2015, 34(1):91-98. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2015.01.012
Chen J, Gao Z J, Chen C K, et al.Application skills on determination of geological sample by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(1):91-98. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2015.01.012
[11] 褚宁, 李卫刚, 蒋晓光, 等.熔融制样波长色散X射线荧光光谱法测定白云石中钙镁硅铁铝[J].岩矿测试, 2014, 33(6):834-838. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/38b8c609-f20e-4dae-884b-25e1f3b44206
Chu N, Li W G, Jiang X G, et al.Determination of calcium, magnesium, silicon, iron and aluminum in dolomite by wavelength dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometry with fusion sample preparation[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2014, 33(6):834-838. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/38b8c609-f20e-4dae-884b-25e1f3b44206
[12] 赵仕华.新疆博格达山北麓白杨河剖面页岩地球化学特征及其地质意义[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2016, 35(2):255-264. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=yskw201602006&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
Zhao S H.Geochemical characteristics of the Baiyanghe shale in the Northern Bogda Mountain of Xinjiang and its geological significance[J].Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2016, 35(2):255-264. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=yskw201602006&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[13] 冀磊, 刘福来, 王舫, 等.点苍山-哀牢山杂岩带中北段嘎洒地区变沉积岩的成因矿物学与变质演化特征[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2016, 35(6):1003-1024. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/magadetail/YSKW201606.htm
Ji L, Liu F L, Wang F, et al.Genetic mineralogy and metamorphic evolution of metasedimentary rocks in Gasa area, middle-north segment of Ailao Mountain metamorphic complex belt[J].Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2016, 35(6):1003-1024. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/magadetail/YSKW201606.htm
-



 下载:
下载: