Investigation of Pore Structure of a Argillaceous Rocks Reservoir in the 5th Member of Xujiahe Formation in Western Sichuan, Using NAM, NMR and AIP-FESEM
-
摘要: 微观孔隙作为泥质岩的有效储集空间,其孔隙结构参数是作为气藏评价及资源量估算的重要依据。本文应用氮气吸附法(NAM)、核磁共振法(NMR)、氩离子抛光及场发射扫描电镜(AIP-FESEM)研究川西须五段泥质岩微观孔隙特征,结果表明:①氩离子抛光及场发射扫描电镜在表征微观孔隙形态与类别时有一定优势,但定量表征孔隙参数时,受图像二值化阈值的影响,表征结果偏差较大,可结合氮气吸附法来定量表征其孔径大小;②核磁共振受岩石骨架影响小,能够更精细反映岩石的物性条件,可定量计算孔隙度与可动流体饱和度,但对样品的孔隙形态反映较差;③综合上述三种方法,在须五段泥质岩中可识别出一定量的纳米级中、大孔,孔径大多介于几十纳米到几百纳米之间,孔隙连通性差,孔隙度主要介于2.3%~7.4%之间,孔隙类型以粒间孔、晶间孔最发育,有机孔隙、微裂缝次之,粒内孔隙最不发育。总体而言,融合了三种技术方法能更精确、更全面地反映泥质岩孔隙结构特征,能得到更完善的储层孔隙结构参数,在定量表征泥质岩孔隙结构中具有广泛的应用前景。
-
关键词:
- 泥质岩 /
- 孔隙结构 /
- 氮气吸附 /
- 核磁共振 /
- 氩离子抛光及场发射扫描电镜
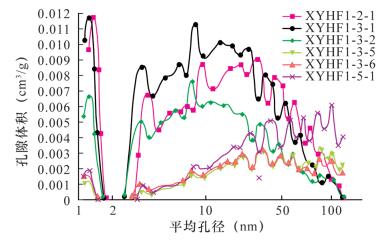
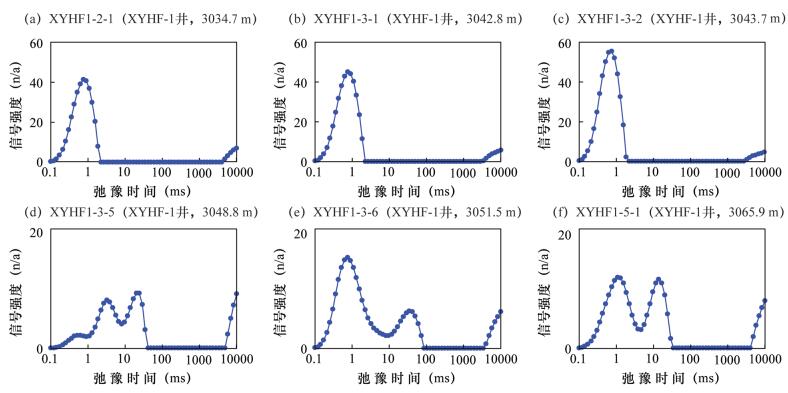
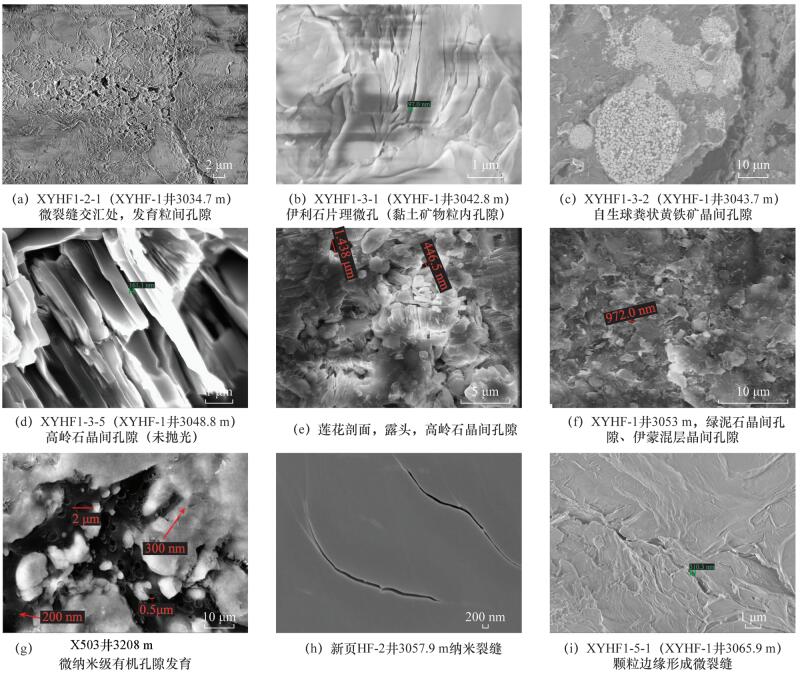
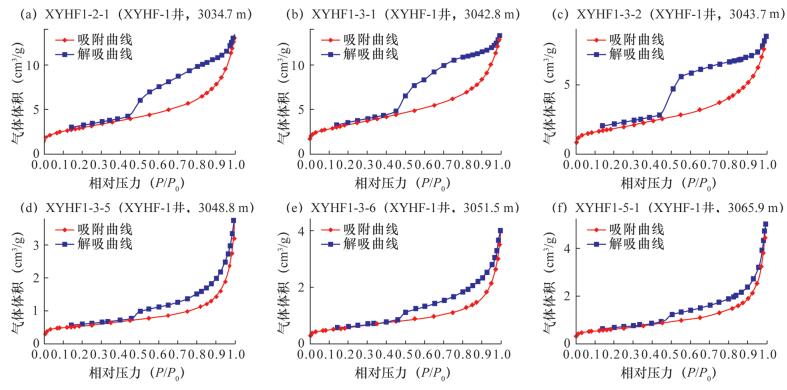
Abstract: Micropore is the effective reservoir for argillaceous rocks, and its structure parameter is the important parameter for the evaluation of gas reservoir and the estimation of the amount of resources. The Nitrogen Adsorption Method (NAM), Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR), and Argon Ionization-Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (AIP-FESEM) were used to analyze micropore characteristics of argillaceous rocks in the 5th Member of Xujiahe Formation of western Sichuan. The results show that: (1) AIP-FESEM has unparalleled advantages in characterizing the morphology and classification of microscopic pores. However, when it was used to quantify the pore parameter, the deviation of results is large, due to the threshold of image binarization. Therefore, it should be combined with the nitrogen adsorption method to quantify its pore size (in Fig.4). (2) As NMR is less affected by the rock skeleton, it can reflect physical properties of the rock more finely. However, the pore shape is poorly reflected by this technique (in Fig.3). (3) Based on the three methods, a certain amount of nanometer scale pore can be identified in the 5th Member of Xujiahe Formation. The pores are mostly several tens of nanometers to several hundred nanometers which have poor porosity of 2.3%-7.4% (in Table 1). The intergranular pores and intercrystalline pores of argillaceous rocks are the most developed, organic pores and micro-cracks aresecodary, and the granule pores least developed. In general, the combination of three techniques can reflect the structural characteristics of argillaceous rocks more accurately and comprehensively, and obtain more perfect pore structure parameters, which has wide application prospects in the quantitative characterization of pore structure of argillaceous rocks. -

-
表 1 须五段泥质岩储层特征参数统计
Table 1. The reservoir characteristics statistics of mud shale in Xu 5
测量方法 分析项目 XYHF1-2-1
(碳质泥岩)XYHF1-3-1
(碳质泥岩)XYHF1-3-2
(碳质泥岩)XYHF1-3-5
(泥岩)XYHF1-3-6
(泥岩)XYHF1-5-1
(砂质泥岩)取样深度
3034.7 m取样深度
3042.8 m取样深度
3043.7 m取样深度
3048.8 m取样深度
3051.5 m取样深度
3065.9 m氮气吸附法 比表面 (m2/g) 10.2 11 6.27 1.44 1.95 2.17 总孔容 (cm3/g) 0.0204 0.0206 0.013 0.0056 0.0062 0.00777 平均孔直径 (nm) 8.03 7.48 8.3 15.6 12.7 14.3 核磁共振法 孔隙度 (%) 6.8 7.2 7.4 2.3 3.9 3.6 束缚水饱和度 (%) 93.72 94.11 95.46 82.88 80.85 88.51 可动水饱和度 (%) 6.28 5.89 4.54 17.12 19.15 11.49 可动流体饱和度 (%) 6.28 5.89 4.54 17.12 19.15 11.49 覆压法 孔隙度 (%) 5.837 5.521 5.445 2.683 2.288 2.161 脉冲渗透率 (mD) 0.000508 0.0006062 0.0094827 0.000577 0.0008933 0.0002319 氦气法 孔隙度 (%) 6.0 - 4.7 1.9 8.9 - 压降渗透率 (mD) 0.0000077 - 0.0000102 0.0000196 0.0000157 - 酒精法 孔隙度 (%) 5.31 6.35 6.5 2.07 2.4 1.44 渗透率 (mD) - - - 0.012 0.011 0.01 注:覆压孔渗测试的围压10342.1355 kPa,测试压力6894.757 kPa;“-”表示样碎无法测量或没有该分析项目。 -
[1] 杨巍, 薛莲花, 唐俊, 等.页岩孔隙度测量实验方法分析与评价[J].沉积学报, 2015, 33(6):1258-1264. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201506018.htm
Yang W, Xue L H, Tang J, et al.Analysis and evaluation of different measuring methods for shale porosity[J].Acta Sendimentologica Sinica, 2015, 33(6):1258-1264. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201506018.htm
[2] 杨峰, 宁正福, 胡昌蓬, 等.页岩储层微观孔隙结构特征[J].石油学报, 2013, 34(2):301-311. doi: 10.1038/aps.2012.162
Yang F, Ning Z F, Hu C P, et al.Characterization of microscopic pore structures in shale reservoirs[J].Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(2):301-311. doi: 10.1038/aps.2012.162
[3] 王玉满, 董大忠, 杨桦, 等.川南下志留统龙马溪组页岩储集空间定量表征[J].中国科学 (地球科学), 2014, 44(6):1348-1356. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201406025.htm
Wang Y M, Dong D Z, Yang H, et al.Quantitative characterization of reservoir space in the Lower Silurian Longmaxi Shale, Southern Sichuan[J].Scientia Sinica Terrae, 2014, 44(6):1348-1356. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201406025.htm
[4] 邹才能, 董大忠, 王社教, 等.中国页岩气形成机理、地质特征与资源潜力[J].石油勘探与开发, 2010, 37(6):641-653. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(11)60001-3
Zou C N, Dong D Z, Wang S J.Geological characteristics, formation mechanism and resource potential of shale gas in China[J].Petrolum Exploration and Development, 2010, 37(6):641-653. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(11)60001-3
[5] 牛露, 朱如凯, 王莉森, 等.华北地区北部中-上元古届泥页岩储层特征及页岩气资源潜力[J].石油学报, 2015, 36(6):664-672. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201506003.htm
Niu L, Zhu R K, Wang L S, et al.Characteristics and evaluation of the Meso-Neoproterozoic shale gas reservoir in the Northern North China[J].Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(6):664-672. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201506003.htm
[6] 马勇, 钟宁宁, 程礼军, 等.渝东南两套富有机质页岩的孔隙结构特征——来自FIB-SEM的新启示[J].石油实验地质, 2015, 37(1):109-116. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201501019.htm
Ma Y, Zhong N N, Cheng L J, et al.Pore structure of two organic-rich shales in Southeastern Chongqing area:Insight from focused ion beam scanning electron microscope (FIB-SEM)[J].Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2015, 37(1):109-116. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201501019.htm
[7] 李娟, 于炳松, 夏响华, 等.黔西北地区上二叠统龙潭组泥页岩储层特征[J].地学前缘, 2015, 22(1):301-311. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201501029.htm
Li J, Yu B S, Xia X H, et al.The characteristics of the Upper Permian shale reservoir in the Northwest of Guizhou Province, China[J].Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(1):301-311. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201501029.htm
[8] 黄家国, 许开明, 郭少斌, 等.基于SEM、NMR和X-CT的页岩储层孔隙结构综合研究[J].现代地质, 2015, 29(1):198-205. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201501024.htm
Huang J G, Xu K M, Guo S B, et al.Comprehensive study on pore structures of shale reservoirs based on SEM, NMR and X-CT[J].Geoscience, 2015, 29(1):198-205. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201501024.htm
[9] 白斌, 朱如凯, 吴松涛, 等.非常规油气致密储层微观孔喉结构表征新技术及意义[J].中国石油勘探, 2014, 19(3):78-86. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201403011.htm
Bai B, Zhu R K, Wu S T, et al.New micro-throat characterization techniques for unconventional tight hydrocarbon reservoir[J].China Petroleum Exploration, 2014, 19(3):78-86. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201403011.htm
[10] Guo Y C, Pang X Q, Chen D X, et al.Evaluation of Upper Triassic T3x5 source rocks (Western Sichuan depression, Sichuan basin) and their hydrocarbon generation and expulsion characteristics:Implication for tight-sand gas and shale gas accumulation potential assessment[J].Natural Resources Research, 2013, 22(2):163-177. doi: 10.1007/s11053-013-9202-z
[11] 周闻达, 王莹, 鲍征宇, 等.等温吸附法在页岩孔隙结构测试中的应用[J].科技通报, 2015, 31(1):12-18. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJTB201501004.htm
Zhou W D, Wang Y, Bao Z Y, et al.The application of isotherm adsorption in measuring the shale pore structure[J].Bulletin of Science and Technology, 2015, 31(1):12-18. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJTB201501004.htm
[12] 杨峰, 宁正福, 孔德涛, 等.高压压汞法和氮气吸附法分析页岩孔隙结构[J].天然气地球科学, 2013, 24(3):450-455. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201303002.htm
Yang F, Ning Z F, Kong D T, et al.Pore structure of shales from high pressure mercury injection and nitrogen adsorption method[J].Natural Gas Geoscience, 2013, 24(3):450-455. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201303002.htm
[13] 孙君昌, 陈静平, 杨正明, 等.页岩储层岩芯核磁共振响应特征实验研究[J].科技导报, 2012, 30(14):25-29. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJDB201214019.htm
Sun J C, Chen J P, Yang Z M, et al.Experimental study of the NMR characteristics of shale reservoir rock[J].Science & Technology Review, 2012, 30(14):25-29. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJDB201214019.htm
[14] 肖秋生, 朱巨义.岩样核磁共振分析方法及其在油田勘探中的应用[J].石油实验地质, 2009, 31(1):97-100. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD200901020.htm
Xiao Q S, Zhu J Y.Analysis method of rock NMR and its application in oil field exploration[J].Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2009, 31(1):97-100. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD200901020.htm
[15] 杨峰, 宁正福, 张世栋, 等.基于氮气吸附实验的页岩孔隙结构表征[J].天然气工业, 2013, 33(4):135-140. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201304031.htm
Yang F, Ning Z F, Zhang S D, et al.Characterization of pore structures in shales through nitrogen adsorption experiment[J].Natural Science, 2013, 33(4):135-140. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201304031.htm
[16] 黄磊, 申维.页岩气储层孔隙发育特征及主控因素分析:以上扬子地区龙马溪组为例[J].地学前缘, 2015, 22(1):374-385. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201501035.htm
Huang L, Shen W.Characterisitics and controlling factors of the formation of pores of a shale gas reservoirs:A case study from Longmaxi Formation of the Upper Yangtze region China[J].Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(1):374-385. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201501035.htm
[17] 赵佩, 李贤庆, 田兴旺, 等.川南地区龙马溪组页岩气储层微孔隙结构特征[J].天然气地球科学, 2014, 25(6):947-956. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201406020.htm
Zhao P, Li X Q, Tian X W, et al.Study on micropore structure characteristics of Longmaxi Formation shale gas reservoirs in the Southern Sichuan Basin[J].Natural Gas Geoscience, 2014, 25(6):947-956. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201406020.htm
[18] 杨超, 张金川, 唐玄.鄂尔多斯盆地陆相页岩微观孔隙类型及对页岩气储渗的影响[J].地学前缘, 2013, 20(4):240-250. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201304024.htm
Yang C, Zhang J C, Tang X.Microscopic pore types and its impact on the storage and permeability of continental shale gas in the Ordos Basin[J].Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(4):240-250. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201304024.htm
[19] 王振华, 陈刚, 李书恒, 等.核磁共振岩心实验分析在低孔渗储层评价中的应用[J].石油实验地质, 2014, 36(6):773-778. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201406019.htm
Wang Z H, Chen G, Li S H, et al.Application of NMR core experimental analysis in evaluation of low-porosity and low-permeability sandstone reservoirs[J].Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2014, 36(6):773-778. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201406019.htm
[20] 于炳松.页岩气储层孔隙分类与表征[J].地学前缘, 2013, 20(4):211-220.
Yu B S.Classification and characterization of gas shale pore system[J].Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(4):211-220.
[21] 韩双彪, 张金川, Horsfield B, 等.页岩气储层孔隙类型及特征研究:以渝东南下古生界为例[J].地学前缘, 2013, 20(3):247-253. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201303030.htm
Han S B, Zhang J C, Horsfield B, et al.Pore types and characteristics of shale gas reservoir:A case study of lower paleozoic shale in Southeast Chongqing[J].Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(3):247-253. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201303030.htm
[22] 王香增, 高胜利, 高潮.鄂尔多斯盆地南部中生界陆相页岩气地质特征[J].石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(3):35-41. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201403007.htm
Wang X Z, Gao S L, Gao C.Geological features of mesozoic continental shale gas in South of Ordos Basin, NW China[J].Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(3):35-41. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201403007.htm
[23] 王亮, 陈云燕, 刘玉霞.川东南彭水地区龙马溪组页岩孔隙结构特征[J].中国石油勘探, 2014, 19(5):80-88.
Wang L, Chen Y Y, Liu Y X.Shale porous structural characteristics of Longmaxi Formation in Pengshui area of Southeast Sichuan Basin[J].China Petroleum Exploration, 2014, 19(5):80-88.
-



 下载:
下载: